系列文章目录
文章目录
- 系列文章目录
- 前言
- 二叉树遍历
- 二叉树的层序遍历
- 4、leetcode 102. [二叉树的层序遍历-java实现](https://blog.csdn.net/qq_41810415/article/details/127479039?spm=1001.2014.3001.5502)
- 5、[107. 二叉树的层序遍历 II-java实现](https://blog.csdn.net/qq_41810415/article/details/127487907?spm=1001.2014.3001.5502)
- 6、[199. 二叉树的右视图](https://leetcode.cn/problems/binary-tree-right-side-view/)
- 7、[637. 二叉树的层平均值](https://leetcode.cn/problems/average-of-levels-in-binary-tree/)
- 8、[429. N 叉树的层序遍历](https://leetcode.cn/problems/n-ary-tree-level-order-traversal/)
- 9、[515. 在每个树行中找最大值](https://leetcode.cn/problems/find-largest-value-in-each-tree-row/)
- 10、[leetcode 116. 填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针-java实现](https://blog.csdn.net/qq_41810415/article/details/127579305?spm=1001.2014.3001.5502)
- 11、[117. 填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针 II](https://blog.csdn.net/qq_41810415/article/details/127579391?spm=1001.2014.3001.5502)
- 二叉树的深度
- 14、 [226. 翻转二叉树](https://leetcode.cn/problems/invert-binary-tree/)
- 15、[leetcode 101. 对称二叉树-java实现](https://blog.csdn.net/qq_41810415/article/details/127443333?spm=1001.2014.3001.5502)
- 16、[222. 完全二叉树的节点个数](https://leetcode.cn/problems/count-complete-tree-nodes/)
- 17、[leetcode 110. 平衡二叉树-java实现](https://blog.csdn.net/qq_41810415/article/details/127490060?spm=1001.2014.3001.5502)
- 18、[257. 二叉树的所有路径](https://leetcode.cn/problems/binary-tree-paths/)
- 19、 04. 左叶子之和
- 20 、 513. 找树左下角的值
- 21、leetcode 112. [路径总和-java实现](https://blog.csdn.net/qq_41810415/article/details/127490859?spm=1001.2014.3001.5501)
- 22、leetcode 113. [路径总和 II-java实现](https://blog.csdn.net/qq_41810415/article/details/127572055?spm=1001.2014.3001.5501)
- 23、leetcode 105. [从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树-java实现](https://blog.csdn.net/qq_41810415/article/details/127483584?spm=1001.2014.3001.5501)
- 24、leetcode 106. [从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树-java实现](https://blog.csdn.net/qq_41810415/article/details/127487661?spm=1001.2014.3001.5501)
