文章目录
基本概念
主要用于解决一些元素分组的问题。它管理一系列不相交的集合,并支持两种操作:
- 合并(Union):把两个不相交的集合合并为一个集合。
- 查询(Find):查询两个元素是否在同一个集合中。
路径压缩
递归版本:
public int find(int x){
if(parents[x] == x) return x;
return parents[x] = find(parents[x]);
}
路径压缩发生在查询的过程中,的目的是为了防止链的长度过长,所以我们让除了根节点以外的元素全部都指向根节点.
迭代版本:
使用help数组来记录i的所有父节点,直到找到根节点.
然后再回过来给之前记录的父节点路径压缩,使它们的parent值都为根节点
public int find(int i){
int hi=0;
while(parent[i]!=i){
help[hi++]=i;
i=parent[i];
}
hi--;
while(hi>=0){
parent[help[hi--]]=i;
}
return i;
}
按秩合并
有些人可能有一个误解,以为路径压缩优化后,并查集始终都是一个菊花图(只有两层的树的俗称)。但其实,由于路径压缩只在查询时进行,也只压缩一条路径,所以并查集最终的结构仍然可能是比较复杂的。
// 按秩合并
public void union(int x, int y){
int xRoot = find(x);
int yRoot = find(y);
if(xRoot != yRoot){
if(rank[yRoot] <= rank[xRoot]) parents[yRoot] = xRoot;// yRoot挂到xRoot上
else parents[xRoot] = yRoot; // xRoot挂到yRoot上
if (rank[xRoot] == rank[yRoot]) rank[xRoot]++; // 秩相同时才加1
}
}
这个要有一点注意就是秩相同时加1,具体看下方的图:
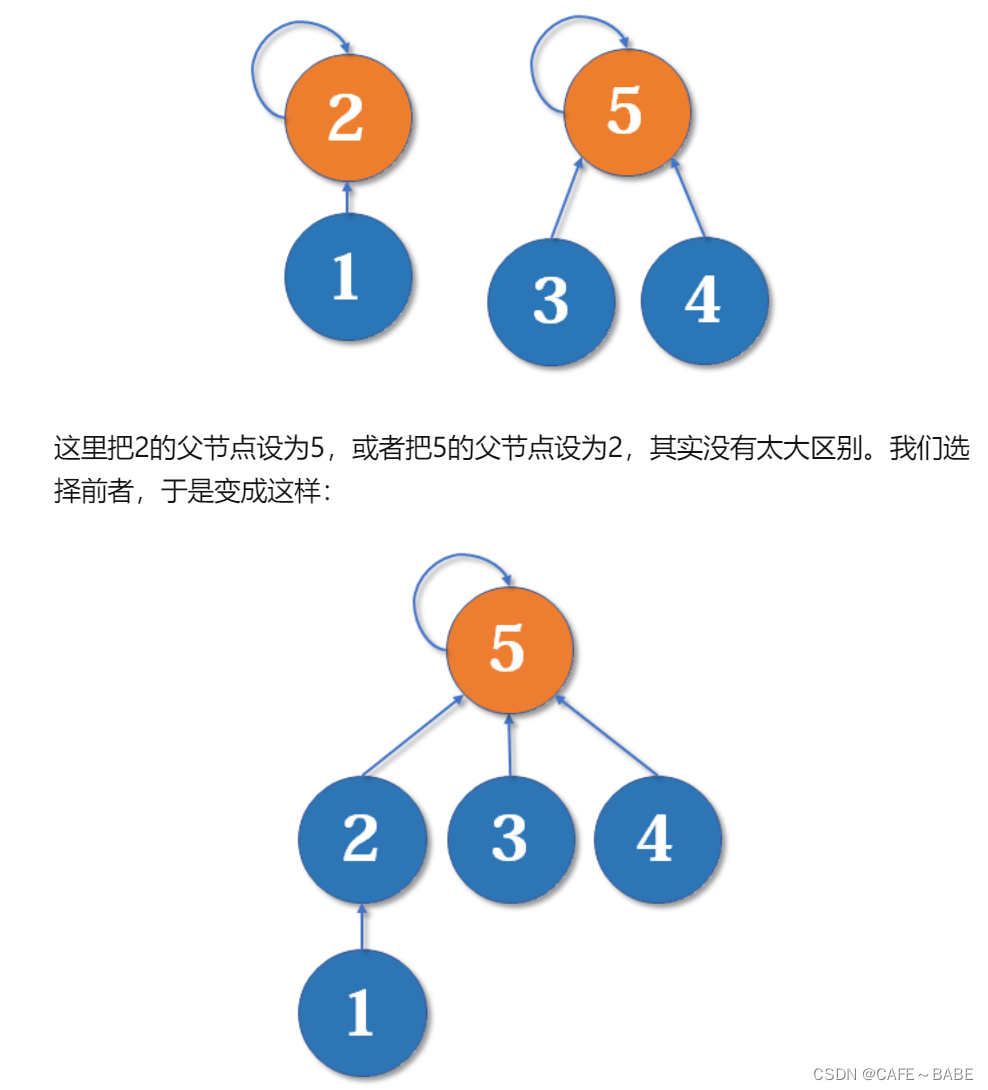
上面这些内容来总结自https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/93647900
按大小合并
按大小合并就是让小的值挂到了大的那个值上面.
public void union(int x,int y){
int xroot=find(x);
int yroot=find(y);
if(xroot!=yroot){
if(size[xroot]<=size[yroot]){
parent[xroot]=yroot;
size[yroot]+=size[xroot];
}
else{
size[xroot]+=size[yroot];
parent[yroot]=xroot;
}
}
}
例题1:路径压缩+按秩求并.
需要注意的是按照秩求并的时候,当祖先不是同一个人的时候,
如果秩不同,秩小的挂到秩大的上面
如果秩相同,x挂到y上面或y挂到x上面都可,如果挂到x上,x的秩加一,如果挂到y上,y的秩加一
private class UnionFind{
private int[] parents;
private int[] rank;
public UnionFind(int[][] isConnected){
int n = isConnected.length;
this.parents = new int[n];
this.rank = new int[n];
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
