👨?🌾 写在前面
上篇文章我们已经了解了前端单元测试的背景和基础的jestapi,本篇文章我会先介绍一下Enzyme,然后结合项目中的一个真实组件,来为它编写测试用例。
👨?🚀 Enzyme
上一篇中我们其实已经简单介绍了enzyme,但这远远不够,在本篇的组件测试用例编写中,我们有很多地方要用到它,因此这里专门来说明一下。
Enzyme是由Airbnb开源的一个React的JavaScript测试工具,使React组件的输出更加容易。Enzyme的API和jQuery操作DOM一样灵活易用,因为它使用的是cheerio库来解析虚拟DOM,而cheerio的目标则是做服务器端的jQuery。Enzyme兼容大多数断言库和测试框架,如chai、mocha、jasmine等。
🙋 关于安装和配置,上一小节已经有过说明,这里就不赘述了
常用函数
enzyme中有几个比较核心的函数,如下:
simulate(event, mock):用来模拟事件触发,event为事件名称,mock为一个event object;instance():返回测试组件的实例;find(selector):根据选择器查找节点,selector可以是CSS中的选择器,也可以是组件的构造函数,以及组件的display name等;at(index):返回一个渲染过的对象;text():返回当前组件的文本内容;html(): 返回当前组件的HTML代码形式;props():返回根组件的所有属性;prop(key):返回根组件的指定属性;state():返回根组件的状态;setState(nextState):设置根组件的状态;setProps(nextProps):设置根组件的属性;
渲染方式
enzyme 支持三种方式的渲染:
shallow:浅渲染,是对官方的Shallow Renderer的封装。将组件渲染成虚拟DOM对象,只会渲染第一层,子组件将不会被渲染出来,因而效率非常高。不需要 DOM 环境, 并可以使用jQuery的方式访问组件的信息;render:静态渲染,它将React组件渲染成静态的HTML字符串,然后使用Cheerio这个库解析这段字符串,并返回一个Cheerio的实例对象,可以用来分析组件的html结构;mount:完全渲染,它将组件渲染加载成一个真实的DOM节点,用来测试DOM API的交互和组件的生命周期,用到了jsdom来模拟浏览器环境。
三种方法中,shallow和mount因为返回的是DOM对象,可以用simulate进行交互模拟,而render方法不可以。一般shallow方法就可以满足需求,如果需要对子组件进行判断,需要使用render,如果需要测试组件的生命周期,需要使用mount方法。
渲染方式部分参考的这篇文章
🐶 “踩坑之路”开启
组件代码
首先,来看下我们需要对其进行测试的组件部分的代码:
?? 因为牵扯到内部代码,所以很多地方都打码了。重在演示针对不同类型的测试用例的编写
import { SearchOutlined } from "@ant-design/icons"
import {
Button,
Col,
DatePicker,
Input,
message,
Modal,
Row,
Select,
Table,
} from "antd"
import { connect } from "dva"
import { Link, routerRedux } from "dva/router"
import moment from "moment"
import PropTypes from "prop-types"
import React from "react"
const { Option } = Select
const { RangePicker } = DatePicker
const { confirm } = Modal
export class MarketRuleManage extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props)
this.state = {
productID: "",
}
}
componentDidMount() {
// console.log("componentDidMount生命周期")
}
getTableColumns = (columns) => {
