一、pytest断言
Pytest中断言是通过 assert 语句实现的,确定预期值和实际值是否一致。
1.1、pytest等值类型断言
import allure
class TestAssert:
@allure.story("pytest-assert方式")
def test_equals(self):
the_biscuit = "Ginger"
my_biscuit = "Gingers"
assert the_biscuit == my_biscuit
执行结果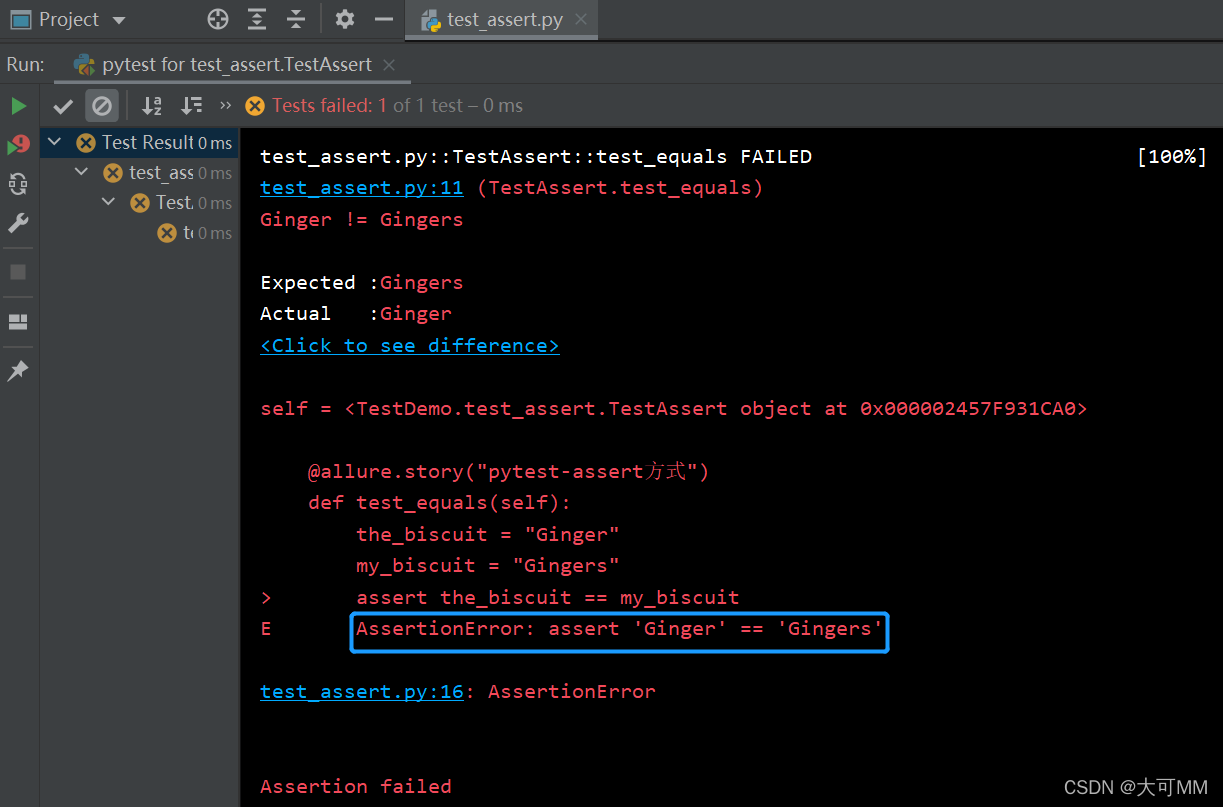
1.2、pytest异常信息提示
如果想在异常的时候输出一些提示信息,这样报错后就方便查看是什么原因了。
def test_equals(self):
the_biscuit = "Ginger"
my_biscuit = "Gingerss"
assert the_biscuit == my_biscuit, '这条用例失败了!'
