本期内容:
?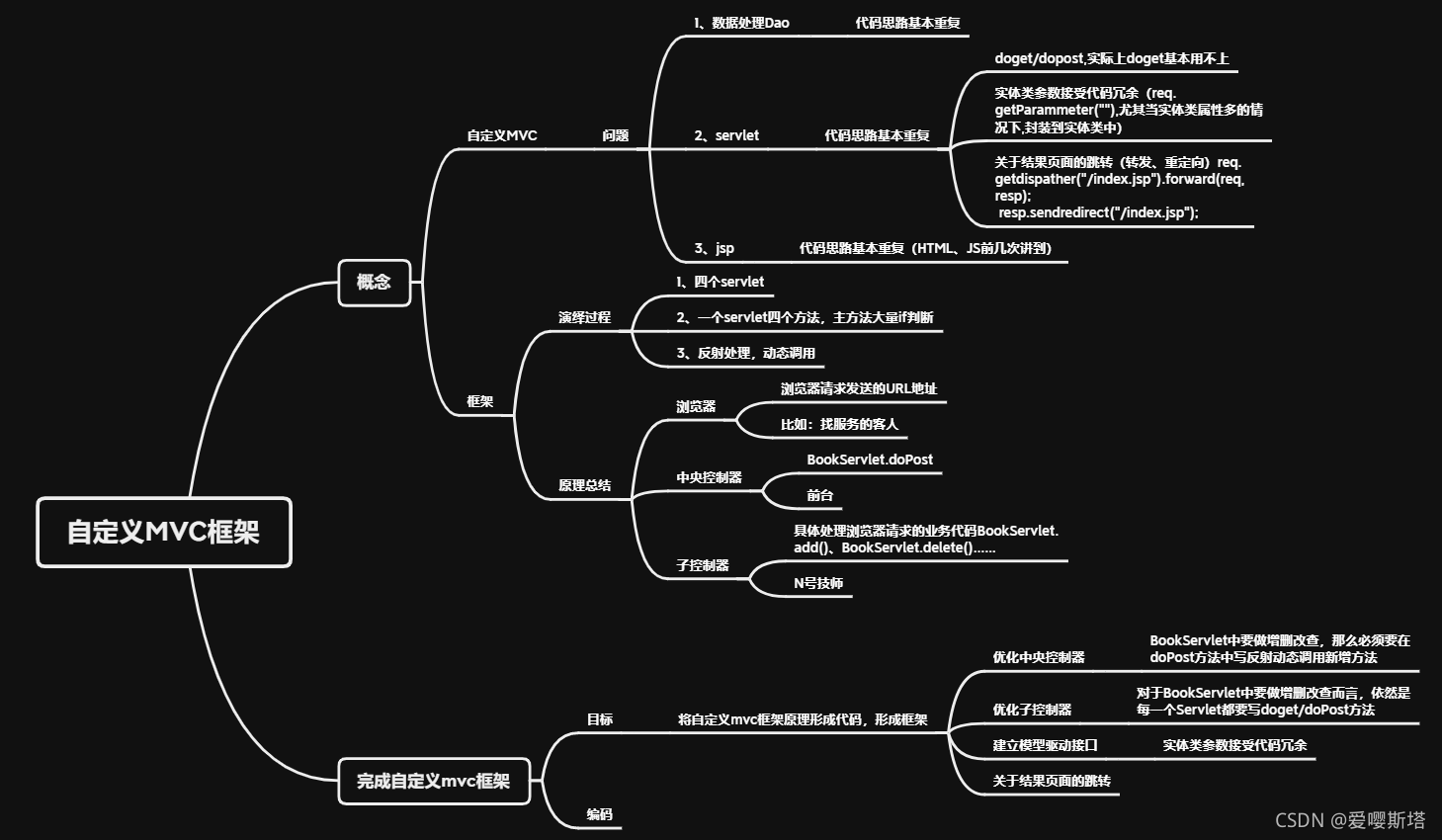
一、概念?
?为什么学习自定义MVC框架?