return [
...columns,
{
key: "operation",
title: "操作",
dataIndex: "operation",
render: (_text, record, _index) => {
return (
<React.Fragment>
<Button
type="primary"
size="small"
style={{ marginRight: "5px" }}
onClick={() => this.handleRuleEdit(record)}
>
编辑
</Button>
<Button
type="danger"
size="small"
onClick={() => this.handleRuleDel(record)}
>
删除
</Button>
</React.Fragment>
)
},
},
]
}
handleSearch = () => {
console.log("点击查询")
const { pagination } = this.props
pagination.current = 1
this.handleTableChange(pagination)
}
render() {
// console.log("props11111", this.props)
const { pagination, productList, columns, match } = this.props
const { selectedRowKeys } = this.state
const rowSelection = {
selectedRowKeys,
onChange: this.onSelectChange,
}
const hasSelected = selectedRowKeys.length > 0
return (
<div className="content-box marketRule-container">
<h2>XX录入系统</h2>
<Row>
<Col className="tool-bar">
<div className="filter-span">
<label>产品ID</label>
<Input
data-test="marketingRuleID"
style={{ width: 120, marginRight: "20px", marginLeft: "10px" }}
placeholder="请输入产品ID"
maxLength={25}
onChange={this.handlemarketingRuleIDChange}
></Input>
<Button
type="primary"
icon={<SearchOutlined />}
style={{ marginRight: "15px" }}
onClick={() => this.handleSearch()}
data-test="handleSearch"
>
查询
</Button>
</div>
</Col>
</Row>
<Row>
<Col>
<Table
tableLayout="fixed"
bordered="true"
rowKey={(record) => `${record.ruleid}`}
style={{ marginTop: "20px" }}
pagination={{
...pagination,
}}
columns={this.getTableColumns(columns)}
dataSource={productList}
rowSelection={rowSelection}
onChange={this.handleTableChange}
></Table>
</Col>
</Row>
</div>
)
}
MarketRuleManage.prototypes = {
columns: PropTypes.array,
}
MarketRuleManage.defaultProps = {
columns: [
{
key: "xxx",
title: "产品ID",
dataIndex: "xxx",
width: "10%",
align: "center",
},
{
key: "xxx",
title: "产品名称",
dataIndex: "xxx",
