C语言之数据结构-线性表(单链表)
1.链表定义:将线性表中各个元素分布在存储器的不同存储块,称为结点,通过地址或指针建立它们之间的联系,所得到的存储结构称为链表结构。
2.单链表的结点中只有数据域和结点的后继指针域两部分组成。
typedef int data_t;
typedef struct Node
{
data_t data;
Node struct *next;
}node_t;
3.对于单链表的基本运算实现:
(1)建立一个单链表,在堆区开辟一块空间,创建一个头结点,并将指针域置为NULL,并返回这块空间的地址。
node_t *creat_linklist()
{
node_t *H=(node_t *)malloc(sizeof(node_t));
if(NULL==H)
{
printf("malloc is fail!\n");
return NULL;
}
memset(H,0,sizeof(node_t));
return H;
}
(2)头插法插入元素
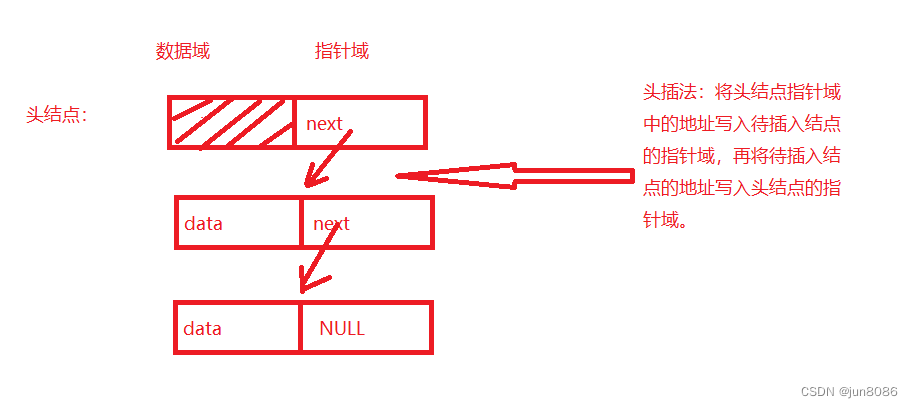
void insert_data_linklist_head(node_t *H,data_t data)
{
node_t *node=creat_linklist();
if(NULL==node)
{
printf("creat newnode is fail!\n");
return ;
}
node->data=data;
node->next=H->next;
H->next=node;
}
(3)单链表判空
int is_empty_linklist(node_t *H)
{
if(NULL==H->next)
{
return 1;
}
else
{
return 0;
}
}
(4)遍历单链表输出元素
void print_data_linklist(node_t *H)
{
if(is_empty_linklist(H))
{
printf("linklist is empty!\n");
return ;
}
node_t *p=NULL;
for(p=H;p->next!=NULL;p=p->next)
{
printf("%d ",p->next->data);
}
printf("\n");
}
(5)根据位置查找结点,返回结点地址
node_t *get_data_linklist(node_t * H,int post)
{
int i=0;
node_t *p=NULL;
if(post<0)
{
printf("post is invalid!\n");
return NULL;
}
for(p=H;p->next!=NULL;p=p->next)
{
i++;
if(post==i)
{
return p->next;
}
}
printf("post is invalid!\n");
return NULL;
}
(6)根据结点位置插入结点
void insert_data_linklist_post(node_t *H,data_t data,int post)
{
node_t *node=creat_node();
if(NULL==node)
{
printf("creat node is fail!\n");
return ;
}
node->data=data;
if(post==1)
{
insert_data_linklist_head(H,data);
return ;
}
node_t *p=get_data_linklist(H,post-1);
if(NULL==p)
{
return ;
}
node->next=p->next;
p->next=node;
}
(7)根据位置删除一个结点
void delete_data_linklist(node_t *H,data_t *data,int post)
{
node_t *q=NULL;
if(post==1)
{
q=H->next;
H->next=q->next;
free(q);
return ;
}
node_t *p=get_data_linklist(H,post-1);
if(NULL==p->next)
{
printf("post is invalid!\n");
return ;
}
q=p->next;
p->next=q->next;
*data=q->data;
free(q);
q=NULL;
}
(8)求链表的长
int get_len_linklist(node_t *H)
{
int i=0;
node_t *p=NULL;
for(p=H;p->next!=NULL;p=p->next)
{
i++;
}
return i;
}
(9)销毁链表(释放所有结点)
void destroy_linklist(node_t *H)
{
node_t *p=NULL;
int len=get_len_linklist(H);
int i=0;
for(i=len;i>0;i--)
{
p=get_data_linklist(H,i);
free(p);
}
free(H);
}
(10)根据元素的值确定元素的位置
int locate_data_linklist(node_t *H,data_t data)
{
int i=0;
node_t *p=NULL;
for(p=H;p->next!=NULL;p=p->next)
{
i++;
if(p->next->data==data)
{
return i;
}
}
printf("data not found \n");
return -1;
}
(11)有序插入
void insert_data_linklist_order(node_t *H,data_t data)
{
int post=0;
node_t *p=NULL;
node_t *q=NULL;
node_t *node=NULL;
for(p=H;p->next!=NULL;p=p->next)
{
if(data<p->next->data)
{
break;
}
}
node=create_node();
node->data=data;
node->next=p->next;
p->next=node;
}
(12)将链表中的元素排序
void order_linklist(node_t *H)
{
node_t *p=create_node();
p->next=H->next;
H->next=NULL;
for(;p->next!=NULL;p=p->next)
{
insert_data_linklist_order(H,p->next->data);
}
destroy_linklist(p);
p=NULL;
}
| 