1. 马踏棋盘算法介绍
将马随机放在国际象棋8×8棋盘的某个方格中,马按走棋规则(马走日字)不断的进行移动
要求每个方格只进入一次,走遍棋盘上全部64个方格(即移动63次)
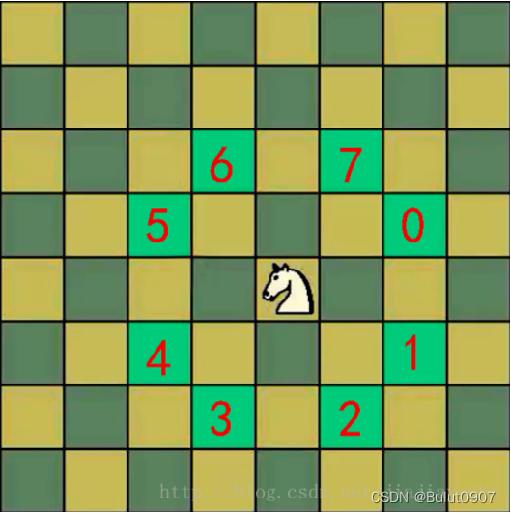
如下所示为一个方格的马能移动的位置
2. 马踏棋盘算法的原理
马踏棋盘问题(骑士周游问题)实际上是图的深度优先搜索(DFS)的应用
假如马儿踏了53个点,坐标为(1,0),发现没有位置可以移动了,就只能进行回溯,查看其他的路径。不断的进行移动和回溯就能走遍所有方格
可以使用贪心算法(greedyalgorithm)对马踏棋盘问题进行优化。先走当前位置的下一个位置的下一个位置个数较小,的下一个位置
3. 马踏棋盘算法的程序实现
马踏棋盘算法的程序实现如下:
import java.awt.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Comparator;
public class HorseChessboard {
// 棋盘的最大行数,从1开始
private static int MAX_ROW;
// 棋盘的最大列数,从1开始
private static int MAX_COLUME;
// 标记棋盘的各个位置是否被访问过。true为已访问,false为未访问
private static boolean[] visited;
// 如果棋盘所有位置都被访问,则为true,否则为false
private static boolean finished;
public static void main(String[] args) {
MAX_ROW = 8;
MAX_COLUME = 8;
visited = new boolean[MAX_ROW * MAX_COLUME];
// 马开始的行号,从1开始
int startRow = 1;
// 马开始的列号,从1开始
int startColumn = 1;
// 创建棋盘。用来保存每个方格都是第几步进入的
int[][] chessboard = new int[MAX_ROW][MAX_COLUME];
// 测试骑士周游问算法耗时
System.out.println("骑士周游算法,开始运行");
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
traversalChessboard(chessboard, startRow - 1, startColumn - 1, 1);
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("共耗时: " + (endTime - startTime) + "毫秒");
// 输出棋盘各个位置都是第几步进入的
for (int[] rows : chessboard) {
for (int step : rows) {
System.out.print(step + "\t");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
// 根据当前位置,将马能走的下一步位置放入一个集合中。下一步位置最多有8种可能
public static ArrayList<Point> getNextPoints(Point currentPoint) {
ArrayList<Point> nextPoints = new ArrayList<Point>();
Point tmpPoint = new Point();
// 先进行赋值,在进行比较
// 表示马儿可以走5这个位置
if ((tmpPoint.x = currentPoint.x - 2) >= 0 && (tmpPoint.y = currentPoint.y - 1) >= 0) {
nextPoints.add(new Point(tmpPoint));
}
// 判断马儿可以走6这个位置
if ((tmpPoint.x = currentPoint.x - 1) >= 0 && (tmpPoint.y = currentPoint.y - 2) >= 0) {
nextPoints.add(new Point(tmpPoint));
}
// 判断马儿可以走7这个位置
if ((tmpPoint.x = currentPoint.x + 1) < MAX_COLUME && (tmpPoint.y = currentPoint.y - 2) >= 0) {
nextPoints.add(new Point(tmpPoint));
}
// 判断马儿可以走0这个位置
if ((tmpPoint.x = currentPoint.x + 2) < MAX_COLUME && (tmpPoint.y = currentPoint.y - 1) >= 0) {
nextPoints.add(new Point(tmpPoint));
}
// 判断马儿可以走1这个位置
if ((tmpPoint.x = currentPoint.x + 2) < MAX_COLUME && (tmpPoint.y = currentPoint.y + 1) < MAX_ROW) {
nextPoints.add(new Point(tmpPoint));
}
