写在前面
- 主要是分类一下刷题遇到的一些题型。
- 有很多思路的图都来源于力扣的题解,如侵权会及时删除。
- 不过代码都是个人实现的,所以有一些值得记录的理解。
一、哈希表
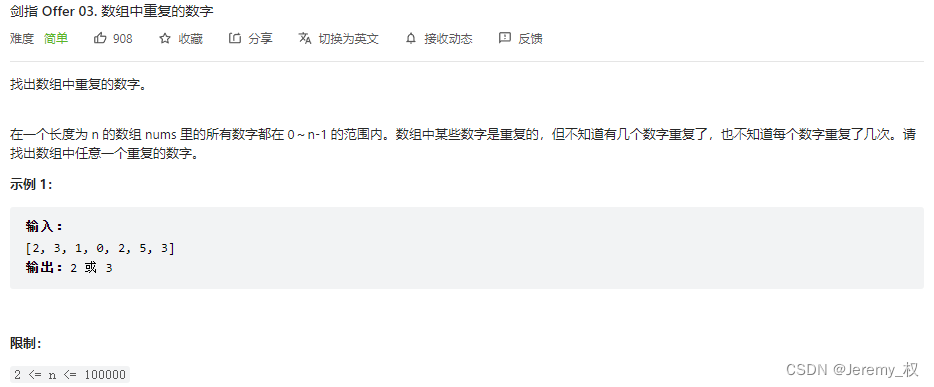
1. 数组中重复的数字
- 题目描述:https://leetcode.cn/problems/shu-zu-zhong-zhong-fu-de-shu-zi-lcof/。
- 思路:
- 由于n比较小,所以直接开一个和n等大的哈希表记录重复的击中即可。
- 代码:
class Solution {
public:
int findRepeatNumber(vector<int>& nums) {
int record[100000];
for(int i=0;i<100000;i++)
{
record[i] = 0;
}
for(int i=0;i<nums.size();i++)
{
if(record[nums[i]])
{
return nums[i];
}
else
{
record[nums[i]] = 1;
}
}
return -1;
}
};
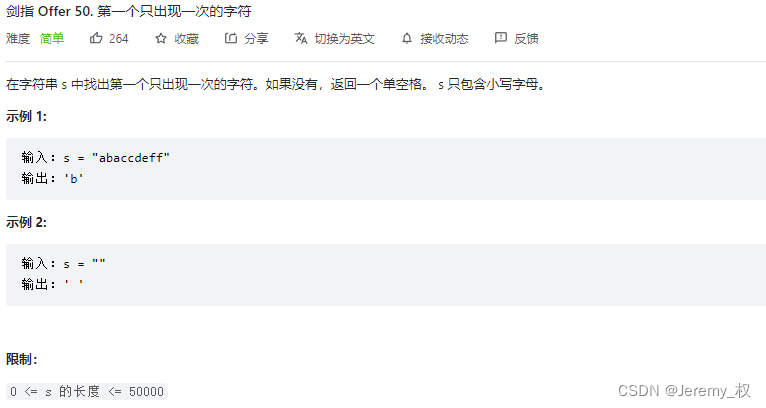
2. 第一个只出现一次的字符
- 思路:
- 用哈希表来记录每个字母出现的次数;
- 注意:这里要求返回第一个出现次数为1的字母,而不是任意一个,因此还要用一个数组(或者队列)来记录
key进入哈希表的顺序,即所谓的有序哈希; - 当然不记录也可以,直接再次访问字符串即可,但由于哈希表的大小(仅26)可能远小于字符串顺序,因此会更加耗时(虽说两种方式时间复杂度都是O(N));
- 代码:
class Solution {
public:
char firstUniqChar(string s) {
// 哈希表
unordered_map<char, int> hash_map;
// 按照入哈希表的顺序记录
vector<char> order_arr;
for(char c: s) {
if(hash_map.count(c) != 0)
{
hash_map[c] += 1;
}
else
{
order_arr.push_back(c);
hash_map[c] = 1;
}
}
// 按照入哈希表的顺序查找
for(int i=0;i<order_arr.size();++i) {
if(hash_map[order_arr[i]] == 1) {
return order_arr[i];
}
}
return ' ';
}
};
二、二维矩阵
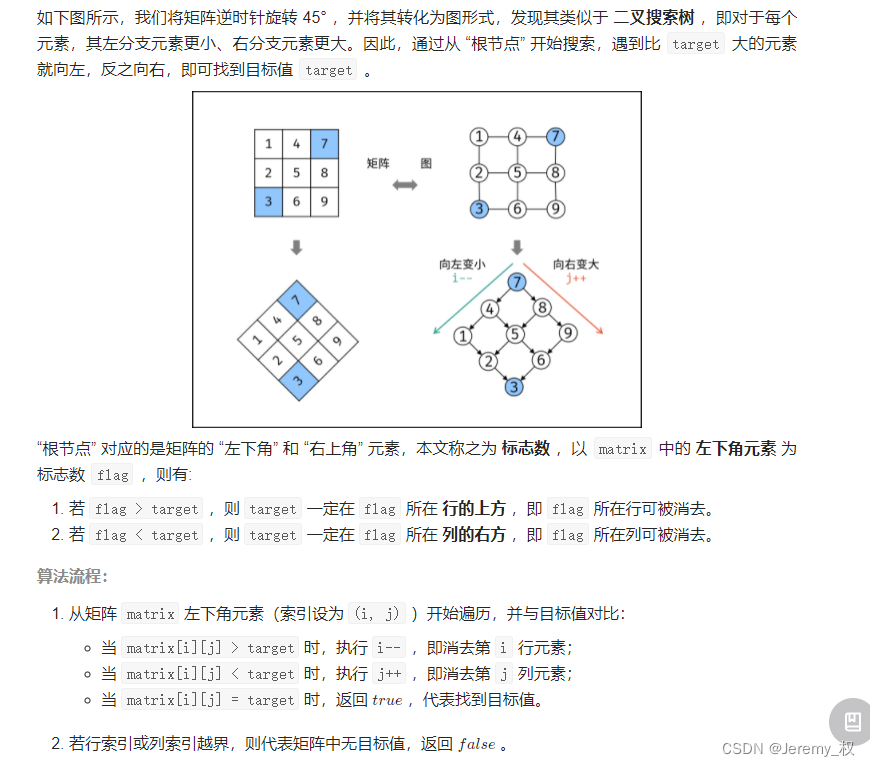
1. 二维数组中的查找
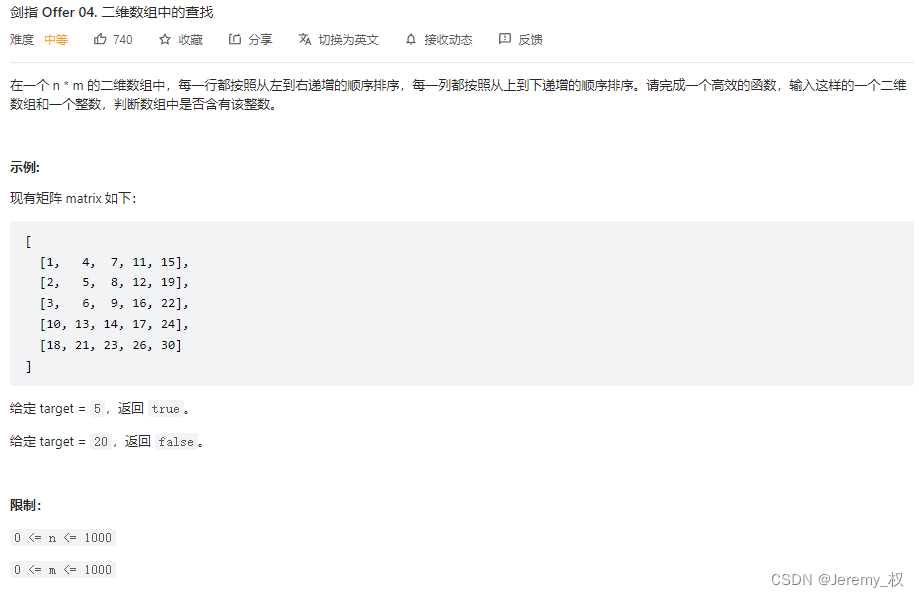
- 思路:
- 利用其排序的特点,从矩阵的右上角,仿照二叉搜索树的方式查找
- 代码:
class Solution {
public:
bool findNumberIn2DArray(vector<vector<int>>& matrix, int target) {
int i = matrix.size()-1;
int j = 0;
while(i>=0 && j<matrix[0].size())
{
if(matrix[i][j]==target)
{
return true;
}
else
{
if(matrix[i][j] < target)
{
j++;
}
else
{
i--;
}
}
}
return false;
}
};
2. 矩阵中的路径
-
题目:https://leetcode.cn/problems/ju-zhen-zhong-de-lu-jing-lcof/


-
思路:
-
就是深度搜索和剪枝(一旦判断有成功就结束整个搜索)
-
代码:
class Solution {
private:
bool trace(vector<vector<char>>& board, string &word, vector<vector<int>>& mark, int i, int j, int k)
{
if(k>=word.length())
{
// word被完整地遍历
return true;
}
if(i<0 || j<0 || i>=board.size() || j>=board[0].size())
{
// 矩阵越界
return false;
}
if(mark[i][j] == 1 || board[i][j] != word[k])
{
// 已被遍历或者不相等
return false;
}
else
{
mark[i][j] = 1;
// 分别从四个方向进行遍历
if(trace(board, word, mark, i+1, j, k+1))
{
return true;
}
if(trace(board, word, mark, i, j+1, k+1))
{
return true;
}
if(trace(board, word, mark, i-1, j, k+1))
{
return true;
}
if(trace(board, word, mark, i, j-1, k+1))
{
return true;
}
// 遍历后恢复mark状态
mark[i][j] = 0;
return false;
}
}
public:
bool exist(vector<vector<char>>& board, string word) {
vector<vector<int>> mark(board.size(), vector<int>(board[0].size(), 0));
for(int i=0;i<board.size();i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<board[0].size();j++)
{
// 逐个深度遍历
if(trace(board, word, mark, i, j, 0))
{
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
};
3. 机器人的运动范围
- 思路:
- 方法一:广度优先遍历,使用队列queue来辅助。
- 方法二:深度优先遍历,使用递归搜索。
- 但无论是广度优先遍历和深度优先遍历,都需要用一个visited矩阵记录走过的地方以便回溯;
- 而且只用往右走和往下走即可,无需回头。
- 方法三:直接遍历数组(相当于从地图的角度看),但要判断当前点是否可达。
- 代码:
class Solution {
private:
bool isReachable(int x, int y, const int &k)
{
int sum = 0;
while(x!=0)
{
sum += (x % 10);
x = x / 10;
}
while(y!=0)
{
sum += (y % 10);
y = y / 10;
}
if(sum<=k)
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
/*广度优先遍历*/
void trace_breadth(const int &m, const int &n, const int &k, int &count, vector<vector<int>> &visited)
{
//vector<vector<int>> visited(m, vector<int>(n, 0)); // 遍历记录矩阵
queue<int> x_queue, y_queue;
x_queue.push(0);
y_queue.push(0);
int x, y;
while(!x_queue.empty())
{
x = x_queue.front();
x_queue.pop();
y = y_queue.front();
y_queue.pop();
if(x<m && y<n && !visited[x][y] && isReachable(x, y, k))
{
++count;
visited[x][y] = 1;
x_queue.push(x+1);
y_queue.push(y);
x_queue.push(x);
y_queue.push(y+1);
}
}
}
/*深度优先搜索*/
void trace_depth(int x, int y, const int &m, const int &n, const int &k, int &count, vector<vector<int>> &visited)
{
if(x<m && y<n && !visited[x][y] && isReachable(x, y, k))
{
++count;
visited[x][y] = 1;
trace_depth(x+1, y, m, n, k, count, visited);
trace_depth(x, y+1, m, n, k, count, visited);
}
return;
}
public:
int movingCount(int m, int n, int k) {
int count = 0;