- 25、654. 最大二叉树
- 26、617. [合并二叉树](https://leetcode.cn/problems/merge-two-binary-trees/)
- 27、700. [二叉搜索树中的搜索](https://leetcode.cn/problems/search-in-a-binary-search-tree/)
- 28、leetcode 98. [验证二叉搜索树-java实现](https://blog.csdn.net/qq_41810415/article/details/127439527?spm=1001.2014.3001.5501)
- 29、leetcode 99. [恢复二叉搜索树-java实现](https://blog.csdn.net/qq_41810415/article/details/127439796?spm=1001.2014.3001.5501)
- 30、530. [二叉搜索树的最小绝对差](https://leetcode.cn/problems/minimum-absolute-difference-in-bst/)
- 31、501. [二叉搜索树中的众数](https://leetcode.cn/problems/find-mode-in-binary-search-tree/)
- 32、236. [二叉树的最近公共祖先](https://leetcode.cn/problems/lowest-common-ancestor-of-a-binary-tree/)
前言
提前要了解二叉树的分类 二叉树的两种存储方式 二叉树的两大种遍历方式以及深度遍历中的三种遍历方式 常常与dfs bfs混合使用
本文只介绍二叉树相关的leetcode习题 对基础的语法知识点不做过多赘述
二叉树遍历
1、leetcode 144. 二叉树的前序遍历
递归法 O(n)
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();
public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
dfs(root);
return ans;
}
public void dfs(TreeNode root){
if(root == null) return;
ans.add(root.val);
dfs(root.left);
dfs(root.right);
}
}
迭代法O(n)
class Solution {
List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();
Stack<TreeNode> st = new Stack<>();
public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
TreeNode cur = root;
while(cur != null || !st.isEmpty()){
while(cur != null){
ans.add(cur.val);
st.push(cur);
cur = cur.left;
}
cur = st.pop();
cur = cur.right;
}
return ans;
}
}
2、 145. 二叉树的后序遍历
先遍历根右左 然后翻转过来
class Solution {
List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();
Stack<TreeNode> st = new Stack<>();
public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
TreeNode cur = root;
while(cur != null || !st.isEmpty()){
while(cur != null){
ans.add(cur.val);
st.push(cur);
cur = cur.right;
}
cur = st.pop();
cur = cur.left;
}
Collections.reverse(ans);
return ans;
}
}
建立一个上一个节点
class Solution {
List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();
Stack<TreeNode> st = new Stack<>();
