417. 太平洋大西洋水流问题
难度中等558
有一个 m × n 的矩形岛屿,与 太平洋 和 大西洋 相邻。 “太平洋” 处于大陆的左边界和上边界,而 “大西洋” 处于大陆的右边界和下边界。
这个岛被分割成一个由若干方形单元格组成的网格。给定一个 m x n 的整数矩阵 heights , heights[r][c] 表示坐标 (r, c) 上单元格 高于海平面的高度 。
岛上雨水较多,如果相邻单元格的高度 小于或等于 当前单元格的高度,雨水可以直接向北、南、东、西流向相邻单元格。水可以从海洋附近的任何单元格流入海洋。
返回网格坐标 result 的 2D 列表 ,其中 result[i] = [ri, ci] 表示雨水从单元格 (ri, ci) 流动 既可流向太平洋也可流向大西洋 。
示例 1:
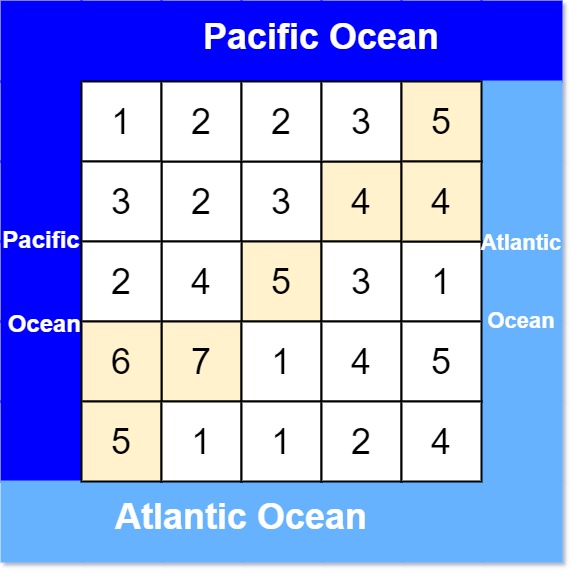
输入: heights = [[1,2,2,3,5],[3,2,3,4,4],[2,4,5,3,1],[6,7,1,4,5],[5,1,1,2,4]]
输出: [[0,4],[1,3],[1,4],[2,2],[3,0],[3,1],[4,0]]
示例 2:
输入: heights = [[2,1],[1,2]]
输出: [[0,0],[0,1],[1,0],[1,1]]
提示:
m == heights.lengthn == heights[r].length1 <= m, n <= 2000 <= heights[r][c] <= 105
题解来自:宫水三叶https://leetcode.cn/problems/pacific-atlantic-water-flow/solution/by-ac_oier-do7d/
从边出发,只要有比自己高的点,就往高处走,直到走不了为止。
最终返回太平洋和大西洋能走到的点的交集。
说明这些点可以流到太平洋和大西洋。
多源BFS
class Solution {
int n, m;
int[][] g;
public List<List<Integer>> pacificAtlantic(int[][] heights) {
g = heights;
m = g.length; n = g[0].length;
Deque<int[]> d1 = new ArrayDeque<>(), d2 = new ArrayDeque<>();
boolean[][] res1 = new boolean[m][n], res2 = new boolean[m][n];
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (i == 0 || j == 0) {
res1[i][j] = true;
d1.addLast(new int[]{i, j});
}
if (i == m - 1 || j == n - 1) {
res2[i][j] = true;
d2.addLast(new int[]{i, j});
}
}
}
bfs(d1, res1); bfs(d2, res2);
List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (res1[i][j] && res2[i][j]) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(i); list.add(j);
ans.add(list);
}
}
}
return ans;
}
int[][] dirs = new int[][]{{1,0},{-1,0},{0,1},{0,-1}};
void bfs(Deque<int[]> d, boolean[][] res) {
while (!d.isEmpty()) {
int[] info = d.pollFirst();
int x = info[0], y = info[1], t = g[x][y];
for (int[] di : dirs) {
int nx = x + di[0], ny = y + di[1];
if (nx < 0 || nx >= m || ny < 0 || ny >= n) continue;
if (res[nx][ny] || g[nx][ny] < t) continue;
d.addLast(new int[]{nx, ny});
res[nx][ny] = true;
}
}
}
}
DFS
class Solution {
int n, m;
int[][] g;
public List<List<Integer>> pacificAtlantic(int[][] heights) {
g = heights;
m = g.length; n = g[0].length;
boolean[][] res1 = new boolean[m][n], res2 = new boolean[m][n];
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (i == 0 || j == 0) {
if (!res1[i][j]) dfs(i, j, res1);
}
if (i == m - 1 || j == n - 1) {
if (!res2[i][j]) dfs(i, j, res2);
}
}
}
List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (res1[i][j] && res2[i][j]) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(i); list.add(j);
ans.add(list);
}
}
}
return ans;
}
int[][] dirs = new int[][]{{1,0},{-1,0},{0,1},{0,-1}};
void dfs(int x, int y, boolean[][] res) {
res[x][y] = true;
for (int[] di : dirs) {
int nx = x + di[0], ny = y + di[1];
if (nx < 0 || nx >= m || ny < 0 || ny >= n) continue;
if (res[nx][ny] || g[nx][ny] < g[x][y]) continue;
dfs(nx, ny, res);
}
}
}