🔰🔰🔰:困难
🔰🔰:中等
🔰:简单
文章目录
- `🔰🔰🔰`927.三等分
- `🔰🔰`811.子域名访问计数
- `🔰🔰`921.使括号有效的最少添加
- `🔰🔰`287.寻找重复数
- `🔰🔰`(贪心)870.优势洗牌
- `🔰🔰`856.括号的分数
- `🔰🔰🔰`(状压DP)801.使序列递增的最小交换次数
- `🔰🔰`53.最大子数组和
- `🔰`1790.仅执行一次字符串交换能否使两个字符串相等
- `🔰🔰`131.分割回文串
- `🔰🔰`5.最长回文子串
- `🔰🔰`817.链表组件
- `🔰🔰`769.最多能完成排序的块
- `🔰🔰🔰`940.不同的子序列 II
- `🔰🔰`1441.用栈操作构建数组
- `🔰🔰🔰`6207.统计定界子数组的数目
- `🔰🔰`886.可能的二分法
- `🔰🔰`904.水果成篮
- `🔰🔰🔰`902.最大为 N 的数字组合
- `🔰`1700.无法吃午餐的学生数量
- `🔰🔰`779.第K个语法符号
- (单调栈)`🔰🔰`901.股票价格跨度
- `🔰🔰🔰`1235.规划兼职工作
- `🔰`1768.交替合并字符串
- `🔰🔰`915.分割数组
- bfs+dfs `🔰🔰`934.最短的桥
- `🔰🔰`560.和为 K 的子数组
- `🔰🔰🔰`862.和至少为 K 的最短子数组
- (单调栈)`🔰🔰`907.子数组的最小值之和
- 🤙欢迎关注泥烟的客栈(常在这里更新)
🔰🔰🔰927.三等分
https://leetcode.cn/problems/three-equal-parts/
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> threeEqualParts(vector<int>& arr) {
int total = 0, len = arr.size();
for(int i = 0 ; i < len; i ++) {
if(arr[i]) total ++;
}
if(total == 0) return {0, 2};
if(total % 3 != 0) return {-1, -1};
int avg = total / 3;
int f[6] = {1, avg, avg + 1, 2*avg, 2*avg + 1, total};
int site[6];
int cnt1 = 0;
for(int i = 0, j = 0 ; i < len; i ++) {
if(!arr[i]) continue;
cnt1 ++;
while(j < 6 && cnt1 == f[j]) site[j ++] = i; //
}
int cnt0 = len - 1 - site[5];
// 判断前两段尾部零是否够用
if(site[2]-site[1]-1 < cnt0 || site[4]-site[3]-1 < cnt0) return {-1, -1};
// 判断三段是否完全相同
if(!judge(arr, site[0], site[1], site[2], site[3])) return {-1, -1};
if(!judge(arr, site[0], site[1], site[4], site[5])) return {-1, -1};
return {site[1]+cnt0, site[3]+cnt0+1};
}
bool judge(vector<int>& arr, int l1, int r1, int l2, int r2){
for(int i = l1, j = l2; i <= r1; i ++, j ++)
if(arr[i]^arr[j])
return false;
return true;
}
};
🔰🔰811.子域名访问计数
https://leetcode.cn/problems/subdomain-visit-count/
class Solution {
public:
vector<string> subdomainVisits(vector<string>& cpdomains) {
unordered_map<string, int> cnt;
for(auto& t : cpdomains)
{
int a = t.find(' ');
int num = stoi(t.substr(0, a));
t = t.substr(a + 1);
while(1)
{
cnt[t] += num;
a = t.find('.');
if(a == -1) break;
t = t.substr(a + 1);
}
}
vector<string> res;
for(auto& [str, n]:cnt)
{
res.push_back(to_string(n) + ' ' + str);
}
return res;
}
};
🔰🔰921.使括号有效的最少添加
https://leetcode.cn/problems/minimum-add-to-make-parentheses-valid/
class Solution {
public:
int minAddToMakeValid(string s) {
int res = 0, v = 0;
for(auto& t : s)
{
v += t == '(' ? 1 : -1;
// 保持v为非负数
if(v < 0) v = 0, res ++;
}
return res + v;
}
};
🔰🔰287.寻找重复数
https://leetcode.cn/problems/find-the-duplicate-number
法一: 原地哈希
将nums[i]存储在nums[nums[i]-1]
- 若i == nums[i]-1, 则游标向后移动
- 若
nums[i] = nums[nums[i]-1],则有重复 - 若
nums[i] != nums[nums[i]-1],则交换
- 若
class Solution {
public:
int findDuplicate(vector<int>& nums) {