public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
TreeNode cur = root;
TreeNode pre = null;
while(cur != null || !st.isEmpty()){
while(cur != null){
st.push(cur);
cur = cur.left;
}
cur = st.peek();
//右边表示没遍历上一个节点
if(cur.right != null && cur.right != pre){
cur = cur.right;
}else{
st.pop();
ans.add(cur.val);
pre = cur;
cur = null;
}
}
return ans;
}
}
3、leetcode 94. 二叉树的中序遍历-java版本
二叉树的层序遍历
4、leetcode 102. 二叉树的层序遍历-java实现
5、107. 二叉树的层序遍历 II-java实现
6、199. 二叉树的右视图
给定一个二叉树的 根节点 root,想象自己站在它的右侧,按照从顶部到底部的顺序,返回从右侧所能看到的节点值。
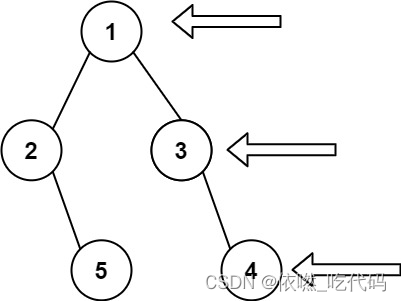
输入: [1,2,3,null,5,null,4]
输出: [1,3,4]
层序遍历的模板 在每一层中把该层中最后一个元素放入队列中即可
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public List<Integer> rightSideView(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();
if(root == null) return ans;
Queue<TreeNode> q = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
q.add(root);
while(!q.isEmpty()){
int len = q.size();
for(int i = 0 ; i < len ; i++){
TreeNode t = q.poll();
if(t.left != null) q.add(t.left);
if(t.right != null) q.add(t.right);
if(i == len-1) ans.add(t.val);
}
}
return ans;
}
}
7、637. 二叉树的层平均值
给定一个非空二叉树的根节点 root , 以数组的形式返回每一层节点的平均值。与实际答案相差 10-5 以内的答案可以被接受。
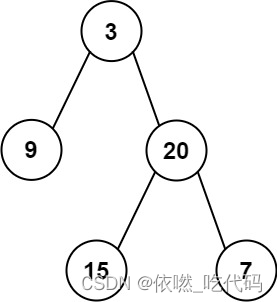
输入:root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
输出:[3.00000,14.50000,11.00000]
解释:第 0 层的平均值为 3,第 1 层的平均值为 14.5,第 2 层的平均值为 11 。
因此返回 [3, 14.5, 11] 。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public List<Double> averageOfLevels(TreeNode root) {
List<Double> ans = new ArrayList<>();
Queue<TreeNode> q = new LinkedList<>();
if(root == null) return ans;
q.add(root);
while(!q.isEmpty()){
int len = q.size();
double sum = 0 ;
for(int i = 0 ; i < len ; i ++){
TreeNode t = q.poll();
sum += t.val;
if(t.left != null) q.add(t.left);
if(t.right != null) q.add(t.right);
}
ans.add(sum/len);
}
return ans;
}
}
8、429. N 叉树的层序遍历
给定一个 N 叉树,返回其节点值的层序遍历。(即从左到右,逐层遍历)。
树的序列化输入是用层序遍历,每组子节点都由 null 值分隔(参见示例)。
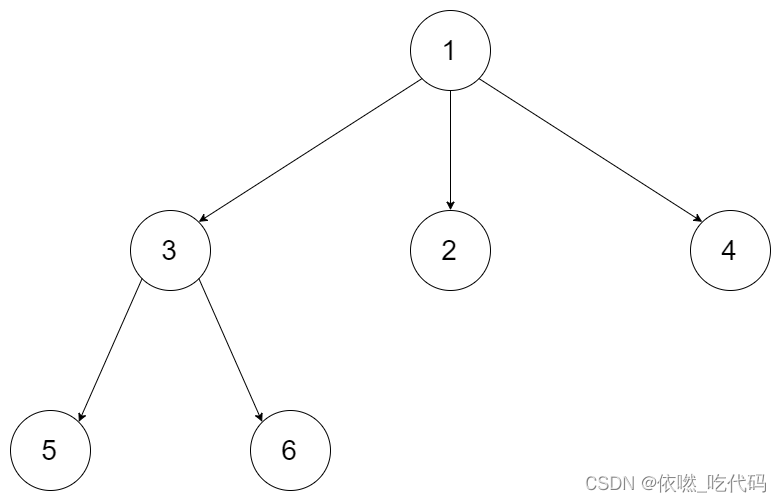
