文章目录
重建索引
使用场景
使用场景有三:
1)、索引的Mapping发生变化:字段类型、分词器、字典更新
2)、索引的Setting发生变化:主分片数要变化
3)、集群内、集群间的数据迁移
es有两种内置api:
1)、updateByQuery:用于==在现有索引上重建
2)、reindex:在其它索引上重建
UpdateByQuery
1、插入数据
先插入测试数据并查看Mapping
PUT blogs/_doc/1
{
"content": "Hadoop is cool",
"keyword": "Hadoop"
}
GET blogs/_mapping
2、改变Mapping
然后改变blogs索引的Mapping,指定content字段的分词器
PUT blogs/_mapping
{
"properties": {
"content": {
"type": "text",
"fields": {
"english": {
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "english"
}
}
}
}
}
3、变更生效
然后执行update_by_query让变更生效
POST blogs/_update_by_query
{
}
4、查询测试
最后执行下面的查询就可以得到想要的那一条样例数据
POST blogs/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"content.english": "Hadoop"
}
}
}
Reindex
当修改Mapping字段时,要使用reindex重建索引
1、新建索引
先创建新的索引,改变某个字段类型(这里是keyword字段)
PUT blogs_fix/
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"content": {
"type": "text",
"fields": {
"english": {
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "english"
}
}
},
"keyword": {
"type": "keyword"
}
}
}
}
2、重建索引
然后使用reindex进行数据导入
POST _reindex
{
"source": {
"index": "blogs"
},
"dest": {
"index": "blogs_fix"
}
}
3、查询测试
最后进行查询,查询keyword字段
POST blogs_fix/_search
{
"size": 0,
"aggs": {
"blog_keyword": {
"terms": {
"field": "keyword",
"size": 10
}
}
}
}
由于keyword类型的fielddata默认时打开的,所以从结果中可以看到Hadoop被查了出来
"buckets" : [
{
"key" : "Hadoop",
"doc_count" : 1
}
]
reindex只会创建不存在的文档,如果文档存在,就会导致版本冲突。
IngestNode与数据预处理
简介
es5.0之后,引入一种新的节点类型,叫做IngestNode。默认情况下,每个结点都是IngestNode。
IngestNode具有数据预处理的能力,可拦截index或bulk请求;也可以对数据进行转换, 并重新返回给index或bulk请求。
有了IngestNode,我们无需logstash就可以对数据进行预处理,比如为某个字段设置默认值、重命名某个字段、对字段值进行分割操作,也可以通过设置Painless脚本,对数据进行更加复杂的加工。
对于IngestNode和logstash,两者的对比如下表所示

Pipeline与Processor
pipeline管道会对通过的数据按顺序进行加工,而processor是es对加工行为的抽象,一个管道就是一组处理器
es内有很多内置的processor,也支持通过插件的方式,实现自定义Processor
_ingest/pipeline/_simulate
_ingest/pipeline/_simulate可以用来测试管道和处理器,pipeline字段设置管道,里面的processors提供处理器数组,而doc字段提供要测试的数据,以下为示例
POST _ingest/pipeline/_simulate
{
"pipeline": {
"description": "Split tags",
"processors": [
{
"split": {
"field": "tags",
"separator": ","
}
}
]
},
"docs": [
{
"_index": "index",
"_id": "id",
"_source": {
"title":"Introducing big data......",
"tags":"hadoop,elasticsearch,spark",
"content":"You konw, for big data"
}
},
{
"_index": "index",
"_id": "idx",
"_source": {
"title":"Introducing cloud computing......",
"tags":"openstack,k8s",
"content":"You konw, for cloud"
}
}
]
}
输出如下,可见tags已经被分割成了数组
{
"docs" : [
{
"doc" : {
"_index" : "index",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "id",
"_source" : {
"title" : "Introducing big data......",
"content" : "You konw, for big data",
"tags" : [
"hadoop",
"elasticsearch",
"spark"
]
},
"_ingest" : {
"timestamp" : "2020-07-25T02:27:20.688319Z"
}
}
},
{
"doc" : {
"_index" : "index",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "idx",
"_source" : {
"title" : "Introducing cloud computing......",
"content" : "You konw, for cloud",
"tags" : [
"openstack",