align: "center",
},
{
key: "xxx",
title: "库存",
dataIndex: "xxx",
align: "center",
// width: "12%"
},
{
key: "xxx",
title: "活动有效期开始",
dataIndex: "xxx",
// width: "20%",
align: "center",
render: (text) => {
return text ? moment(text).format("YYYY-MM-DD HH:mm:ss") : null
},
},
{
key: "xxx",
title: "活动有效期结束",
dataIndex: "xxx",
// width: "20%",
align: "center",
render: (text) => {
return text ? moment(text).format("YYYY-MM-DD HH:mm:ss") : null
},
},
],
}
const mapStateToProps = ({ marketRuleManage }) => ({
pagination: marketRuleManage.pagination,
productList: marketRuleManage.productList,
productDetail: marketRuleManage.productDetail,
})
const mapDispatchToProps = (dispatch) => ({
queryMarketRules: (data) =>
dispatch({ type: "marketRuleManage/queryRules", payload: data }),
editMarketRule: (data) =>
dispatch({ type: "marketRuleManage/editMarketRule", payload: data }),
delMarketRule: (data, cb) =>
dispatch({ type: "marketRuleManage/delMarketRule", payload: data, cb }),
deleteByRuleId: (data, cb) =>
dispatch({ type: "marketRuleManage/deleteByRuleId", payload: data, cb }),
})
export default connect(mapStateToProps, mapDispatchToProps)(MarketRuleManage)
简单介绍一下组件的功能:这是一个被connect包裹的高阶组件,页面展示如下:

我们要添加的测试用例如下:
1、页面能够正常渲染
2、DOM测试:标题应该为XX录入系统
3、组件生命周期可以被正常调用
4、组件内方法handleSearch(即“查询”按钮上绑定的事件)可以被正常调用
5、产品 ID 输入框内容更改后,state中productID值会随之变化
6、MarketRuleManage组件应该接受指定的props参数
测试页面快照
明确了需求,让我们开始编写第一版的测试用例代码:
import React from "react"
import { mount, shallow } from "enzyme"
import MarketRuleManage from "../../../src/routes/marketRule-manage"
describe("XX录入系统页面", () => {
// 使用 snapshot 进行 UI 测试
it("页面应能正常渲染", () => {
const wrapper = shallow(<MarketRuleManage />)
expect(wrapper).toMatchSnapshot()
})
})
执行npm run test:
npm run test对应的脚本是jest --verbose
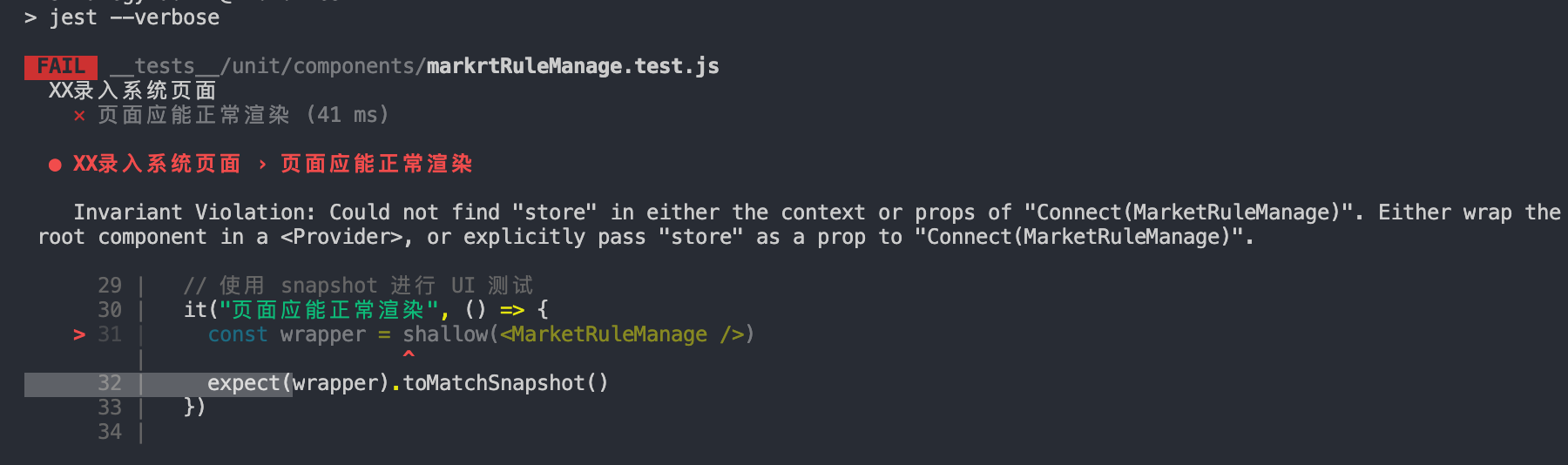
报错了:
Either wrap the root component in a <Provider>, or explicitly pass "store" as a prop to "Connect(MarketRuleManage)".意思就是我们需要给connect包裹的组件传递一个store。