vector<vector<int>> visited(m, vector<int>(n, 0)); // 遍历记录矩阵
// 方法一
//trace_breadth(m, n, k, count, visited);
// 方法二
//trace_depth(0, 0, m, n, k, count, visited);
// 方法三:用数组的顺序遍历也可以,无需判断是否重复经过,但要判断是否可达
for(int i=0;i<m;++i)
{
for(int j=0;j<n;++j)
{
bool mark = false;
if(i-1>=0 && visited[i-1][j])
{
mark = true; // 从上面可达
}
if(j-1>=0 && visited[i][j-1])
{
mark = true; // 从左边可达
}
if(i==0 && j==0)
{
mark = true; // 原点
}
if(!isReachable(i, j, k))
{
mark = false;
}
if(mark)
{
++count;
visited[i][j] = 1;
}
}
}
return count;
}
};
4. 顺时针打印矩阵
-
思路:
-
用一个大循环和四个次循环,同时维护四个边界变量,模拟顺时针走势;
-
四个边界变量均为紧确界(闭区间),等号可以取到;
-
用所有的元素数量作为退出循环的标志,每个次循环做完之后都要判断一次;
-
做完一行/一列之后,该边界值就要加1;
-
返回空vector的写法为
return vector<int>()(推荐)或者return {};(C++11); -
代码:
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> spiralOrder(vector<vector<int>>& matrix) {
vector<int> re;
// r->row, c->column, u->up, b->bottom, l:left, r->right;
int ru = 0, cl = 0;
int rb = matrix.size() - 1;
if(rb >= 0) {
int cr = matrix[0].size() - 1;
// 总共是n个元素,作为退出循环的标志
int n = matrix.size() * matrix[0].size();
int i, j;
while(true) {
for(i=ru, j=cl;j<=cr;++j) {
re.push_back(matrix[i][j]);
n--;
}
++ru; // 一行做完,上界+1
if (n <= 0) {
break;
}
for(i=ru, j=cr;i<=rb;++i) {
re.push_back(matrix[i][j]);
n--;
}
--cr; // 一列做完,右界-1
if (n <= 0) {
break;
}
for(i=rb, j=cr;j>=cl;--j) {
re.push_back(matrix[i][j]);
n--;
}
--rb; // 一行做完,下界-1
if (n <= 0) {
break;
}
for(i=rb, j=cl;i>=ru;--i) {
re.push_back(matrix[i][j]);
n--;
}
++cl; // 一列做完,左界+1
if (n <= 0) {
break;
}
}
}
return re;
}
};
三、字符串
1. 替换空格
-
思路:
-
其实就是字符串的简单遍历处理。
-
代码:
class Solution {
public:
string replaceSpace(string s) {
string re_s;
re_s.resize(30000);
int i, j=0;
for(i=0;i<s.size();i++)
{
if(s[i] == ' ')
{
re_s[j++]='%';
re_s[j++]='2';
re_s[j++]='0';
}
else
{
re_s[j++]=s[i];
}
}
return re_s;
}
};
2. 字符串的排列
- 思路:
- 主要的难点是字符串中有重复的字符,因此需要从全排列中剔除掉这些重复的排列;
- 思路是使用深度优先搜索+剪枝;
- 每一次深搜前都判断当前字符是否被处理过;
- 通过交换字符可以达到遍历所有组合的效果(个人觉得这里设计得十分巧妙);
- 用
unordered_set可以判断重复元素,当然也可以用unordered_map; - 代码:
class Solution {
private:
vector<string> re;
void dfs(string &s, int x) {
if(x == s.length()) {
re.push_back(s);
return;
}
unordered_set<char> set;
for(int i=x;i<s.length();++i) {
// 只有之前还没有处理过的情况下才进行深搜
if(set.find(s[i]) == set.end()) {
set.insert(s[i]);
// 交换元素,因此字符串长度可以缩减
swap(s[i], s[x]);
dfs(s, x + 1);
// 交换元素,复原字符串
swap(s[i], s[x]);
}
}
}
public:
vector<string> permutation(string s) {
dfs(s, 0);
return re;
}
};
3. 数字序列中某一位的数字
-
思路:
-
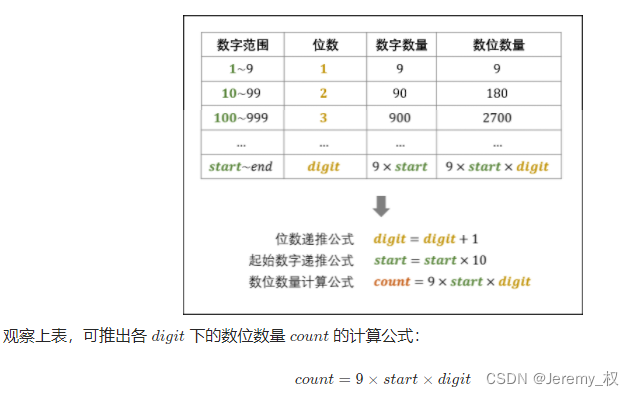
其实就是找规律,既要找到当前n表示的数字,也要记录它前面的数字和字符数量;
-
注意计算的中间结果有可能超过int最大范围,一个简单粗暴的解决方法是将所有中间变量定义为long类型;
-
提取数字的余数时用到了一个小技巧,就是将数字转成字符串再输出,这样就不用逆序求余输出了;
-
代码:
class Solution {
/*
0,
1-9, 1*9:1
10-99, 9+2*90:2
100-999, 9+2*90+3*900:3
1000-9999, 9+2*90+3*900+4*9000:4
重点是找到当前n所表示数字的digit_carry, digit_real_num, digit_char_num
*/
public:
int findNthDigit(int n) {
if(n < 10) {
return n;
}
long digit_carry = 2; // 进位数
long digit_real_num = 9; // 该进位数-1下的最大数字数量
long digit_char_num = 9; // 该进位数-1下的最大字符数量
long digit_tmp = 9;
while(digit_char_num + digit_carry*digit_tmp*10 < n) {
digit_char_num += digit_carry*digit_tmp*10;
digit_real_num += digit_tmp*10;
digit_tmp = digit_tmp*10;
++digit_carry;
}
//printf("%d, %d, %d\n", digit_carry, digit_real_num, digit_char_num);
int quotient = (n - digit_char_num) / digit_carry;
int reminder = (n - digit_char_num) % digit_carry;
int real_num = digit_real_num + quotient;
//printf("%d, %d, %d\n", quotient, reminder, real_num);
if(reminder > 0) {
real_num += 1;
}
// to_string 函数:将数字常量转换为字符串,返回值为转换完毕的字符串
string s = to_string(real_num);
return s[(reminder+digit_carry-1)%digit_carry] - '0';
}
};
4. 把数组排成最小的数
-
思路:
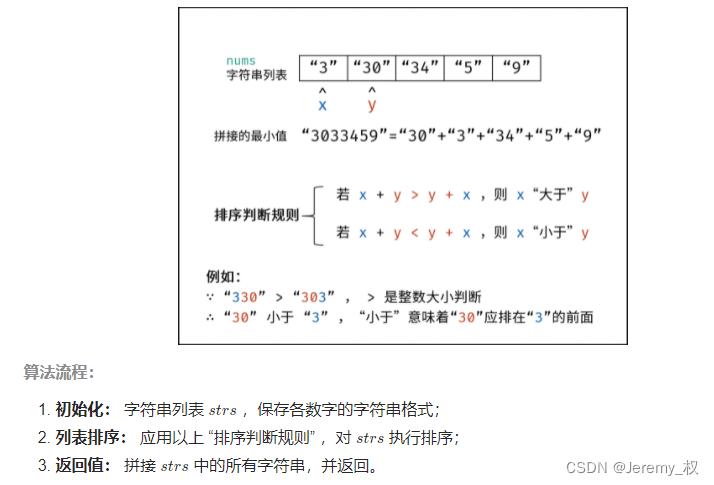
-
就是将数组转成字符串按照字典序进行排序,然后依次把排序后的序列拼接起来;
-
所以核心是完成一个自定义规则的排序;
-
自己实现的话当然是快排最好(
立刻给我写个快排出来!叉腰); -
如果是不自己实现而用
sort函数的话也不错,时间上要比自己的快排要更快; -
注意
sort函数是cmp函数的逻辑是:返回true则第一个参数排在前面; -
这应该算是一道经典的排序题;
-
代码:
class Solution {
private:
void quick_sort(vector<string> &str_arr, int low, int high) {
if(low > high) {
return;
}
string pivot = str_arr[low];
int i = low;
int j = high;
while(i < j) {
// 从high开始倒序遍历,把比pivot大的放左边