输入:root = [1,null,3,2,4,null,5,6]
输出:[[1],[3,2,4],[5,6]]
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public int val;
public List<Node> children;
public Node() {}
public Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
}
public Node(int _val, List<Node> _children) {
val = _val;
children = _children;
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(Node root) {
List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
Queue<Node> q = new LinkedList<>();
if(root == null) return ans;
q.add(root);
while(!q.isEmpty()){
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
int len = q.size();
for(int i = 0 ; i < len ; i ++){
Node t = q.poll();
res.add(t.val);
for(Node c : t.children) q.add(c);
}
ans.add(res);
}
return ans ;
}
}
9、515. 在每个树行中找最大值
给定一棵二叉树的根节点 root ,请找出该二叉树中每一层的最大值。
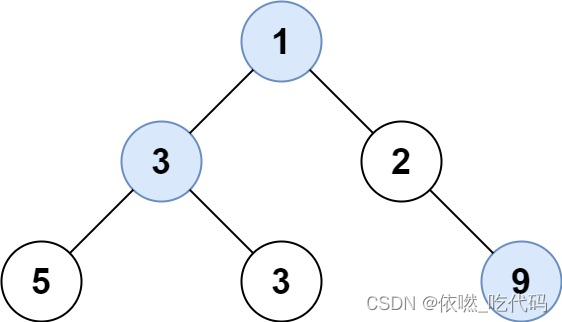
输入: root = [1,3,2,5,3,null,9]
输出: [1,3,9]
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public List<Integer> largestValues(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();
Queue<TreeNode> q = new LinkedList<>();
if(root == null) return ans;
q.add(root);
while(!q.isEmpty()){
int len = q.size();
int m = Integer.MIN_VALUE ;
for(int i = 0 ; i < len ; i++){
TreeNode t = q.poll();
m = Math.max(m,t.val);
if(t.left != null) q.add(t.left);
if(t.right != null) q.add(t.right);
}
ans.add(m);
}
return ans;
}
}
10、leetcode 116. 填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针-java实现
11、117. 填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针 II
二叉树的深度
12、leetcode 104. 二叉树的最大深度-java实现
13、leetcode 111. 二叉树的最小深度-java实现
14、 226. 翻转二叉树
给你一棵二叉树的根节点 root ,翻转这棵二叉树,并返回其根节点。
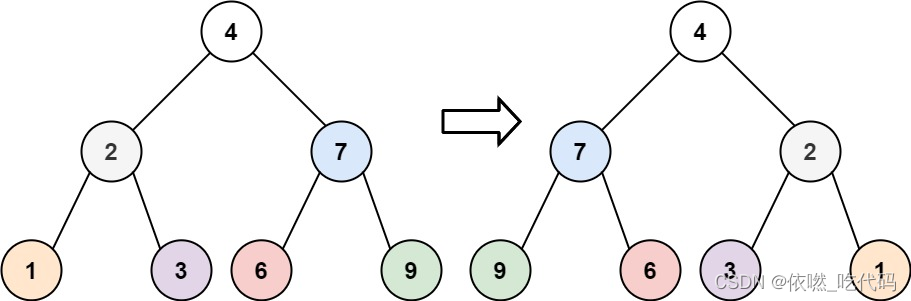
输入:root = [4,2,7,1,3,6,9]
输出:[4,7,2,9,6,3,1]
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode invertTree(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) return root;
TreeNode t = root.left;
root.left = root.right;
root.right = t ;
invertTree(root.left);
invertTree(root.right);
return root;
}
}
15、leetcode 101. 对称二叉树-java实现
