A. Mocha and Math
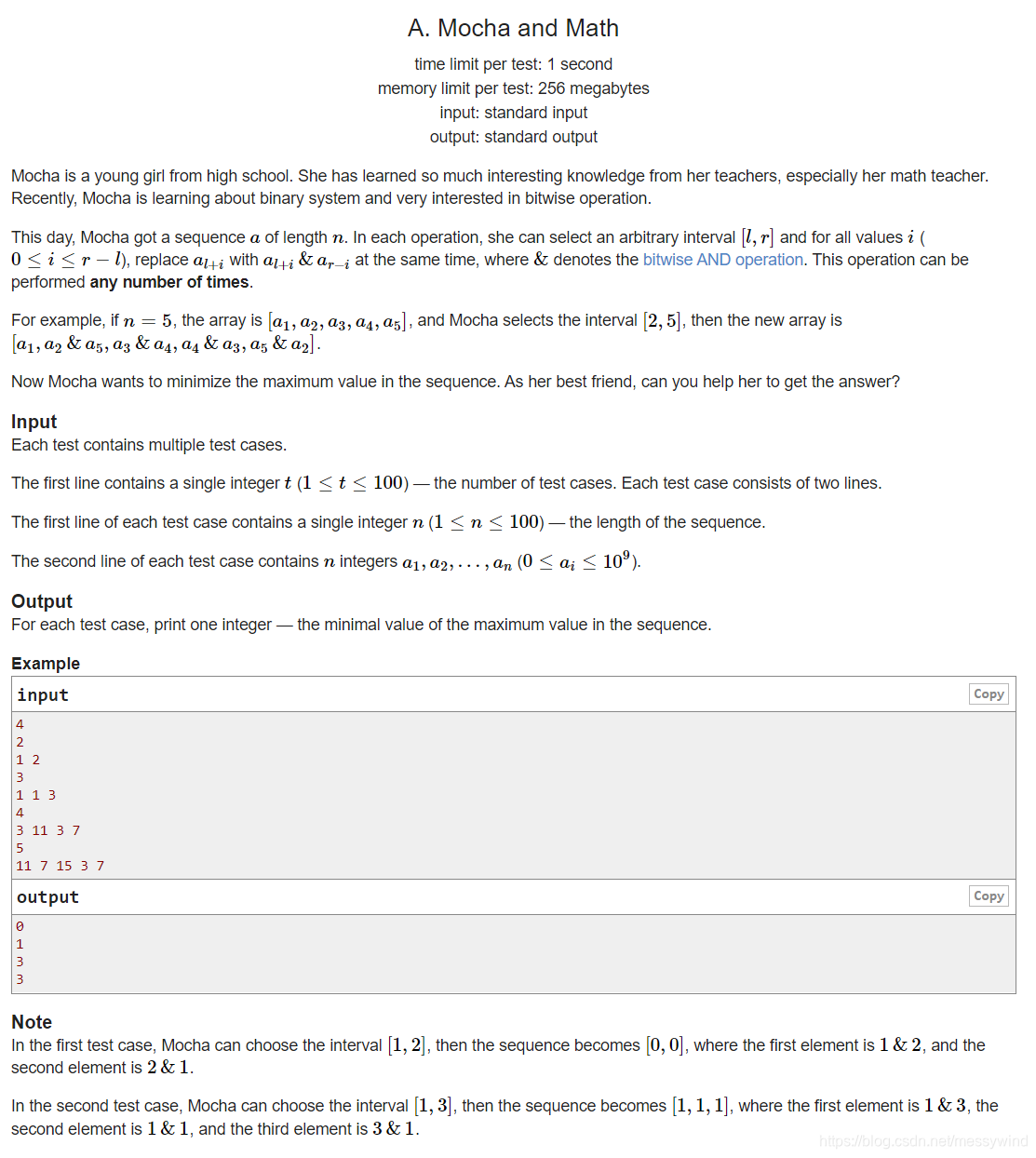
分析: 贪心,答案为 a 1 & a 2 & ? & a n a_1 \& a_2 \& \cdots \&a_n a1?&a2?&?&an?