parents[i] = i;
rank[i] = 1;
}
}
// 带路径压缩的查找
public int find(int x){
if(parents[x] == x) return x;
return parents[x] = find(parents[x]);
}
// 按秩合并
public void union(int x, int y){
int xRoot = find(x);
int yRoot = find(y);
if(xRoot != yRoot){
if(rank[yRoot] <= rank[xRoot]) parents[yRoot] = xRoot;// yRoot挂到xRoot上
else parents[xRoot] = yRoot; // xRoot挂到yRoot上
if (rank[xRoot] == rank[yRoot]) rank[xRoot]++; // 秩相同时才加1
}
}
}
对应例题:
剑指Offer II 116. 省份数量
https://leetcode.cn/problems/bLyHh0/
class Solution {
int mergedCount = 0;
public int findCircleNum(int[][] isConnected) {
int n = isConnected.length;
UnionFind uf = new UnionFind(isConnected);
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
for(int j = i + 1; j < n; j++){
if(isConnected[i][j] == 1) uf.union(i, j);
}
}
return n - mergedCount;
}
private class UnionFind{
private int[] parents;
private int[] rank;
public UnionFind(int[][] isConnected){
int n = isConnected.length;
this.parents = new int[n];
this.rank = new int[n];
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
parents[i] = i;
rank[i] = 1;
}
}
// 带路径压缩的查找
public int find(int x){
if(parents[x] == x) return x;
return parents[x] = find(parents[x]);
}
// 按秩合并
public void union(int x, int y){
int xRoot = find(x);
int yRoot = find(y);
if(xRoot != yRoot){
mergedCount++; // 只有不属于一个集合时,合并才次数加1
if(rank[yRoot] <= rank[xRoot]) parents[yRoot] = xRoot;// yRoot挂到xRoot上
else parents[xRoot] = yRoot; // xRoot挂到yRoot上
if (rank[xRoot] == rank[yRoot]) rank[xRoot]++; // 秩相同时才加1
}
}
}
}
leetcode 200.岛的数量
对于那些是1的点,判断它的右边和下边的1是否已经被合并了.