16、222. 完全二叉树的节点个数
给你一棵 完全二叉树 的根节点 root ,求出该树的节点个数。
完全二叉树 的定义如下:在完全二叉树中,除了最底层节点可能没填满外,其余每层节点数都达到最大值,并且最下面一层的节点都集中在该层最左边的若干位置。若最底层为第 h 层,则该层包含 1~ 2h 个节点。
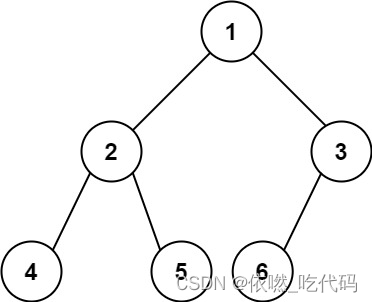
输入:root = [1,2,3,4,5,6]
输出:6
用二分的思想 O(log^2 n)
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public int countNodes(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) return 0 ;
int x = 1 , y = 1 ;
TreeNode l = root.left ;
TreeNode r = root.right ;
while(l != null){//如果是root 的话 那么x y 初始化要是0
l = l.left ;
x++;
}
while(r != null){
r = r.right;
y++;
}
//二者相同为满二叉树 2^x -1
if(x == y) return (1 << x) -1;
//递归到左边算加上根节点 在递归到右边算
return countNodes(root.left) + 1 + countNodes(root.right);
}
}
17、leetcode 110. 平衡二叉树-java实现
18、257. 二叉树的所有路径
给你一个二叉树的根节点 root ,按 任意顺序 ,返回所有从根节点到叶子节点的路径。
叶子节点 是指没有子节点的节点。
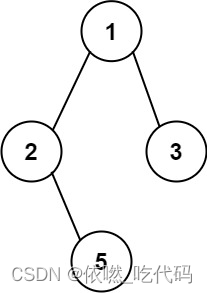
输入:root = [1,2,3,null,5]
输出:[“1->2->5”,“1->3”]
时间复杂度 O(n)
1、从根结点出发,递归走所有的路径,并把路径的值记录下来
2、递归过程中
若左子树和右子树都为null,则返回记录的路径s
若左子树不为null,则把左子树的值加入到路径中,递归到左子树
若右子树不为null,则把右子树的值加入到路径中,递归到右子树
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
List<String> ans = new ArrayList<>();
public List<String> binaryTreePaths(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) return ans ;
dfs(root,""+root.val);
return ans;
}
public void dfs(TreeNode root,String s){
if(root.left ==null && root.right ==null){
ans.add(s);
return ;
}
if(root.left != null) dfs(root.left,s + "->"+root.left.val);
if(root.right != null) dfs(root.right,s + "->"+root.right.val);
}
}
19、 04. 左叶子之和
原文链接
给定二叉树的根节点 root ,返回所有左叶子之和。
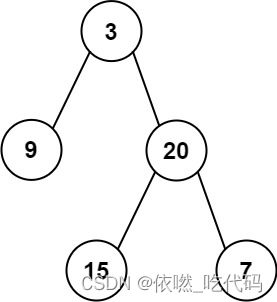
输入: root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
输出: 24
解释: 在这个二叉树中,有两个左叶子,分别是 9 和 15,所以返回 24
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
int sum = 0 ;
public int sumOfLeftLeaves(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return 0;
if(root.left != null){//判断是否是左节点
if(root.left.left == null && root.left.right == null){//判断是叶子节点
sum += root.left.val;
}
}
sumOfLeftLeaves(root.left);