MVC怎么出现:各司其职
?MVC含义:模型层(model) 视图层(view) 控制层(controller)
? ? ? ? 以前问题:
????????????????1、数据处理Dao?? ??? ?(代码思路基本重复)
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? 2、servlet?? ??? ?(代码思路基本重复)
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ①doget/dopost,实际上doget基本用不上
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?? ②实体类参数接受代码冗余(req.getParammeter(""),尤其当实体类属性多的情况下,封装到实体类中)
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ③关于结果页面的跳转(转发、重定向)
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ????????req.getdispather("/index.jsp").forward(req,resp);
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ????????resp.sendredirect("/index.jsp");
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? 3、jsp?? ?(代码思路基本重复HTML、js)?? ?
<!-- 绝大多数人开发采用这种方式做增删改查(servlet层) -->
?? ?<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath }/book/add">新增</a>
?? ?<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath }/book/delete">删除</a>
?? ?<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath }/book/edit">修改</a>
?? ?<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath }/book/list">查询</a>?
?每个方法还要写一个servlet:

第二种:
优点:相较于前一种,代码量减少,由原来的四个类变成一个类
缺点:每一次新增一个方法,都要改动原有逻辑,是代码过于冗余
?<!-- 少数人开发采用这种方式做增删改查(servlet层) -->
?? ?<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath }/book.action?methodName=add">新增</a>
?? ?<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath }/book.action?methodName=delete">删除</a>
?? ?<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath }/book.action?methodName=edit">修改</a>
?? ?<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath }/book.action?methodName=list">查询</a>
?? ?<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath }/book.action?methodName=load">回显</a>
?只要写一个servlet
package com.lv.servlet;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
@WebServlet("/book.action")
public class BookServlet extends HttpServlet{
?? ?@Override
?? ?protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
?? ??? ?doPost(req, resp);
?? ?}
?? ?
?? ?@Override
?? ??? ?protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {?? ??? ?String methodName = req.getParameter("methodName");
? ? ? ? if("add".equals(methodName)) {
? ? ? ? ? ? add(req,resp);
? ? ? ? }else if("edit".equals(methodName)) {
? ? ? ? ? ? edit(req,resp);
? ? ? ? }else if("delete".equals(methodName)) {
? ? ? ? ? ? delete(req,resp);
? ? ? ? }else if("list".equals(methodName)) {
? ? ? ? ? ? list(req,resp);
? ? ? ? }else if("load".equals(methodName)) {
? ? ? ? ? ? load(req,resp);
? ? ? ? }?? ??? ?}
?? ?private void load(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) {
?? ??? ?System.out.println("bookDao.load()");
?? ?}?? ?private void list(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) {
?? ??? ?System.out.println("bookDao.list()");
?? ?}?? ?private void delete(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) {
?? ??? ?System.out.println("bookDao.delete()");
?? ?}?? ?private void edit(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) {
?? ??? ?System.out.println("bookDao.edit()");
?? ?}?? ?private void add(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) {
?? ??? ?System.out.println("bookDao.add()");
?? ?}
?? ?private void ref(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) {
?? ??? ?System.out.println("bookDao.ref()");
?? ?}}
框架:反射+设计模式(极大的减少了代码量,把重复性的代码交给框架完成,让程序员关注点放在项目业务上)
????????1、通用分页指点+通用的增删改
? ? ? ? 2、各层(主要体现在mc层)数据Dao层、控制层代码缩减
? ? ? ? 3、前台代码的缩减优化
对以上第二种的解决方案:
? ? ? ? ? ? ? 调用哪一个方法,实际上是取决于methodName,加if不是必要条件
? ? ? ? ? ? ? 直白一点,也就是说动态调用methodName方法,并且是当前类实例的methodName方法
<!-- 反射优化 -->
?? ?<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath }/book.action?methodName=add">新增</a>
?? ?<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath }/book.action?methodName=delete">删除</a>
?? ?<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath }/book.action?methodName=edit">修改</a>
?? ?<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath }/book.action?methodName=list">查询</a>
?? ?<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath }/book.action?methodName=load">回显</a>
每一次新增一个方法,不需要改动原有逻辑,只要在最下增加一个方法就好
package com.lv.servlet;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
@WebServlet("/book.action")
public class BookServlet extends HttpServlet{
?? ?@Override
?? ?protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
?? ??? ?doPost(req, resp);
?? ?}
?? ?