记录合并的次数,然后再使用1的个数-合并的个数
class Solution {
private int islandCount=0;
private int mergeCount=0;
public int numIslands(char[][] grid) {
int m=grid.length;
int n=grid[0].length;
UnionFind unionFind=new UnionFind(grid);
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if(grid[i][j]=='1'){
if((j+1)<n&&grid[i][j+1]=='1'){
unionFind.union(i*n+j,i*n+j+1);
}
if((i+1)<m&&grid[i+1][j]=='1'){
unionFind.union(i*n+j,(i+1)*n+j);
}
}
}
}
return islandCount-mergeCount;
}
private class UnionFind{
private int[] parents=null;
private int[] rank=null;
public UnionFind(char[][] grid){
int n = grid.length;
int m=grid[0].length;
parents=new int[n*m];
rank=new int[n*m];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
if(grid[i][j]=='1'){
islandCount++;
int k=i*m+j;
parents[k]=k;
rank[k]=1;
}
}
}
}
//带有路径压缩的查找
public int find(int x){
if(parents[x]==x)
return x;
else
return parents[x]=find(parents[x]);
}
public void union(int x,int y){
int xroot=find(x);
int yroot=find(y);
//只有祖先节点不是同一个才合并
if(xroot!=yroot){
mergeCount++;
if(rank[yroot]<=rank[xroot]) parents[yroot]=xroot;
else parents[xroot]=yroot;
if(rank[yroot]==rank[xroot]) rank[xroot]++;
}
}
}
}
例题2:路径压缩+按size合并
按照size合并就是按照一个集合中的数目进行合并.
和按照秩合并类似,只不过秩是按照树的高度合并的
leetcode 695 岛屿的最大面积
这道题基本上和岛的数量是差不多的,只是合并的方式不一样.
class Solution {
public int maxAreaOfIsland(int[][] grid) {
int n=grid.length;
int m=grid[0].length;
UnionFind unionFind=new UnionFind(grid);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
int k=i*m+j;
if(grid[i][j]==1){
if((j+1<m)&&grid[i][j+1]==1)
unionFind.union(k,k+1);
if((i+1<n)&&grid[i+1][j]==1)
unionFind.union(k,k+m);
}
}
}
int max=0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
max=Math.max(max,unionFind.size[i*m+j]);
}
}
return max;
}
class UnionFind{
private int[] parent;
private int[] size; // 保存树的大小
public UnionFind(int[][] grid) {
int n= grid.length;
int m=grid[0].length;
parent=new int[n*m];
size=new int[n*m];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
if(grid[i][j]==1){
int k=i*m+j;
parent[k]=k;
size[k]=1;
}
}
}
}
public int find(int x){
if(parent[x]==x)
return x;
else
return parent[x]=find(parent[x]);
}
public void union(int x,int y){
int xroot=find(x);
int yroot=find(y);
if(xroot!=yroot){
if(size[xroot]<=size[yroot]){
parent[xroot]=yroot;
size[yroot]+=size[xroot];
}
else{
size[xroot]+=size[yroot];
parent[yroot]=xroot;
}
}
}
}
}
例题3:路径压缩+直接合并
leetcode 128 最长连续序列
https://leetcode.cn/problems/longest-consecutive-sequence/
这题是采用hashMap来指定父亲节点的.