while(i<j && pivot + str_arr[j] <= str_arr[j] + pivot) {
--j;
}
if(i < j) {
str_arr[i] = str_arr[j];
++i;
}
// 从low开始顺序遍历,把比pivot小的放右边
while(i<j && str_arr[i] + pivot <= pivot + str_arr[i]) {
++i;
}
if(i < j) {
str_arr[j] = str_arr[i];
--j;
}
}
str_arr[i] = pivot;
quick_sort(str_arr, low, i-1);
quick_sort(str_arr, i+1, high);
}
public:
string minNumber(vector<int>& nums) {
vector<string> str_arr;
// 转字符串数组
for(int num: nums) {
str_arr.push_back(to_string(num));
}
// 自己实现的快排
// quick_sort(str_arr, 0, str_arr.size() - 1);
// 用sort函数
sort(str_arr.begin(), str_arr.end(), [](string &a, string &b) {
if(a+b < b+a) {
return true;
}
else {
return false;
}
});
// 拼接结果
string re;
for(string str: str_arr) {
re.append(str);
}
return re;
}
};
5. 把字符串转换成整数
- 思路:
- 非常繁琐但又不太繁琐的字符串处理;
- 确实是比其他的算法来得“繁琐”,但在字符串处理里面又不算太繁琐(=0=~常规操作);

-
难点是如何判断数字越界;
-
这里非常巧妙的利用了数字在乘10之前的值和最大值作比较,而且同时根据res和x进行判断;
-
负数是 x > = 8 x>=8 x>=8越界,正数是 x > = 7 x>=7 x>=7越界,这样可以避免出现正的
2147483648;

-
代码:
class Solution {
public:
int strToInt(string str) {
int i = 0;
// 处理开头的空格
while(str[i] == ' ') {
++i;
}
// 处理'+'和'-'
bool is_negative = false;
if(str[i] == '-') {
is_negative = true;
++i;
}
else {
if(str[i] == '+') {
// is_negative = false;
++i;
}
}
// 第一个字符不是数字,不能有效转换直接返回0
if(str[i]<'0' || str[i]>'9') {
return 0;
}
// 转换数字
int res = 0;
int max_bound = 214748364; // 2^31-1 整除以 10
while(str[i]>='0' && str[i]<='9') {
int x = str[i] - '0';
// 非常巧妙地在乘10之前就判断数字是否超过int最大值
if(res > max_bound) {
if(is_negative) { return -2147483648; }
else { return 2147483647; }
}
if(res == max_bound) {
// 这里的判断非常巧妙地使用了等于号,避免了出现正值的2147483648而溢出
if(is_negative && x >= 8) { return -2147483648; }
else { if(!is_negative && x >=7) { return 2147483647; } }
}
res = res * 10 + x;
++i;
}
// 转换正负值
if(is_negative) {
res = -res;
}
return res;
}
};
6. 翻转单词顺序
-
思路:
-
很麻烦的字符串处理,但符合字符串处理的一贯特点(也就是麻烦{{{(>_<)}}});
-
C++的做法利用类似双指针会比较好,别的方法也蛮复杂的,而且可以用的库函数不多;
-
两个指针一个记录单词的
起点-1,一个记录单词的终点,然后用substr函数截取字串; -
难点在于去除连续的空格,也要注意指针移动时字符串数组越界的问题;
-
两个数组越界分别是写作了
while(i >= 0 && s[i] == ' ');- 和
if(re.length() > 0 && re[re.length() - 1] == ' '); - 先判断是否越界再作进一步的判断;
-
代码:
class Solution {
public:
string reverseWords(string s) {
// 处理空字符串
if(s.length() == 0) {
return "";
}
string re;
int i = s.length() - 1;
int j;
// 去除末尾的空格
while(i >= 0 && s[i] == ' ') {
--i;
}
j = i;
while(i >= 0) {
if(s[i] == ' ') {
re.append(s.substr(i+1, j-i));
re.append(" ");
// 去除单词之间的空格
while(i >= 0 && s[i] == ' ') {
--i;
}
j = i;
}
else {
--i;
}
}
// 处理最后的单词
if(i != j)
{
re.append(s.substr(i+1, j-i));
}
// 去除最后的空格
if(re.length() > 0 && re[re.length() - 1] == ' ') {
re = re.substr(0, re.length() - 1);
}
return re;
}
};
7. 左旋转字符串
- 思路:
- 不那么复杂的字符串处理;
- 两种处理的思路:
- 一种是通过切片来拼接字符串(这种比较API优雅);
- 一种是通过循环求余来重组字符串(这种比较底层优雅);
- 总之都可以很优雅
(不是);
- 代码:
- 切片拼接:
class Solution {
public:
string reverseLeftWords(string s, int n) {
string re;
re.append(s.substr(n, s.length() - n));
re.append(s.substr(0, n));
return re;
}
};
- 循环求余拼接:
class Solution {
public:
string reverseLeftWords(string s, int n) {
string re(s);
for(int i=n;i<n+s.length();++i) {
re[i-n] = s[i%s.length()];
}
return re;
}
};
四、链表
1. 从尾到头打印链表
-
思路:
-
使用了额外的栈来辅助输出,涉及链表和栈的基本用法。
-
代码:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> reversePrint(ListNode* head) {
ListNode* cur = head;
vector<int> arr;
if(!cur)
{
return arr;
}
arr.push_back(cur->val);
while(cur->next)
{
cur = cur->next;
arr.push_back(cur->val);
}
vector<int> final_arr(arr);
for(int i=0;i<arr.size();i++)
{
final_arr[i] = arr[arr.size() - 1 - i];
}
return final_arr;
}
};
2. 删除链表的节点
- 思路:
- 就是简单的链表删除节点操作。
- 注意需要额外考虑头节点的删除。
- 代码:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* deleteNode(ListNode* head, int val) {
ListNode *cur = head;
ListNode *pre = head;
while(cur)
{
if(cur->val==val)
{
if(cur==head)
{
// 考虑头节点的移动,因为最终返回的是头节点
head = cur->next;
}
else
{
// 注意是pre->next
pre->next = cur->next;
}
//delete cur;
cur = nullptr;
pre = nullptr;
break;
}
else
{
pre = cur;
cur = cur->next;
}
}
return head;
}
};
3. 反转链表
- 思路:
- 直接遍历一次整个链表,然后用一前一中一后三个指针直接修改节点之间的指向
- 注意初始头节点->next最后要置空
- 注意