?? ?@Override
?? ??? ?protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
?? ??? ?String methodName = req.getParameter("methodName");?? ??? ?try {
?? ??? ??? ?Method m = this.getClass().getDeclaredMethod(methodName, HttpServletRequest.class,HttpServletResponse.class);
?? ??? ??? ?m.setAccessible(true);
?? ??? ??? ?m.invoke(this,req, resp);
?? ??? ??? ?
?? ??? ?} catch (Exception e) {
?? ??? ??? ?// TODO Auto-generated catch block
?? ??? ??? ?e.printStackTrace();
?? ??? ?}?
?? ??? ?}?? ?private void load(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) {
?? ??? ?System.out.println("bookDao.load()");
?? ?}?? ?private void list(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) {
?? ??? ?System.out.println("bookDao.list()");?
?? ?}?? ?private void delete(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) {
?? ??? ?System.out.println("bookDao.delete()");
?? ?}?? ?private void edit(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) {
?? ??? ?System.out.println("bookDao.edit()");
?? ?}?? ?private void add(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) {
?? ??? ?System.out.println("bookDao.add()");
?? ?}
?? ?private void ref(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) {
?? ??? ?System.out.println("bookDao.ref()");
?? ?}}
?
总结:
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? 反射可以修复上面改动代码才能解决需求问题的缺陷
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? 反射这段代码,相当于中央控制器,并不直接处理浏览器请求
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? 处理浏览器请求的是子控制器
二、完成自定义MVC框架
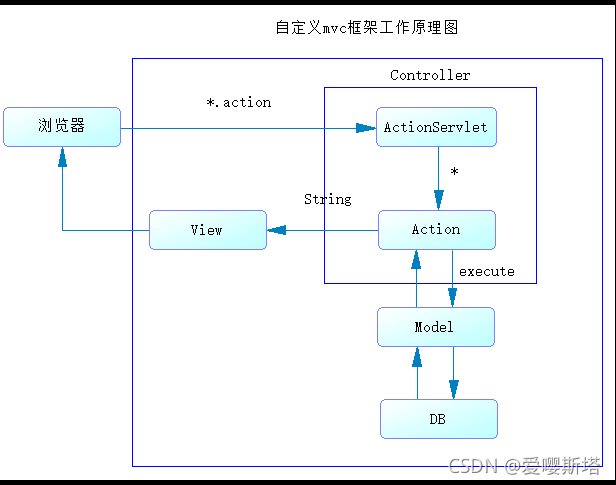
1、自定义MVC框架工作原理:
?2、中央控制器的优化及子控制器的优化
需解决的问题:
1.BookServlet中要做增删改查,那么必须要在doPost方法中写反射动态调用新增方法
? ? ? ?? GoodsServlet要做增删改查,那么必须要在doPost方法中写反射动态调用新增方法
结论:反射动态调用新增方法代码是重复的的,但是这段又是必须的,也就是还需要进一步优化,优化中央控制器
2.对于BookServlet中要做增删改查而言,依然是每一个Servlet都要写doget/doPost方法
? ? ? ? ? 但是实际上对处理业务有用的代码,往往是我们新加的,只需关注业务(add/delete/...)
? ? ? ? ?? 优化子控制器
ActionSupport类中放入放射动态调用方法:
package com.lv.framework;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;public class ActionSupport implements Action{
?? ?@Override
?? ?public String execute(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) {
?? ??? ?String methodName = req.getParameter("methodName");
?? ??? ?String res=null;
?? ??? ?
?? ??? ?try {
?? ??? ??? ?Method m = this.getClass().getDeclaredMethod(methodName, HttpServletRequest.class,HttpServletResponse.class);
?? ??? ??? ?m.setAccessible(true);
?? ??? ??? ?res=(String) m.invoke(this,req, resp);
?? ??? ??? ?
?? ??? ?} catch (Exception e) {
?? ??? ??? ?// TODO Auto-generated catch block
?? ??? ??? ?e.printStackTrace();
?? ??? ?}
?? ??? ?return res;?
?? ?}
}
?
BookAction相当于以前的BookServlet,从父类继承了execute方法,就把反射动态调用方法的代码继承过来了
package com.lv.framework;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;import com.lv.entity.Book;
public class BookAction extends ActionSupport implements ModelDriver<Book>{
?? ?private String add(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) {
?? ??? ?System.out.println("bookDao.add(book)");
?? ??? ?return "list";
?? ?}
?? ?