int n = nums.size();
for(int i = 0; i < n; )
{
int site = nums[i]-1;
if(site == i) {
i ++;
continue;
}
if(nums[site] == nums[i]) return nums[i];
else swap(nums[site], nums[i]);
}
return -1;
}
};
🔰🔰(贪心)870.优势洗牌
https://leetcode.cn/problems/advantage-shuffle/
思路:
和田忌赛马差不多, 这里麻烦在于nums2保持不变
将nums1数组的最小值与nums2数组的最小值相比较
- 如果前者更大, 则将该数放到nums2数组的最小值所处的位置
- 如果后者更大, 则将该数放到nums2数组的最大值所处的位置(采用破罐子好摔的战略,即我连 你小的数都比不过,那我临走前要和你大的数比,而我的大数养精蓄锐)
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> advantageCount(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2) {
int n = nums1.size();
vector<int> res(n);
vector<pair<int, int>> v2(n);
for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++) v2[i] = {nums2[i], i};
sort(v2.begin(), v2.end());
sort(nums1.begin(), nums1.end());
int l = 0, r = n-1;
for(int i = 0; i < n ; i ++)
{
int site = nums1[i] > v2[l].first ? v2[l++].second : v2[r--].second;
res[site] = nums1[i];
}
return res;
}
};
🔰🔰856.括号的分数
https://leetcode.cn/problems/score-of-parentheses
class Solution {
public:
int scoreOfParentheses(string s) {
int res = 0, x = 0, len = s.size();
for(int i = 0; i < len; i ++)
{
if(s[i] == '(') x ++;
else{
x --;
res += (s[i-1] == '(') ? 1 << x : 0;
}
}
return res;
}
};
🔰🔰🔰(状压DP)801.使序列递增的最小交换次数
https://leetcode.cn/problems/minimum-swaps-to-make-sequences-increasing/
思路:
f[i][j] => 在[0, i]区间内的最小交换次数, j=0/1表示第i个位置是否交换
f[0][0] = 0, f[0][1] = 1
可分为如下两种情况更新f[][]
nums1[i]>nums1[i-1] && nums2[i]>nums2[i-1]f[i][0] = min{f[i][0], f[i-1][0]}f[i][1] = min{f[i][1], f[i-1][1]+1}
nums1[i]>nums2[i-1] && nums2[i]>nums1[i-1]f[i][0] = min{f[i][0], f[i-1][1]}f[i][1] = min{f[i][1], f[i-1][0]+1}
class Solution {
public:
int minSwap(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2) {
int n = nums1.size();
int f[n+5][2];
memset(f, 0x3f, sizeof(f));
f[0][0] = 0, f[0][1] = 1;
for(int i = 1; i < n; i ++)
{
if(nums1[i]>nums1[i-1] && nums2[i]>nums2[i-1]){
f[i][0] = min(f[i][0], f[i-1][0]);
f[i][1] = min(f[i][1], f[i-1][1]+1);
}
if(nums1[i]>nums2[i-1] && nums2[i]>nums1[i-1]){
f[i][0] = min(f[i][0], f[i-1][1]);
f[i][1] = min(f[i][1], f[i-1][0]+1);
}
}
return min(f[n-1][0], f[n-1][1]);
}
};
🔰🔰53.最大子数组和
https://leetcode.cn/problems/maximum-subarray/
前面的累加若是大于零,则对最终的最大值是有贡献的
若是小于零, 则可以不考虑, 从当前位置重新加起
class Solution {
public:
int maxSubArray(vector<int>& nums) {
int n = nums.size();
int res = INT_MIN, t = -1;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++)
{
t = (t < 0) ? nums[i] : nums[i]+t;
res = (res > t) ? res : t;
}
return res;
}
};
🔰1790.仅执行一次字符串交换能否使两个字符串相等
https://leetcode.cn/problems/check-if-one-string-swap-can-make-strings-equal/
逐个比对同一位置上的字符, 若不同, 记录下当前位置. 并且cnt++
- cnt > 2, ?