sumOfLeftLeaves(root.right);
return sum ;
}
}
20 、 513. 找树左下角的值
原题
给定一个二叉树的 根节点 root,请找出该二叉树的 最底层 最左边 节点的值。
假设二叉树中至少有一个节点。
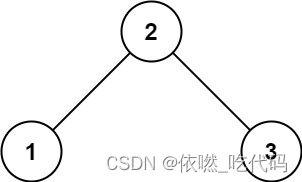
输入: root = [2,1,3]
输出: 1
dfs加一个最大深度 每次更新它
如果层序遍历的话 加一个i=0的判断就可以遍历到最后一层的第一个点了
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
int t = 0 , maxh ;
public int findBottomLeftValue(TreeNode root) {
dfs(root,1);//加一个深度
return t ;
}
public void dfs(TreeNode root,int h){
if(root == null) return ;
if(h > maxh){//更新最大深度 终止条件
maxh = h ;
t = root.val;
}
dfs(root.left , h+1);
dfs(root.right,h+1);
}
}
21、leetcode 112. 路径总和-java实现
22、leetcode 113. 路径总和 II-java实现
23、leetcode 105. 从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树-java实现
24、leetcode 106. 从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树-java实现
25、654. 最大二叉树
给定一个不重复的整数数组 nums 。 最大二叉树 可以用下面的算法从 nums 递归地构建:
创建一个根节点,其值为 nums 中的最大值。
递归地在最大值 左边 的 子数组前缀上 构建左子树。
递归地在最大值 右边 的 子数组后缀上 构建右子树。
返回 nums 构建的 最大二叉树 。
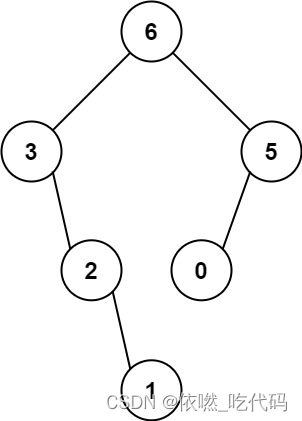
输入:nums = [3,2,1,6,0,5]
输出:[6,3,5,null,2,0,null,null,1]
解释:递归调用如下所示:- [3,2,1,6,0,5] 中的最大值是 6 ,左边部分是 [3,2,1] ,右边部分是 [0,5] 。
- [3,2,1] 中的最大值是 3 ,左边部分是 [] ,右边部分是 [2,1] 。
- 空数组,无子节点。
- [2,1] 中的最大值是 2 ,左边部分是 [] ,右边部分是 [1] 。
- 空数组,无子节点。
- 只有一个元素,所以子节点是一个值为 1 的节点。
- [0,5] 中的最大值是 5 ,左边部分是 [0] ,右边部分是 [] 。
- 只有一个元素,所以子节点是一个值为 0 的节点。
- 空数组,无子节点。
以树上任意一点x为根构成的子树中,
1. 各节点的pos是连续的,且对pos的中序遍历即为原序列顺序(由pos满足二叉查找树可得)
2. x点的val为全子树最小(由val满足堆可得) 这道题是最大



这是n^2级别
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode constructMaximumBinaryTree(int[] nums) {
return dfs(nums,0,nums.length-1);
}
public TreeNode dfs(int[] nums , int l , int r){
if(l > r ) return null;
int root = l ;
for(int i = l+1 ; i <= r ; i++){
if(nums[root] < nums[i] ) root = i ;
}
TreeNode res = new TreeNode(nums[root]);
res.left = dfs(nums,l ,root-1);
res.right = dfs(nums,root+1 , r );
return res;
}
}
单调栈做法O(n)

完整的题解参考这篇
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode constructMaximumBinaryTree(int[] nums) {
Stack<TreeNode> st = new Stack<>();
