效果
![]()
一:题目描述
?二:思路
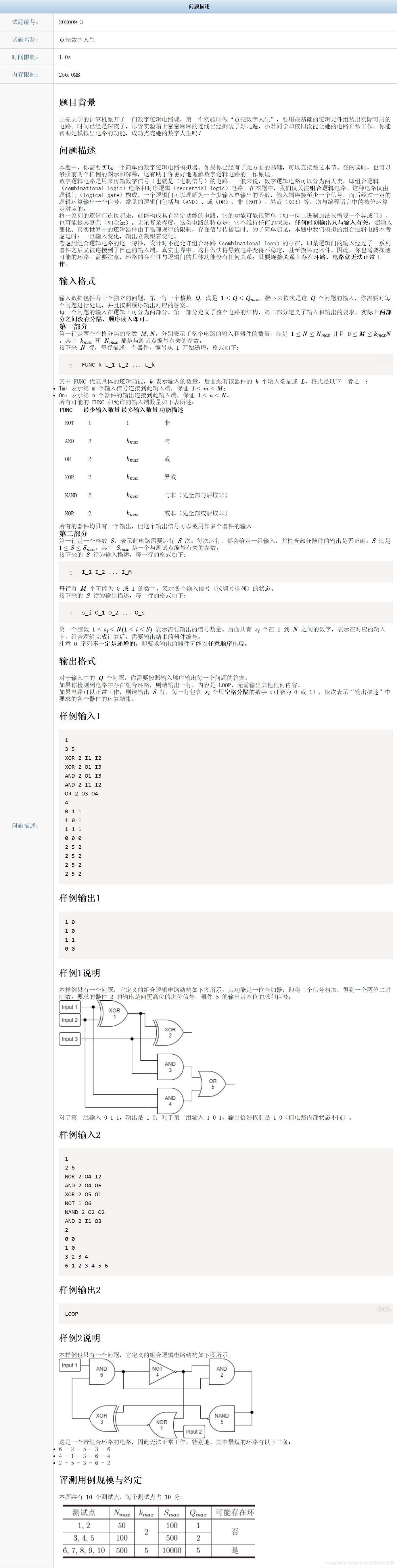
1.????????每个逻辑门抽象成一个类,如下:
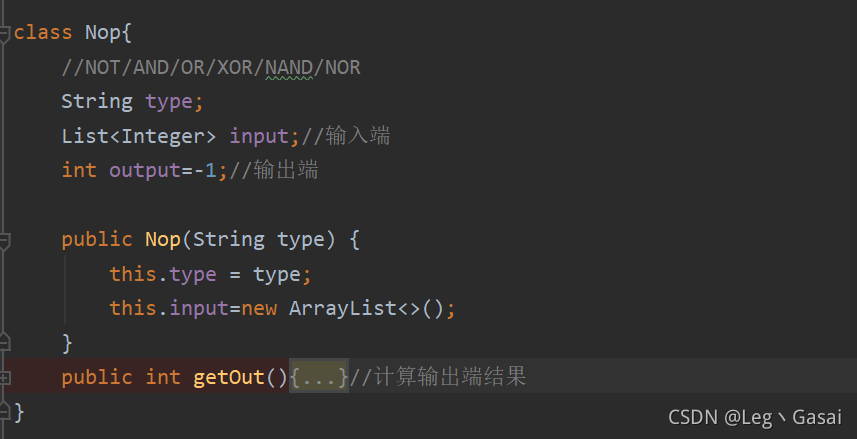
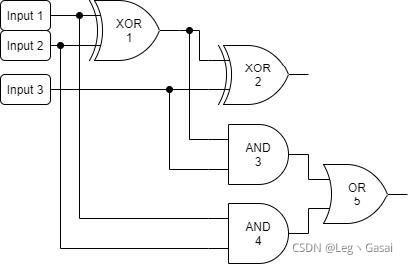
2.????????题目本质可以抽象成图,考虑怎么简化图首先逻辑门可以抽象成节点,用编号1-n表示,建图的时候可以先不考虑逻辑门功能(先存到一个数组中即可)。在拓扑排序时,再考虑逻辑门功能实现。于是,一个电路图就简单的简化成了一张有向图。如下图所示
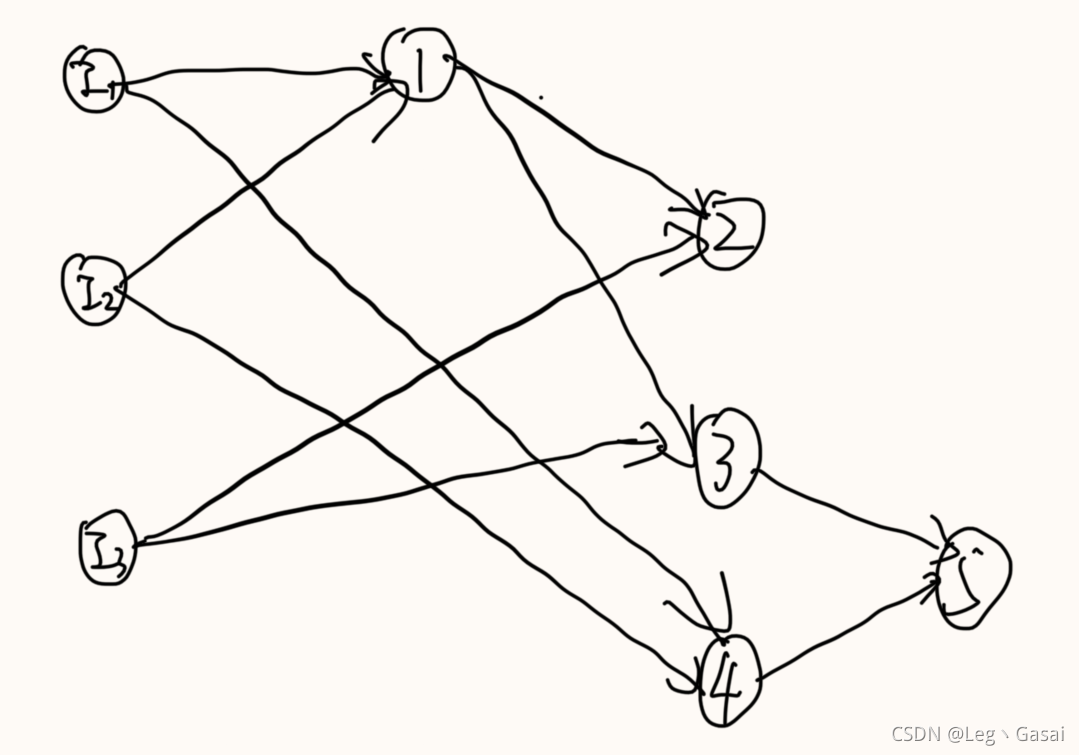
3.????????判环过程可以在简化的图中进行。可以用spfa或者拓扑排序判环
4.????????由于逻辑门的信号传输是有顺序的,可用拓扑排序来确定每个逻辑门的输出。
拓扑排序时,先将入度为0的点入队。
队列非空时,依次弹出节点,弹出的节点记为x,遍历x的每条出边,边的另一节点记为y。
弹出节点的输出信号一定是确定的,因为其每个输入信号(入边)都确定了。将x输出的信号传递给y,保存在y的input数组中。
y节点入度减1,当入度为0,进入队列。循环上述步骤,直到队列为空。y
5.????????执行一遍拓扑排序后,所有逻辑门的输出信号output都可以确定。
完整代码如下:
import java.io.BufferedInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.StreamTokenizer;
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
static StreamTokenizer st=new StreamTokenizer(new BufferedInputStream(System.in));
static int nextInt() throws IOException{
st.nextToken();
return (int)st.nval;
}
static String next() throws IOException{
st.nextToken();
return st.sval;
}
static int Q;//问题个数
static int m;//信号输入个数
static int n;//器件个数
static Nop nops[]=new Nop[550];
static int head[]=new int[550];
static int ne[]=new int[50000];
static int to[]=new int[50000];
static int cnt=1;
static int du[]=new int[550];
static void init(){//初始化
Arrays.fill(head,0);
Arrays.fill(nops,null);
Arrays.fill(ne,0);
Arrays.fill(to,0);
Arrays.fill(du,0);
cnt=1;
}
static void add(int u,int v){
to[cnt]=v;