- cnt = 0, ?
- cnt = 1, ?
- cnt = 2
s1[ch[0]] == s2[ch[1]] && s1[ch[1]] == s2[ch[0]], ?- ?
class Solution {
public:
bool areAlmostEqual(string s1, string s2) {
int n = s1.size();
int cnt = 0, ch[105];
for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++)
{
if(s1[i]!=s2[i]) ch[cnt++] = i;
if(cnt == 3) return false;
}
if(cnt == 0) return true;
if(cnt == 1) return false;
if(s1[ch[0]] == s2[ch[1]] && s1[ch[1]] == s2[ch[0]]) return true;
return false;
}
};
🔰🔰131.分割回文串
https://leetcode.cn/problems/palindrome-partitioning/
递归回溯
class Solution {
public:
int len;
vector<string> path;
vector<vector<string>> res;
vector<vector<string>> partition(string s) {
len = s.size();
dfs(0, s);
return res;
}
void dfs(int u, string s) {
if(u == len){
res.push_back(path);
return ;
}
for(int i = u; i < len; i ++) {
if(check(s, u, i)) {
path.push_back(s.substr(u, i+1-u));
dfs(i+1, s);
path.pop_back();
}
}
}
//判断从l到r是否为回文串
bool check(string s, int l, int r) {
while(l <= r) {
if(s[l ++] != s[r --]) return false;
}
return true;
}
};

通过dp预处理优化
class Solution {
public:
int len;
bool st[20][20];
vector<string> path;
vector<vector<string>> res;
vector<vector<string>> partition(string s) {
len = s.size();
dp(s);
dfs(0, s);
return res;
}
void dfs(int u, string s) {
if(u == len){
res.push_back(path);
return ;
}
for(int i = u; i < len; i ++) {
if(st[u][i]) {
path.push_back(s.substr(u, i+1-u));
dfs(i+1, s);
path.pop_back();
}
}
}
void dp(string s)
{
memset(st, false, sizeof st);
for(int i = 0; i < len; i ++) st[i][i] = true;
for(int i = 0; i < len-1; i ++) {
if(s[i] == s[i+1]) st[i][i+1] = true;
}
for(int k = 3; k <= len; k ++) {
for(int l = 0; l + k - 1 < len; l ++) {
int r = l + k - 1;
if(s[l] == s[r] && st[l+1][r-1]) st[l][r] = true;
}
}
}
};

🔰🔰5.最长回文子串
https://leetcode.cn/problems/longest-palindromic-substring/
🔰🔰817.链表组件
https://leetcode.cn/problems/linked-list-components/
解题思路
模拟, 哈希

大致过程如下
左游标pl, 右游标pr
若pl所在的结点值存在,
res++
pr从pl开始向右移动直到为空或者值不存在就停止
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int numComponents(ListNode* head, vector<int>& nums) {
int n = nums.size(), res = 0;
bool st[10010];
memset(st, false, sizeof st);
for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++) st[nums[i]] = true;
for(ListNode* pl = head, *pr = nullptr; pl != nullptr; )
{
if(st[pl->val])
{
res ++;
pr = pl->next;
while(pr != nullptr && st[pr->val]) pr = pr->next;
if(pr) pl = pr->next;
else break;
}
else pl = pl->next;
}
return res;
}
};
🔰🔰769.最多能完成排序的块
https://leetcode.cn/problems/max-chunks-to-make-sorted/
class Solution {
public:
int maxChunksToSorted(vector<int>& arr) {
int n = arr.size();
int res = 0, _max = -1, _min = 100;
for(int i = 0, j = 0; i < n; )