// 判断马儿可以走2这个位置
if ((tmpPoint.x = currentPoint.x + 1) < MAX_COLUME && (tmpPoint.y = currentPoint.y + 2) < MAX_ROW) {
nextPoints.add(new Point(tmpPoint));
}
// 判断马儿可以走3这个位置
if ((tmpPoint.x = currentPoint.x - 1) >= 0 && (tmpPoint.y = currentPoint.y + 2) < MAX_ROW) {
nextPoints.add(new Point(tmpPoint));
}
// 判断马儿可以走4这个位置
if ((tmpPoint.x = currentPoint.x - 2) >= 0 && (tmpPoint.y = currentPoint.y + 1) < MAX_ROW) {
nextPoints.add(new Point(tmpPoint));
}
return nextPoints;
}
// 将当前位置的下一个位置,按当前位置的下一个位置的下一个位置个数,从小到大进行排列
// nextPoints是当前位置,马能走的下一步位置集合
// 比如当前位置的下一个位置A和B,A的下一个位置有2个,B的下一个位置有3个,则A在前,B在后
public static void sortNextPoints(ArrayList<Point> nextPoints) {
nextPoints.sort(new Comparator<Point>() {
@Override
public int compare(Point point1, Point point2) {
// 获取point1的下一个位置的个数
int point1NextPointCount = getNextPoints(point1).size();
// 获取point2的下一个位置的个数
int point2NextPointCount = getNextPoints(point2).size();
// 按从小到大排列
if (point1NextPointCount < point2NextPointCount) {
return -1;
} else if (point1NextPointCount == point2NextPointCount) {
return 0;
} else {
return 1;
}
}
});
}
// 骑士周游算法实现
// 参数pointX: 马当前的point X
// 参数pointY: 马当前的point Y
// 参数step: 马已经走的步数
public static void traversalChessboard(int[][] chessboard, int pointX, int pointY, int step) {
chessboard[pointX][pointY] = step;
// 标记当前位置为已访问
visited[pointY * MAX_COLUME + pointX] = true;
// 获取当前位置可以走的下一个位置的集合
ArrayList<Point> nextPoints = getNextPoints(new Point(pointX, pointY));
// 使用贪心算法进行优化
// 将当前位置的下一个位置,按当前位置的下一个位置的下一个位置个数,从小到大进行排列(非递减, 即具有相同大小的递增排列)
// 这样就会先走当前位置的下一个位置的下一个位置个数较小,的下一个位置
sortNextPoints(nextPoints);
// 遍历nextPoints。如果下一个位置没有访问,则进行访问
// 如果都访问过,会执行完该方法,进行回溯
for (Point nextPoint : nextPoints) {
if (!visited[nextPoint.y * MAX_COLUME + nextPoint.x]) {
traversalChessboard(chessboard, nextPoint.x, nextPoint.y, step + 1);
}
}
// 如果步数还不够,且finished为false,则表示还未走完,表示走不通了
// 则在回溯前,需要对这一步已经设置的状态进行重置
if (step < MAX_ROW * MAX_COLUME && !finished) {
chessboard[pointX][pointY] = 0;
visited[pointY * MAX_COLUME + pointX] = false;
} else {
// 如果步数够了,则finished为true
// 如果步数够了,finished为true,则还是finished为true
finished = true;
}
}
}
运行程序,最后显示的结果如下:
骑士周游算法,开始运行
共耗时: 26毫秒
1 38 15 30 61 40 13 28
16 31 36 39 14 29 58 41
37 2 49 60 55 62 27 12
32 17 54 35 52 59 42 57
3 48 33 50 63 56 11 26
18 21 64 53 34 51 8 43
47 4 23 20 45 6 25 10
22 19 46 5 24 9 44 7