目录
一、链表的概念及结构
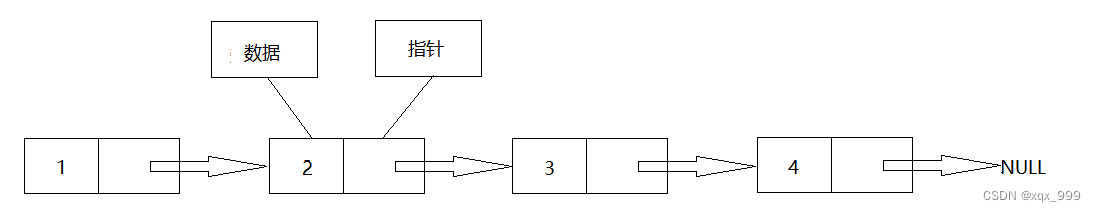
?单链表的物理结构:
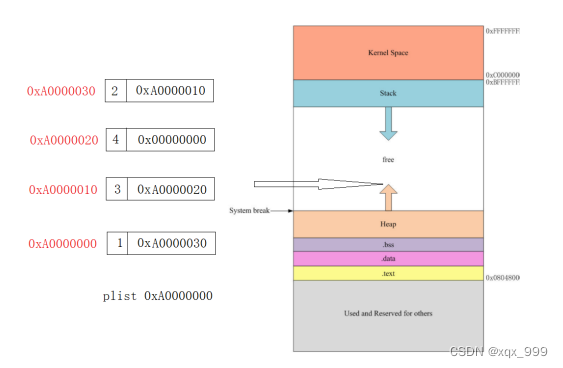
?2.不带头单链表、带头单链表
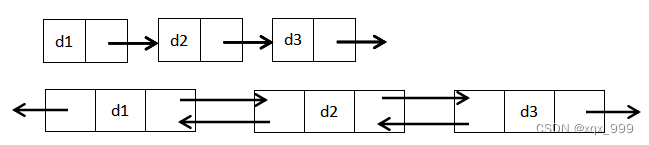
3.单链表、循环单链表
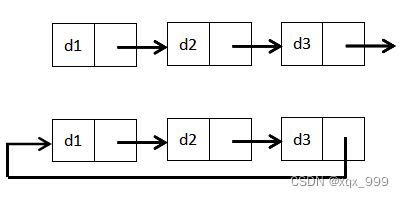
虽然有这么多的链表的结构,但是我们实际中最常用还是两种结构:
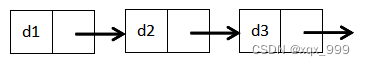
无头单向非循环链表:
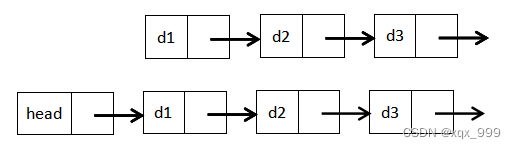
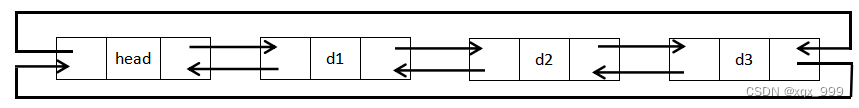
带头双向循环链表:
二、单链表的实现(无头+单向+非循环链表)
1.单链表节点定义
typedef int SLTDataType;
//定义一个链表节点
typedef struct SListNode {
SLTDataType data; //数据
struct SListNode* next; //指针,指向下一个节点
}SLTNode;2.单链表的接口实现
(1)动态申请一个节点
//动态申请一个节点
SLTNode* BuyListNode(SLTDataType x) {
SLTNode* newnode = (SLTNode*)malloc(sizeof(SLTNode));
//判断节点是否申请成功
if (newnode == NULL) {
printf("malloc fail\n");
exit(-1);
}
newnode->data = x;
newnode->next = NULL;
return newnode;
}(2)单链表打印
//打印链表
void SListPrint(SLTNode* phead) {
SLTNode* cur = phead;
while (cur != NULL) {
printf("%d-> ", cur->data);
cur = cur->next;
}
printf("NULL\n");
}(3)单链表的销毁?