先将数组中的每一个数num和num+1进行联合(当然num+1要在nums数组中)
接着进行压缩查找find,让所有的数都指向它的连续序列中最大的那个数
最后遍历所有的nums数组,找到最长的那个连续序列
import java.util.HashMap;
class Solution {
public int longestConsecutive(int[] nums) {
if(nums.length<2)
return nums.length;
UnionFind unionFind=new UnionFind(nums);
//对于num+1属于nums数组的那些进行合并
//100,4,200,1,3,2
//1->2,3->4,2->3 for(int num:nums){
unionFind.union(num,num+1);
}
int max=0;
//经过路径压缩,查找最长的连续的集合里面的元素个数
//unionFind.find(num)是祖先1->4,2->4,3->4
//最后结果当max等于1时最大,是4-1+1=4
for(int num:nums){
max=Math.max(max,unionFind.find(num)-num+1);
}
return max;
}
static class UnionFind{
HashMap<Integer,Integer> hashMap=new HashMap<>();
public UnionFind(int[] nums){
for(int num:nums){
hashMap.put(num,num);
}
}
//带有路径压缩的查找
public int find(int i){
if(hashMap.get(i)==i)
return i;
else{
int p=hashMap.get(i);
hashMap.put(i,find(p));
return hashMap.get(i);
}
}
//直接合并
public void union(int x,int y){
if(hashMap.containsKey(y)){
hashMap.put(x,y);
}
}
}
}
例题4:使用到了并查集
如果题目对并查集内部的一些实现没有涉及的话,就直接套用下面的这个模板就可以了,简单方便.
public static class UnionFind {
private int[] f;
private int[] s;
private int[] h;
public UnionFind(int N) {
f = new int[N + 1];
s = new int[N + 1];
h = new int[N + 1];
for (int i = 0; i <= N; i++) {
f[i] = i;
s[i] = 1;
}
}
private int find(int i) {
int hi = 0;
while (i != f[i]) {
h[hi++] = i;
i = f[i];
}
while (hi > 0) {
f[h[--hi]] = i;
}
return i;
}
public boolean same(int i, int j) {
return find(i) == find(j);
}
public void union(int i, int j) {
int fi = find(i);