"k8s"
]
},
"_ingest" : {
"timestamp" : "2020-07-25T02:27:20.68834Z"
}
}
}
]
}
如果要增加处理功能,只需要在processors里面加一个处理器即可,比如要新增一个字段并给定默认值
POST _ingest/pipeline/_simulate
{
"pipeline": {
"description": "Split tags",
"processors": [
{
"split": {
"field": "tags",
"separator": ","
}
},
{
"set": {
"field": "views",
"value": "0"
}
}
]
},
"docs": [
{
"_index": "index",
"_id": "id",
"_source": {
"title":"Introducing big data......",
"tags":"hadoop,elasticsearch,spark",
"content":"You konw, for big data"
}
},
{
"_index": "index",
"_id": "idx",
"_source": {
"title":"Introducing cloud computing......",
"tags":"openstack,k8s",
"content":"You konw, for cloud"
}
}
]
}
管道api
测试完管道后,就可以使用管道api进行数据的预处理了
先要新增一个管道,名字为blog_pipeline,并指定描述信息和处理器数组
PUT _ingest/pipeline/blog_pipeline
{
"description": "a blog pipeline",
"processors": [
{
"split": {
"field": "tags",
"separator": ","
}
},
{
"set": {
"field": "views",
"value": 0
}
}
]
}
完成后我们可以查看pipeline
GET _ingest/pipeline/blog_pipeline
结果如下
{
"blog_pipeline" : {
"description" : "a blog pipeline",
"processors" : [
{
"split" : {
"field" : "tags",
"separator" : ","
}
},
{
"set" : {
"field" : "views",
"value" : 0
}
}
]
}
}
然后我们可以对这个管道进行测试,提供测试数据即可
POST _ingest/pipeline/blog_pipeline/_simulate
{
"docs": [
{
"_index": "index",
"_id": "id",
"_source": {
"title":"Introducing big data......",
"tags":"hadoop,elasticsearch,spark",
"content":"You konw, for big data"
}
},
{
"_index": "index",
"_id": "idx",
"_source": {
"title":"Introducing cloud computing......",
"tags":"openstack,k8s",
"content":"You konw, for cloud"
}
}
]
}
通过管道插入数据
随后我们可以用指定管道的方式插入数据
PUT tech_blogs/_doc/2?pipeline=blog_pipeline
{
"title":"Introducing cloud computing......",
"tags":"openstack,k8s",
"content":"You konw, for cloud"
}
用普通的方式插入另一条数据作为对比
PUT tech_blogs/_doc/1
{
"title":"Introducing big data......",
"tags":"hadoop,elasticsearch,spark",
"content":"You konw, for big data"
}
然后做以下数据查询
POST tech_blogs/_search
{
}
输出如下,明显可以看到两者的区别
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "tech_blogs",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "1",
"_score" : 1.0,
"_source" : {
"title" : "Introducing big data......",
"tags" : "hadoop,elasticsearch,spark",
"content" : "You konw, for big data"
}
},
{
"_index" : "tech_blogs",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "2",
"_score" : 1.0,
"_source" : {
"title" : "Introducing cloud computing......",
"content" : "You konw, for cloud",
"views" : 0,
"tags" : [
"openstack",
"k8s"
]
}
}
]
通过管道重建索引
利用管道进行重建索引的方式如下,必须指定重建条件,比如某个字段不存在
POST tech_blogs/_update_by_query?pipeline=blog_pipeline
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must_not": {
"exists": {
"field": "views"
}
}
}
}
}
上面语句的作用就是对那些不存在views字段的数据按照blog_pipeline管道进行处理,我们可以再做查询验证一下,可以看到普通的数据也被处理了
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "tech_blogs",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "1",
"_score" : 1.0,
"_source" : {
"title" : "Introducing big data......",