{
_max = max(_max, arr[j]);
_min = min(_min, arr[j]);
if(_max == j && _min == i)
{
res ++;
_max = -1, _min = 100;
i = j + 1;
}
j ++;
}
return res;
}
};
其实只用最大值就可以
class Solution {
public:
int maxChunksToSorted(vector<int>& arr) {
int n = arr.size();
int res = 0, _max = -1;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++) {
_max = max(_max, arr[i]);
if(_max == i) {
res ++;
_max = -1;
}
}
return res;
}
};
🔰🔰🔰940.不同的子序列 II
f[i] : 以当前字母结尾的子序列数量
last[i] : 字母’a’+i 最后出现的位置
对于每一种字符,我们只需要找到其最后一次出现的位置(并且在位置 i 之前),并将对应的 f 值累加进 f[i] 即可
class Solution {
public:
int distinctSubseqII(string s) {
int n = s.size();
int MOD = 1e9+7, res = 0;
int last[26], f[2010];
for(int i = 0; i < 26; i ++) last[i] = -1;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++) f[i] = 1;
for(int i = 0; i < n ; i ++)
{
for(int j = 0; j < 26; j ++)
if(last[j] != -1)
f[i] = (f[i] + f[last[j]])%MOD;
last[s[i] - 'a'] = i;
}
for(int i = 0; i < 26; i ++)
if(last[i] != -1)
res = (res + f[last[i]]) % MOD;
return res;
}
};
初步优化
上面写法中过程中的f[i]表示以当前字母结尾的子序列数量
不妨用g[i] 表示当前情况下, 以'a'+i 字母结尾的子序列数量总数
最后累加g[]即可
class Solution {
public:
int distinctSubseqII(string s) {
int n = s.size();
int MOD = 1e9+7, res = 0;
int g[26];
for(int i = 0; i < 26; i ++) g[i] = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n ; i ++)
{
int sum = 1;
for(int j = 0; j < 26; j ++)
sum = (sum + g[j]) % MOD;
g[s[i] - 'a'] = sum;
}
for(int i = 0; i < 26; i ++)
res = (res + g[i]) % MOD;
return res;
}
};
🔰🔰1441.用栈操作构建数组
https://leetcode.cn/problems/build-an-array-with-stack-operations/
模拟
class Solution {
public:
vector<string> buildArray(vector<int>& target, int n) {
int len = target.size();
vector<string> res;
if(target[0]==1) res.push_back("Push");
else{
for(int j = 0; j < target[0]-1; j ++){
res.push_back("Push");
res.push_back("Pop");
}
res.push_back("Push");
}
for(int i = 1; i < len; i ++)
{
if(target[i]-target[i-1] == 1) res.push_back("Push");
else{
int d = target[i]-target[i-1]-1;
for(int j = 0; j < d; j ++){
res.push_back("Push");
res.push_back("Pop");
}
res.push_back("Push");
}
}
return res;
}
};
🔰🔰🔰6207.统计定界子数组的数目
https://leetcode.cn/problems/count-subarrays-with-fixed-bounds/
滑动数组
更新最大最小值所在的位置, 在该区间之前(直到不满足条件的数值)的数的个数,
即为定界子数组的数量
class Solution {
public:
long long countSubarrays(vector<int>& nums, int minK, int maxK) {
int n = nums.size();
int imin = -1, imax = -1, iout = -1;
long long res = 0L;
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
if(nums[i] == minK) imin = i;
if(nums[i] == maxK) imax = i;
if(nums[i] < minK || nums[i] > maxK) iout = i;
res += max(min(imin, imax)-iout, 0);
}
return res;
}
};
🔰🔰886.可能的二分法
https://leetcode.cn/problems/possible-bipartition/
二分图, 染色法