head==nullptr的情况 - 代码:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
/*
连续定义时每个指针变量都要加*
*/
ListNode *first, *second, *temp;
first = head;
if(first)
{
second = head->next;
while(second)
{
temp = second->next;
second->next = first;
first = second;
second = temp;
}
head->next = NULL;
}
return first;
}
};
4. 合并两个排序的链表
- 思路:
- 用一个新的头节点,然后逐个比较两个原有列表的头节点,逐个插入到新的链表中;
- 如果不用伪头节点,则要单独处理头节点;
- 下图是采用了伪头节点的,也就是
prehead指向的节点,最终返回的是prehead->next; - 别的链表的题目也可以尝试使用伪头节点来避免单独处理头节点;
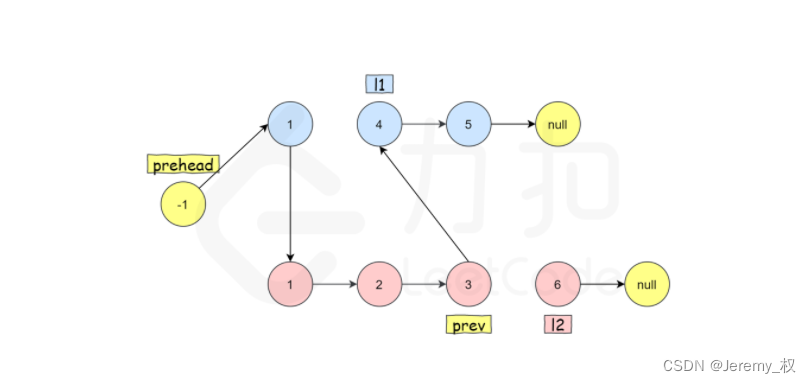
- 代码:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* mergeTwoLists(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) {
// 一方为空,则直接返回非空链表
if(!l1)
{
return l2;
}
if(!l2)
{
return l1;
}
// 新建伪头节点
ListNode* head = new ListNode(-1);
// 处理两个非空链表
// 非头节点用pre处理
// 三步走:pre->next = node; node = node->next; pre = pre->next;
ListNode* pre = head;
while(l1 && l2)
{
if(l1->val <= l2->val)
{
pre->next = l1;
l1 = l1->next;
}
else
{
pre->next = l2;
l2 = l2->next;
}
pre = pre->next;
}
// 处理剩下的非空链表
// 直接拼接就行
if(l1)
{
pre->next = l1;
}
else
{
pre->next = l2;
}
// 伪头节点要舍弃
return head->next;
}
};
5. 复杂链表的复制
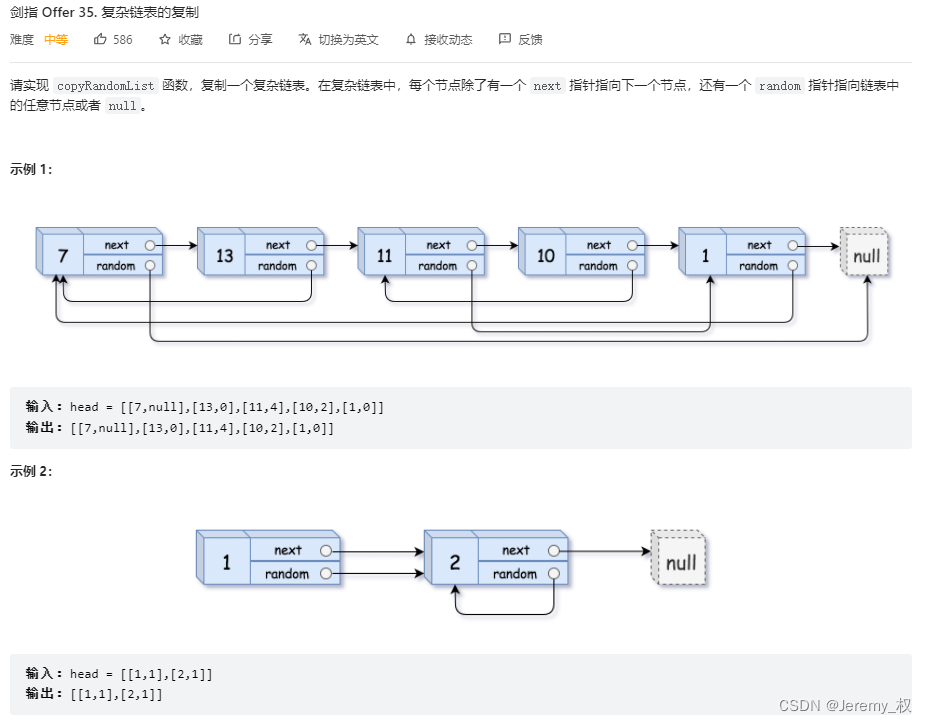
-
总的思路:
-
其实和普通的链表复制相比,这里的难点是要处理random指针指向的节点未新建情况;
-
而且新节点random指向的是新节点值,且值要和原节点random指向的节点值相同;
-
思路1:
-
递归处理random和next;
-
如果指针指向的节点还没有新建,则继续递归先新建该复制节点,再返回来用指针指向;
-
由于是随机新建复制节点,而不是顺序新建复制节点,所以还要用哈希表记录当前已经新建的复制节点;
-
这样的时间复杂度是O(N),空间复杂度也是O(N),因为用了空间为N的哈希表;
-
代码1:
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public:
int val;
Node* next;
Node* random;
Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
next = NULL;
random = NULL;
}
};
*/
class Solution {
private:
unordered_map<Node*, Node*> cachedMap;
public:
Node* copyRandomList(Node* head) {
if(head == nullptr) {
return nullptr;
}
else {
if(cachedMap.count(head) == 0) {
cachedMap[head] = new Node(head->val);
cachedMap[head]->next = copyRandomList(head->next);
cachedMap[head]->random = copyRandomList(head->random);
}
return cachedMap[head];
}
}
};
- 思路2:
- 分三次遍历原链表;
- 第一次遍历只新建复制节点,同时将复制节点放在原节点之后;
- 第二次遍历按照原链表的random指向,修改复制节点的random指向;
- 由于此时所有的复制节点都已经新建了,所以不会有random指向的节点仍没有新建的情况;
- 第三次遍历分离两个链表;
- 这样的时间复杂度是O(N),空间复杂度降为O(1),避免了哈希表的使用;
- 但时间复杂度上应该要高一点,这里是O(3N),上面思路1是O(N),虽然它们的数量级相同;
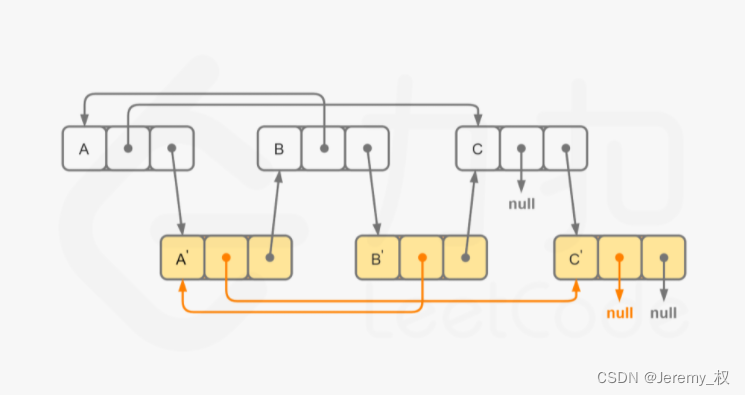
- 代码2:
class Solution {
public:
Node* copyRandomList(Node* head) {
if(head == nullptr) {
return nullptr;
}
Node* cur = head;
// 原地拷贝
while(cur != nullptr) {
Node* tmp = new Node(cur->val);
tmp->next = cur->next;
cur->next = tmp;
// cur只遍历原序列的节点
cur = tmp->next;
}
// 改random指向
cur = head;
while(cur != nullptr) {
if(cur->next->random == nullptr) {
if(cur->random == nullptr) {
cur->next->random = nullptr;
}
else {
cur->next->random = cur->random->next;
}
}
// cur只遍历原序列的节点,因为原序列也有可能random == nullptr
cur = cur->next->next;
}
// 两个链表分离
Node* new_head = head->next;
cur = head;
Node* new_cur = new_head;
while(cur != nullptr) {
// cur在原序列中走到下一个cur
cur->next = new_cur->next;
cur = cur->next;
if(cur != nullptr) {
// new_cur在新序列中走到下一个new_cur
// cur如果走到了尽头,那么new_cur就不需要再进一步了
new_cur->next = cur->next;
new_cur = new_cur->next;
}
}
return new_head;
}
};
五、二叉树
1. 重建二叉树
-
题目:https://leetcode.cn/problems/zhong-jian-er-cha-shu-lcof/submissions/
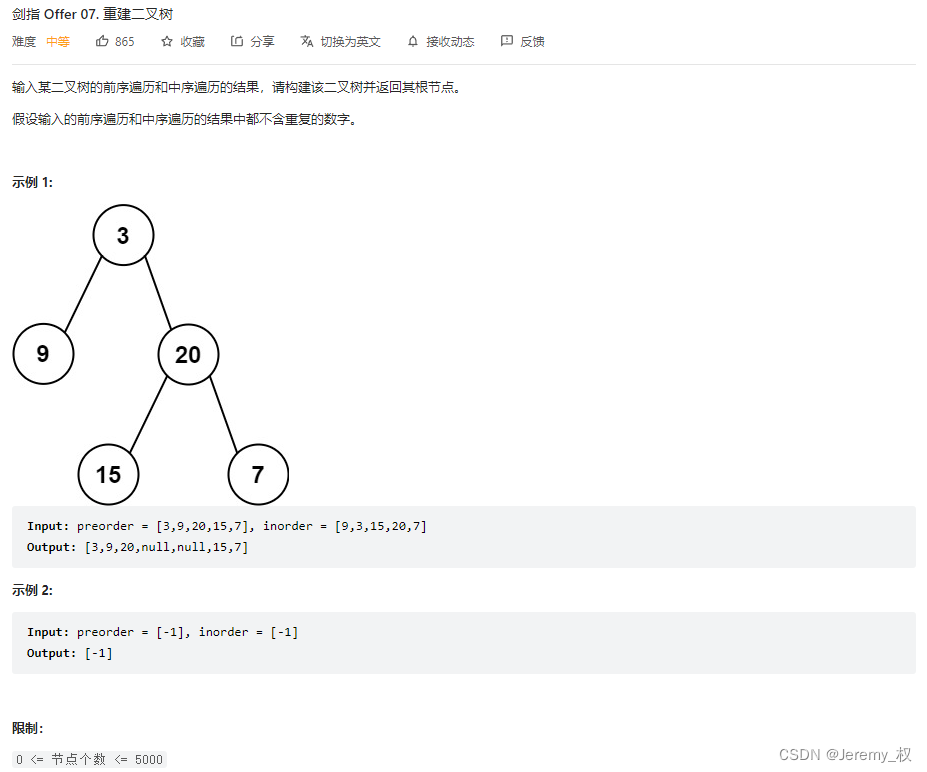
-
思路:
-
先按照前序遍历确定根节点,再按照中序遍历划分子树
-
通过哈希表快速定位根节点能够节省时间
-
用递归的方式求解

-
代码:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
private:
unordered_map<int, int> inorder_map;
TreeNode* myBuildTree(int preorder_left, int preorder_right, int inorder_left, int inorder_right, vector<int>& preorder, vector<int>& inorder){
if(preorder_left>preorder_right)
{
return nullptr; // edge control
}
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(preorder[preorder_left]); // record the root value
int left_length = inorder_map[preorder[preorder_left]] - inorder_left; // length of left sub-tree
root->left = myBuildTree(preorder_left+1, preorder_left+left_length, inorder_left, inorder_left+left_length-1, preorder, inorder); // deal with the left tree
int right_length = inorder_right - inorder_map[preorder[preorder_left]]; // length of right sub-tree