int fj = find(j);
if (fi != fj) {
if (s[fi] >= s[fj]) {
f[fj] = fi;
s[fi] = s[fi] + s[fj];
} else {
f[fi] = fj;
s[fj] = s[fi] + s[fj];
}
}
}
}
leetcode 684.冗余连接
这题不难,只要找出最后的一个已经是属于同一个集合的一条边就可以了
class Solution {
public int[] findRedundantConnection(int[][] edges) {
int n=edges.length;
UnionFind unionFind=new UnionFind(n);
int a=0,b=0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if(unionFind.same(edges[i][0],edges[i][1])){
a=edges[i][0];
b=edges[i][1];
}else {
unionFind.union(edges[i][0],edges[i][1]);
}
}
return new int[]{a,b};
}
public static class UnionFind {
private int[] f;
private int[] s;
private int[] h;
public UnionFind(int N) {
f = new int[N + 1];
s = new int[N + 1];
h = new int[N + 1];
for (int i = 0; i <= N; i++) {
f[i] = i;
s[i] = 1;
}
}
private int find(int i) {
int hi = 0;
while (i != f[i]) {
h[hi++] = i;
i = f[i];
}
while (hi > 0) {
f[h[--hi]] = i;
}
return i;
}
public boolean same(int i, int j) {
return find(i) == find(j);
}
public void union(int i, int j) {
int fi = find(i);
int fj = find(j);
if (fi != fj) {
if (s[fi] >= s[fj]) {
f[fj] = fi;
s[fi] = s[fi] + s[fj];
} else {
f[fi] = fj;
s[fj] = s[fi] + s[fj];
}
}
}
}
}
leetcode 685.冗余连接2
冗余连接形成的图主要有以下两种形式:
- 有入度为2的点
- 成环
- 有度为2的点且成环
first 记录到入度为2的点的第一条边
second记录到入度为2的点的第二条边
circle 记录第一次访问该点时成环的边
对于不存在入度为2的点的有向图来说(也就是只成环),first等于null,那么直接返回circle就可以
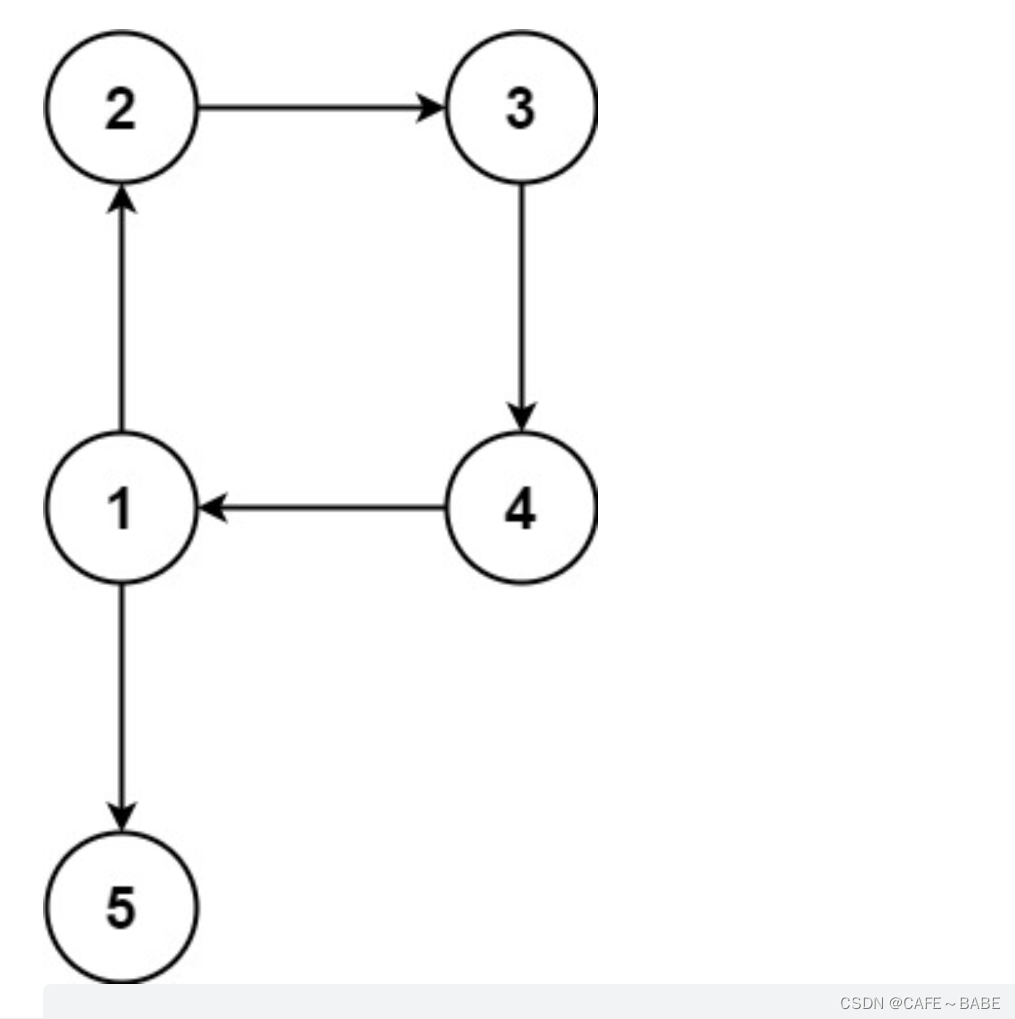
对于存在入度为2的点的有向图来说,要怎么判断到底时第一个出现的边
冗余还是第二个出现的边冗余呢?
这个时候我们就要看circle的值了.我们前面提到过,circle记录的是第一次出现访问这个点的时候就成环的那一个边.