//单链表的销毁?
void SListDestroy(SLTNode** phead) {
assert(*phead); //断言,不满足条件会报错
SLTNode* cur = *phead;
while (cur) {
SLTNode* next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
*phead = NULL;
}(4)单链表尾插
有两种情况:1.若链表为空链表,直接将该节点作为首节点;
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? 2.若链表不为空,让最后一个节点指向该节点。
//单链表尾插
void SListPushBack(SLTNode** phead, SLTDataType x) {
SLTNode* newnode = (SLTNode*)malloc(sizeof(SLTNode));
newnode->data = x;
newnode->next = NULL;
if (*phead == NULL)
*phead = newnode;
else {
SLTNode* tail = *phead;
while (tail->next != NULL) {
tail = tail->next;
}
tail->next = newnode;
}
}(5)单链表的头插
先让该节点指向链表的首节点,再让首节点指向该节点。
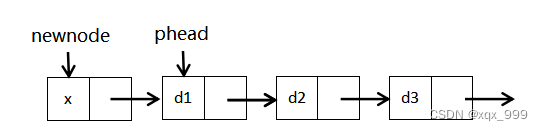
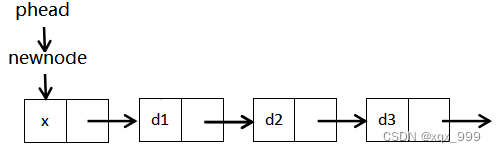 ???
???
//单链表的头插
void SListPushFront(SLTNode** phead, SLTDataType x){
SLTNode* newnode = BuyListNode(x);
newnode->next = *phead;
*phead = newnode;
}(6)单链表的尾删
1.若链表只有一个节点,直接将该节点删除。
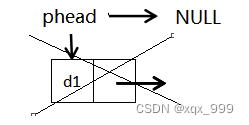
?2.若链表不只有一个节点,先找到尾结点的前一个节点,然后删除尾结点,再让尾结点的前一个节点指向NULL。
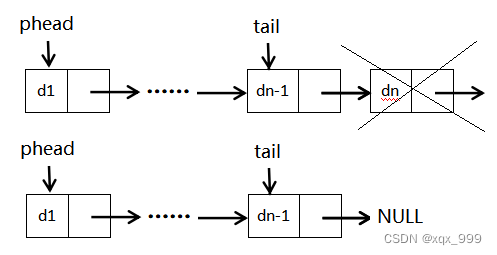
//单链表的尾删
void SListPopBack(SLTNode** phead) {
assert(*phead != NULL); //断言,不满足条件会报错
if ((*phead)->next == NULL) {
free(*phead);
*phead = NULL;
}
else {
SLTNode* tail = *phead;
while (tail->next->next) {
tail = tail->next;
}
free(tail->next);
tail->next = NULL;
}
}(7)单链表头删
先记录第二个节点的地址,再删除首节点,最后让首节点指向第二个节点。
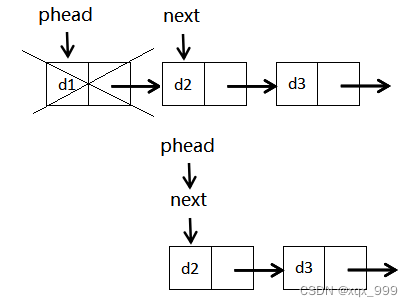
//单链表头删
void SListPopFornt(SLTNode** phead) {
assert(*phead != NULL);
SLTNode* next = (*phead)->next;
free(*phead);
*phead = next;
}(8)单链表查找
//单链表查找
SLTNode* SListFind(SLTNode* phead, SLTDataType x) {
SLTNode* cur = phead;
while (cur) {
if (cur->data == x) {
return cur;
}
else {
cur = cur->next;
}
}
return NULL;
}(9)单链表在pos位置之前插入x
1.若pos指向首节点,相当于头插。
2.若pos没有指向首节点,先找到pos位置的前一个节点,再让该节点指向新节点,最后让新节点指向pos位置的节点。
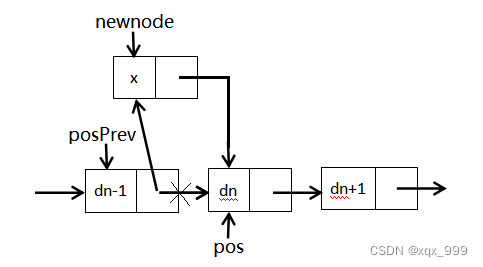
//单链表在pos位置之前插入x
void SListInsert(SLTNode** phead, SLTNode* pos, SLTDataType x) {
SLTNode* newnode = BuyListNode(x);
if (*phead == pos) {
newnode->next = *phead;
*phead = newnode;
}
else {
//找到pos的前一个位置
SLTNode* posPrev = *phead;
while (posPrev->next != pos) {
posPrev = posPrev->next;
}
posPrev->next = newnode;
newnode->next = pos;
}
}(10)单链表删除pos位置的值
1.若pos指向首节点,先让首节点指向下一个节点,再删除pos位置的节点。
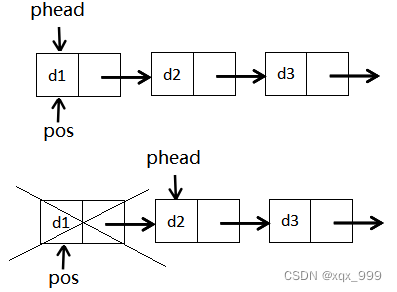
?2.若pos没有指向首节点,先找到pos位置的前一个节点,让该节点指向pos位置的后一个节点,最后再删除pos位置的节点。