dfs
借助dislikes[]构造边, 相邻的两点不应在同一集合, 若在染色的过程中出现矛盾的情况, 则无法分配成功
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> color;
vector<vector<int>> g;
bool dfs(int u, int cl) {
color[u] = cl;
for(int ne: g[u]) {
if(color[ne] == cl) return false;
// 如果未分组, 且被分到另一组后不合理
if(color[ne] == 0 && !dfs(ne, 3-cl)) return false;
}
return true;
}
bool possibleBipartition(int n, vector<vector<int>>& dislikes) {
color.resize(n);
g.resize(n);
for(auto& p: dislikes) {
int a = p[0]-1, b = p[1]-1;
g[a].push_back(b);
g[b].push_back(a);
}
for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++)
{
if(!color[i] && !dfs(i, 1))
return false;
}
return true;
}
};
时间复杂度:O(n+m)
空间复杂度:O(n+m)

并查集
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> p;
void add(int a, int b) {
p[find(a)] = p[find(b)];
}
int find(int x) {
if(x != p[x]) p[x] = find(p[x]);
return p[x];
}
bool query(int a, int b) {
return find(a) == find(b);
}
bool possibleBipartition(int n, vector<vector<int>>& dislikes) {
p.resize(n*2+10);
for(int i = 1; i <= n*2; i ++) p[i] = i;
for(auto& t : dislikes){
int a = t[0], b = t[1];
if(query(a, b)) return false;
add(a, b+n);
add(b, a+n);
}
return true;
}
};
时间复杂度:O(n+m)
空间复杂度:O(n)

🔰🔰904.水果成篮
https://leetcode.cn/problems/fruit-into-baskets/
class Solution {
public:
int totalFruit(vector<int>& fruits) {
int n = fruits.size();
int res = 0;
unordered_map<int, int> mp;
for(int i = 0, j = 0; j < n; j ++)
{
++mp[fruits[j]];
while(mp.size() > 2){
int x = fruits[i++];
if(--mp[x] == 0) mp.erase(x);
}
res = max(res, j-i+1);
}
return res;
}
};

优化
🔰🔰🔰902.最大为 N 的数字组合
https://leetcode.cn/problems/numbers-at-most-n-given-digit-set/
dfs, 超时
class Solution {
public:
int num;
int atMostNGivenDigitSet(vector<string>& digits, int n) {
num = 0;
dfs(digits, 0, n, num);
return num;
}
void dfs(vector<string>& digits, int u, int n, int num) {
if(u > n) return ;
if(u && u <= n) ++num;
for(auto& d : digits) {
dfs(digits, u*10+d[0]-'0', n, num);
}
}
};
数位DP
class Solution {
public:
int atMostNGivenDigitSet(vector<string>& digits, int n) {
string s = to_string(n);
int len = s.size(), dp[len];
memset(dp, -1, sizeof(dp));
function<int(int, bool, bool)> f = [&](int u, bool is_limit, bool is_num) -> int {
if(u == len) return is_num; //方案数, 0 or 1
if(!is_limit && is_num && dp[u] >= 0) return dp[u];
int res = 0;
if(!is_num) res = f(u+1, false, false);
char up = is_limit ? s[u] : '9';
for(auto& d : digits) {
if(d[0] > up) break;
res += f(u+1, is_limit && d[0] == up, true);
}
if(!is_limit && is_num) dp[u] = res;
return res;
};
return f(0, true, false);
}
};
🔰1700.无法吃午餐的学生数量
https://leetcode.cn/problems/number-of-students-unable-to-eat-lunch/
class Solution {
public:
int countStudents(vector<int>& students, vector<int>& sandwiches) {
int n = students.size();
int cnt[2] = {0, 0};
for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++) cnt[students[i]] ++;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++)
if(cnt[sandwiches[i]]-- == 0)
return cnt[1-sandwiches[i]]; //return cnt[sandwiches[i]^1];
return 0;
}
};
🔰🔰779.第K个语法符号
https://leetcode.cn/problems/k-th-symbol-in-grammar/
递归模拟
class Solution {
public:
int kthGrammar(int n, int k) {
if(n == 1) return 0;
if(k <= (1<<(n-2))) return kthGrammar(n-1, k);
return kthGrammar(n-1, k-(1<<(n-2)))^1;
}
};
?位运算, 奇偶校验
class Solution {
public:
int kthGrammar(int N, unsigned int K) {
K -= 1;
K ^= K >> 1;
K ^= K >> 2;
K = (K & 0x11111111U) * 0x11111111U;
return (K >> 28) & 1;
}
};
(单调栈)🔰🔰901.股票价格跨度
https://leetcode.cn/problems/online-stock-span/
class StockSpanner {
public:
StockSpanner() {
}
int next(int price) {
int res = 1;
while(!st.empty() && st.top().first <= price) {
res += st.top().second;
st.pop();
}
st.push({price, res});
return res;
}
private:
stack<pair<int ,int>> st;
};
/**
* Your StockSpanner object will be instantiated and called as such:
* StockSpanner* obj = new StockSpanner();
* int param_1 = obj->next(price);
*/
🔰🔰🔰1235.规划兼职工作
https://leetcode.cn/problems/maximum-profit-in-job-scheduling/
动态规划
class Jobs{
public:
int startTime;
int endTime;
int profit;
Jobs(){
}
Jobs(int a, int b, int c):startTime(a), endTime(b), profit(c){
}
};
class Solution {
public:
int jobScheduling(vector<int>& startTime, vector<int>& endTime, vector<int>& profit) {
int n = startTime.size();
vector<Jobs> jobs(n);
for(int i = 0; i <n; ++i)
jobs[i] = Jobs(startTime[i], endTime[i], profit[i]);
//按截止时间排序
sort(jobs.begin(), jobs.end(), [](const Jobs& a, const Jobs& b) -> bool{
return a.endTime < b.endTime;
});
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
int maxProfit = jobs[i].profit;
for(int j = i - 1; j >= 0; --j) {
if(jobs[j].endTime <= jobs[i].startTime){
maxProfit = max(maxProfit, jobs[j].profit+jobs[i].profit);
break;
}else{
maxProfit = max(maxProfit, jobs[j].profit);
}
}
jobs[i].profit = maxProfit;
}
return jobs[n-1].profit;
}
};
二分优化
🔰1768.交替合并字符串
https://leetcode.cn/problems/merge-strings-alternately/
class Solution {
public:
string mergeAlternately(string word1, string word2) {
int n = word1.size(), m = word2.size();
int i = 0, j = 0;
string res ;
while(i < n && j < m)
{
if(i < n) res += word1[i++];
if(j < m) res += word2[j++];
}
while(i < n) {
res += word1[i++];
}
while(j < m) {
res += word2[j++];
}
return res;
}
};
🔰🔰915.分割数组
https://leetcode.cn/problems/partition-array-into-disjoint-intervals/
从右往左初始化rightmin(当前位置右边的最小值)数组
再从左往右扫描即可
class Solution {
