前言
我们都知道测试用例执行失败后,我们会提交相应缺陷到公司缺陷平台,那我们自动化测试完成了,对于执行失败的用例,是不是也需要将失败的用例也提交相应缺陷呢,这种肯定的。作为测试人员,提交缺陷是我们工作的必不可缺少的部分,如何测试人员不提交缺陷了,那就代表已经脱离了测试人员的职责了。
那么在做自动化测试的时候,肯定希望如果用例执行失败了就自动提交缺陷,这样大大减少了人工再去提交缺陷的时间成本,那我们该怎么做呢,我们在这里面需要考虑一些问题。
- 在用例执行过程中,如何获取用例执行状态
- 如何对接缺陷系统,提交缺陷
获取用例执行状态
pytest框架 pytest_runtest_makereport 查看源码:
def pytest_runtest_makereport(item: Item, call: CallInfo[None]) -> TestReport:
return TestReport.from_item_and_call(item, call)
说明:item是测试用例,call是测试步骤,具体执行过程如下:
- 先执行when=‘setup’ 返回setup 的执行结果
- 然后执行when=‘call’ 返回call 的执行结果
- 最后执行when='teardown’返回teardown 的执行结果
使用方法:
@hookimpl(hookwrapper=True)
def pytest_runtest_makereport(item: Item, call: CallInfo[None]):
outcome = yield
rep = outcome.get_result()
xfailed = item._store.get(xfailed_key, None)
# unittest special case, see setting of unexpectedsuccess_key
if unexpectedsuccess_key in item._store and rep.when == "call":
reason = item._store[unexpectedsuccess_key]
.............
基本使用
根据源码及使用方式,我们先尝试使用一下:
conftest.py
# !/usr/bin/python3
# _*_coding:utf-8 _*_
""""
# @Time :2021/7/20 18:39
# @Author : king
# @File :conftest.py
# @Software :PyCharm
# @blog :https://blog.csdn.net/u010454117
# @WeChat Official Account: 【测试之路笔记】
"""
from _pytest.config import hookimpl
@hookimpl(hookwrapper=True)
def pytest_runtest_makereport(item, call):
out = yield
report = out.get_result()
print("当前有哪些方法", report.__dict__)
print("***************************************")
test_report.py
# !/usr/bin/python3
# _*_coding:utf-8 _*_
""""
# @Time :2021/7/20 18:45
# @Author : king
# @File :test_report.py
# @Software :PyCharm
# @blog :https://blog.csdn.net/u010454117
# @WeChat Official Account: 【测试之路笔记】
"""
import pytest
def test_01():
"""用例描述:test_01"""
print("我是测试用例 test_01 ")
if __name__ == '__main__':
pytest.main()
执行 pytest -v -s test_report.py ,查看结果:
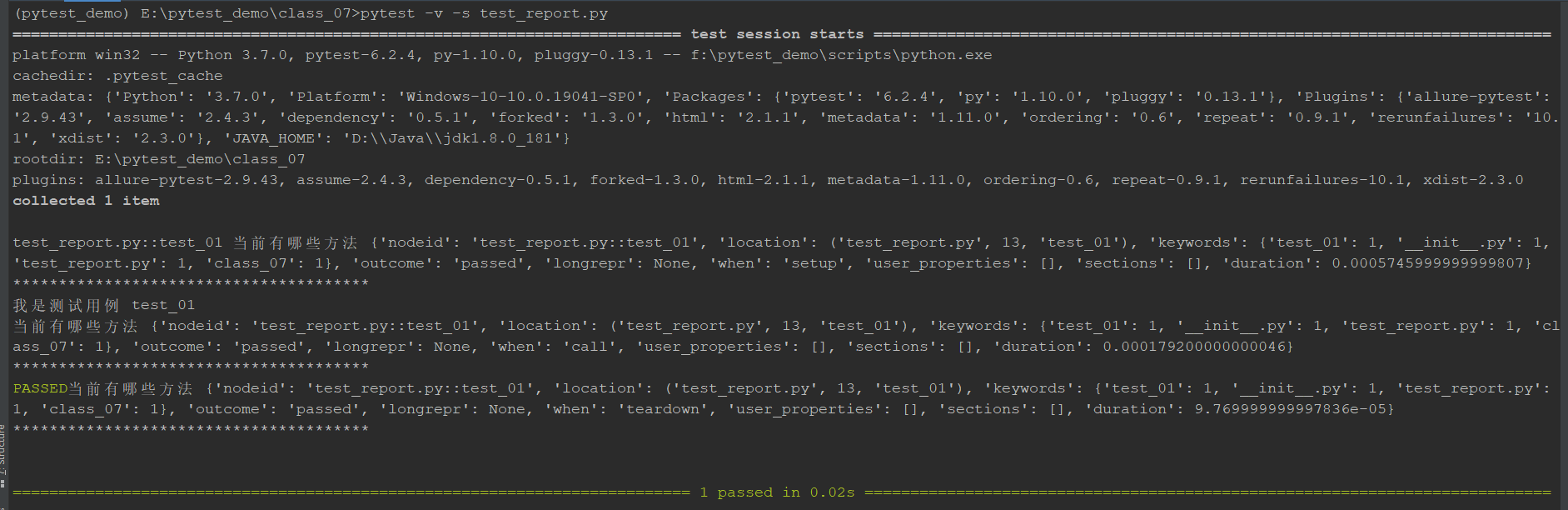
从执行结果可以看出来 pytest_runtest_makereport 经过三个阶段:'when': 'setup'、'when': 'call' 、'when': 'teardown'
