关于SpringMVC的执行流程
先贴一张SpringMVC的执行流程图
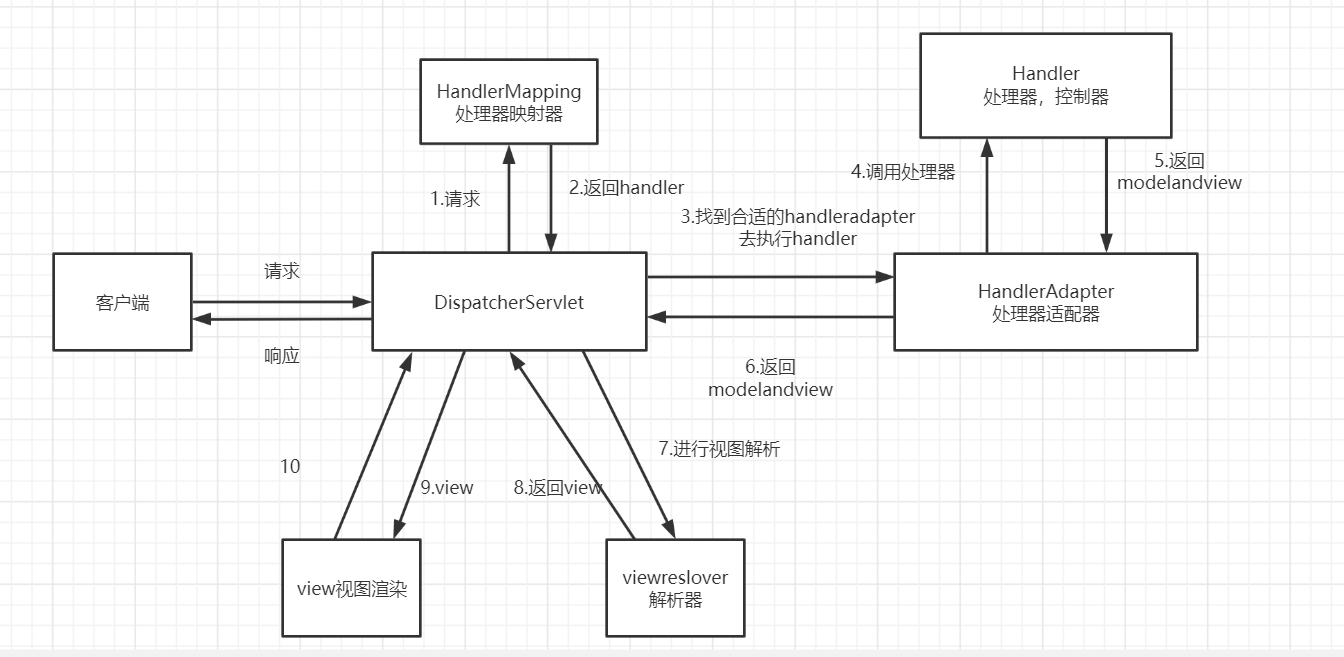
然后一步一步Debug去观察一下源码是怎么做到的
首先一个请求发送到后端时会把请求打到DispatcherServlet上,而主要处理请求的方法是doService方法
doService方法主要做的事
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
String resumed = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).hasConcurrentResult() ? " resumed" : "";
logger.debug("DispatcherServlet with name '" + getServletName() + "'" + resumed +
" processing " + request.getMethod() + " request for [" + getRequestUri(request) + "]");
}
// Keep a snapshot of the request attributes in case of an include,
// to be able to restore the original attributes after the include.
Map<String, Object> attributesSnapshot = null;
//处理Include标签的请求
if (WebUtils.isIncludeRequest(request)) {
attributesSnapshot = new HashMap<String, Object>();
Enumeration<?> attrNames = request.getAttributeNames();
while (attrNames.hasMoreElements()) {
String attrName = (String) attrNames.nextElement();
if (this.cleanupAfterInclude || attrName.startsWith("org.springframework.web.servlet")) {
attributesSnapshot.put(attrName, request.getAttribute(attrName));
}
}
}
// Make framework objects available to handlers and view objects.