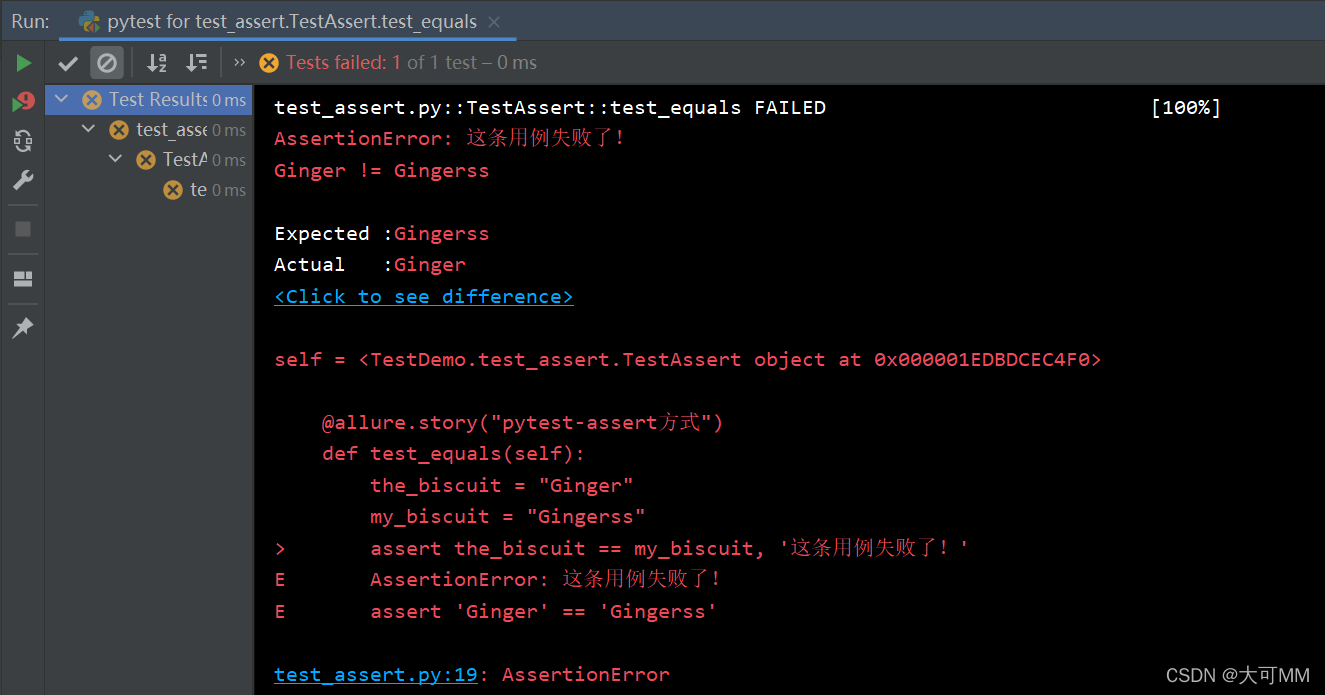
1.3、pytest集合类型断言
def test_dict(self):
assert {"a": 0, "b": 1, "c": 0} == {"a": 0, "b": 2, "d": 0}
def test_dict2(self):
assert {"a": 0, "b": {"c": 2}} == {"a": 0, "b": {"c": 2}}
def test_list(self):
assert [0, 1, 2] == [0, 1, 2]
def test_tuple(self):
assert (0, 1, 2) == (0, 1, 2)
1.4、pytest其他类型断言
assert xx # 判断xx为真
assert not xx # 判断xx不为真
assert a > b # 判断a大于b
assert a < b # 判断a小于b
assert a != b # 判断a不等于b
assert a in b # 判断b包含a
assert a not in b # 判断b不包含a
二、hamcrest断言
由于pytest自带的断言方式有限,并不能覆盖我们所有业务测试场景,这时候就需要用到hamcrest第三方断言库。
2.1、hamcrest等值断言
@allure.story("hamcrest 方式")
def test_equals(self):
the_biscuit = "Ginger"
my_biscuit = "Gingerss"
assert_that(my_biscuit, equal_to(the_biscuit), "等值字段校验失败!")