public:
int partitionDisjoint(vector<int>& nums) {
int n = nums.size();
int rightmin[n+5];
int tmin = 1e6+10;
for(int i = n - 2; i >= 0; --i){
rightmin[i] = tmin < nums[i+1] ? tmin : nums[i+1];
tmin = rightmin[i];
}
int res, tmax = -1;
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i){
tmax = tmax > nums[i] ? tmax: nums[i];
if(tmax <= rightmin[i]){
res = i+1;
break;
}
}
return res;
}
};
bfs+dfs 🔰🔰934.最短的桥
https://leetcode.cn/problems/shortest-bridge/
#define x first
#define y second
typedef pair<int ,int> PII;
class Solution {
public:
int n, m;
int dx[4] = {-1, 0, 1, 0}, dy[4] = {0, 1, 0, -1};
queue<PII> q;
vector<vector<int>> g, dist;
// 将一座岛置为0, 并加入队列
void dfs(int x, int y) {
g[x][y] = 0;
dist[x][y] = 0;
q.push({x, y});
for(int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) {
int nx = x + dx[i], ny = y + dy[i];
if(nx < 0 || nx >= n || ny < 0 || ny >= m || !g[nx][ny]) continue;
dfs(nx, ny);
}
}
int bfs() {
while(q.size()) {
PII t = q.front();
q.pop();
for(int i = 0; i < 4; ++i){
int nx = t.x + dx[i], ny = t.y + dy[i];
if(nx < 0 || nx >= n || ny < 0 || ny >= m) continue;
// 待更新
if(dist[t.x][t.y] + 1 >= dist[nx][ny]) continue;
dist[nx][ny] = dist[t.x][t.y] + 1;
if(g[nx][ny]) return dist[nx][ny]-1;
q.push({nx, ny});
}
}
return -1;
}
int shortestBridge(vector<vector<int>>& grid) {
n = grid.size(), m = grid[0].size();
g = grid;
dist = vector<vector<int>>(n, vector<int>(m, 1e6));
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
for(int j = 0; j < m; ++j)
if(grid[i][j]){
dfs(i, j);
return bfs();
}
return -1;
}
};
🔰🔰560.和为 K 的子数组
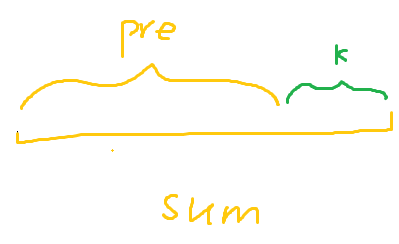
https://leetcode.cn/problems/subarray-sum-equals-k/
- 如果利用前缀和数组, 再二重循环暴力求解, 时间复杂度为O(n^2)
- 优化写法: 在每次累加前缀和后, 判断是否前面曾出现一个前缀和
pre_sum = sum - k, 即此时存在和为k的子数组在中间夹着. 时间复杂度为O(n)
class Solution {
public:
int subarraySum(vector<int>& nums, int k) {
int n = nums.size();
int cnt = 0, sum = 0;
unordered_map<int, int> mp;
mp[0] = 1;
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
sum += nums[i];
cnt += mp[sum-k];
++mp[sum];
}
return cnt;
}
};
🔰🔰🔰862.和至少为 K 的最短子数组
https://leetcode.cn/problems/shortest-subarray-with-sum-at-least-k/
暴力解法, 超时
时间复杂度:O(n^2)
空间复杂度:O(n)
class Solution {
public:
int shortestSubarray(vector<int>& nums, int k) {
int n = nums.size();
int sum[n+10];
sum[0] = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if(nums[i] >= k) return 1;
}
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
sum[i+1] = sum[i]+nums[i];
}
int res = 1e5+10;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
for(int j = i+1; j <= n; ++j) {
if(sum[j] - sum[i-1] >= k)
res = min(res, j-i+1);
}
}
return res == 1e5+10 ? -1:res;
}
};
双端队列
在上面的双层循环中,还有一定的优化空间