root->right = myBuildTree(preorder_left+1+left_length, preorder_right, inorder_left+left_length+1, inorder_right, preorder, inorder); // deal with the right tree
return root;
}
public:
TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& preorder, vector<int>& inorder) {
for(int i=0;i<inorder.size();i++)
{
inorder_map[inorder[i]] = i;
}
return myBuildTree(0, preorder.size()-1, 0, inorder.size()-1, preorder, inorder);
}
};
2. 树的子结构
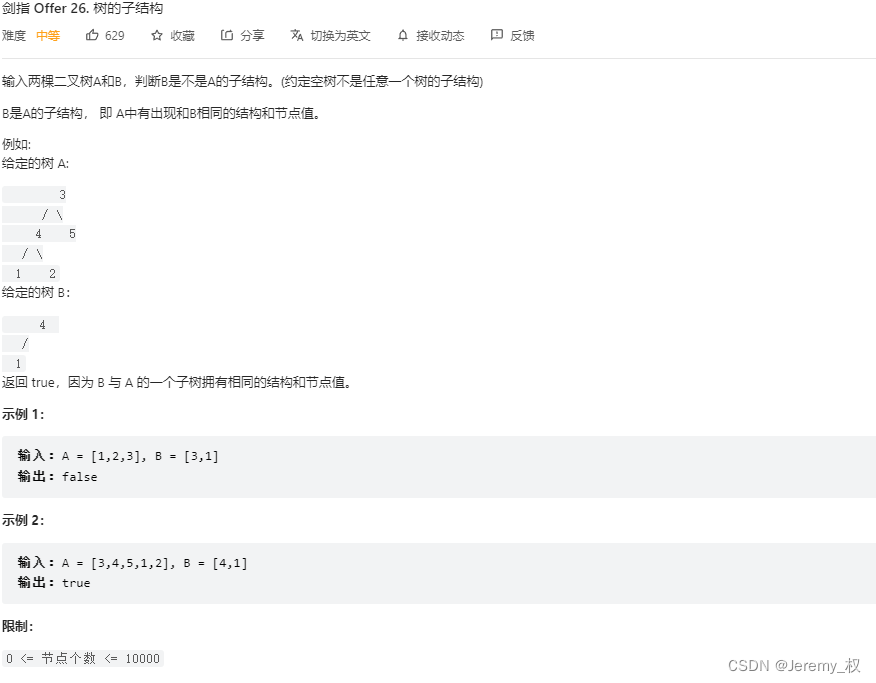
- 思路:

- 代码:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
private:
// 判断A树是否包含同根B树
bool recur(TreeNode* A, TreeNode* B) {
if(B == nullptr) {
// B树为空,则匹配完成
return true;
}
else {
// A树为空或者值不相等,则不匹配
if(A == nullptr) {
return false;
}
if(A->val != B->val) {
return false;
}
// 注意凡是A->***的情况都要提前判断A是否为空值
return recur(A->left, B->left) && recur(A->right, B->right);
}
}
public:
// 判断A树是否包含B树子结构
bool isSubStructure(TreeNode* A, TreeNode* B) {
if(B == nullptr) {
// 按照定义,B树为空则不可能是A的子结构
return false;
}
else {
if(A == nullptr) {
return false;
}
// 注意凡是A->***的情况都要提前判断A是否为空值
return recur(A, B) || isSubStructure(A->left, B) || isSubStructure(A->right, B);
}
}
};
3. 二叉树的镜像
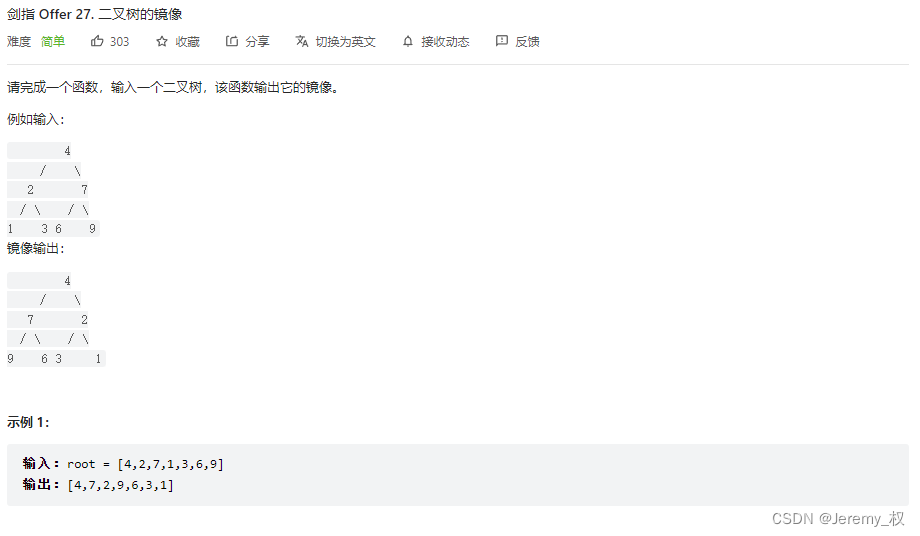
-
思路:
-
就是用递归的思想;
-
先递归处理左右子树,让左右子树镜像;
-
然后再交换左右子树;
-
代码:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* mirrorTree(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == nullptr)
{
return nullptr;
}
// 递归处理左右子树
TreeNode* temp_left = mirrorTree(root->left);
TreeNode* temp_right = mirrorTree(root->right);
// 交换左右子树
root->left = temp_right;
root->right = temp_left;
return root;
}
};
4. 对称的二叉树
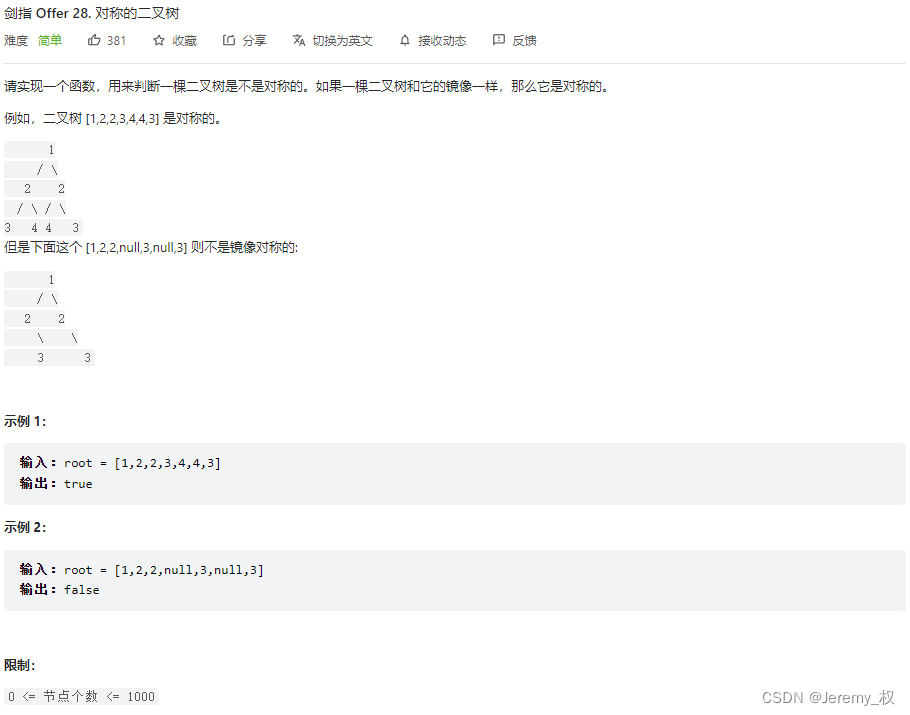
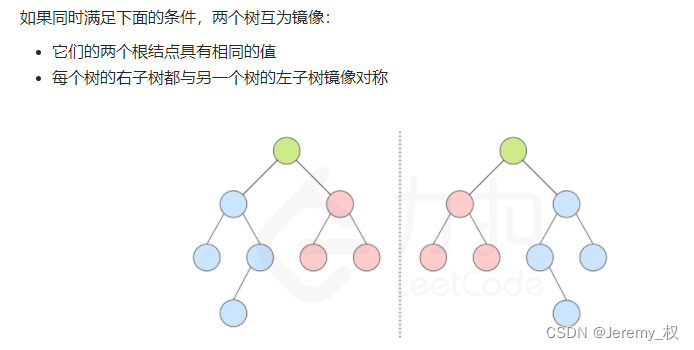
- 思路:
- 还是递归;
- 转换为判断两棵子树是否为镜像;
- 左树的左子树和右树的右子树镜像,左树的右子树和右树的左子树镜像;
- 代码:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
private:
bool check(TreeNode* left, TreeNode* right) {
if(left == nullptr && right == nullptr)
{
// 左右两树都是空
return true;
}
if(left == nullptr || right == nullptr) {
// 只有一棵树为空
return false;
}
if(left->val != right->val) {
// 左右两树值不相等
return false;
}
if(check(left->left, right->right) && check(left->right, right->left))
{
// 两两分别镜像
return true;
}
else {
return false;
}
}
public:
bool isSymmetric(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == nullptr) {
// 使用->前首先要判断节点是否为空
return true;
}
else {
return check(root->left, root->right);
}
}
};
5. 从上到下打印二叉树
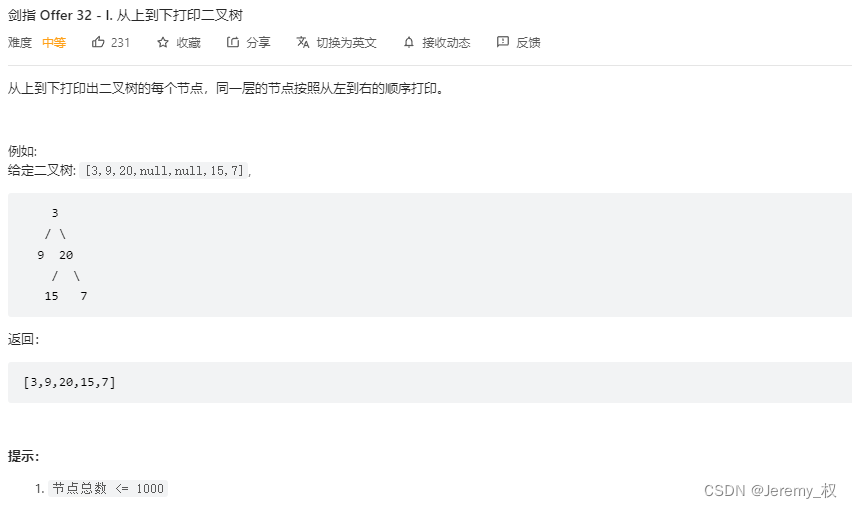
-
思路:
-
就是用广度优先遍历二叉树就可以了;
-
注意考虑二叉树为空的情况;
-
遍历时从队列取数据记得要同时完成
s.front()和s.pop(); -
代码:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> levelOrder(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> re;
queue<TreeNode*> q;
q.push(root);
while(!q.empty()) {
// 从队列中取数据
TreeNode* tmp = q.front();
if(tmp != nullptr) {
re.push_back(tmp->val);
q.push(tmp->left);
q.push(tmp->right);
}
// 从队列中删数据
q.pop();
}
return re;
}
};
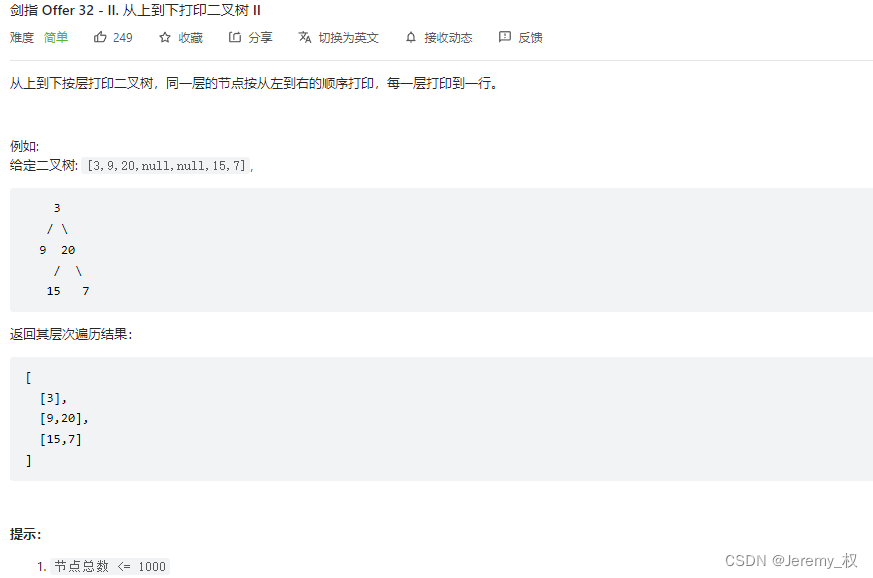
变体1. 按层输出的从上到下打印二叉树
-
题目:https://leetcode.cn/problems/cong-shang-dao-xia-da-yin-er-cha-shu-ii-lcof/
-
思路1:
-
考虑用两个队列来实现,每个队列代表一层,轮流处理;
-
但这种方式消耗会大一些;
-
代码1:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(TreeNode* root) {
vector<vector<int>> re;
queue<TreeNode*> q1;
queue<TreeNode*> q2;
q1.push(root);
while(!q1.empty() || !q2.empty()) {
vector<int> cur;
while(!q1.empty()) {
TreeNode* tmp = q1.front();
if(tmp != nullptr) {
cur.push_back(tmp->val);
q2.push(tmp->left);
q2.push(tmp->right);
}
q1.pop();
}
if(!cur.empty()) {
re.push_back(cur);
}
cur.clear();
while(!q2.empty())
{
TreeNode* tmp = q2.front();
if(tmp != nullptr) {
cur.push_back(tmp->val);
q1.push(tmp->left);
q1.push(tmp->right);
}
q2.pop();
}
if(!cur.empty()) {
re.push_back(cur);
}
}
return re;
}
};
- 思路2:
- 每次开始处理队列的时候,先记录队列的长度;
- 因为这个时候队列中的所有元素都是同一层的;
- 然后集中处理完这些元素,再进行下一次的队列处理;
- 这样只需要用一个队列即可完成;
- 代码2:
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(TreeNode* root) {
vector<vector<int>> re;
queue<TreeNode*> q;
q.push(root);
while(!q.empty()) {
vector<int> cur;
int q_size = q.size();
// 记录当前队列的长度,这些元素都是同一层的
for(int i=0;i<q_size;i++) {
TreeNode* tmp = q.front();
