文章目录
打家劫舍 III
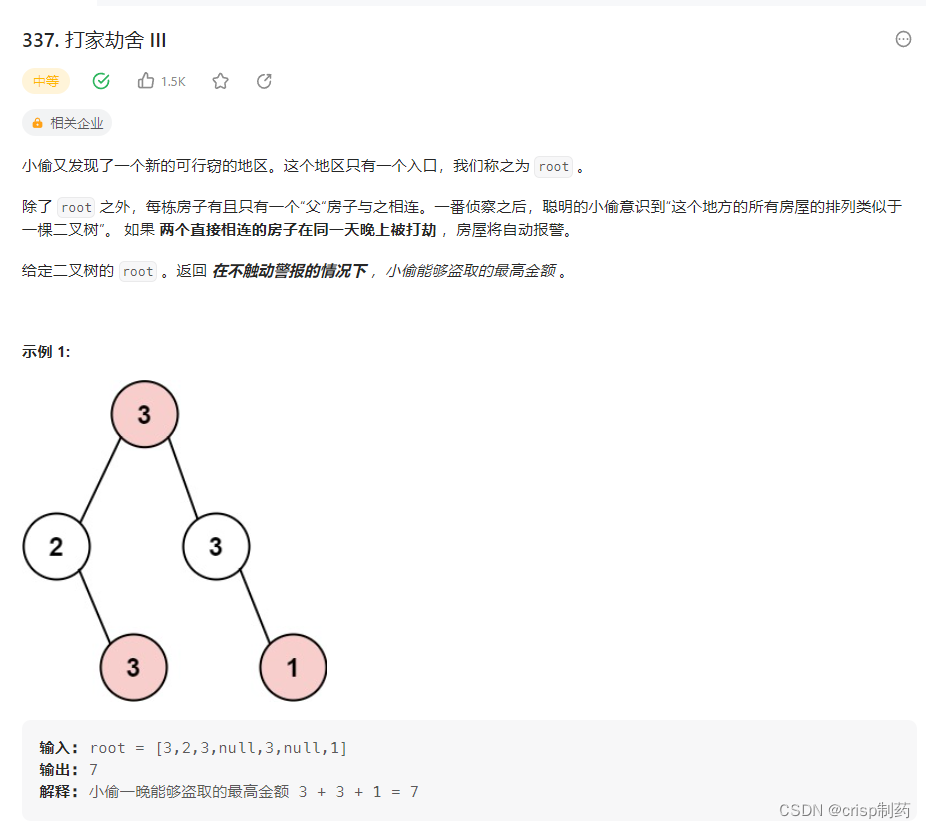
public class Solution {
// 树的后序遍历
public int rob(TreeNode root) {
int[] res = dfs(root);
return Math.max(res[0], res[1]);
}
private int[] dfs(TreeNode node) {
if (node == null) {
return new int[]{0, 0};
}
// 分类讨论的标准是:当前结点偷或者不偷
// 由于需要后序遍历,所以先计算左右子结点,然后计算当前结点的状态值
int[] left = dfs(node.left);
int[] right = dfs(node.right);
// dp[0]:以当前 node 为根结点的子树能够偷取的最大价值,规定 node 结点不偷
// dp[1]:以当前 node 为根结点的子树能够偷取的最大价值,规定 node 结点偷
int[] dp = new int[2];
dp[0] = Math.max(left[0], left[1]) + Math.max(right[0], right[1]);
dp[1] = node.val + left[0] + right[0];
return dp;
}
}
卖股票的最佳时机

dp[i][0]:规定了今天不持股,有以下两种情况:
昨天不持股,今天什么都不做;
昨天持股,今天卖出股票(现金数增加),
dp[i][1]:规定了今天持股,有以下两种情况:
昨天持股,今天什么都不做(现金数与昨天一样);
昨天不持股,今天买入股票(注意:只允许交易一次,因此手上的现金数就是当天的股价的相反数)。
class Solution {
public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {
int len = prices.length;
// 特殊判断
if (len < 2) {
return 0;
}
int[][] dp = new int[len][2];
// dp[i][0] 下标为 i 这天结束的时候,不持股,手上拥有的现金数
// dp[i][1] 下标为 i 这天结束的时候,持股,手上拥有的现金数
// 初始化:不持股显然为 0,持股就需要减去第 1 天(下标为 0)的股价
dp[0][0] = 0;
dp[0][1] = -prices[0];
// 从第 2 天开始遍历
for (int i = 1; i < len; i++) {
// 不持股的话就可能前一天也不持股直接转移状态,或者是今天才,所以就前一天持股的状态加上price【i】
dp[i][0] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][0], dp[i - 1][1] + prices[i]);
dp[i][1] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][1], -prices[i]);
}
return dp[len - 1][0];
}
}
买卖股票的最佳时机 II
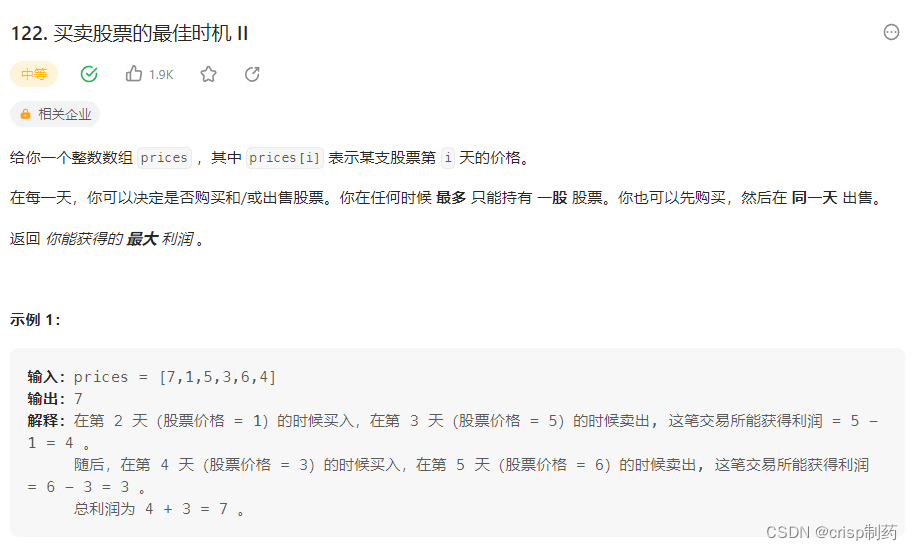
这题的交易次数变成了无数次,其实和上题类似,注意状态转移方程的修改就好。
class Solution {