比如当sum[x1] >= sum[x2](x1 < x2)时,表明x1到x2之间的元素的和是负数或0,则sum[xn] - sum[x1] >= K时
必有sum[xn] - sum[x2] >= K,那么这个时候我们只计算xn - x2即可(x1到x2之间的元素可以全部跳过),就不需要计算xn - x1了,因为后者一定是更大的,不满足我们要选最小的条件。
另一个角度,当sum[x2] - sum[x1] >= K时,x1就可以跳过了,为什么呢?因为x1到x2已经满足了大于K,再继续从x1开始向后再找,也不会再有比x2距离x1更近的了,毕竟我们要求的是最小的x2 - x1。
以上的两种分析,情况1是把位于末尾没用的x1扔掉,情况2是把指向前面的已经满足条件的x1的指针向后移动1位,这是就需要比较当前最小值与此时刚符合条件的值的大小了。
class Solution {
public:
int shortestSubarray(vector<int>& nums, int k) {
int n = nums.size();
long sum[n+10];
sum[0] = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if(nums[i] >= k) return 1;
}
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
sum[i+1] = sum[i]+nums[i];
}
long res = 1e5+10;
deque<int> dq;
for(int i = 0; i <= n; ++i) {
while(!dq.empty() && sum[i] <= sum[dq.back()]) {
dq.pop_back();
}
while(!dq.empty() && sum[i] - sum[dq.front()] >= k) {
int len = i - dq.front();
dq.pop_front();
res = res < len ? res : len;
}
dq.push_back(i);
}
return res == 1e5+10 ? -1:res;
}
};
(单调栈)🔰🔰907.子数组的最小值之和
https://leetcode.cn/problems/sum-of-subarray-minimums/
参考: 0x3f 贡献法+单调栈
利用单调栈初始化left[]和right[]
class Solution {
const int MOD = 1e9+7;
public:
int sumSubarrayMins(vector<int>& arr) {
int n = arr.size();
vector<int> left(n, -1);
vector<int> right(n, n);
int stk[n], k = -1;
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
while(k != -1 && arr[stk[k]] >= arr[i]) --k;
if(k != -1) left[i] = stk[k];
stk[++k] = i;
}
k = -1;
for(int i = n-1; i >= 0; --i) {
while(k != -1 && arr[stk[k]] > arr[i]) --k;
if(k != -1) right[i] = stk[k];
stk[++k] = i;
}
long res = 0L;
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
res += (long)arr[i]*(i-left[i])*(right[i]-i);
}
return res%MOD;
}
};

在更新left时,可以同时更新right
对于栈顶元素 t,如果 t 右侧有多个小于或等于 t 的元素,那么 t 只会因为右侧第一个小于或等于 t 的元素而出栈,这恰好符合右边界的定义
class Solution {
const int MOD = 1e9+7;
public:
int sumSubarrayMins(vector<int>& arr) {
int n = arr.size();
vector<int> left(n, -1);
vector<int> right(n, n);
int stk[n], k = -1;
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
while(k != -1 && arr[stk[k]] >= arr[i]) {
right[stk[k]] = i;
--k;
}
if(k != -1) left[i] = stk[k];
stk[++k] = i;
}
long res = 0L;
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
res += (long)arr[i]*(i-left[i])*(right[i]-i);
}
return res%MOD;
}
};

栈顶下面的元素正好也是栈顶的左边界, 甚至连 left 和 right 数组都可以不要,直接在出栈的时候计算贡献
class Solution {
const int MOD = 1e9+7;
public:
int sumSubarrayMins(vector<int>& arr) {
arr.push_back(-1); //右哨兵
int n = arr.size();
int stk[n], k = -1;
long res = 0L;
stk[++k] = -1; //左哨兵
for(int r = 0; r < n; ++r) {
while(k > 0 && arr[stk[k]] >= arr[r]) {
int t = stk[k--];
res += (long) arr[t]*(t - stk[k])*(r - t);
}
stk[++k] = r;
}
return res%MOD;
}
};