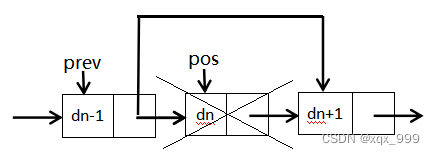
//单链表删除pos位置的值
void SListErase(SLTNode** phead, SLTNode* pos) {
if (*phead == pos) {
*phead = pos->next;
free(pos);
}
else {
SLTNode* prev = *phead;
while (prev->next != pos) {
prev = prev->next;
}
prev->next = pos->next;
free(pos);
}
}3.单链表测试代码
void test() {
SLTNode* phead = NULL;
printf("尾插:");
SListPushBack(&phead, 1);
SListPushBack(&phead, 2);
SListPushBack(&phead, 3);
SListPrint(phead);
printf("头插:");
SListPushFront(&phead, 4);
SListPushFront(&phead, 5);
SListPrint(phead);
printf("尾删:");
SListPopBack(&phead);
SListPrint(phead);
printf("头删:");
SListPopFornt(&phead);
SListPrint(phead);
printf("在1前插入6:");
SLTNode* find = SListFind(phead, 1);
SListInsert(&phead, find, 6);
SListPrint(phead);
printf("删除1:");
find = SListFind(phead, 1);
SListErase(&phead, find);
SListPrint(phead);
}
int main()
{
test();
return 0;
}三、双向链表的实现(带头+双向+循环链表)
1.双向链表节点定义
typedef int LTDataType;
//定义一个链表节点
typedef struct LTNode
{
LTDataType data;
struct LTNode* next;
struct LTNode* prev;
}LTNode;2.双向链表的接口实现
(1)创建返回链表的头节点
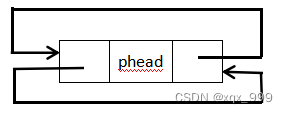
//创建返回链表的头节点
LTNode* ListInit() {
LTNode* phead = (LTNode*)malloc(sizeof(LTNode));
phead->next = phead;
phead->prev = phead;
return phead;
}(2)动态申请一个节点
// 动态申请一个节点
LTNode* BuyListNode(LTDataType x)
{
LTNode* newnode = (LTNode*)malloc(sizeof(LTNode));
newnode->data = x;
newnode->next = NULL;
newnode->prev = NULL;
return newnode;
}(3)双向链表销毁
// 双向链表销毁
void ListDestory(LTNode* phead) {
assert(phead);
LTNode* cur = phead->next;
while (cur != phead) {
LTNode* next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
free(phead);
phead = NULL;
}(4)双向链表打印
void ListPrint(LTNode* phead) {
assert(phead);
LTNode* cur = phead->next;
while (cur != phead) {
printf("%d ", cur->data);
cur = cur->next;
}
printf("\n");
}(5)双向链表尾插
先找到尾节点(头节点的前指针指向的就是尾节点),先让尾节点的后指针指向新节点,新节点的前指针指向尾节点,后指针指向头节点,最后再让头节点的前指针指向新节点。
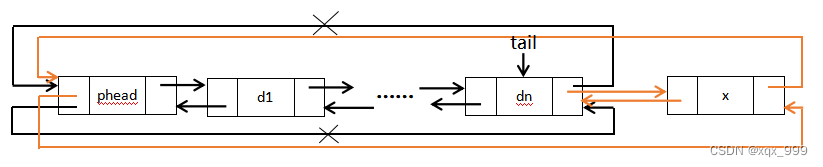
// 双向链表尾插
void ListPushBack(LTNode* phead, LTDataType x) {
assert(phead);
LTNode* tail = phead->prev;
LTNode* newnode = BuyListNode(x);
tail->next = newnode;
newnode->prev = tail;
newnode->next = phead;
phead->prev = newnode;
}(6)双向链表尾删
先找到尾节点的前一个节点(tailPrev),再删除尾节点,让tailPrev的后指针指向头节点,头节点的前指针指向tailPrev。

// 双向链表尾删
void ListPopBack(LTNode* phead) {
assert(phead);
assert(phead->next != phead); //链表为空
LTNode* tail = phead->prev;