for(int x : nums){
TreeNode node = new TreeNode(x);
//找到最大值
while(!st.isEmpty() && st.peek().val < x ){
//将小于最大值的那个节点的左儿子
node.left = st.peek() ;
st.pop();
}
if(!st.empty()) st.peek().right = node;
st.push(node);
}
while(st.size()>1) st.pop();
return st.peek();
}
}
26、617. 合并二叉树
想象一下,当你将其中一棵覆盖到另一棵之上时,两棵树上的一些节点将会重叠(而另一些不会)。你需要将这两棵树合并成一棵新二叉树。合并的规则是:如果两个节点重叠,那么将这两个节点的值相加作为合并后节点的新值;否则,不为 null 的节点将直接作为新二叉树的节点。
返回合并后的二叉树。
注意: 合并过程必须从两个树的根节点开始。
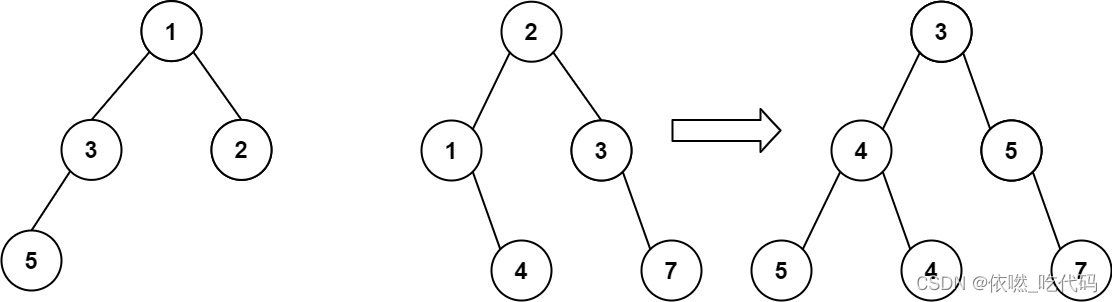
输入:root1 = [1,3,2,5], root2 = [2,1,3,null,4,null,7]
输出:[3,4,5,5,4,null,7]
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode mergeTrees(TreeNode root1, TreeNode root2) {
if(root1 == null) return root2;
if(root2 == null) return root1;
root1.val += root2.val;
root1.left = mergeTrees(root1.left ,root2.left);
root1.right = mergeTrees(root1.right , root2.right);
return root1;
}
}
27、700. 二叉搜索树中的搜索
给定二叉搜索树(BST)的根节点 root 和一个整数值 val。
你需要在 BST 中找到节点值等于 val 的节点。 返回以该节点为根的子树。 如果节点不存在,则返回 null 。
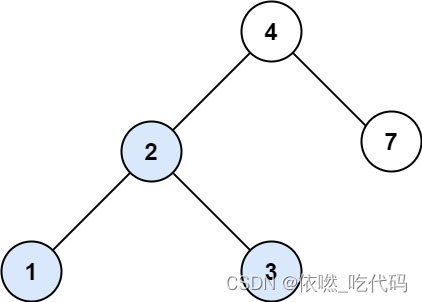
输入:root = [4,2,7,1,3], val = 2
输出:[2,1,3]
时间复杂度就是二叉树的高度
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode searchBST(TreeNode root, int val) {
if(root == null) return root ;
if(root.val == val) return root ;
if(root.val > val ) return searchBST(root.left,val);
else return searchBST(root.right,val);
}
}
28、leetcode 98. 验证二叉搜索树-java实现
29、leetcode 99. 恢复二叉搜索树-java实现
30、530. 二叉搜索树的最小绝对差
给你一个二叉搜索树的根节点 root ,返回 树中任意两不同节点值之间的最小差值 。
差值是一个正数,其数值等于两值之差的绝对值。
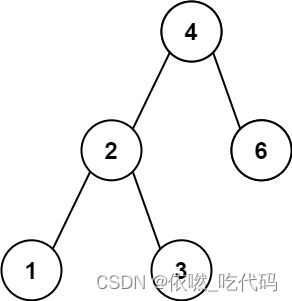
输入:root = [4,2,6,1,3]
输出:1
二叉搜索树中序遍历是递增的 最小值就是当前相邻两个节点之间
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
int m = Integer.MAX_VALUE ;
TreeNode pre ;//记录前一个节点
//因为是中序遍历 二叉搜索树中 所以pre.val 一定小与root.val 这个Math.abs可以不加
public int getMinimumDifference(TreeNode root) {
dfs(root);
return m ;
}
public void dfs(TreeNode root){
if(root == null) return ;
dfs(root.left);
if(pre != null){
m = Math.min(m , root.val - pre.val );
// m = Math.min(m , Math.abs(root.val - pre.val ));
}
pre = root ;