经过一番搜索,我在stackoverflow找到了答案,需要使用redux-mock-store中的configureMockStore来模拟一个假的store。来调整一下测试代码:
import React from "react"
?import { Provider } from "react-redux"
?import configureMockStore from "redux-mock-store"
import { mount, shallow } from "enzyme"
import MarketRuleManage from "../../../src/routes/marketRule-manage"
?const mockStore = configureMockStore()
?const store = mockStore({
? marketRuleManage: {
? pagination: {},
? productList: [],
? productDetail: {},
? },
?})
?const props = {
? match: {
? url: "/",
? },
?}
describe("XX录入系统页面", () => {
// 使用 snapshot 进行 UI 测试
it("页面应能正常渲染", () => {
? const wrapper = shallow(<Provider store={store}>
? <MarketRuleManage {...props} />
? </Provider>)
expect(wrapper).toMatchSnapshot()
})
})
再次运行npm run test:
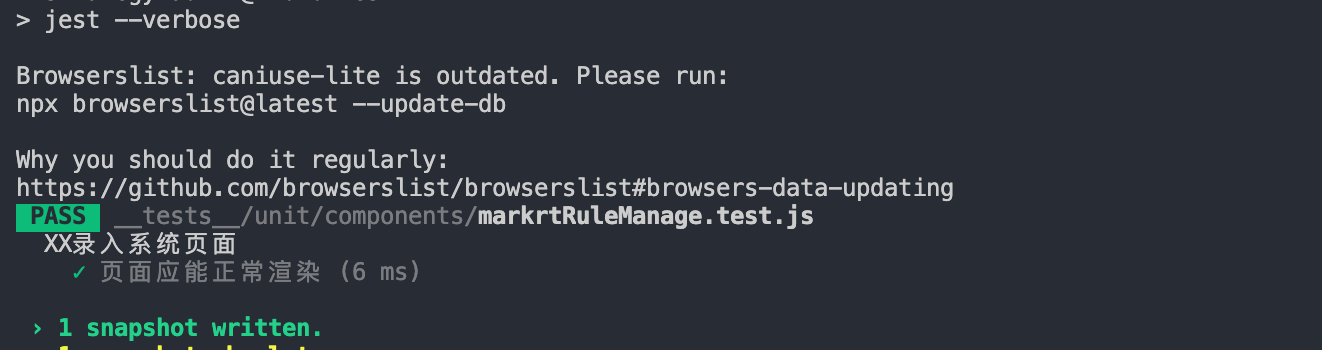
ok,第一条测试用例通过了,并且生成了快照目录__snapshots__。
测试页面DOM
我们接着往下,来看第二条测试用例:DOM测试:标题应该为XX录入系统。
修改测试代码:
import React from "react"
import { Provider } from "react-redux"
import configureMockStore from "redux-mock-store"
import { mount, shallow } from "enzyme"
import MarketRuleManage from "../../../src/routes/marketRule-manage"
const mockStore = configureMockStore()
const store = mockStore({
marketRuleManage: {
pagination: {},
productList: [],
productDetail: {},
},
})
const props = {
match: {
url: "/",
},
}
describe("XX录入系统页面", () => {
// 使用 snapshot 进行 UI 测试
it("页面应能正常渲染", () => {
const wrapper = shallow(<Provider store={store}>
<MarketRuleManage {...props} />
</Provider>)
expect(wrapper).toMatchSnapshot()
})
// 对组件节点进行测试
it("标题应为'XX录入系统'", () => {
const wrapper = shallow(<Provider store={store}>
<MarketRuleManage {...props} />
</Provider>)
expect(wrapper.find("h2").text()).toBe("XX录入系统")
})
})
运行npm run test:
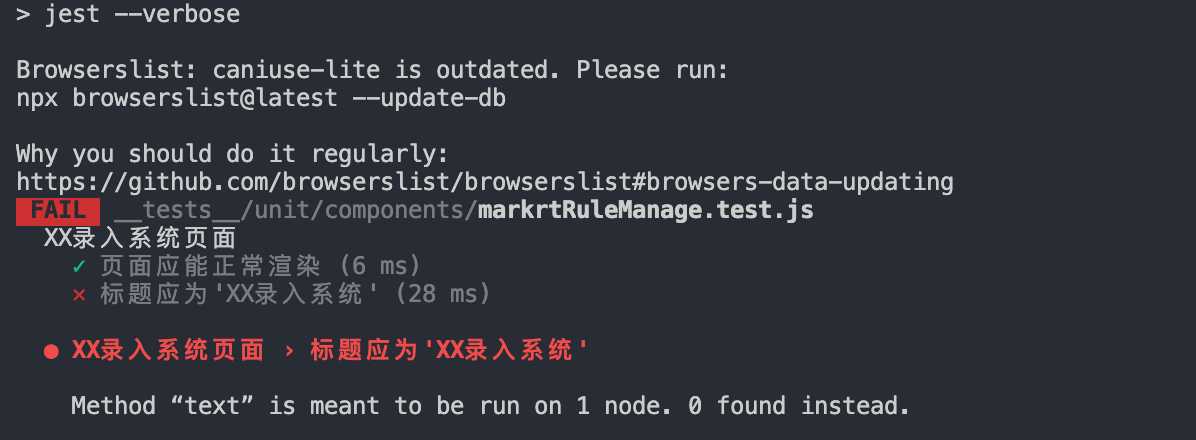
纳尼?Method “text” is meant to be run on 1 node. 0 found instead.找不到h2标签?