?? ?private void edit(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) {
?? ??? ?System.out.println("bookDao.edit()");
?? ??? ?
?? ?}
?? ?
?? ?private String toEdit(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) {
?? ??? ?System.out.println("bookDao.toEdit()");
?? ??? ?return "toEdit";
?? ?}
?? ?private void list(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) {
?? ??? ?System.out.println("bookDao.list()");
?? ??? ?
?? ?}?? ?private void load(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) {
?? ??? ?System.out.println("bookDao.load()");
?? ??? ?
?? ?}?? ?@Override
?? ?public Book getModel() {
?? ??? ?// TODO Auto-generated method stub
?? ??? ?return book;
?? ?}}
?
?我们现在还需要之前所讲的建模有关的知识,引用:

?config.xml文件中:
path内为跳转的界面路径,
false代表转发,true则为重定向
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<config>
?? ?<!--?
?? ??? ?在这里每加一个配置,就相当于actions.put("/goods", new GoodsAction());
?? ??? ?这样就解决了代码灵活性的问题
?? ? -->
?? ?<action path="/book" type="com.lv.framework.BookAction">
?? ??? ?<forward name="list" path="/bookList.jsp" redirect="false" />
?? ??? ?<forward name="toEdit" path="/bookEdit.jsp" redirect="true" />
?? ?</action>
</config>
DispatchServlet中央控制器
package com.lv.framework;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;import org.apache.commons.beanutils.BeanUtils;
import com.lv.xml.ActionModel;
import com.lv.xml.ConfigModel;
import com.lv.xml.ConfigModelFactory;
import com.lv.xml.ForwardModel;
//jsp跳转为/book.action/goods.action/order.action……都会跳转到这个类
@WebServlet("*.action")
public class DispatchServlet extends HttpServlet{
//?? ?再当前中央控制器中必然会有所有子控制器的集合
//?? ?缺陷:如果有商品的增删改查-->意味着要改动代码-->代码的设计不够灵活
//?? ?思考:在不改动代码的情况下,中央控制器也能找到对应的子控制器去处理浏览器请求
//?? ?方案:把加子控制器的逻辑/动作,放到配置文件中完成(Dbutil改连接信息是放在代码中完成/现在是放在Properties)
//?? ?放在配置文件中完成的好处在于:代码更加灵活,修改相关信息不用动代码
//?? ?private Map<String, ActionSupport> actions=new HashMap<String, ActionSupport>();
//?? ?ConfigModel对象又通过建模的知识,把所有的的配置信息给读取过来
?? ?private ConfigModel configModel=null;?? ?
//?? ?初始化所有的子控制器到当前的中央控制器中
?? ??? ?public void init() throws ServletException {
//?? ??? ??? ?在集合中就有了一个子控制器
//?? ??? ??? ? actions.put("/book", new BookAction());
//?? ??? ??? ? actions.put("/goods", new GoodsAction());
//?? ??? ??? ? ……
?? ??? ??? ? try {
?? ??? ??? ??? ?configModel=ConfigModelFactory.build();
?? ??? ??? ?} catch (Exception e) {
?? ??? ??? ??? ?// TODO Auto-generated catch block
?? ??? ??? ??? ?e.printStackTrace();
?? ??? ??? ?}
?? ??? ?}
?? ?
?? ?@Override
?? ?protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
?? ??? ?doPost(req, resp);
?? ?}
?? ?
?? ?@Override
?? ??? ?protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
//?? ??? ??? ?将子控制器与浏览器请求关联起来,寻找能够处理请求的子控制器
//?? ??? ?如何找到浏览器这个路径:http://localhost:8080/book.action?methodName=add-->BookAction.add();
?? ??? ?/*
?? ??? ? * 思路
?? ??? ? * 1.url-->/book
?? ??? ? * 2.通过/book字符串在actions找到BookAction
?? ??? ? * 3.调用BookAction的add,想要调用add,实际上只要统一调用execute就可以了
?? ??? ? */
//?? ??? ?获取到浏览器的请求地址
?? ??? ?String url = req.getRequestURI();
//?? ??? ?1.url-->/book
?? ??? ?url=url.substring(url.lastIndexOf("/"), url.lastIndexOf("."));
?? ??? ?