dfs(root.right);
}
}
31、501. 二叉搜索树中的众数
给你一个含重复值的二叉搜索树(BST)的根节点 root ,找出并返回 BST 中的所有 众数(即,出现频率最高的元素)。
如果树中有不止一个众数,可以按 任意顺序 返回。
假定 BST 满足如下定义:
结点左子树中所含节点的值 小于等于 当前节点的值
结点右子树中所含节点的值 大于等于 当前节点的值
左子树和右子树都是二叉搜索树
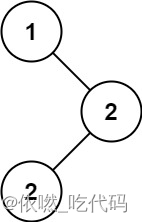
输入:root = [1,null,2,2]
输出:[2]
进阶:你可以不使用额外的空间吗?(假设由递归产生的隐式调用栈的开销不被计算在内)
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
int maxCount = 0 ;
int count = 0 ;
TreeNode pre;
public int[] findMode(TreeNode root) {
dfs(root) ;
int[] ans = new int[res.size()];
for(int i = 0 ; i < res.size() ; i++) ans[i] = res.get(i);
return ans ;
}
public void dfs(TreeNode root){
if(root == null) return ;
dfs(root.left);
//第一个或者连续相等的
if(pre == null || root.val == pre.val ) count++;
else count = 1 ;
pre = root ;//更新
if(count > maxCount){
res = new ArrayList<>();
res.add(root.val);
maxCount = count;
} else if(count == maxCount){
res.add(root.val);
}
dfs(root.right);
}
}
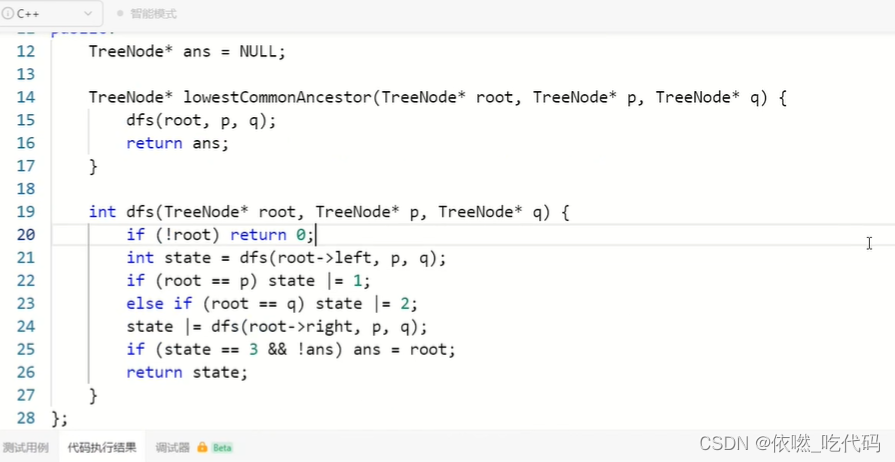
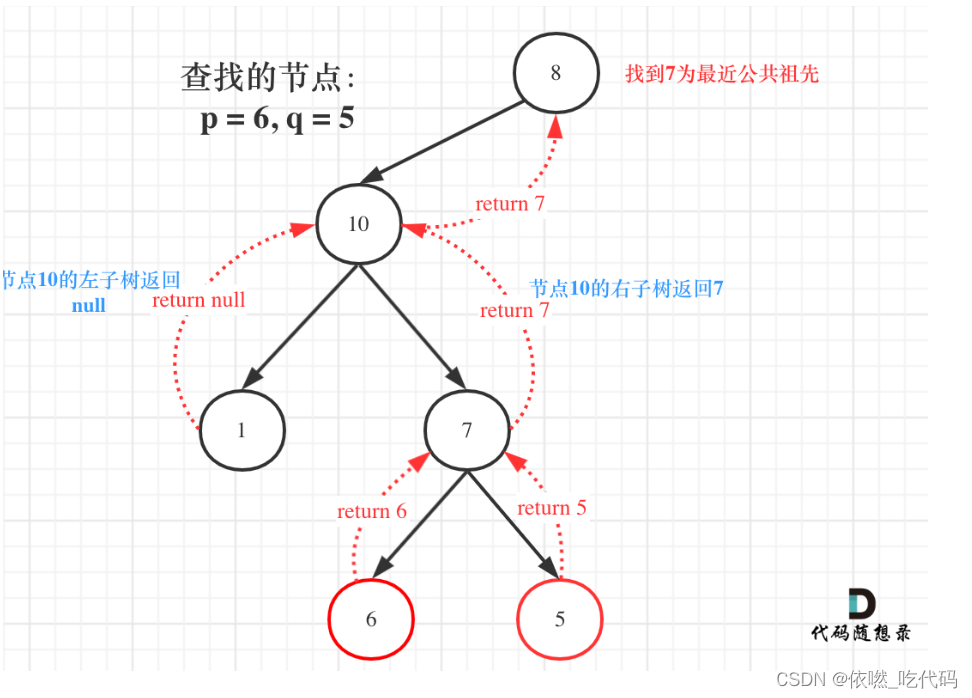
32、236. 二叉树的最近公共祖先
给定一个二叉树, 找到该树中两个指定节点的最近公共祖先。
百度百科中最近公共祖先的定义为:“对于有根树 T 的两个节点 p、q,最近公共祖先表示为一个节点 x,满足 x 是 p、q 的祖先且 x 的深度尽可能大(一个节点也可以是它自己的祖先)。”
输入:root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], p = 5, q = 1
输出:3
解释:节点 5 和节点 1 的最近公共祖先是节点 3 。
输入:root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], p = 5, q = 4
输出:5
解释:节点 5 和节点 4 的最近公共祖先是节点 5 。因为根据定义最近公共祖先节点可以为节点本身。
题解
在递归函数有返回值的情况下:如果要搜索一条边,递归函数返回值不为空的时候,立刻返回,如果搜索整个树,直接用一个变量left、right接住返回值,这个left、right后序还有逻辑处理的需要,也就是后序遍历中处理中间节点的逻辑(也是回溯)。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
return dfs(root , p ,q );
}
public TreeNode dfs(TreeNode root , TreeNode p , TreeNode q){
if(root == null || root == p || root == q) return root;
TreeNode left = dfs(root.left , p ,q );
TreeNode right = dfs(root.right, p , q);
if( left == null && right == null){
return null ;
}else if(left == null && right != null){
return right ;
}else if(left != null && right == null){
return left;
}else {
return root ;
}
}
}
还有一种方法是通过二进制的表示方式来保存q和p 1 0
这样子 采用的是中序遍历