if(tmp != nullptr) {
cur.push_back(tmp->val);
q.push(tmp->left);
q.push(tmp->right);
}
q.pop();
}
if(!cur.empty()) {
re.push_back(cur);
}
}
return re;
}
};
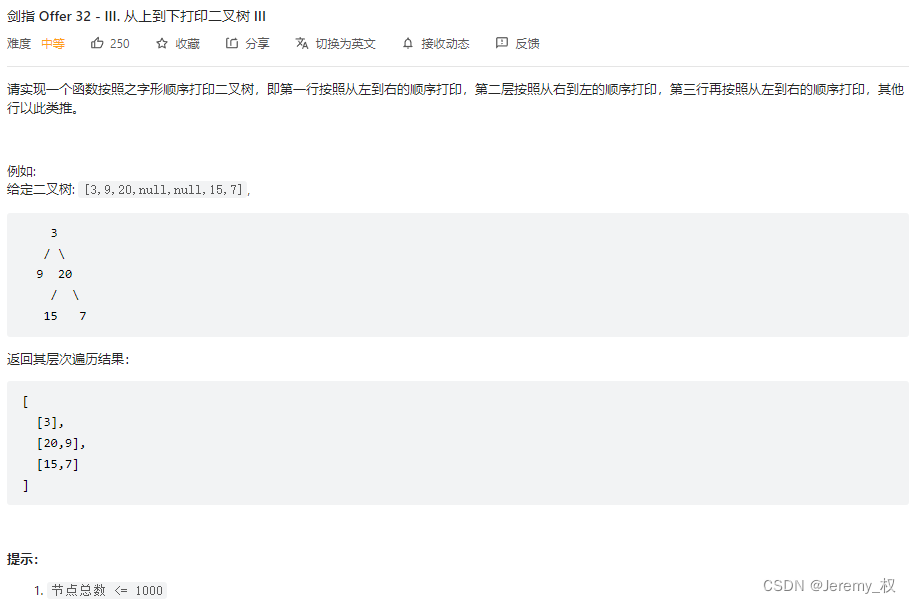
变体2. 按层之字形输出的从上到下打印二叉树
-
思路:
-
还是同变体1的思路,增加使用队列的长度来批量处理一层的元素;
-
仍是用队列进行广度优先遍历;
-
但存储元素的值使用双向队列
deque代替vector,这样就可以做到不同层的反序输出; -
代码:
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(TreeNode* root) {
vector<vector<int>> re;
queue<TreeNode*> q;
bool is_left = true;
q.push(root);
while(!q.empty()) {
int q_size = q.size();
// 用deque代替vector保存序列
deque<int> dq;
for(int i=0;i<q_size;++i) {
TreeNode* tmp = q.front();
if(tmp != nullptr) {
if(is_left) {
// 从后压入,正序
dq.push_back(tmp->val);
}
else {
// 从前压入,反序
dq.push_front(tmp->val);
}
// printf("%d\n", tmp->val);
q.push(tmp->left);
q.push(tmp->right);
}
q.pop();
}
if(!dq.empty()) {
// emplace_back连续复制
re.emplace_back(vector<int>{dq.begin(), dq.end()});
}
// 翻转序列
is_left = !is_left;
}
return re;
}
};
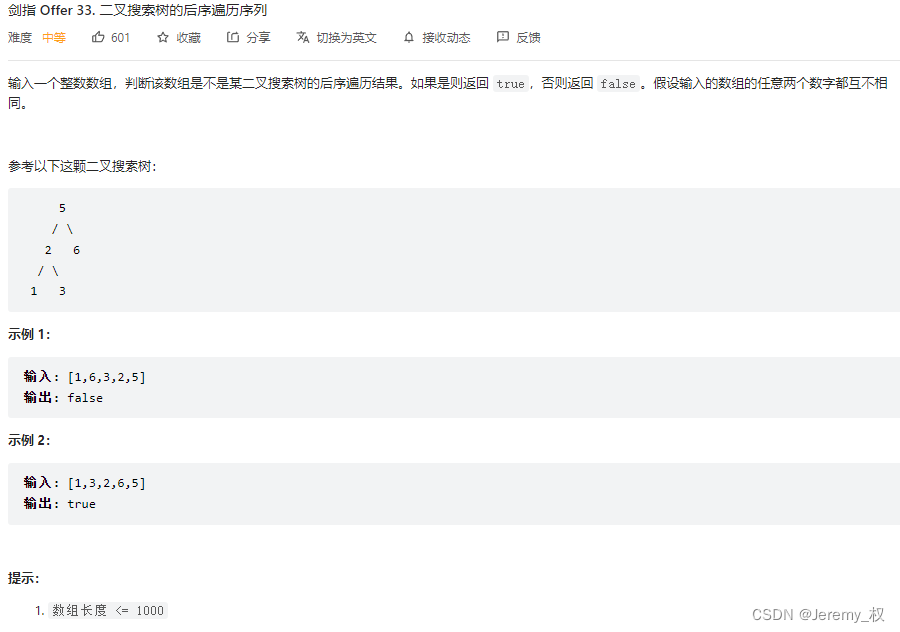
6. 二叉搜索树的后序遍历序列
-
题目:https://leetcode.cn/problems/er-cha-sou-suo-shu-de-hou-xu-bian-li-xu-lie-lcof/
-
思路:
-
注意不是普通的二叉树而是二叉搜索树;
-
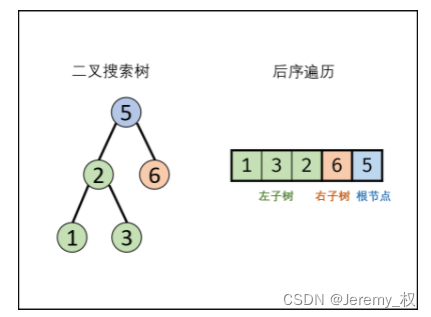
二叉搜索树的特点是左子树的值均小于根节点,右子树的值均大于根节点;
-
后序遍历的最后一个元素一定是根节点;
-
因此核心思路就是先找到右子树,然后验证右子树的节点值是否都大于根节点;
-
从左往右遍历到第一个大于根节点的值的节点(
left+1),假定该节点左边均为左子树; -
从该节点开始验证右子树节点是否都大于根节点的值;
-
递归验证左子树和右子树;
-
另外,要注意没有左子树或者没有右子树的情况;
-
代码:
class Solution {
private:
// left:左子树根节点,right:右子树根节点,root:根节点
bool backOrderTraverse(vector<int>& postorder, int begin, int end) {
if(begin == end) {
// 只有一个节点
return true;
}
if(postorder[begin] < postorder[end]) {
int left = begin;
// 找左子树根节点设为left
while(left+1<end && postorder[left + 1]<postorder[end]) {
left++;
}
// 判断右子树的合法性
for(int i=left+1;i<end;i++) {
if(postorder[i]<postorder[end]) {
return false;
}
}
// left一定在end左边且不重合
// 但left+1有可能和end重合,因为可能没有右子树,所以还是要用end
return backOrderTraverse(postorder, begin, left) && backOrderTraverse(postorder, left+1, end);
}
else {
// 没有左子树,直接判断右子树的合法性
for(int i=begin;i<end;i++) {
if(postorder[i]<postorder[end]) {
return false;
}
}
// 不可能没有右子树,所以可以用end-1
return backOrderTraverse(postorder, begin, end-1);
}
}
public:
bool verifyPostorder(vector<int>& postorder) {
if(postorder.size() == 0) {
return true;
}
else {
// 递归验证序列是否满足二叉搜索树定义
return backOrderTraverse(postorder, 0, postorder.size()-1);
}
}
};
7. 二叉树中和为某一值的路径
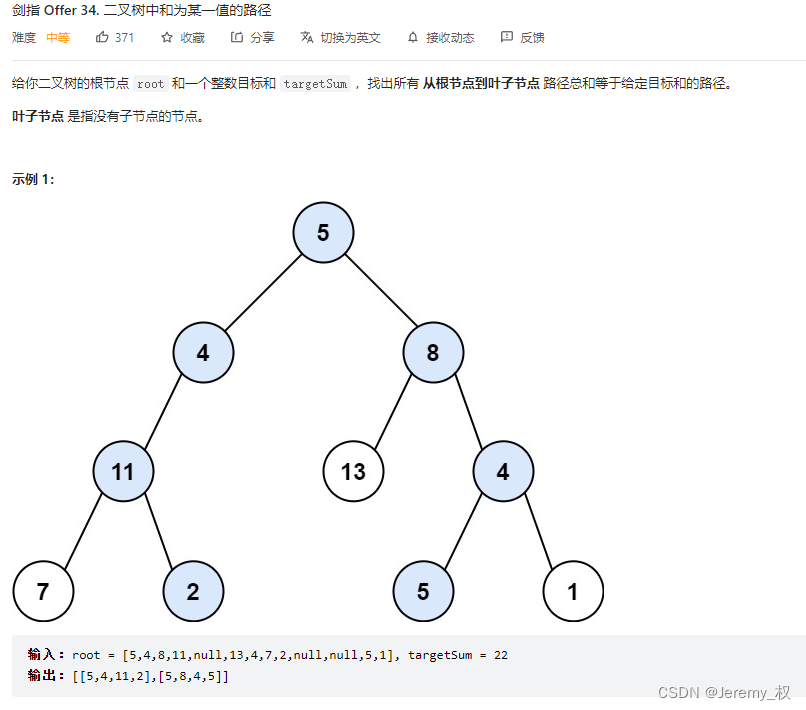
-
思路:
-
深度搜索遍历即可;
-
用一个vector保存当前的路径;
-
在叶子节点处,即
cur->left==nullptr && cur->right==nullptr时判断路径是否符合要求; -
注意给定的叶子节点和路径和有可能是负数;
-
代码:
class Solution {
private:
void traverse(TreeNode* cur, int rest, vector<int> &cur_path, vector<vector<int>> &re) {
if(cur == nullptr) {
// 遇到空节点就返回
return;
}
cur_path.push_back(cur->val);
if(rest - cur->val == 0 && cur->left == nullptr && cur->right == nullptr) {
// 当前是叶子节点且值为0
re.push_back(cur_path);
}
traverse(cur->left, rest-cur->val, cur_path, re); // 遍历左边
traverse(cur->right, rest-cur->val, cur_path, re); // 遍历右边
cur_path.pop_back();
}
public:
vector<vector<int>> pathSum(TreeNode* root, int target) {
vector<vector<int>> re;
vector<int> cur_path;
traverse(root, target, cur_path, re);
return re;
}
};
8. 二叉搜索树与双向链表
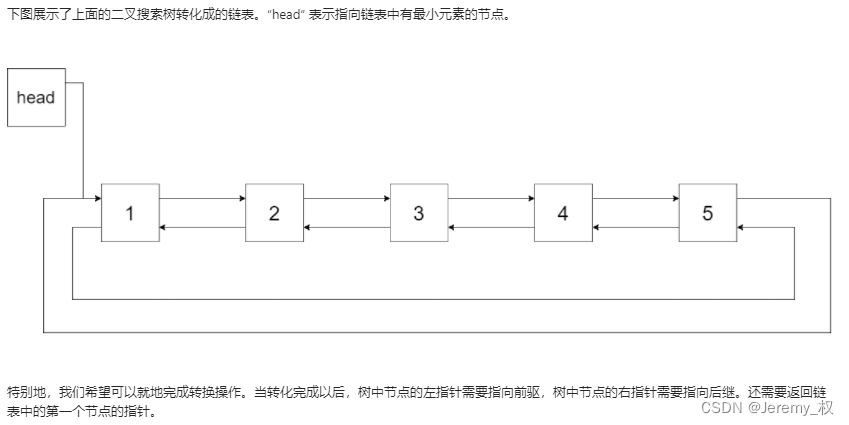
- 思路:
- 二叉搜索树能和双向链表相互转换的关键是:树有左右两个指针,双向链表也有前后两个指针;
- 核心是用中序遍历,因为中序遍历二叉搜索树之后能够得到有序序列;
- 可以简化成按照中序遍历打印节点的顺序处理节点,如下:
void dfs(Node* root) {
if(root == nullptr) {
return;
}
// 处理左节点
dfs(root->left);
// 处理当前节点
printf("%d\n", root->val);
// 处理右节点
dfs(root->right);
}
-
重点是只需处理当前的root节点,同时记录一个pre节点记录之前的一个节点;
-
处理结束后需要额外修改头节点和尾节点的指针,形成循环链表;
-
代码:
class Solution {
private:
Node *pre = nullptr, *head = nullptr;
void dfs(Node* root) {
if(root == nullptr) {
return;
}
// 处理左节点
dfs(root->left);
// 处理当前节点
if(pre == nullptr) {
// 第一次访问到的节点是头节点
pre = root;
head = root;
}
else {
pre->right = root; // 前向指针
root->left = pre; // 后向指针
pre = root; // 移动pre指针
}
// 处理右节点
dfs(root->right);
}
public:
Node* treeToDoublyList(Node* root) {
if(root == nullptr) {
return nullptr;
}
dfs(root);
// 修改头尾指针为循环指向
head->left = pre;
pre->right = head;
return head;
}
};
9. 二叉搜索树的第k大节点

-
思路:
-
因为二叉搜索树的中序遍历是有序的,所以仿照中序遍历即可;
-
但注意这里找的是第k大的节点,而中序遍历是从小到大的,因此需要按照中序遍历的逆序,也就是“右->根->左”的顺序来遍历即可;
-
要用两个全局变量保存当前计数和第k大节点的值;
-
可以进行剪枝,因为一旦搜索到目标值,就不需要再往下遍历了;
-
代码:
class Solution {
private:
int re;
int count;
void traverse(TreeNode* root, int k) {
if(root == nullptr) {
return;
}
else {
traverse(root->right, k);
if(count == k) {
// 提前剪枝
return;
}
++count;
if(count == k) {
re = root->val;
return;
}
traverse(root->left, k);
}
}
public:
int kthLargest(TreeNode* root, int k) {
count = 0;
traverse(root, k);
return re;
}
};
10. 二叉树的深度
-
思路:
-
就做一遍遍历二叉树即可;
-
一种思路是从顶往下记录深度,然后到null节点时用一个全局变量记录最大值,这种方式类似于先序遍历,根节点的处理就是将深度+1;
-
另一种思路是从底往上返回左右子树的最大高度,最后从root返回最大的高度,这种实现起来代码更加简洁一点,但需要用后序遍历,因为root的高度由左右子树高度决定;
-
代码:
-
下面的代码用了第二种思路实现:
class Solution {
private:
int traverse(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == nullptr) {
return 0;
}
return max(traverse(root->left), traverse(root->right)) + 1;
}
public:
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
return traverse(root);
}
};
11. 平衡二叉树
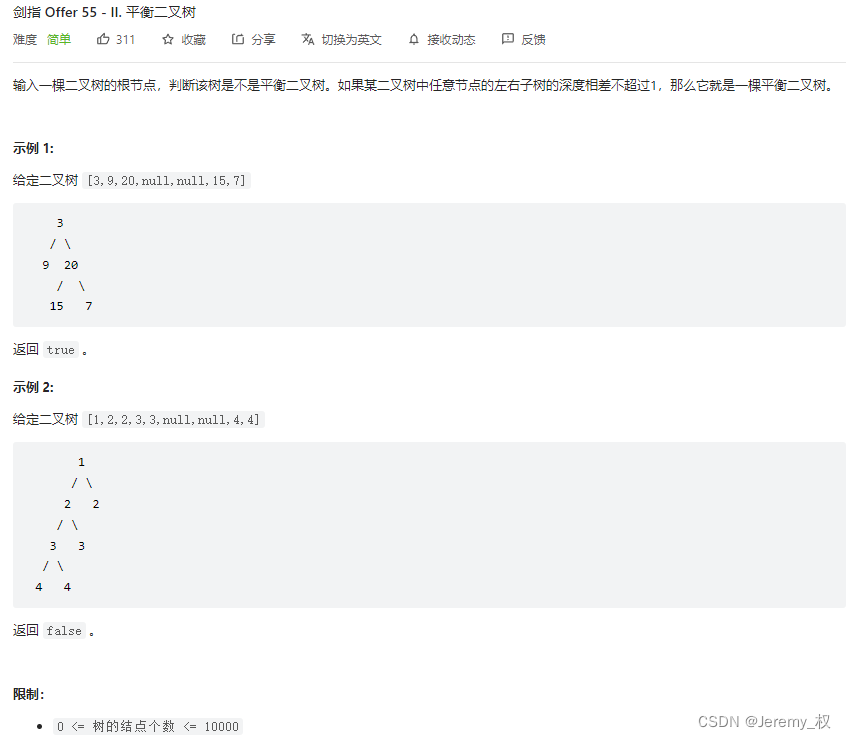
- 思路:
- 和10. 二叉树的深度很像;
- 可以用从底往上的方法来遍历二叉树,也就是后序遍历;
- 同时用一个全局变量记录结果,并可用于提前剪枝;
- 剪枝是在每一个递归调用(除最后一个)后进行的,作用是避免进入之后的递归调用;
- 当然提前剪枝后最终的返回值就不是树的高度了,虽然使用了
int返回类型; - 代码:
class Solution {
private:
bool re;
int traverse(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == nullptr) {
return 0;
}
int left = traverse(root->left);
if(re == false) {
// 提前剪枝
return -1;
}
int right = traverse(root->right);
if(abs(left - right) > 1) {
re = false;
}
return max(left, right) + 1;
}
public:
bool isBalanced(TreeNode* root) {
re = true;
traverse(root);
return re;
}
};
12. 二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先

- 思路:
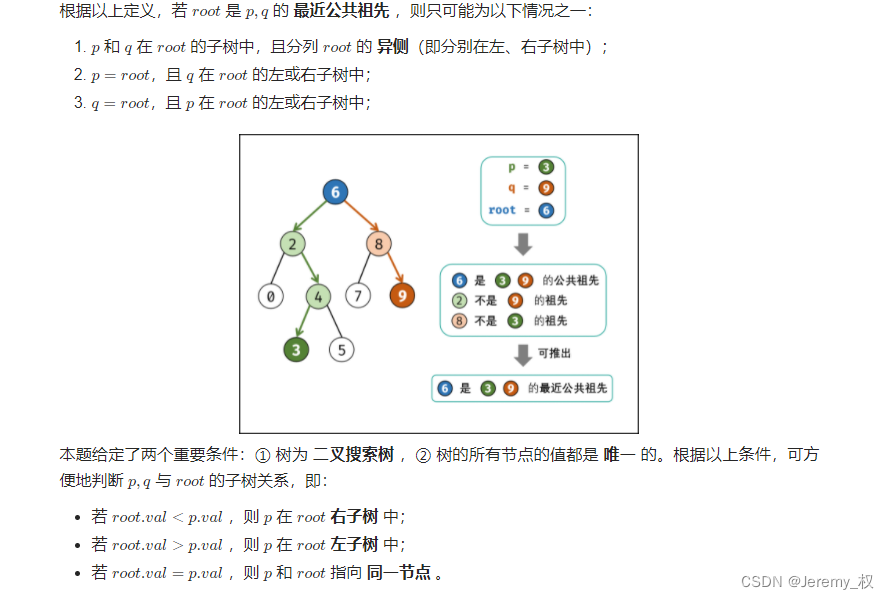
-
核心其实是利用了二叉搜索树来判断
p和q节点是在root的左子树还是右子树; -
实现的话是用了递归,当然也可以用while循环来迭代遍历,因为
p和q相对于root的位置是已知的,因此深搜的路径是确定的,无需回溯; -
代码:
class Solution {
public:
/*
root是最近公共祖先有三种情况:
1. p和q分别在root的左右子树
2. p在root的左子树或右子树,q在root
3. q在root的左子树或右子树,p在root
因此需要递归(也就是不是最近公共祖先)的情况只剩两种:
1. p和q都在root的左子树
2. p和q都在root的右子树
二叉搜索树直接可以通过值来确定p和q是在左子树还是右子树
*/
TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {
if(p->val < root->val && q->val < root->val) {
// 均在左子树上
return lowestCommonAncestor(root->left, p, q);
}
if(p->val > root->val && q->val > root->val) {
// 均在右子树上
return lowestCommonAncestor(root->right, p, q);
}
// 剩下的是root为公共祖先的三种情况
return root;
}
};
变体. 二叉树的最近公共祖先
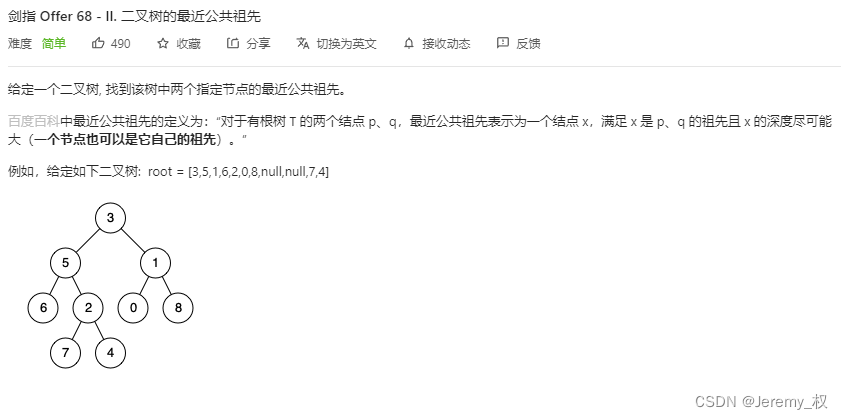
-
思路:
-
其实思路和上面的是很像的,只不过去掉了二叉搜索树这个前提,改为一般的二叉树;
-
也就是说,现在无法通过单纯的值比较来确定
p和q节点是在左子树上还是右子树上; -
只能通过深度搜索来确定,所以这样最坏情况下整棵树的所有节点都会被遍历到;
-
值得注意的是,需要单独处理root是
p或者q节点而另一个节点在它的左右子树中的情况,在这种情况下,root就是要找的最近父节点; -
代码:
class Solution {
public:
/*
相当巧妙的递归,分成两个阶段:
1. 还没有找到最近的父节点时 -> left和right若不为空,则代表该子树包含p或者q
根据这个可以找到最近的父节点
2. 已经找到最近的父节点时 -> left或者right若不为空,则代表该子树包含最近的父节点
此时不可能出现左右子树不同时为空的情况,之后再逐层往回传递该父节点即可
*/
TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {
if(root == nullptr) {
return nullptr;
}
if(root == p || root == q) {
// 如果另一个节点在root的子树中
// 则root节点其实就是所要找的最近父节点
// 如果不在root子树中,也没有必要继续往下遍历了
return root;
}
TreeNode *left = lowestCommonAncestor(root->left, p, q);
TreeNode *right = lowestCommonAncestor(root->right, p, q);
if(left == nullptr) {
// p和q都不在左边
// 也隐含了p和q既都不在左边也都不在右边
return right;
}
if(right == nullptr) {
// p和q都不在右边
return left;
}
// p和q分别位于左右子树中,则root是最近公共父节点
return root;
}
};
六、队列和栈
1. 用两个栈实现队列
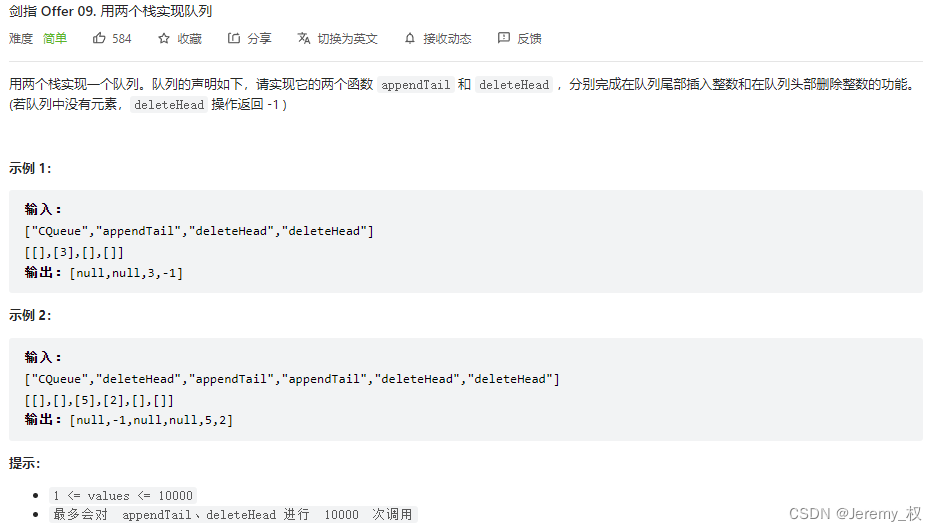
-
思路:
-
用两个栈,一个存输入数据,一个反序压栈,做输出。

-
代码:
class CQueue {
stack<int> input_stack, output_stack;
public:
CQueue() {
}
/*
双栈:一个用于读入数据,一个用于将数据反序并输出
输入:直接压入栈A
输出:栈B有就直接输出,没有就将A的所有元素过到B中
*/
void appendTail(int value) {
input_stack.push(value);
}
int deleteHead() {
if(!output_stack.empty())
{
int re = output_stack.top();
output_stack.pop();
return re;
}
else
{
if(input_stack.empty())
{
return -1;
}
else
{
while(!input_stack.empty())
{
output_stack.push(input_stack.top());
input_stack.pop();
}
int re = output_stack.top();
output_stack.pop();
return re;
}
}
}
};
/**
* Your CQueue object will be instantiated and called as such:
* CQueue* obj = new CQueue();
* obj->appendTail(value);