//?? ??? ?2.通过/book字符串在actions找到BookAction
//?? ??? ?ActionSupport actrion = actions.get(url);
//?? ??? ?原来在Map中寻找子控制器——>现在在配置文件中寻找子控制器
?? ??? ?/**
?? ??? ? * 思路:
?? ??? ? * 1.通过/book找到对应的ActionModel对象
?? ??? ? * 2.通过ActionModel对象拿到类的全路径名com.lv.framework.BookAction
?? ??? ? * 3.反射实例化对象
?? ??? ? */
?? ??? ?ActionModel actionModel = configModel.pop(url);
//?? ??? ?拿到类的全路径名
?? ??? ?String type = actionModel.getType();
?? ??? ?ActionSupport action;
?? ??? ?try {
?? ??? ??? ?action = (ActionSupport) Class.forName(type).newInstance();
//?? ??? ??? ?完成实体类参数的封装
?? ??? ??? ?if(action instanceof ModelDriver) {
//?? ??? ??? ??? ?当前子控制器实现了模型驱动接口
?? ??? ??? ??? ?ModelDriver m=(ModelDriver) action;
//?? ??? ??? ??? ?Book/Goods……
?? ??? ??? ??? ?Object bean=m.getModel();
//?? ??? ??? ??? ?所有的请求参数都在这,需要将所有的请求参数封装到Book/Goods……
?? ??? ??? ??? ?BeanUtils.populate(bean, req.getParameterMap());
?? ??? ??? ?}
//?? ??? ??? ?执行业务逻辑 BookAction.add方法的返回值"list"
?? ??? ??? ?/**
?? ??? ??? ? * 1、书籍新增那么跳转书籍展示页面BookList.jsp 转发
?? ??? ??? ? * 2、书籍编辑跳转编辑页面BookEdit.jsp 重定向
?? ??? ??? ? */
?? ??? ??? ?String res=action.execute(req, resp);
?? ??? ??? ?ForwardModel forwardModel=actionModel.pop(res);
?? ??? ??? ?String path=forwardModel.getPath();
?? ??? ??? ?boolean isredirect = forwardModel.isRedirect();
?? ??? ??? ?if(isredirect) {
?? ??? ??? ??? ?resp.sendRedirect(req.getContextPath()+path);
?? ??? ??? ?}else {
?? ??? ??? ??? ?req.getRequestDispatcher(path).forward(req, resp);
?? ??? ??? ?}
?? ??? ??? ?
?? ??? ?} catch (Exception e) {
?? ??? ??? ?// TODO Auto-generated catch block
?? ??? ??? ?e.printStackTrace();
?? ??? ?}
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? }}
?
3、建立模型驱动接口
解决的问题:
实体类参数接受代码冗余(req.getParammeter(“”),尤其当实体类属性多的情况,封装到实体类中
如:
book.setBid(req.getParameter("bid"));
book.setBname(req.getParameter("bname"));
book.setPrice(req.getParameter("price"));
book.setAthor(req.getParameter("athor"));
book.setPublish(req.getParameter("publish"));
ModelDriver模型驱动接口:
package com.lv.framework;
/**
?* 模型驱动接口
?* 作用:帮助“中央控制器”完成参数封装的工程
?*/
public interface ModelDriver<T> {
?? ?/**
?? ? * GoodsAction-->goods
?? ? * BookAction-->book
?? ? * ...
?? ? * @return
?? ? */
?? ?T getModel();
}
?
在中央控制器的操作:
//?? ?ConfigModel对象又通过建模的知识,把所有的的配置信息给读取过来
?? ?private ConfigModel configModel=null;?? ?