代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
using namespace std;
int T, n, x;
signed main() {
cin >> T;
while (T --) {
int res = (1 << 32) - 1;
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) cin >> x, res &= x;
cout << res << endl;
}
}
B. Mocha and Red and Blue
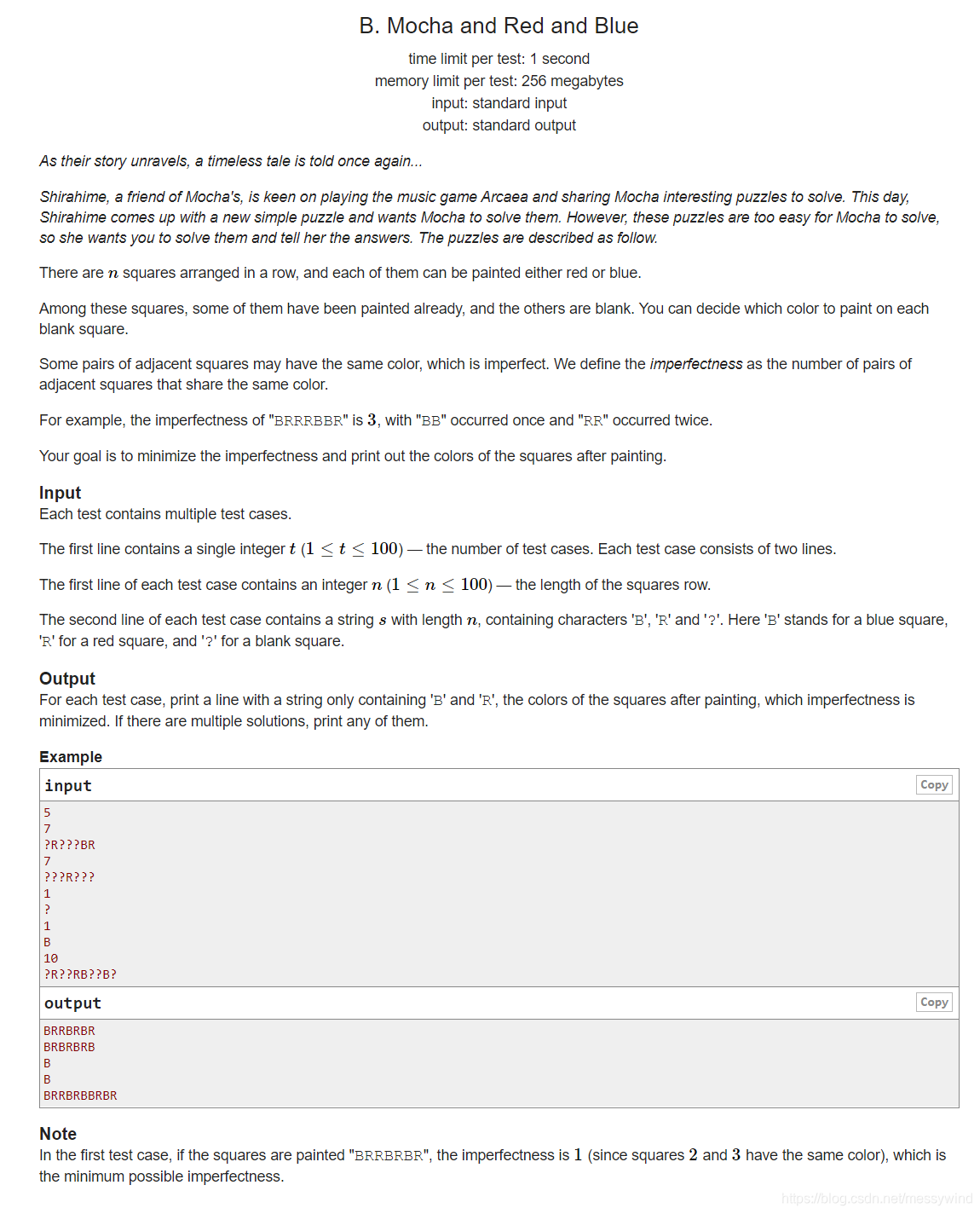
分析: 递推一遍即可,需要注意的是如果前两个数都是 ? \text{?} ? ,那么需要判断填 B \text{B} B 和填 R \text{R} R 的两种情况。
代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int T, n;
map<char, char> mp;
signed main() {
mp['B'] = 'R', mp['R'] = 'B';
cin >> T;
while (T --) {
string str;
int s1 = 0, s2 = 0;
cin >> n >> str;
if (n == 1) {
if (str[0] == '?') {
cout << 'B' << endl;
} else {
cout << str << endl;
}
continue;
}
string tmp = str;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++) {
if (str[i] == '?') {
if (!i) {
if (str[i + 1] == '?') {
str[i] = 'B';
} else {