这样我们就可以使用属性 when 和 outcome 来判断用例执行结果,那我们该怎么来使用,在哪个阶段进行判断。再看下用例存在setup和teardown时的情况。
在contest.py 增加一个fixture函数,如下:
@pytest.fixture(scope="session", autouse=True)
def login():
print("setup 前置操作")
yield
print("teardown 后置操作")
执行 pytest -v -s test_report.py ,查看结果:

由于我们用例执行过程中可能出现前置操作失败、用例执行失败、在后置操作失败等情况,接下来我们看下这些情况,执行结果如何:
setup执行失败
修改contest.py 的fixture函数,如下:
@pytest.fixture(scope="session", autouse=True)
def login():
print(1/0)
print("setup 前置操作")
yield
print("teardown 后置操作")
执行 pytest -v -s test_report.py ,查看结果:
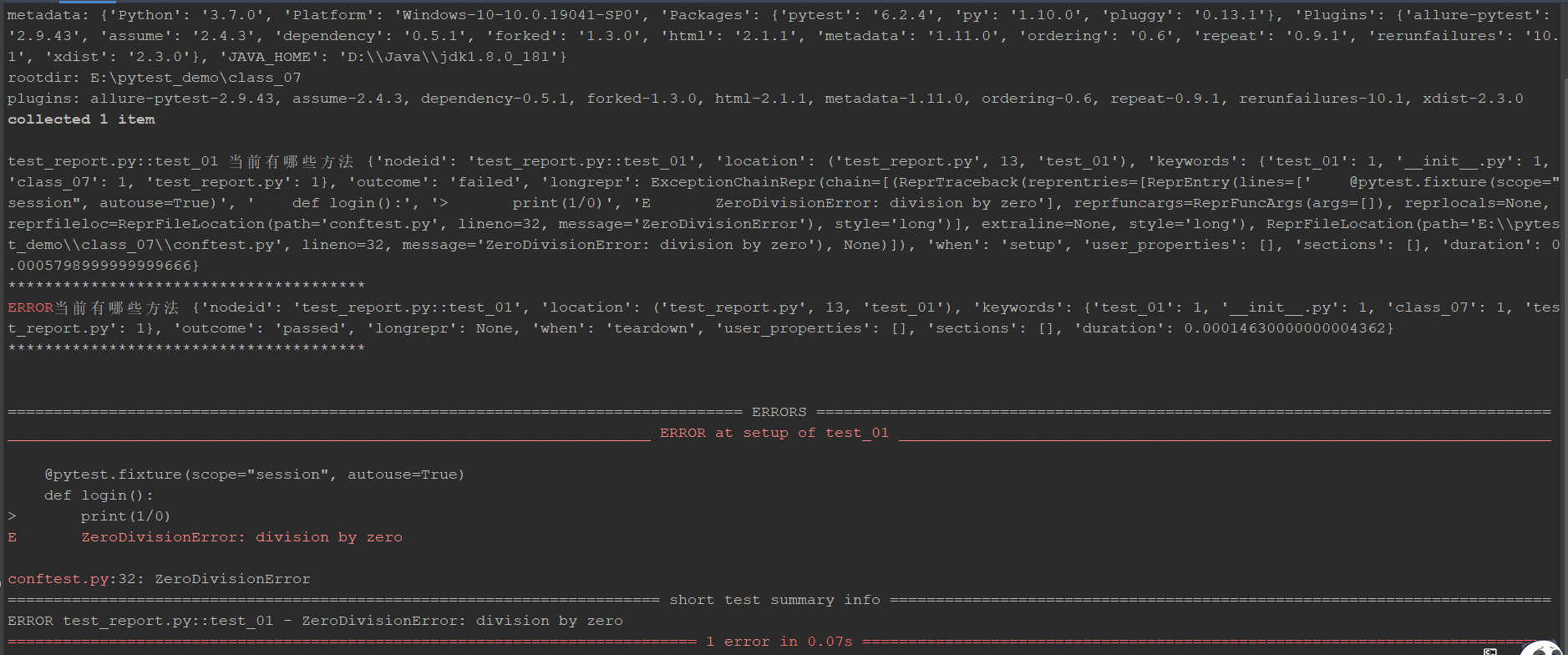
call 用例执行失败
修改test_report.py ,如下:
def test_01():
"""用例描述:test_01"""
print("我是测试用例 test_01 ")
assert 1 == 3
执行 pytest -v -s test_report.py ,查看结果:
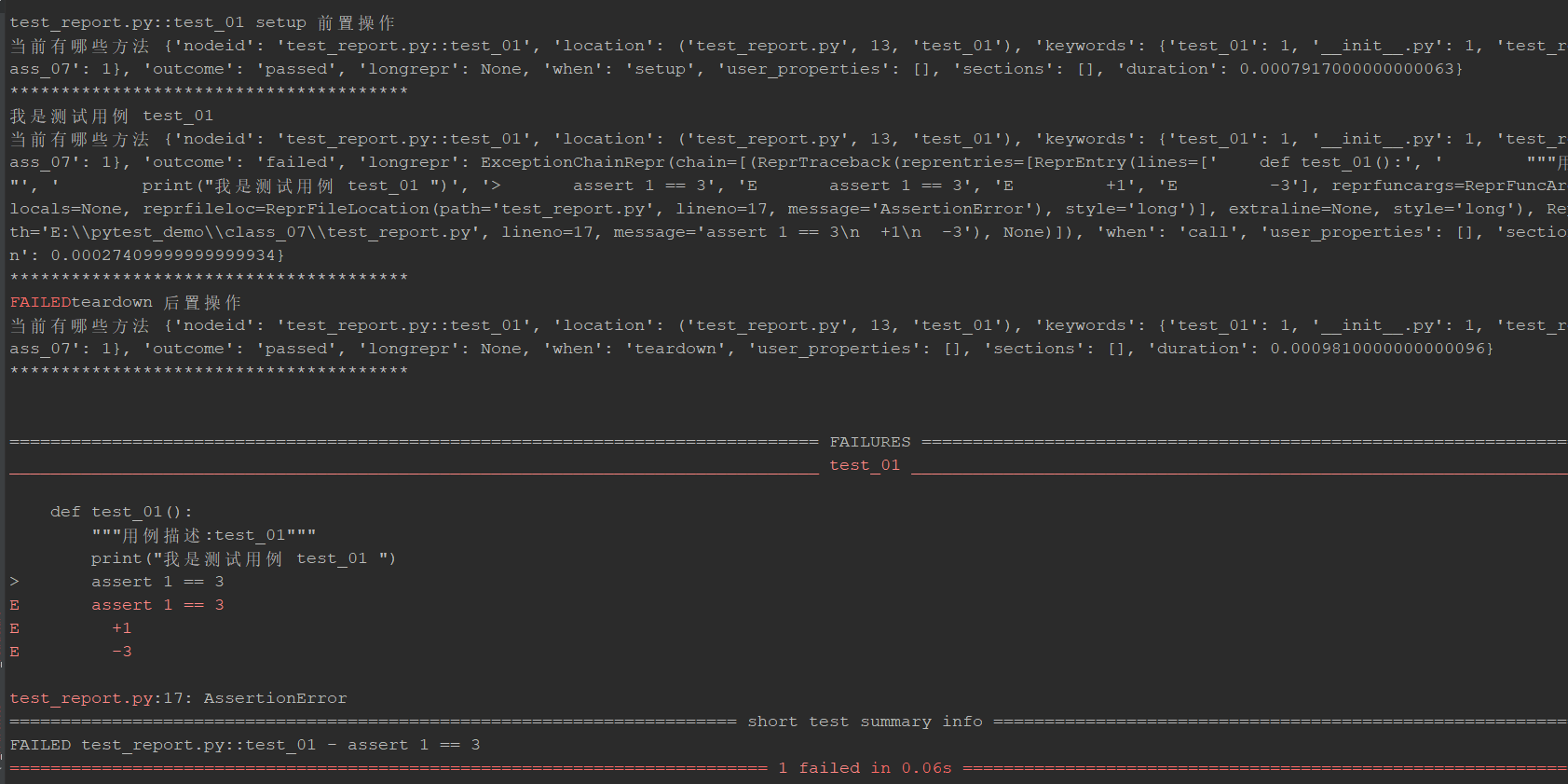
teardown 执行失败
修改contest.py 的fixture函数,如下:
@pytest.fixture(scope="session", autouse=True)
def login():
print("setup 前置操作")
yield
print(1/0)
print("teardown 后置操作")
执行 pytest -v -s test_report.py ,查看结果:
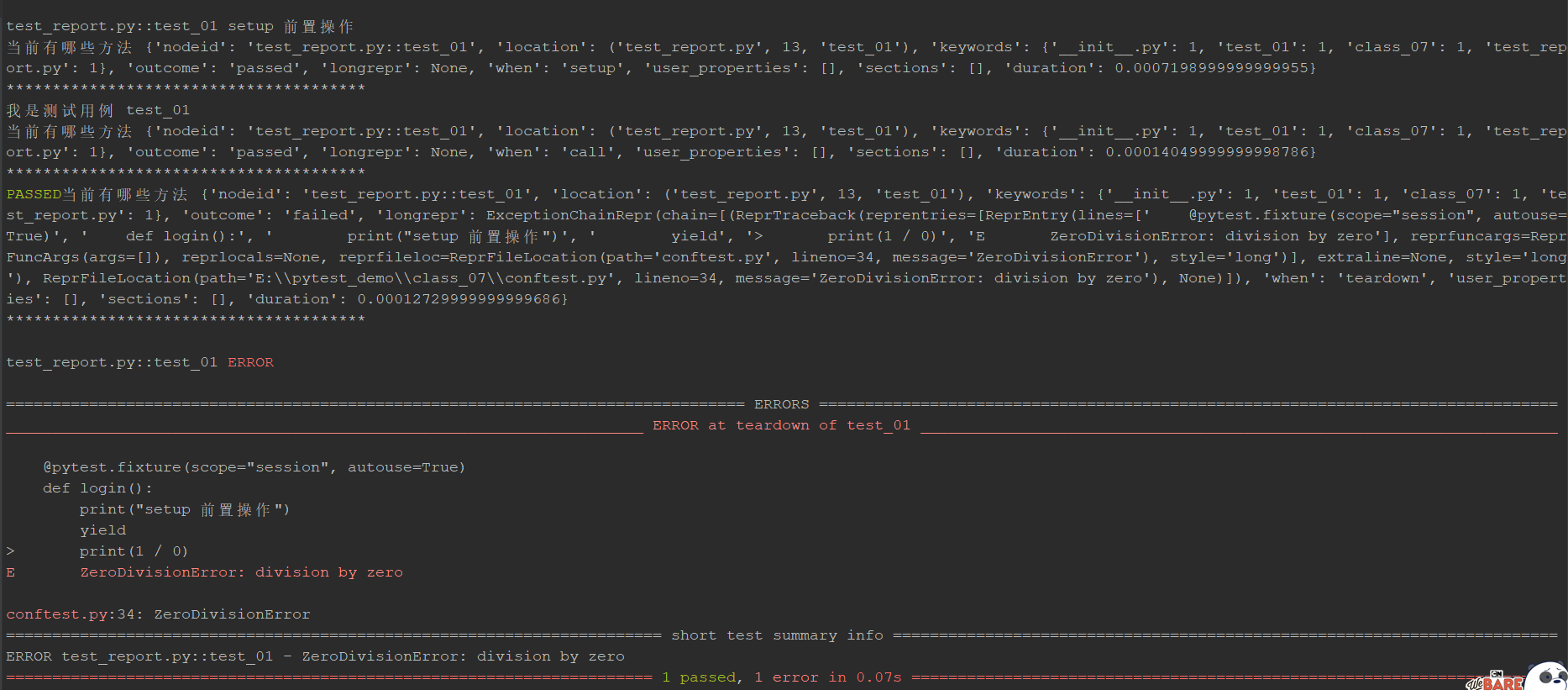
结论:
从用例执行结果来看,我们保证setup和teardown执行成功,主要关注用例执行部分出错,所有我们一般只关注 call 执行部分
所以我们一般如下写法:
from _pytest.config import hookimpl
@hookimpl(hookwrapper=True)
def pytest_runtest_makereport(item, call):
# 获取hooks方法的调用结果
out = yield
# 从hooks方法的调用结果中获取测试结果
report = out.get_result()
if report.when == "call" and report.outcome == 'failed':
"""
这里可以编写提交缺陷部分代码
"""
pass
对接缺陷系统,提交缺陷
下面由于公司是redmie系统,通过查看提交缺陷api,存在提交缺陷接口:
redmine 提交缺陷api
redminelib.managers.ResourceManager.create(**fields)
"""
Creates new Issue resource with given fields and saves it to the Redmine.
Parameters:
project_id (int or string) – (required). Id or identifier of issue’s project.
subject (string) – (required). Issue subject.
tracker_id (int) – (optional). Issue tracker id.
description (string) – (optional). Issue description.
status_id (int) – (optional). Issue status id.
priority_id (int) – (optional). Issue priority id.
category_id (int) – (optional). Issue category id.
fixed_version_id (int) – (optional). Issue version id.
is_private (bool) – (optional). Whether issue is private.
assigned_to_id (int) – (optional). Issue will be assigned to this user id.
watcher_user_ids (list) – (optional). User ids watching this issue.
parent_issue_id (int) – (optional). Parent issue id.
start_date (string or date object) – (optional). Issue start date.
due_date (string or date object) – (optional). Issue end date.
estimated_hours (int) – (optional). Issue estimated hours.
done_ratio (int) – (optional). Issue done ratio.
custom_fields (list) – (optional). Custom fields as [{‘id’: 1, ‘value’: ‘foo’}].
uploads (list) – (optional). Uploads as [{'': ''}, ...], accepted keys are:
path (required). Absolute file path or file-like object that should be uploaded.
filename (optional). Name of the file after upload.
description (optional). Description of the file.
content_type (optional). Content type of the file.