所以如果circle的值不为null,那么说明第二条边出现前就成环了,所以first就是冗余的
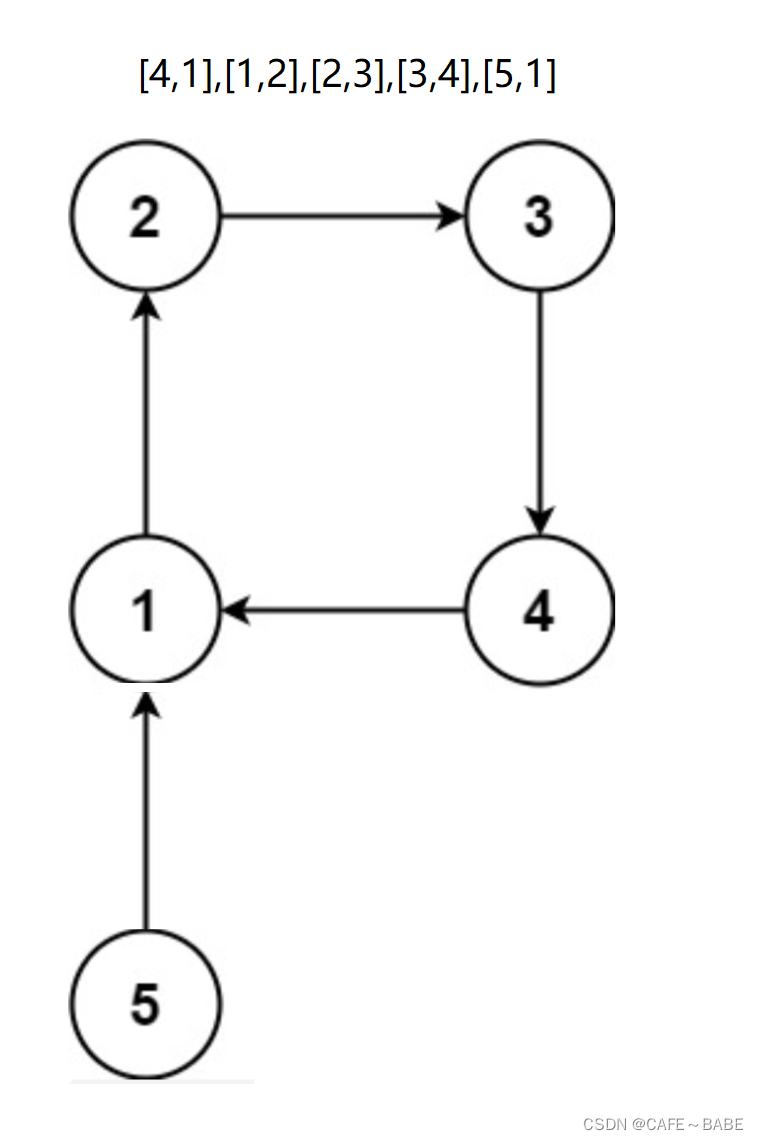
如果circle的值为null,那么要不然就是第二条边出现的时候成环了,
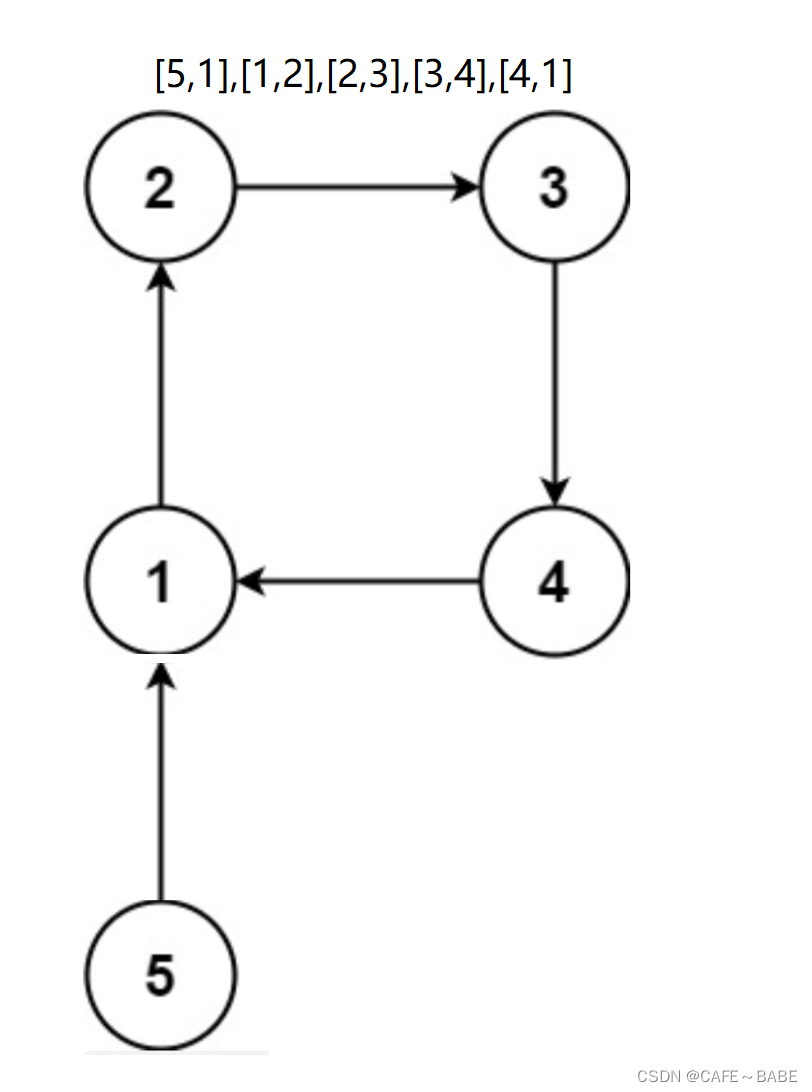
要不然就是未成环但是多了一条多余指向该节点的边.题目中说要返回二维数组中最后出现的边
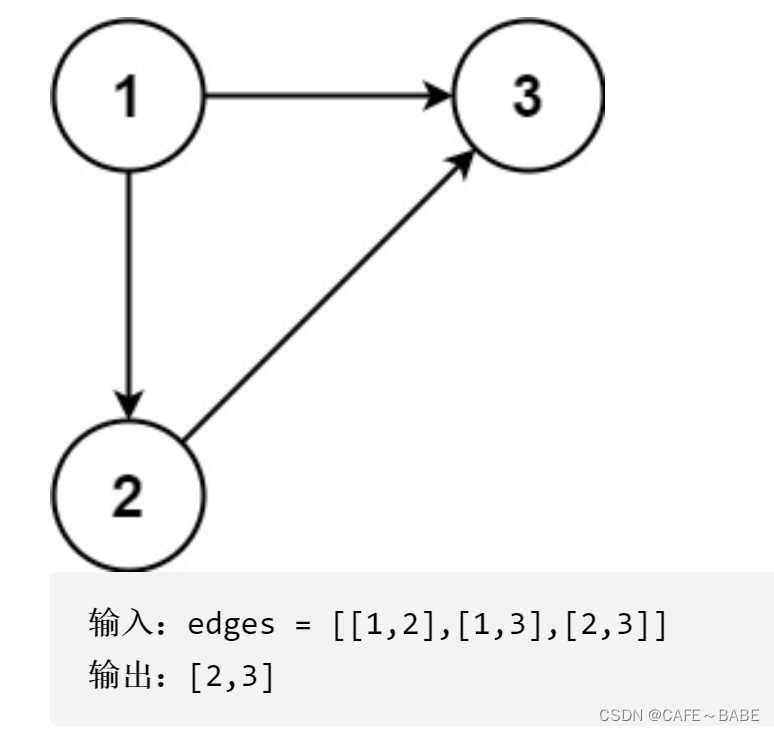
这个要删除的就是最后出现的边2,3
class Solution {
public int[] findRedundantDirectedConnection(int[][] edges) {
int n=edges.length;
int[] first=null;
int[] second=null;
int[] circle=null;
int[] pre=new int[n+1];
UnionFind unionFind=new UnionFind(n);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
int from=edges[i][0];
int to=edges[i][1];
//第二次访问,也就是入度为2的点
if(pre[to]!=0){
first=new int[]{pre[to],to};
second=edges[i];
//第一次访问到
}else{
pre[to]=from;
if(unionFind.same(from,to)){
circle=edges[i];
}else{
unionFind.union(from,to);
}
}
}
//如果first是null,说明没有入度为2的点,直接返回最后成环的边
//如果first不是null,说明有入度为2的点,判断circle是否为null
//如果circle不为null,说明第一条边成的环
//如果circle为null,说明第二条边成的环或者是多余的边
return first!=null?((circle!=null)?first:second):circle;
}
public static class UnionFind {
private int[] f;
private int[] s;
private int[] h;
public UnionFind(int N) {
f = new int[N + 1];
s = new int[N + 1];