我们在开篇介绍enzyme时,知道它有三种渲染方式,那这里我们改为mount试试。再次运行npm run test:
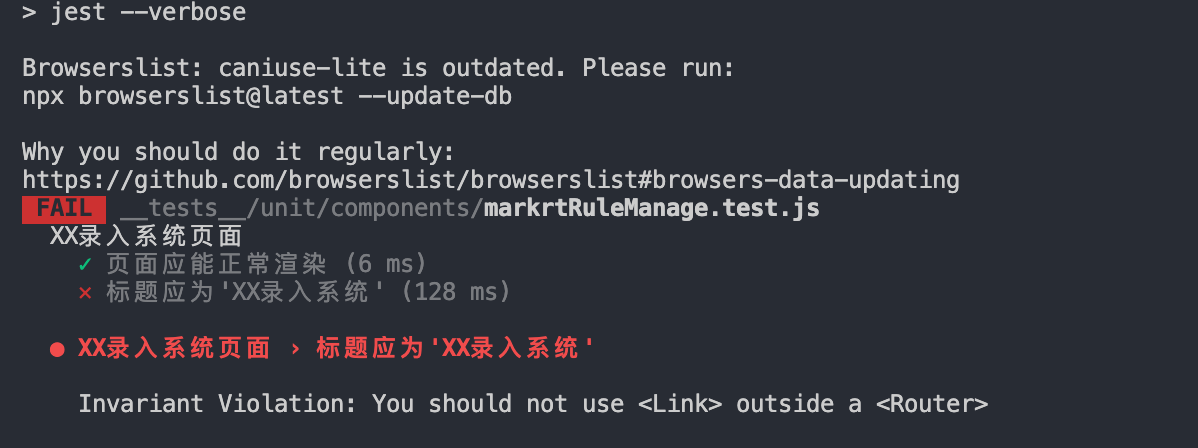
漂亮,又出来一个新的错误:Invariant Violation: You should not use <Link> outside a <Router>
一顿搜索,再次在stackoverflow找到了答案(不得不说 stackoverflow 真香),因为我的项目中用到了路由,而这里是需要包装一下的:
import { BrowserRouter } from 'react-router-dom';
import Enzyme, { shallow, mount } from 'enzyme';
import { shape } from 'prop-types';
// Instantiate router context
const router = {
history: new BrowserRouter().history,
route: {
location: {},
match: {},
},
};
const createContext = () => ({
context: { router },
childContextTypes: { router: shape({}) },
});
export function mountWrap(node) {
return mount(node, createContext());
}
export function shallowWrap(node) {
return shallow(node, createContext());
}
这里我把这部分代码提取到了一个单独的routerWrapper.js文件中。
然后我们修改下测试代码:
import React from "react"
import { Provider } from "react-redux"
import configureMockStore from "redux-mock-store"
import { mount, shallow } from "enzyme"
import MarketRuleManage from "../../../src/routes/marketRule-manage"
?import {
? mountWrap,
? shallowWithIntlWrap,
? shallowWrap,
?} from "../../utils/routerWrapper"
const mockStore = configureMockStore()
const store = mockStore({
marketRuleManage: {
pagination: {},
productList: [],
productDetail: {},
},
})
const props = {
match: {
url: "/",
},
}
?const wrappedShallow = () =>
shallowWrap(
<Provider store={store}>
<MarketRuleManage {...props} />
</Provider>
)
?const wrappedMount = () =>
mountWrap(
<Provider store={store}>
<MarketRuleManage {...props} />
</Provider>
)
describe("XX录入系统页面", () => {
// 使用 snapshot 进行 UI 测试
it("页面应能正常渲染", () => {
🔧 const wrapper = wrappedShallow()
expect(wrapper).toMatchSnapshot()
})
// 对组件节点进行测试
it("标题应为'XX录入系统'", () => {
🔧 const wrapper = wrappedMount()
expect(wrapper.find("h2").text()).toBe("XX录入系统")
})
})
?? 注意代码中的图标,? 代表新增代码,🔧 代表代码有修改
运行npm run test:
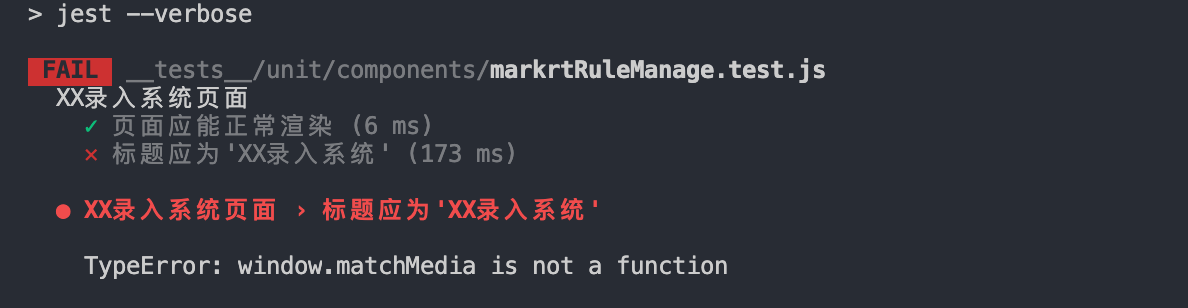
报错TypeError: window.matchMedia is not a function,这又是啥错误啊!!