Returns:
Resource object
"""
>>> from io import BytesIO
>>> issue = redmine.issue.create(
... project_id='vacation',
... subject='Vacation',
... tracker_id=8,
... description='foo',
... status_id=3,
... priority_id=7,
... assigned_to_id=123,
... watcher_user_ids=[123],
... parent_issue_id=345,
... start_date=datetime.date(2014, 1, 1),
... due_date=datetime.date(2014, 2, 1),
... estimated_hours=4,
... done_ratio=40,
... custom_fields=[{'id': 1, 'value': 'foo'}, {'id': 2, 'value': 'bar'}],
... uploads=[{'path': '/absolute/path/to/file'}, {'path': BytesIO(b'I am content of file 2')}]
... )
>>> issue
<redminelib.resources.Issue #123 "Vacation">
安装库
pip install python-redmine
使用
class NewIssue(object):
"""
redmine自动提交缺陷类封装
"""
def __init__(self, subject="", description="", picture_path=None):
"""
:param subject: 缺陷主题
:param description: 缺陷描述
:param picture_path: 附件绝对路径(主要为图片)
"""
self.subject = subject
self.description = description
self.picture_path = picture_path
# 读取配置文件
yaml_path = os.path.join(path, "redmine_config.yaml")
pmp_config = ReadYaml(yaml_path, "issue").read_data()
if pmp_config and pmp_config.get("redmineConfig", None):
self.url = pmp_config["redmineConfig"]["url"] # redmine的域名
self.username = pmp_config["redmineConfig"]["username"] # redmine用户名
self.password = pmp_config["redmineConfig"]["password"] # redmine用户密码
self.assigned_to_id = pmp_config["redmineConfig"]["assigned_to_id"] # 缺陷指派人ID
self.project_id = pmp_config["redmineConfig"]["project_id"] # 项目ID
self.red_mine = Redmine(url=self.url, username=self.username, password=self.password)
def __create_issue_pic(self):
issue = self.red_mine.issue.create(
project_id=self.project_id, # 缺陷提交项目ID
subject=self.subject, # 缺陷主题
tracker_id=1, # 跟踪
description=self.description, # 缺陷描述
status_id=1, # 缺陷状态
priority_id=2, # 缺陷优先级
assigned_to_id=self.assigned_to_id, # 指派人
start_date=time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d", time.localtime()),
custom_fields=[
{"id": 14, "value": "一般"}, # 缺陷等级
{"id": 2, "value": "功能错误"}, # 缺陷类型
{"id": 3, "value": 1425}, # 缺陷版本
],
uploads=[
{"path": self.picture_path, "filename": self.subject + ".png"} # 缺陷附件,主要为图片附件
]
)
return issue
def __create_issue(self):
issue = self.red_mine.issue.create(
project_id=self.project_id, # 缺陷提交项目ID
subject=self.subject, # 缺陷主题
tracker_id=1, # 跟踪
description=self.description, # 缺陷描述
status_id=1, # 缺陷状态
priority_id=2, # 缺陷优先级
assigned_to_id=self.assigned_to_id, # 指派人
start_date=time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d", time.localtime()),
custom_fields=[
{"id": 14, "value": "一般"}, # 缺陷等级
{"id": 2, "value": "功能错误"}, # 缺陷类型
{"id": 3, "value": 1519}, # 缺陷版本
]
)
return issue
def submit_issue(self):
try:
if self.picture_path is None:
issue = self.__create_issue()
else:
issue = self.__create_issue_pic()
if str(issue) == self.subject:
return True
except Exception as e:
traceback.print_exc()
return False
综合案例
contest.py 的 pytest_runtest_makereport 写法
import pytest
@pytest.hookimpl(hookwrapper=True, tryfirst=True)
def pytest_runtest_makereport(item, call):
"""
:param call:
:param item: 单条用例执行结果
:return:
"""
result = yield
report = result.get_result()
if report.when == "call" and report.outcome == "failed":
if PublicData.res and item.function.__doc__ not in PublicData.issue:
if item.function.__doc__ is None:
subject = "XXX"
else:
subject = item.function.__doc__
description = """
请求方法:{}
请求参数:{}
请求地址:{}
返回数据:{}
""".format(PublicData.res.request.method,
PublicData.res.request.body,
PublicData.res.url,
PublicData.res.text)
NewIssue(subject=subject, description=description).submit_issue()
PublicData.issue.append(item.function.__doc__)
总结
- pytest_runtest_makereport 的使用
- pytest_runtest_makereport 和redmine 配置提交缺陷
以上为内容纯属个人理解,如有不足,欢迎各位大神指正,转载请注明出处!
如果觉得文章不错,欢迎关注微信公众号,微信公众号每天推送相关测试技术文章