h = new int[N + 1];
for (int i = 0; i <= N; i++) {
f[i] = i;
s[i] = 1;
}
}
private int find(int i) {
int hi = 0;
while (i != f[i]) {
h[hi++] = i;
i = f[i];
}
while (hi > 0) {
f[h[--hi]] = i;
}
return i;
}
public boolean same(int i, int j) {
return find(i) == find(j);
}
public void union(int i, int j) {
int fi = find(i);
int fj = find(j);
if (fi != fj) {
if (s[fi] >= s[fj]) {
f[fj] = fi;
s[fi] = s[fi] + s[fj];
} else {
f[fi] = fj;
s[fj] = s[fi] + s[fj];
}
}
}
}
}
例题5:动态初始化
leetcode 305 岛屿数量II
但是leetcode上这道题是会员,可以去lintcode上面去做
![[Pasted image 20221006124053.png]]
/**
* Definition for a point.
* class Point {
* int x;
* int y;
* Point() { x = 0; y = 0; }
* Point(int a, int b) { x = a; y = b; }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
/**
* @param n: An integer
* @param m: An integer
* @param operators: an array of point
* @return: an integer array
*/
public List<Integer> numIslands2(int m, int n, Point[] operators) {
// write your code here
List<Integer> res=new ArrayList<>();
UnionFind unionFind=new UnionFind(m,n);
for(Point point:operators){
res.add(unionFind.connect(point.x,point.y));