查阅相关资料,matchMedia是挂载在window上的一个对象,表示指定的媒体查询字符串解析后的结果。它可以监听事件。通过监听,在查询结果发生变化时,就调用指定的回调函数。
显然jest单元测试需要对matchMedia对象做一下mock。经过搜索,在stackoverflow这里找到了答案:
Object.defineProperty(window, 'matchMedia', {
writable: true,
value: jest.fn().mockImplementation(query => ({
matches: false,
media: query,
onchange: null,
addListener: jest.fn(), // Deprecated
removeListener: jest.fn(), // Deprecated
addEventListener: jest.fn(),
removeEventListener: jest.fn(),
dispatchEvent: jest.fn(),
})),
});
把上述代码写到一个单独的matchMedia.js文件中,然后在上面的routerWrapper.js文件中引入:
import { mount, shallow } from "enzyme"
import { mountWithIntl, shallowWithIntl } from "enzyme-react-intl"
import { shape } from "prop-types"
import { BrowserRouter } from "react-router-dom"
?import "./matchMedia"
// Instantiate router context
const router = {
history: new BrowserRouter().history,
route: {
location: {},
match: {},
},
}
const createContext = () => ({
context: { router },
childContextTypes: { router: shape({}) },
})
// ...
此时重新运行npm run test:

ok,第二条测试用例也顺利通过了~
测试生命周期
来看第三条测试 case:组件生命周期可以被正常调用
使用spyOn来mock组件的componentDidMount。添加测试代码:
// 测试组件生命周期
it("组件生命周期", () => {
const componentDidMountSpy = jest.spyOn(
MarketRuleManage.prototype,
"componentDidMount"
)
const wrapper = wrappedMount()
expect(componentDidMountSpy).toHaveBeenCalled()
componentDidMountSpy.mockRestore()
})
运行npm run test:
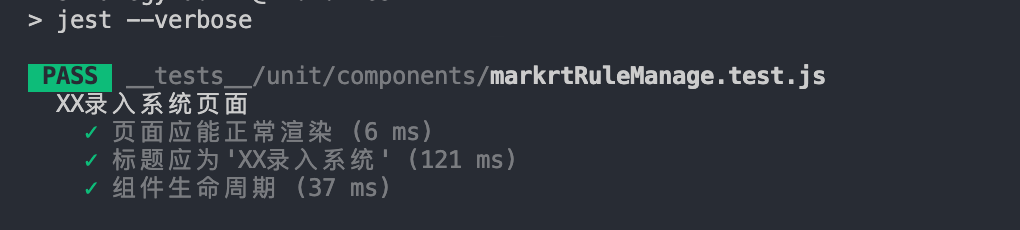
用例顺利通过~
记得要在用例最后对
mock的函数进行mockRestore()
测试组件的内部函数
接着来看第四条测试 case:组件内方法handleSearch(即“查询”按钮上绑定的事件)可以被正常调用。
添加测试代码:
// 测试组件的内部函数
it("组件内方法handleSearch可以被正常调用", () => {
const wrapper = wrappedMount()
const instance = wrapper.instance()
const spyFunction = jest.spyOn(instance, "handleSearch")
instance.handleSearch()
expect(spyFunction).toHaveBeenCalled() // handleSearch被调用了一次
spyFunction.mockRestore()
})
执行npm run test:

报错了:Cannot spy the handleSearch property because it is not a function; undefined given instead!