str[i] = mp[str[i + 1]];
}
} else {
str[i] = mp[str[i - 1]];
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++) {
if (tmp[i] == '?') {
if (!i) {
if (tmp[i + 1] == '?') {
tmp[i] = 'R';
} else {
tmp[i] = mp[tmp[i + 1]];
}
} else {
tmp[i] = mp[tmp[i - 1]];
}
}
}
for (int i = 1; i < n; i ++) {
if (str[i] == str[i - 1]) s1 ++;
}
for (int i = 1; i < n; i ++) {
if (tmp[i] == tmp[i - 1]) s2 ++;
}
if (s1 > s2) {
cout << tmp << endl;
} else {
cout << str << endl;
}
}
}
C. Mocha and Hiking
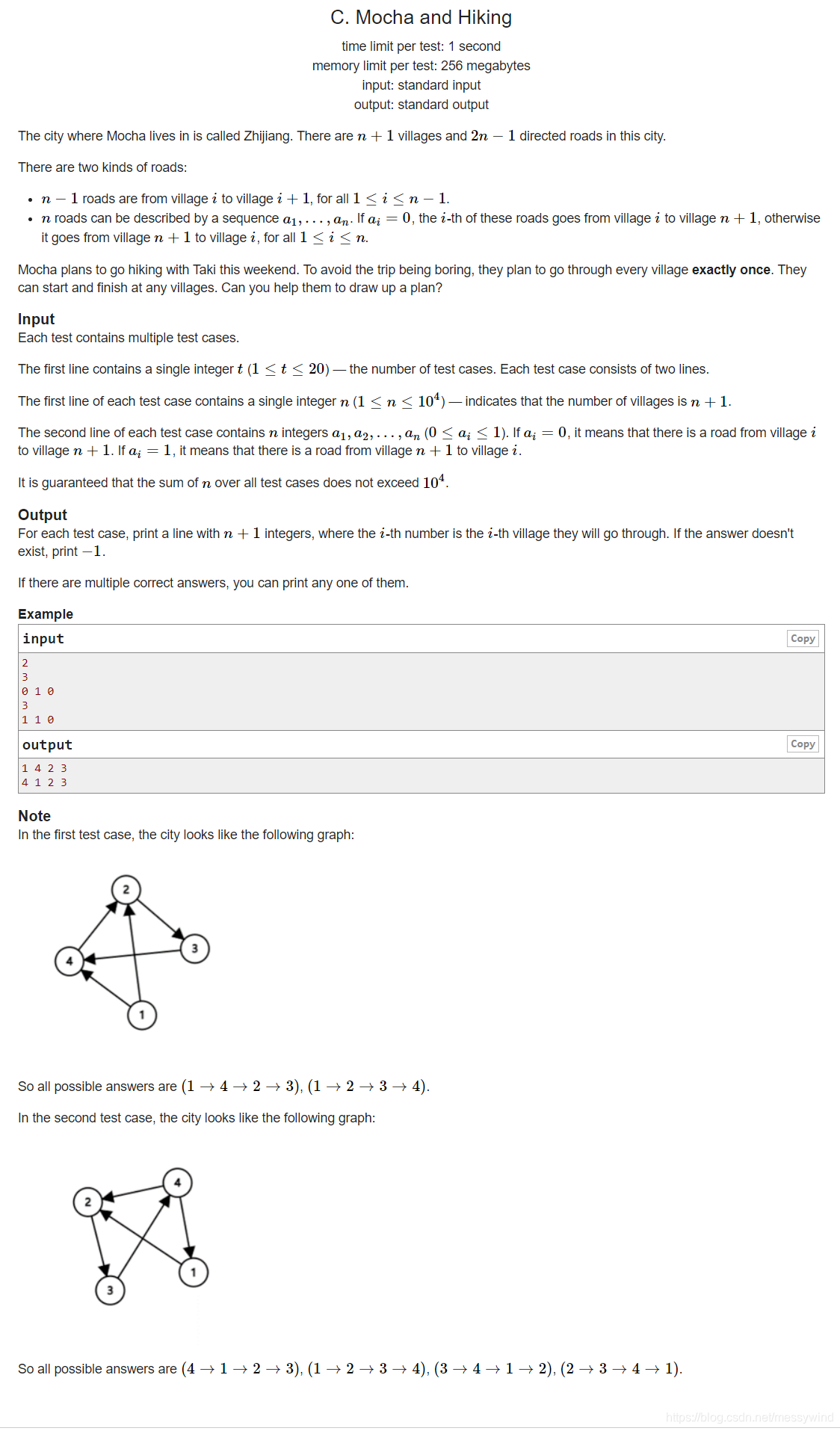
分析: 如果 a n = 0 a_n = 0 an?=0 ,那么就可以按顺序地从 1 1 1 走到 n + 1 n + 1 n+1 ,如果 a 1 = 1 a_1 = 1 a1?=1 那么第 n + 1 n + 1 n+1 个点可以先走到第一个点,然后再从 2 2 2 走到 n n n ,如果序列中出现了连续的 01 01 01 ,假设 a i = 0 , a i + 1 = 1 a_{i} =0,a_{i + 1}=1 ai?=0,ai+1?=1 ,那么可以从 i i i 走到 n + 1 n + 1 n+1,再从 n + 1 n + 1 n+1 走到 i + 1 i + 1 i+1 ,再从 i + 1 i + 1 i+1 走到 n n n ,一定是以上三种情况,不可能出现无解的情况。