"content" : "You konw, for big data",
"views" : 0,
"tags" : [
"hadoop",
"elasticsearch",
"spark"
]
}
},
{
"_index" : "tech_blogs",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "2",
"_score" : 1.0,
"_source" : {
"title" : "Introducing cloud computing......",
"content" : "You konw, for cloud",
"views" : 0,
"tags" : [
"openstack",
"k8s"
]
}
}
]
Painless脚本
自es5之后,引入了Painless脚本,扩展了java语法。6.0开始,es只支持Painless,而groovy、python和js都不再被支持
painless支持所有的java数据类型和javaAPI子集,它具有高性能、安全、支持显式类型或动态定义类型的特性
painless的用途有:
1)、对文档字段进行加工处理,比如更新或删除字段、处理数据聚合,这里涉及到两个painless字段:用于对返回的字段进行提前计算的ScriptField和用于对文档算分进行处理的FunctionScore
2)、在IngestPipeline中执行脚本
3)、在UpdateByQuery重建索引时对数据进行处理
不同上下文场景中的painless的语法还不一样,参加下表
| 上下文 | 语法 |
|---|---|
| Ingestion | ctx.field_name |
| Update | ctx._source.field_name |
| Search & Aggregation | doc[“field_name”] |
管道与painless脚本
在管道中进行预处理时的painless脚本使用示例如下
POST _ingest/pipeline/_simulate
{
"pipeline": {
"description": "Painless split tags",
"processors": [
{
"split": {
"field": "tags",
"separator": ","
}
},
{
"script": {
"source": """
if (ctx.containsKey("content")) {
ctx.content_length = ctx.content.length();
} else {
ctx.content_length = 0;
}
"""
}
},
{
"set": {
"field": "views",
"value": 0
}
}
]
},
"docs": [
{
"_index": "index",
"_id": "id",
"_source": {
"title":"Introducing big data......",
"tags":"hadoop,elasticsearch,spark",
"content":"You konw, for big data"
}
},
{
"_index": "index",
"_id": "idx",
"_source": {
"title":"Introducing cloud computing......",
"tags":"openstack,k8s",
"content":"You konw, for cloud"
}
}
]
}
输出结果如下,可以看到painless脚本计算出来的content_length字段
{
"docs" : [
{
"doc" : {
"_index" : "index",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "id",
"_source" : {
"title" : "Introducing big data......",
"content" : "You konw, for big data",
"content_length" : 22,
"views" : 0,
"tags" : [
"hadoop",
"elasticsearch",
"spark"
]
},
"_ingest" : {
"timestamp" : "2020-07-25T03:02:46.246037Z"
}
}
},
{
"doc" : {
"_index" : "index",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "idx",
"_source" : {
"title" : "Introducing cloud computing......",
"content" : "You konw, for cloud",
"content_length" : 19,
"views" : 0,
"tags" : [
"openstack",
"k8s"
]
},
"_ingest" : {
"timestamp" : "2020-07-25T03:02:46.246041Z"
}
}
}
]
}
painless脚本更新数据
update数据时使用painless脚本的示例如下,这里传入参数
POST tech_blogs/_update/1
{
"script": {
"source": """
ctx._source.views += params.new_views
""",
"params": {
"new_views": 20
}
}
}
执行后,再进行数据查询,可以看到id为1的数据的views字段增加了20
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "tech_blogs",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "2",
"_score" : 1.0,
"_source" : {
"title" : "Introducing cloud computing......",
"content" : "You konw, for cloud",
"views" : 0,
"tags" : [
"openstack",
"k8s"
]
}
},
{
"_index" : "tech_blogs",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "1",
"_score" : 1.0,
"_source" : {
"title" : "Introducing big data......",