没办法,只能搜一下,寻求答案,首先在stackoverflow得到了如下方案:

大致意思就是要用shallowWithIntl()来包裹一下组件,然后被包裹的组件需要用dive()一下。
我立即修改了代码,再次运行npm run test,结果依然是一样的。
没办法,接着搜索,在enzyme 的#365issue看到了似乎很接近的答案:

就是在jest.spyOn()之后对组件进行强制更新:wrapper.instance().forceUpdate()和wrapper.update()。
接着修改代码、调试,依然无效。
我,郁闷了。。。
中间也找了很多方案,但都没用。
这时正好在内部文档上看到了一个其他 BU 大佬写的单元测试总结,于是就厚着脸皮去找大佬聊了聊,果不其然,这招很凑效,一语点醒梦中人:你的组件被connect包裹,是一个高阶组件,需要拿instance之前做下find操作,这样才能拿到真实组件的实例。
感谢完大佬,我立即去实践:
// 测试组件的内部函数
it("组件内方法handleSearch可以被正常调用", () => {
const wrapper = wrappedMount()
const instance = wrapper.find("MarketRuleManage").instance()
const spyFunction = jest.spyOn(instance, "handleSearch")
instance.handleSearch()
expect(spyFunction).toHaveBeenCalled() // handleSearch被调用了一次
spyFunction.mockRestore()
})
迫不及待的npm run test:
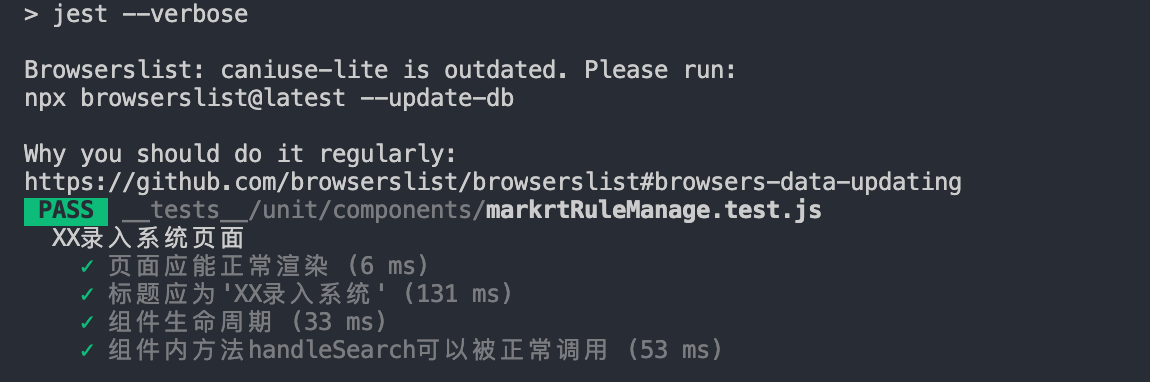
嗯,测试用例顺利通过,真香!
写完这个用例,我不禁反思:小伙子,基础还是不太行啊
还是要多写多实践才行啊!