ne[cnt]=head[u];
head[u]=cnt++;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
Q=nextInt();
for (int i = 0; i < Q; i++) {
init();
m=nextInt();
n=nextInt();
for (int i1 = 1; i1 <=n; i1++) {
String type=next();
int inputsNum=nextInt();
for (int j = 0; j < inputsNum; j++) {
String in=next();
char t=in.charAt(0);
int u=Integer.valueOf(in.substring(1));
du[i1]++;
//起始输入点
if(t=='I'){
add(u+n,i1);
}
//其他器件
else{
add(u,i1);
}
}
Nop nop = new Nop(type);
nops[i1]=nop;
}
for (int k = 1; k <=m; k++) {
nops[k+n]=new Nop("SUPER");
}
int s=nextInt();
List<List<Integer>> inputs = new ArrayList<>();
List<List<Integer>> ques = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i1 = 0; i1 < s; i1++) {
List<Integer> sign = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i2 = 0; i2 < m; i2++) {
sign.add(nextInt());
}
inputs.add(sign);
}
for (int p = 0; p < s; p++) {
int num=nextInt();
List<Integer> q = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i1 = 0; i1 < num; i1++) {
q.add(nextInt());
}
ques.add(q);
}
if(isLoop()==false){
System.out.println("LOOP");
continue;
}
for (int i1 = 0; i1 < s; i1++) {
query(inputs.get(i1),ques.get(i1));
}
}
}
static void query(List<Integer> input,List<Integer> ques){
for (int i = 1; i <=n; i++) {//清空所有信号
nops[i].input=new ArrayList<>();
}
for (int i = 1; i <= input.size(); i++) {
nops[i+n].output=input.get(i-1);
}
topo();
ArrayList<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