}
return res;
}
public static class UnionFind{
int[] size;
int[] help;
int[] parent;
int row;
int col;
int sets=0;//记录岛屿的个数
//初始化操作,只进行赋值
public UnionFind(int m,int n){
row=m;col=n;
sets=0;
int len=m*n;
size=new int[len];
help=new int[len];
parent=new int[len];
}
public int index(int i,int j){
return i*col+j;
}
//迭代版本的带有路径压缩的查找
public int find(int i){
int hi=0;
while(parent[i]!=i){
help[hi++]=i;
i=parent[i];
}
hi--;
while(hi>=0){
parent[help[hi--]]=i;
}
return i;
}
public void union(int r1,int c1,int r2,int c2){
if(r1<0||r1==row||r2<0||r2==row||c1<0||c1==col||c2<0||c2==col)
return;
int i1=index(r1,c1);
int i2=index(r2,c2);
//如果i1和i2的下标是0,还没有被赋值为1,直接返回
if(size[i1]==0||size[i2]==0)
return;
int f1=find(i1);
int f2=find(i2);
if(f1!=f2){
if(size[f1]<=size[f2]){
size[f2]+=size[f1];
parent[f1]=f2;
}else{
size[f1]+=size[f2];
parent[f2]=f1;
}
sets--;
}
}
public int connect(int r,int c){
int index=index(r,c);
//使用size[index]的值是否为0来判断这个index下标是否被访问过
if(size[index]==0){
size[index]=1;
parent[index]=index;
sets++;
union(r,c,r+1,c);
union(r,c,r,c+1);
union(r,c,r-1,c);
union(r,c,r,c-1);
}
return sets;
}
}
}