LTNode* tailPrev = tail->prev;
free(tail);
tail = NULL;
tailPrev->next = phead;
phead->prev = tailPrev;
}(7)双向链表头插
先找到第一个节点(next),再让头节点的后指针指向新节点,新节点的前指针指向头节点,最后再让新节点的后指针指向next,next的前指针指向新节点。
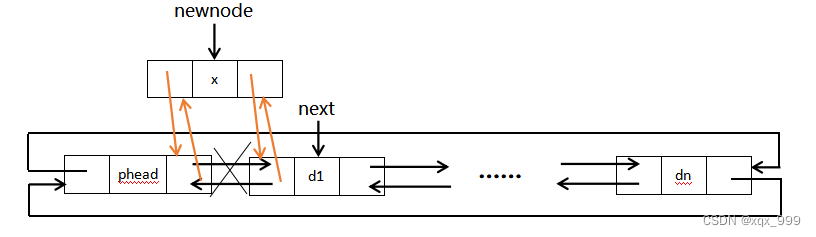
// 双向链表头插
void ListPushFront(LTNode* phead, LTDataType x) {
assert(phead);
LTNode* newnode = BuyListNode(x);
LTNode* next = phead->next;
phead->next = newnode;
newnode->prev = phead;
newnode->next = next;
next->prev = newnode;
}(8)双向链表头删
先找到第一个节点(next)和第二个节点(nextNext),再删除next节点,让头节点的后指针指向nextNext,nextNext的前指针指向头节点。
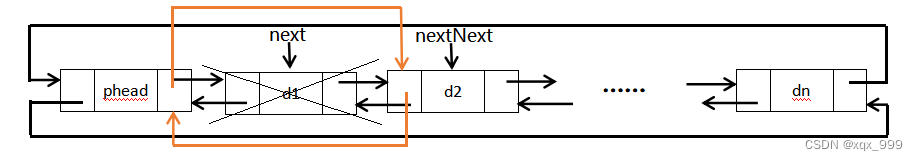
// 双向链表头删
void ListPopFront(LTNode* phead) {
assert(phead);
assert(phead->next != phead); //链表为空
LTNode* next = phead->next;
LTNode* nextNext = next->next;
free(next);
next = NULL;
phead->next = nextNext;
nextNext->prev = phead;
}(9)双向链表查找
// 双向链表查找
LTNode* ListFind(LTNode* phead, LTDataType x)
{
assert(phead);
LTNode* cur = phead->next;
while (cur != phead) {
if (cur->data == x)
return cur;
cur = cur->next;
}
return NULL;
}(10)双向链表在pos的前面进行插入
先找到pos的前一个节点(posPrev),让posPrev的后指针指向新节点,新节点的前指针指向posPrev,最后让新节点的后指针指向pos,pos的前指针指向新节点。
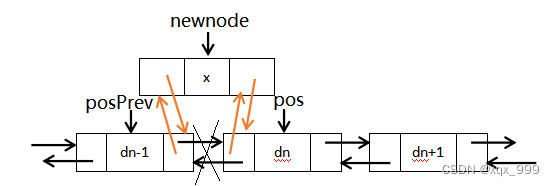
// 双向链表在pos的前面进行插入
void ListInsert(LTNode* pos, LTDataType x) {
assert(pos);
LTNode* posPrev = pos->prev;
LTNode* newnode = BuyListNode(x);
posPrev->next = newnode;
newnode->prev = posPrev;
newnode->next = pos;
pos->prev = newnode;
}(11)双向链表删除pos位置的节点
先找到pos的前一个节点(posPrev)和后一个节点(posNext),再删除pos节点,让posPrev的后指针指向posNext,posNext的前指针指向posPrev。
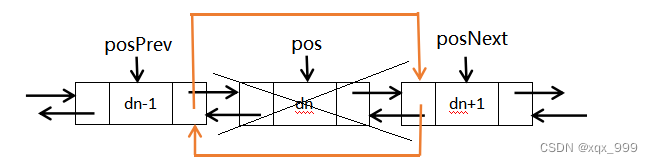
// 双向链表删除pos位置的节点
void ListErase(LTNode* pos) {
assert(pos);
LTNode* posPrev = pos->prev;
LTNode* posNext = pos->next;
free(pos);
pos = NULL;
posPrev->next = posNext;
posNext->prev = posPrev;
}3.双向链表测试代码
void test() {
LTNode* head = ListInit();
printf("尾插:");
ListPushBack(head, 1);
ListPushBack(head, 2);
ListPushBack(head, 3);
ListPrint(head);
printf("尾删:");
ListPopBack(head);
ListPrint(head);
printf("头插:");
ListPushFront(head, 4);
ListPushFront(head, 5);
ListPrint(head);
printf("头删:");
ListPopFront(head);
ListPrint(head);
printf("头删:");
ListPopFront(head);
ListPrint(head);
printf("在2之前插入8、9:");
LTNode* find = ListFind(head, 2);
ListInsert(find, 8);
ListInsert(find, 9);
ListPrint(head);
printf("删除8:");
find = ListFind(head, 8);
ListErase(find);
ListPrint(head);
}
int main()
{
test();
printf("\n");
return 0;
}