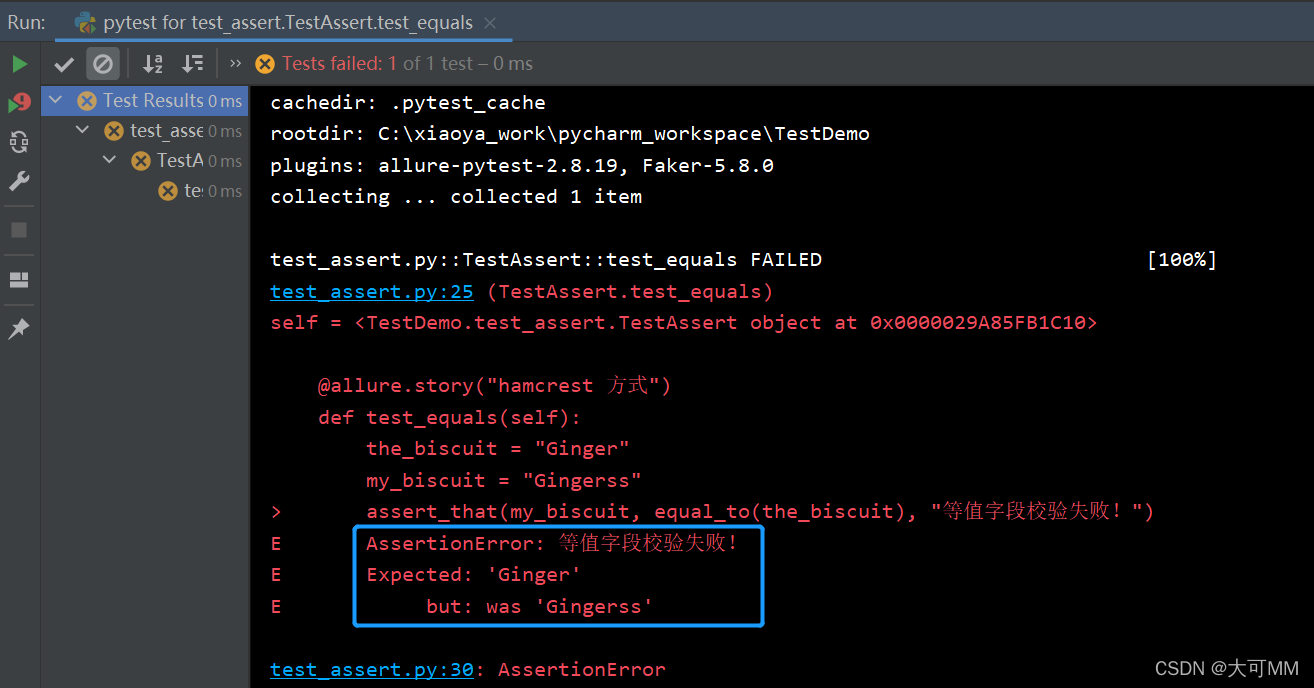
2.2、hamcrest文本类型断言
assert_that(actual, equal_to(expected)) # 实际值等于期望值
assert_that(actual, equal_to_ignoring_case(expected)) # 忽略大小写情况下,实际值等于期望值
assert_that(actual, equal_to_ignoring_whitespace(expected)) # 忽略头尾的任意个空格情况下,实际值等于期望值。注意,字符串中的空格不能忽略
assert_that(actual, contains_string(substring)) # actual包含字符串substring
assert_that(actual, starts_with(prefix)) # actual以子字符串开始
assert_that(actual, ends_with("suffix")) # actual以子字符串结尾
2.3、hamcrest数字类型断言
assert_that(actual, greater_than(expected)) # 实际值大于期望值
assert_that(actual, greater_than_or_equal_to(expected)) # 实际值大于等于期望值
assert_that(actual, less_than(expected)) # 实际值小于于期望值
assert_that(actual, less_than_or_equal_to(expected)) # 实际值小于等于期望值
assert_that(14.7, close_to(15.2, 0.5)) # 匹配接近给定的数字值,在15.2-0.5 ~ 15.2+0.5之间
2.4、hamcrest对象类型断言
assert_that({"a": 1, "b": "b"}, equal_to({"a": 1, "b": "b"})) # 匹配相等对象
assert_that([1, "ab"], has_length(2)) # 长度匹配
assert_that({"a": 1, "b": "b"}, instance_of(dict)) # 匹配对象类型
三、jsonschema
实际工作中,除了常用的字段断言外,有时还需要对数据结构进行校验。比如必填值、null、数据类型、最大值、最小值等等断言,这个时候就可以定义JSON数据结构以及校验JSON数据内容模板来进行断言。
官方的参考文档如下:http://json-schema.org/latest/json-schema-validation.html
参考文章:https://blog.csdn.net/qiumengchen12/article/details/77067613