"content" : "You konw, for big data",
"views" : 20,
"tags" : [
"hadoop",
"elasticsearch",
"spark"
]
}
}
]
保存painless脚本
我们可以在集群中保存脚本,update_views就是脚本名字
#在集群中保存脚本
POST _scripts/update_views
{
"script": {
"lang": "painless",
"source": """
ctx._source.views += params.new_views
"""
}
}
使用时,把原来的source字段换成脚本名即可
POST tech_blogs/_update/1
{
"script": {
"id": "update_views",
"params": {
"new_views": 40
}
}
}
painless脚本查询数据
在query中使用painless脚本的方法如下,这次使用random获取随机数,并且与views字段值相加返回给rand_views字段
GET tech_blogs/_search
{
"script_fields": {
"rand_views": {
"script": {
"lang": "painless",
"source": """
java.util.Random random = new Random();
doc['views'].value + random.nextInt(100)
"""
}
}
},
"query": {
"match_all": {}
}
}
某一次输出如下
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "tech_blogs",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "2",
"_score" : 1.0,
"fields" : {
"rand_views" : [
78
]
}
},
{
"_index" : "tech_blogs",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "1",
"_score" : 1.0,
"fields" : {
"rand_views" : [
131
]
}
}
]
另一次输出如下
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "tech_blogs",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "2",
"_score" : 1.0,
"fields" : {
"rand_views" : [
64
]
}
},
{
"_index" : "tech_blogs",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "1",
"_score" : 1.0,
"fields" : {
"rand_views" : [
145
]
}
}
]
painless脚本相关参数
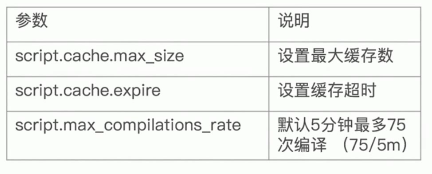
最后,由于编译脚本的开销很大,所以es会将脚本编译后缓存起来,默认缓存100个脚本,相关参数和说明如下所示
数据建模
简介
数据建模:功能需求+性能需求
功能需求方面:要考虑实体属性、实体间的关系和搜索相关的配置等
性能需求方面,要考虑索引模板(分片数量等)和索引映射(字段配置、关系处理等)
字段建模
对字段进行建模:确定字段类型->是否要全文搜索及分词->是否要聚合排序->是否要进行额外的存储
字段类型:Text与Keyword
Text用于全文本字段,会被分词,默认不支持聚合分析和排序,除非打开fieldata
Keyword用于id、枚举和不需要分词的文本,适用于filter、排序和聚合
设置多字段类型:默认会为文本设置成text类型,并设置一个keyword的子字段;再进行NLP时,通过增加英文、拼音和标准分词器,提升搜索结构
数值类型:尽量选择贴近的类型,比如能用byte就不用long
枚举类型:keyword,性能更好
检索
如果不需要检索、排序和聚合,就把enable设为false
如果仅仅不需要检索,把index设为false即可
对需要检索但不用归一化的字段,可以通过关闭index_options/norms字段节约存储
聚合排序
如果不需要检索、排序和聚合,就把enable设为false
如果仅仅不需要排序或聚合,就把fielddata设为false
对于更新频繁且聚合查询的keyword字段,可以把eager_global_ordinals设为true
额外的存储
如果需要的话,就把store设置为true,一般结合enable设为false使用,不过更建议先增加压缩比。
使用时,一般把_source的enable设为false,然后把需要检索的字段的store设为true,最后查询时指定store_fields即可
指标性数据适合disable,因为不常更新
建议
如何处理关联关系
- 对象:优先考虑反归一化
- 嵌入对象:当数据包含数组而且有查询需求时使用
- 父子文档:关联文档更新频繁
避免过多字段
字段过多不容易维护,而且由于Mapping信息保存在集群状态中,数据量太大也会对集群性能有影响,最后删除或修改数据需要重建索引
默认最大字段数为1000,可以通过设置index.mapping.total_fields.limit来更改
文档中字段太多的原因:
Dynamic和strict:Dynamic为true时,未知字段会被自动加入;为false时,新字段不会被索引,但是会被保存;为strict时,新字段不会被索引,写入直接报错。strict模式可以控制到字段级别
对于此,我们可以使用嵌入对象来管理字段
避免正则查询
主要是通配符查询、前缀查询属于term查询,性能不好,尤其是把通配符放前面时
解决方法时:把一个字符串字段转换为多个字段
避免空值引起的聚合不准
这时我们可以在Mapping中设置null_value,给定null对应的值
为索引的映射加入_meta信息
也可以把Mapping文件上传到git进行版本管理
压力测试
安装压力测试工具esrally
[root@localhost git-2.9.2]# pip3 install esrally
而后进行压力测试,指定es版本号,有时要运行两次下面的命令
[root@localhost git-2.9.2]# esrally --distribution-version=7.6.0 --test-mode
结语
ElasticSearch7的学习笔记至此结束。