for (Integer que : ques) {
res.add(nops[que].getOut());
}
for (int i = 0; i < res.size(); i++) {
System.out.printf(res.get(i)+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
static boolean isLoop(){
int visnum=0;
int rudu[];
rudu=du.clone();
Queue<Integer> q=new LinkedList<>();
for (int i = 1; i <=m+n; i++) {
if(rudu[i]==0)
q.offer(i);
}
while (!q.isEmpty()){
Integer x = q.poll();//出队
visnum++;//访问点+1
for(int i=head[x];i!=0;i=ne[i]){
int y=to[i];
rudu[y]--;
if(rudu[y]==0){
q.offer(y);
}
}
}
return visnum==m+n;
}
static void topo(){
int rudu[];
rudu=du.clone();
Queue<Integer> q=new LinkedList<>();
for (int i = 1; i <=m+n; i++) {
if(rudu[i]==0)
q.offer(i);
}
while (!q.isEmpty()){
Integer x = q.poll();//出队
for(int i=head[x];i!=0;i=ne[i]){
int y=to[i];
rudu[y]--;
nops[y].input.add(nops[x].getOut());
if(rudu[y]==0){
q.offer(y);
}
}
}
}
}
class Nop{
//NOT/AND/OR/XOR/NAND/NOR/SUPER(指输入信号节点,超级节点)
String type;
List<Integer> input;//输入端
int output=-1;//输出端
public Nop(String type) {
this.type = type;
this.input=new ArrayList<>();
}
public int getOut(){//计算输出端结果
if(output!=-1) return output;
if(type.equals("NOT")){
return input.get(0)==0?1:0;
}
else if(type.equals("SUPER")){
return output;
}else if(type.equals("AND")){
for (Integer integer : input) {
if(integer==0) return 0;
}
return 1;
}else if(type.equals("OR")){
for (Integer integer : input) {
if(integer==1) return 1;
}
return 0;
}else if(type.equals("XOR")){