//?? ?初始化所有的子控制器到当前的中央控制器中
?? ??? ?public void init() throws ServletException {
//?? ??? ??? ?在集合中就有了一个子控制器
//?? ??? ??? ? actions.put("/book", new BookAction());
//?? ??? ??? ? actions.put("/goods", new GoodsAction());
//?? ??? ??? ? ……
?? ??? ??? ? try {
?? ??? ??? ??? ?configModel=ConfigModelFactory.build();
?? ??? ??? ?} catch (Exception e) {
?? ??? ??? ??? ?// TODO Auto-generated catch block
?? ??? ??? ??? ?e.printStackTrace();
?? ??? ??? ?}
?? ??? ?}
?中央控制器内中doPast:
//?? ??? ?2.通过/book字符串在actions找到BookAction
//?? ??? ?ActionSupport actrion = actions.get(url);
//?? ??? ?原来在Map中寻找子控制器——>现在在配置文件中寻找子控制器
?? ??? ?/**
?? ??? ? * 思路:
?? ??? ? * 1.通过/book找到对应的ActionModel对象
?? ??? ? * 2.通过ActionModel对象拿到类的全路径名com.lv.framework.BookAction
?? ??? ? * 3.反射实例化对象
?? ??? ? */
?? ??? ?ActionModel actionModel = configModel.pop(url);
//?? ??? ?拿到类的全路径名
?? ??? ?String type = actionModel.getType();
?? ??? ?ActionSupport action;
?? ??? ?try {
?? ??? ??? ?action = (ActionSupport) Class.forName(type).newInstance();
//?? ??? ??? ?完成实体类参数的封装
?? ??? ??? ?if(action instanceof ModelDriver) {
//?? ??? ??? ??? ?当前子控制器实现了模型驱动接口
?? ??? ??? ??? ?ModelDriver m=(ModelDriver) action;
//?? ??? ??? ??? ?Book/Goods……
?? ??? ??? ??? ?Object bean=m.getModel();
//?? ??? ??? ??? ?所有的请求参数都在这,需要将所有的请求参数封装到Book/Goods……
?? ??? ??? ??? ?BeanUtils.populate(bean, req.getParameterMap());
?? ??? ??? ?}
BookAction中实现ModelDriver<Book>:
package com.lv.framework;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;import com.lv.entity.Book;
public class BookAction extends ActionSupport implements ModelDriver<Book>{
//?? ?当前子控制器在哪里调用?把子控制器与浏览器请求关联起来
?? ?public Book book=new Book();
?? ?private String add(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) {
?? ??? ?System.out.println(book);
?? ??? ?System.out.println("bookDao.add(book)");
?? ??? ?return "list";
?? ?}
?? ??? ?@Override
?? ?public Book getModel() {
?? ??? ?// TODO Auto-generated method stub
?? ??? ?return book;
?? ?}}
?
界面:?

输出结果:
![]()
?4、页面的跳转
子控制器:?处理浏览器请求,针对于add/ref/other进行向上抽取、抽象
package com.lv.framework;
import java.io.IOException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;/**
?* 子控制器
?* 针对于add/ref/other进行向上抽取、抽象
?*/
@WebServlet("/Action")
public interface Action{
?? ?/*private void add(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) {
?? ??? ?System.out.println("bookDao.edit()");
?? ??? ?
?? ?}*/
//?? ?这个方法就是add/ref/other进行向上抽取的抽象方法
//?? ?作用:能够处理浏览器的“所有”请求,包括add/ref/other
//?? ?通过返回值来决定跳转哪一个页面,至于重定向还是转发,由中央控制器决定
?? ?public String execute(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp);
?? ?
}
?
?中央控制器决定:
/**
?? ??? ??? ? * 1、书籍新增那么跳转书籍展示页面BookList.jsp 转发
?? ??? ??? ? * 2、书籍编辑跳转编辑页面BookEdit.jsp 重定向
?? ??? ??? ? */
?? ??? ??? ?String res=action.execute(req, resp);
?? ??? ??? ?ForwardModel forwardModel=actionModel.pop(res);
?? ??? ??? ?String path=forwardModel.getPath();
?? ??? ??? ?boolean isredirect = forwardModel.isRedirect();// ? ? ? ? isredirect指是重定向
?? ??? ??? ?if(isredirect) {
?? ??? ??? ??? ?resp.sendRedirect(req.getContextPath()+path);
?? ??? ??? ?}else {
?? ??? ??? ??? ?req.getRequestDispatcher(path).forward(req, resp);
?? ??? ??? ?}
?? ??? ??? ?
?? ??? ?} catch (Exception e) {
?? ??? ??? ?// TODO Auto-generated catch block
?? ??? ??? ?e.printStackTrace();
?? ??? ?}
内容结束~~~