* int param_2 = obj->deleteHead();
*/
2. 栈的压入、弹出序列
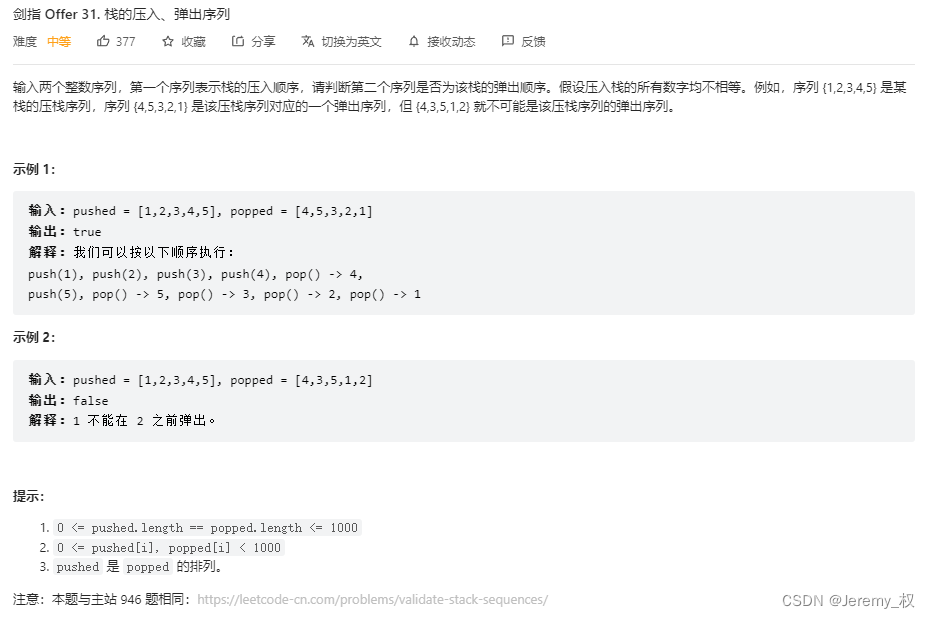
-
思路:
-
直接用栈来模拟,验证能不能得到popped序列;
-
分别用两个指针指向两序列当前正在验证的元素;
-
栈每压入一个pushed的元素,就尝试弹出所有能和popped序列对应的元素;
-
直到压入全部元素,此时验证popped序列对应元素是否都能被栈弹出(也就是指针是否到尽头);
-
另外,两个序列长度不等时立刻就能判断它们一定不对应;
-
使用
s.top()前一定要先判断s.empty(); -
代码:
class Solution {
public:
bool validateStackSequences(vector<int>& pushed, vector<int>& popped) {
stack<int> s;
if(pushed.size() != popped.size()) {
// 两个序列长度不相等
return false;
}
int index1 = 0;
int index2 = 0;
// 下面的while包含了两个序列为空的特殊情况
while(index1 < pushed.size()) {
s.push(pushed[index1]);
++index1;
// 使用s.top()的时候一定要先判断s.empty()
while(!s.empty() && s.top() == popped[index2]) {
s.pop();
++index2;
}
}
if(index2!=popped.size()) {
return false;
}
else {
return true;
}
}
};
3. 包含min函数的栈 [单调栈]
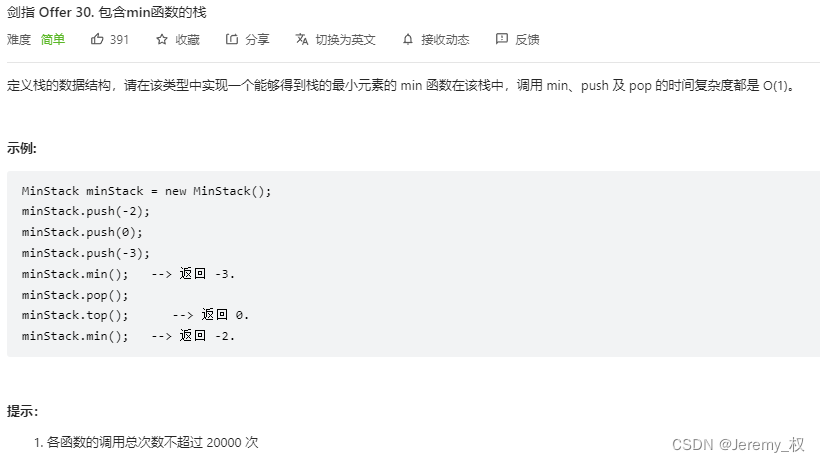
-
思路:
-
这里使用了单调栈的结构;
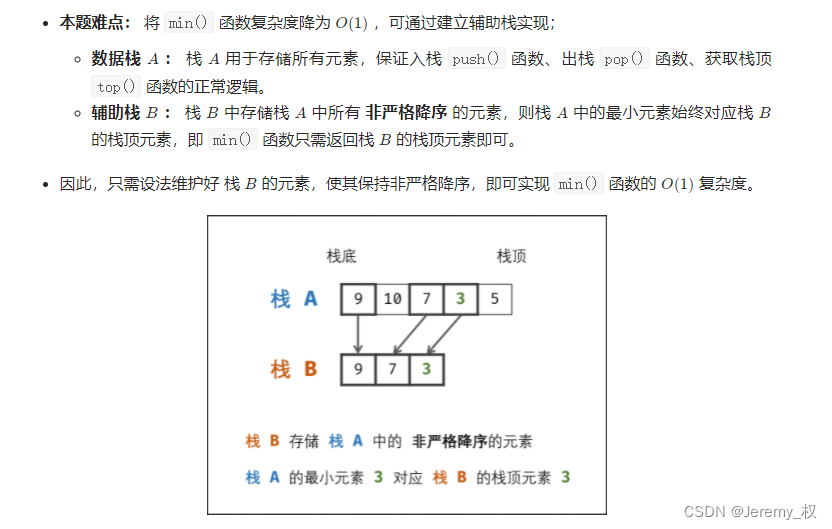
-
min_stack是单调非增序列,且为栈结构; -
这种结构可以维护一个滑动窗口的最大值序列;
-
但注意,单调栈只能维护一个最值,如果是要维护k个最值的话是不能用这种方法的,因为最大值入栈的时候必然是要把所有栈内元素弹出,因此无法维护k个最值,而是要用堆来实现,参考十一、1.最小的k个数;
-
代码:
class MinStack {
private:
std::stack<int> stack;
std::stack<int> min_stack;
public:
/** initialize your data structure here. */
MinStack() {
}
void push(int x) {
stack.push(x);
if(!min_stack.empty()) {
// 压入栈顶(必定是栈内最小值)和x之间的最小值
min_stack.push(std::min(min_stack.top(), x));
}
else {
min_stack.push(x);
}
}
void pop() {
stack.pop();
min_stack.pop();
}
int top() {
return stack.top();
}
int min() {
return min_stack.top();
}
};
/**
* Your MinStack object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MinStack* obj = new MinStack();
* obj->push(x);
* obj->pop();
* int param_3 = obj->top();
* int param_4 = obj->min();
*/
4. 滑动窗口的最大值 [单调栈]
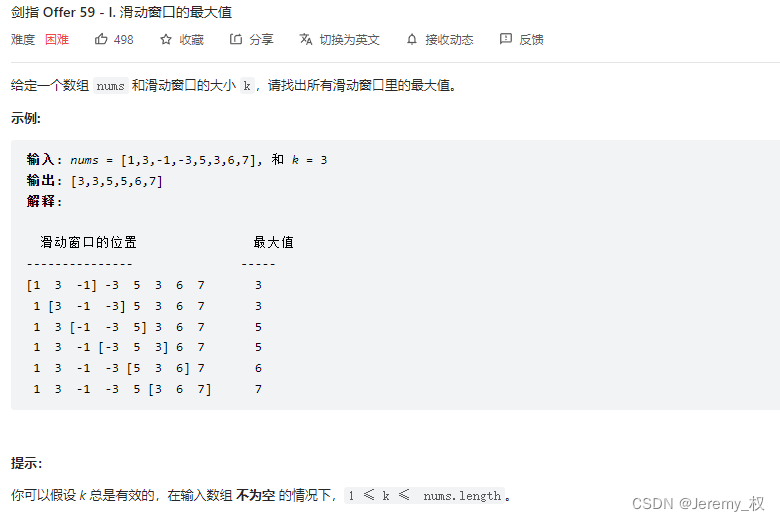
- 思路:
- 如果是暴力解的话,也就是用嵌套循环遍历,时间复杂度是O(k*N);
- 其实这一题和上面的4. 滑动窗口的最大值很像,也是类似滑动窗口,也是要保存一系列最值(而非单个最值),因此也可以用单调栈解决,时间复杂度降为O(2N);
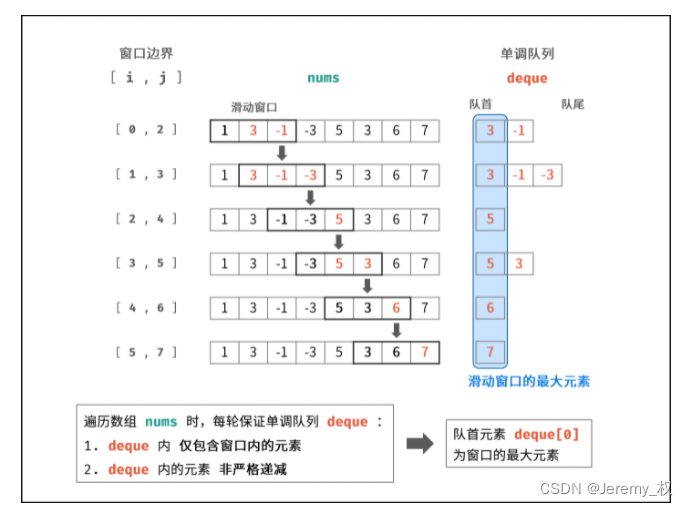
- 这里虽然说是用了双端队列
deque实现单调队列,但核心还是维护一个单调栈,栈内单调非增; - 那为什么不直接用栈来实现呢?主要是因为滑动窗口的左指针也移动,所以栈底(也就是队列首)的元素可能不在窗口内了,需要从栈底弹出元素,这是栈无法做到的;
- 仅当栈底元素恰好等于滑动窗口左外第一个元素时,也就是刚好移出了滑动窗口时,才从栈底弹出元素,其他情况仍是维护一个单调栈;
- 原因是入栈的顺序的按照遍历的顺序的,如果栈底的元素不是刚好移出窗口的那个元素,那么它和栈内的其他元素一定都是在窗口里面的元素(因为入栈时间晚);
- 注意等于的元素也是要保留在栈内的,也就是说一定是要单调非增而不是单调减,这是为了应对当前元素是最大值(或者以后会成为最大值)的情况,因为所有的最大值或者潜在可能的最大值都应该保留在栈内;
- 代码:
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> maxSlidingWindow(vector<int>& nums, int k) {
deque<int> queue;
vector<int> re;
int i;
// 滑动窗口还没有形成
for(i=0;i<k;++i) {
while(!queue.empty() && queue.back() < nums[i]) {
queue.pop_back();
}
queue.push_back(nums[i]);
}
re.push_back(queue.front());
// 滑动窗口已形成
for(i=k;i<nums.size();++i) {
// 移除滑动窗口最左侧的最大值
if(queue.front() == nums[i-k]) {
queue.pop_front();
}
// 确保queue.front()是最大值且queue中的值均大于等于nums[i]
// 等于一定要保留,否则会将多个相等的最大值都移除queue,即使它们在滑动窗口中
// 也就是说queue只能是一个单调非增队列
// 因为是单调非增,所以只能从后面删,此时的queue充当stack,即维护一个单调栈
while(!queue.empty() && queue.back() < nums[i]) {
queue.pop_back();
}
queue.push_back(nums[i]);
re.push_back(queue.front());
}
return re;
}
};
5. 队列的最大值 [单调栈]
-
思路:
-
还是单调栈的思路;
-
其实是4. 滑动窗口的最大值的变体,相当于是将定长的滑动窗口改成变长的滑动窗口;
-
在形式上和3. 包含min函数的栈是一样的,只是栈是先入后出,相当于滑动窗口的左指针不移动,队列是先入先出,左指针会一直移动;
-
只要左指针移动,就需要使用双向队列来实现栈;
-
注意是均摊的时间复杂度为O(1),因为就某次入队操作而言,
max_queue可能不是1次操作就能完成的(也可能不需要操作),但所有元素入栈后,max_queue的总操作次数是O(N),所以均摊下来是O(1); -
代码:
class MaxQueue {
private:
deque<int> max_queue; // 用双端队列实现单调栈
queue<int> queue;
public:
MaxQueue() {
}
int max_value() {
if(queue.empty()) {
return -1;
}
return max_queue.front();
}
void push_back(int value) {
queue.push(value);
while(!max_queue.empty() && max_queue.back() < value) {
// 维持max_queue内单调非增的性质
max_queue.pop_back();
}
max_queue.push_back(value);
}
int pop_front() {
if(queue.empty()) {
return -1;
}
int re = queue.front();
if(max_queue.front() == queue.front()) {
// 如果queue弹出的值恰好等于最大值,则单调栈也弹出栈底元素
// 也就是移除滑动窗口最左侧的最大值
max_queue.pop_front();
}
queue.pop();
return re;
}
};
/**
* Your MaxQueue object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MaxQueue* obj = new MaxQueue();
* int param_1 = obj->max_value();
* obj->push_back(value);
* int param_3 = obj->pop_front();
*/