int res=0;
for (Integer integer : input) {
res^=integer;
}
return res;
}else if(type.equals("NAND")){
for (Integer integer : input) {
if(integer==0) return 1;
}
return 0;
}else{
for (Integer integer : input) {
if(integer==1) return 0;
}
return 1;
}
}
}?三:注意点
- 对于每个独立的问题执行前,都要初始化所有数组以及变量。
- 对于每一次输入信号,需要先清空所有逻辑门的输入信号。
四:部分测试用例

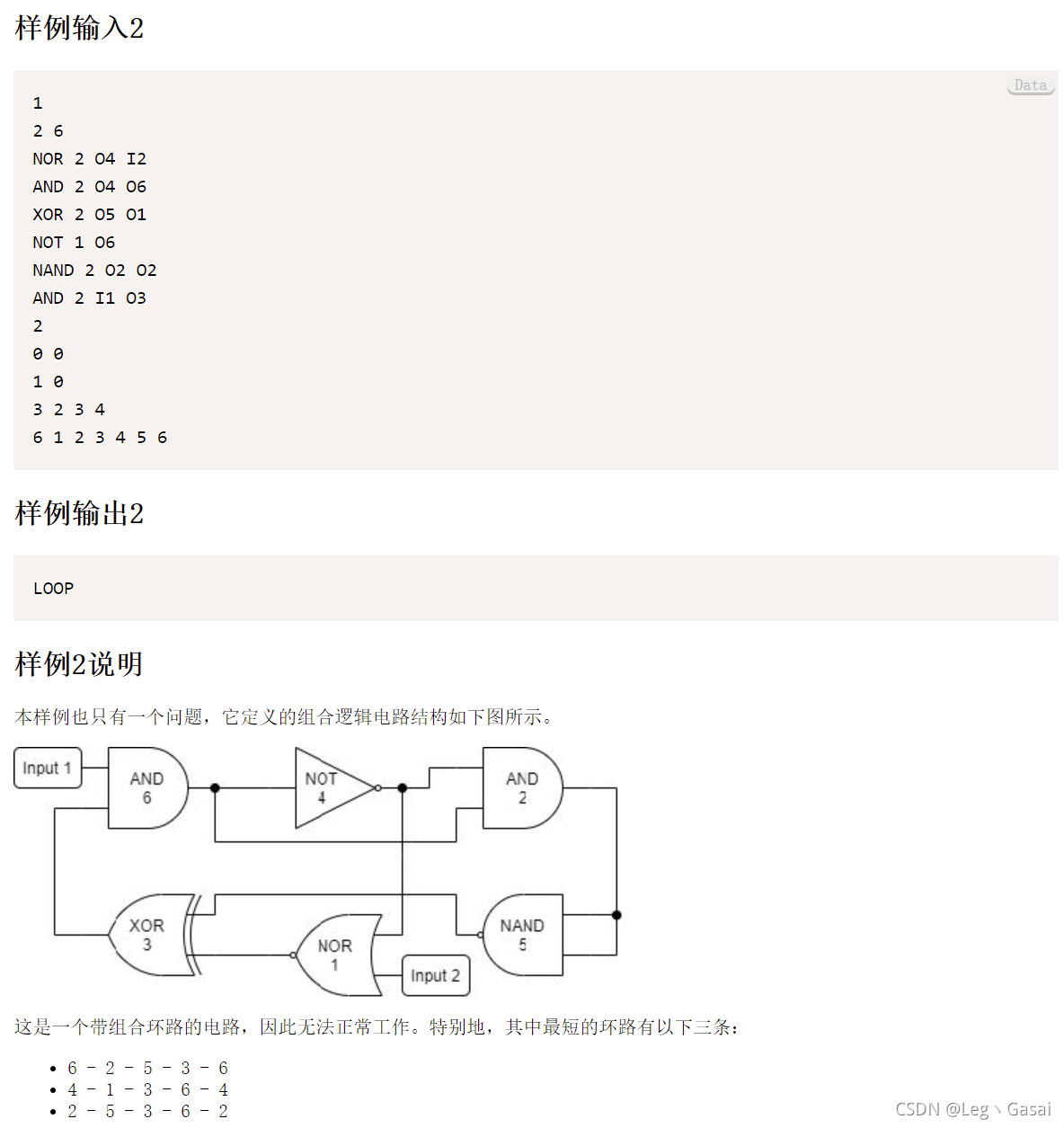
样例3
输入:
1
3 9
AND 3 I1 I2 I3
OR 3 I1 I2 I3
AND 2 I1 I2
AND 2 I1 I3
AND 2 I2 I3
OR 2 O1 O7
AND 2 O2 O8
NOT 1 O9
OR 3 O3 O4 O5
8
0 0 0
0 0 1
0 1 0
0 1 1
1 0 0
1 0 1
1 1 0
1 1 1
2 6 9
2 6 9
2 6 9
2 6 9
2 6 9
2 6 9
2 6 9
2 6 9
输出:?
0 0
1 0
1 0
0 1
1 0
0 1
0 1
1 1
 ?
?
?样例4
输入
4
3 5
XOR 2 I1 I2
XOR 2 O1 I3
AND 2 O1 I3
AND 2 I1 I2
OR 2 O3 O4
4
0 1 1
1 0 1
1 1 1
0 0 0
2 5 2
2 5 2
2 5 2
2 5 2
2 6
NOR 2 O4 I2
AND 2 O4 O6
XOR 2 O5 O1
NOT 1 O6
NAND 2 O2 O2
AND 2 I1 O3
2
0 0
1 0
3 2 3 4
6 1 2 3 4 5 6
3 9
AND 3 I1 I2 I3
OR 3 I1 I2 I3
AND 2 I1 I2
AND 2 I1 I3
AND 2 I2 I3
OR 2 O1 O7
AND 2 O2 O8
NOT 1 O9
OR 3 O3 O4 O5
8
0 0 0
0 0 1
0 1 0
0 1 1
1 0 0
1 0 1
1 1 0
1 1 1
2 6 9
2 6 9
2 6 9
2 6 9
2 6 9
2 6 9
2 6 9
2 6 9
3 8
NAND 2 O2 O3
NAND 2 I1 O4
NAND 2 I2 O4
NAND 2 I1 I2
NAND 2 O6 O7
NAND 2 O1 O8
NAND 2 I3 O8
NAND 2 O1 I3
8
0 0 0
0 0 1
0 1 0
0 1 1
1 0 0
1 0 1
1 1 0
1 1 1
1 5
1 5
1 5
1 5
1 5
1 5
1 5
1 5
输出?
1 0?
1 0?
1 1?
0 0?
LOOP
0 0?
1 0?
1 0?
0 1?
1 0?
0 1?
0 1?
1 1?
0?
1?
1?
0?
1?
0?
0?
1?
部分测试数据参考:https://blog.csdn.net/H_X_P_/article/details/108569908?