测试组件 state
废话少说,我们来看第五条测试用例:产品 ID 输入框内容更改后,state中productID值会随之变化
添加测试代码:
// 测试组件state
it("产品ID输入框内容更改后,state中productID会随之变化", () => {
const wrapper = wrappedMount()
const inputElm = wrapper.find("[data-test='marketingRuleID']").first()
const userInput = 1111
inputElm.simulate("change", {
target: { value: userInput },
})
// console.log(
// "wrapper",
// wrapper.find("MarketRuleManage").instance().state.productID
// )
const updateProductID = wrapper.find("MarketRuleManage").instance().state
.productID
expect(updateProductID).toEqual(userInput)
})
这里其实是模拟用户的输入行为,然后使用simulate监听输入框的change事件,最终判断input的改变是否能同步到state中。
这个用例其实是有点
BDD的意思了
我们运行npm run test:
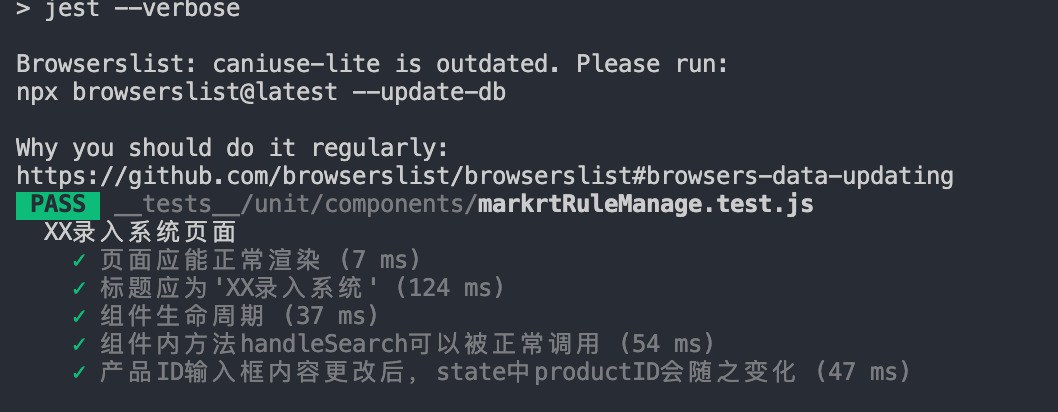
用例顺利通过~
测试组件 props
终于来到了最后一个测试用例:MarketRuleManage组件应该接受指定的props参数
添加测试代码:
// 测试组件props
it("MarketRuleManage组件应该接收指定的props", () => {
const wrapper = wrappedMount()
// console.log("wrapper", wrapper.find("MarketRuleManage").instance())
const instance = wrapper.find("MarketRuleManage").instance()
expect(instance.props.match).toBeTruthy()
expect(instance.props.pagination).toBeTruthy()
expect(instance.props.productList).toBeTruthy()
expect(instance.props.productDetail).toBeTruthy()
expect(instance.props.queryMarketRules).toBeTruthy()
expect(instance.props.editMarketRule).toBeTruthy()
expect(instance.props.delMarketRule).toBeTruthy()
expect(instance.props.deleteByRuleId).toBeTruthy()
expect(instance.props.columns).toBeTruthy()
})
执行npm run test:
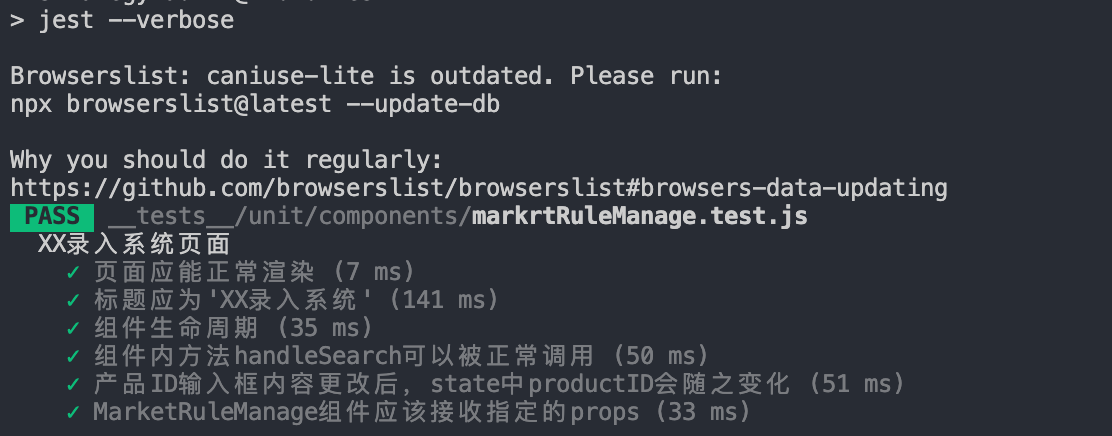
到这里,我们所有的测试用例就执行完了~
我们执行的这 6 条用例基本可以比较全面的涵盖React的组件单元测试了,当然因为我们这里用的是dva,那么难免也要对model进行测试,这里我放一下一个大佬的dva-example-user-dashboard 单元测试,里面已经列举的比较详细了,我就不班门弄斧了。