public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {
if(prices.length == 0 || prices == null){
return 0;
}
int length = prices.length;
int [][] dp = new int [length][2];
dp[0][0]=0;
dp[0][1]=-prices[0];
for(int i=1;i<length;i++){
dp[i][0]=Math.max(dp[i-1][0],dp[i-1][1]+prices[i]);
dp[i][1]=Math.max(dp[i-1][1],dp[i-1][0]-prices[i]);
}
return dp[length-1][0];
}
}
买卖股票的最佳时机 III
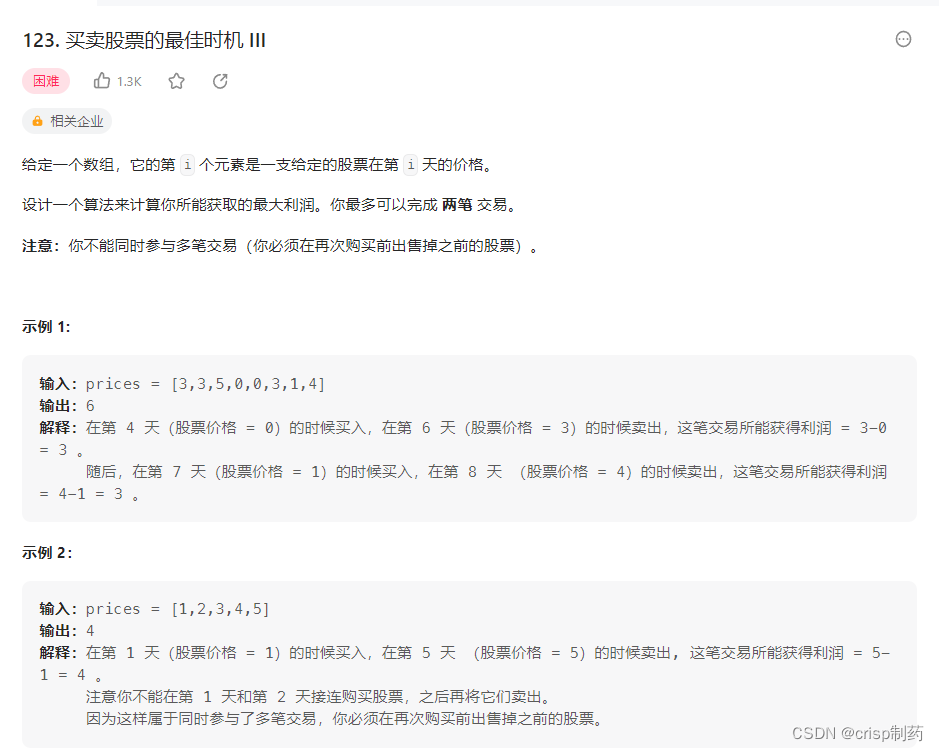
情况三和情况一相似,区别之处是,对于情况三,每天有四个未知变量:T[i][1][0]、T[i][1][1]、T[i][2][0]、T[i][2][1],中间那一维是表示交易第几次,因为这题是要交易两次
public class Solution {
public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {
int len = prices.length;
if (len < 2) {
return 0;
}
// 第 2 维的 0 没有意义,1 表示交易进行了 1 次,2 表示交易进行了 2 次
// 为了使得第 2 维的数值 1 和 2 有意义,这里将第 2 维的长度设置为 3
int[][][] dp = new int[len][3][2];
// 理解如下初始化
// 第 3 维规定了必须持股,因此是 -prices[0]
dp[0][1][1] = -prices[0];
// 还没发生的交易,必须由前面状态转移得到,所以持股的时候应该初始化为负无穷
dp[0][2][1] = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
for (int i = 1; i < len; i++) {
// 转移顺序先持股,再卖出
dp[i][1][1] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][1][1], -prices[i]) ;
dp[i][1][0] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][1][0], dp[i - 1][1][1] + prices[i]);
dp[i][2][1] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][2][1], dp[i - 1][1][0] - prices[i]);
dp[i][2][0] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][2][0], dp[i - 1][2][1] + prices[i]);
}
//题目说的是最多可以买两次,不一定是一定要买两次,所以是从买1次和买2次中取最大值
return Math.max(dp[len - 1][1][0], dp[len - 1][2][0]);
}
}