代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e4 + 5;
int T, n, a[N];
signed main() {
cin >> T;
while (T --) {
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) cin >> a[i];
if (!a[n]) {
for (int i = 1; i <= n + 1; i ++) cout << i << " ";
} else if (a[1] == 1) {
cout << n + 1 << " ";
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) cout << i << " ";
} else {
int flag = 0;
vector<int> ans;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i ++) {
ans.push_back(i);
if (a[i] == 0 && a[i + 1] == 1) {
flag = 1;
ans.push_back(n + 1);
for (int j = i + 1; j <= n; j ++) ans.push_back(j);
break;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < ans.size(); i ++) cout << ans[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
}
Mocha and Diana (Easy Version)
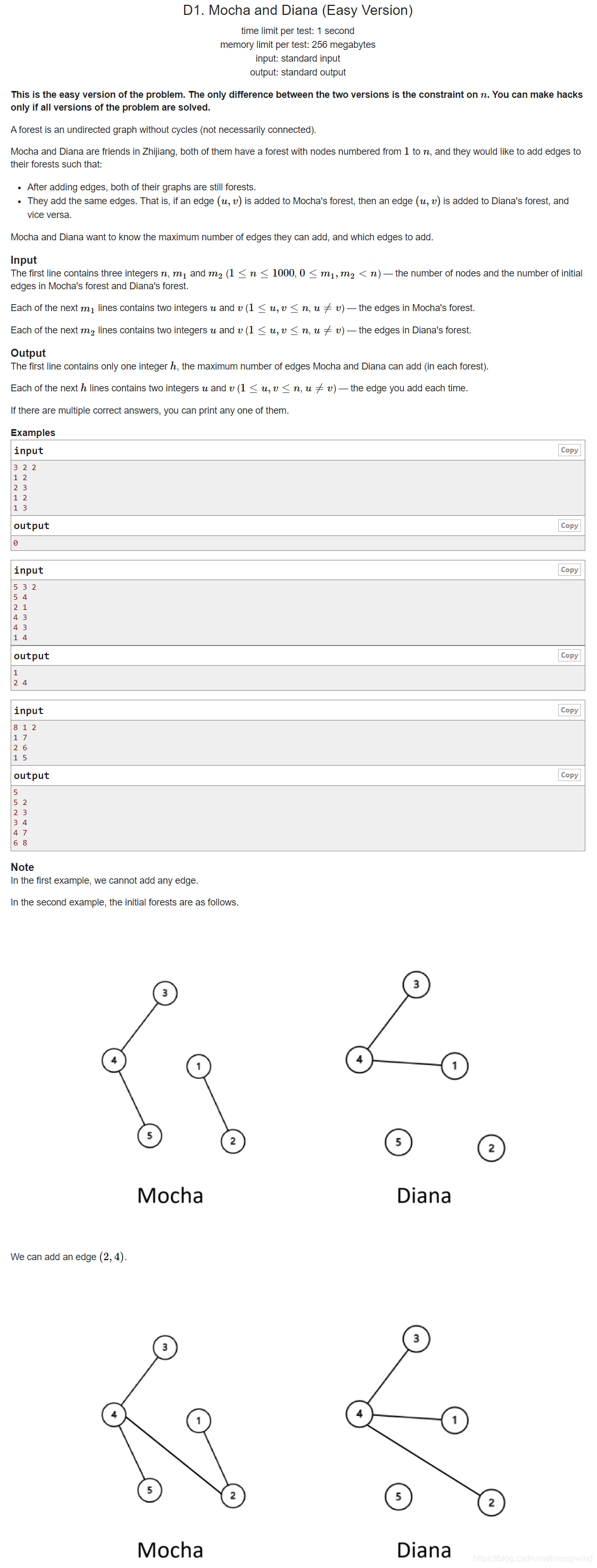
分析: 每个图建一个并查集,
O
(
n
2
)
O(n^2)
O(n2) 暴力判断是否有环
代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e4 + 5;
int T, n, m1, m2, u, v, p1[N], p2[N], cnt1, cnt2;
int find(int p[], int x) {
return p[x] == x ? p[x] : p[x] = find(p, p[x]);
}
signed main() {
cin >> n >> m1 >> m2;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) p1[i] = p2[i] = i;
while (m1 --) {
cin >> u >> v;
u = find(p1, u), v = find(p1, v);
if (u != v) p1[u] = v;
}
while (m2 --) {
cin >> u >> v;
u = find(p2, u), v = find(p2, v);
if (u != v) p2[u] = v;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) cnt1 += p1[i] == i, cnt2 += p2[i] == i;
cout << min(cnt1, cnt2) - 1 << endl;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) {
for (int j = i + 1; j <= n; j ++) {
if (find(p1, i) != find(p1, j) && find(p2, i) != find(p2, j)) {
p1[find(p1, i)] = find(p1, j), p2[find(p2, i)] = find(p2, j);
cout << i << " " << j << endl;
}
}
}
}