// 将上下文存储到Attribute
request.setAttribute(WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, getWebApplicationContext());
// 将国际化解析器存储到Attribute中
request.setAttribute(LOCALE_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.localeResolver);
// 将主题解析器存储到Attribute中
request.setAttribute(THEME_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.themeResolver);
// 将主题存储到Attribute中
request.setAttribute(THEME_SOURCE_ATTRIBUTE, getThemeSource());
FlashMap inputFlashMap = this.flashMapManager.retrieveAndUpdate(request, response);
if (inputFlashMap != null) {
request.setAttribute(INPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, Collections.unmodifiableMap(inputFlashMap));
}
request.setAttribute(OUTPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, new FlashMap());
request.setAttribute(FLASH_MAP_MANAGER_ATTRIBUTE, this.flashMapManager);
概括一下doService方法的作用就是
1、保存请求快照
2、共享上下文信息,本地解析,主题解析等对象给 handler和view对象
然后会把请求交给doDispatch方法进行处理
try {
doDispatch(request, response);
}
然后进入doDispatch方法来看一下具体的处理(主要列出我认为比较重要的代码)
try {
//判断是否为文件上传请求
processedRequest = checkMultipart(request);
multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request);
// Determine handler for the current request.
//根据请求找到对应的handler,下一步会进入该方法去看
mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);
if (mappedHandler == null || mappedHandler.getHandler() == null) {
noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response);
return;
}
// Determine handler adapter for the current request.
// 为handler找到对应的HandlerAdapter(处理器适配器)
HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());
// Process last-modified header, if supported by the handler.
String method = request.getMethod();
// 判断一下是不是GET方法
boolean isGet = "GET".equals(method);
if (isGet || "HEAD".equals(method)) {
//getLastModified方法的作用下面也会说
long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Last-Modified value for [" + getRequestUri(request) + "] is: " + lastModified);
}
if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) {
return;
}
}
if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) {
return;
}
// Actually invoke the handler.
// 调用适配器,返回modelandreview
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
return;
}
applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv);
mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv);
**来看一下mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);**是怎么做的
protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
// 遍历handlerMappings
for (HandlerMapping hm : this.handlerMappings) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace(
"Testing handler map [" + hm + "] in DispatcherServlet with name '" + getServletName() + "'");
}
//根据请求找到对应的处理器链
HandlerExecutionChain handler = hm.getHandler(request);
if (handler != null) {
return handler;
}
}
return null;
}
在深入看一下hm.getHandler是怎么做的
public final HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
// 从当前请求解析出要查找的url,然后继续寻找 handler
Object handler = getHandlerInternal(request);
// 如果handler为null,会去找默认的Handler
if (handler == null) {
handler = getDefaultHandler();
}
if (handler == null) {
return null;
}
// Bean name or resolved handler?
// 通过Bean去找handler
if (handler instanceof String) {
String handlerName = (String) handler;
handler = getApplicationContext().getBean(handlerName);
}
// 返回处理器链
HandlerExecutionChain executionChain = getHandlerExecutionChain(handler, request);
if (CorsUtils.isCorsRequest(request)) {
CorsConfiguration globalConfig = this.corsConfigSource.getCorsConfiguration(request);
CorsConfiguration handlerConfig = getCorsConfiguration(handler, request);
CorsConfiguration config = (globalConfig != null ? globalConfig.combine(handlerConfig) : handlerConfig);
executionChain = getCorsHandlerExecutionChain(request, executionChain, config);
}
return executionChain;
}
getHandlerInternal中的两个方法
// 从请求头中获取lookPath,lookPath中存储着要查找的urlPath
String lookupPath = getUrlPathHelper().getLookupPathForRequest(request);
//找到真正需要执行的handlerMethod
HandlerMethod handlerMethod = lookupHandlerMethod(lookupPath, request);
来看一下比较重要的一行代码HandlerExecutionChain executionChain = getHandlerExecutionChain(handler, request);
比较重要的代码
//将拦截器封装到chain中返回
for (HandlerInterceptor interceptor : this.adaptedInterceptors) {
if (interceptor instanceof MappedInterceptor) {
MappedInterceptor mappedInterceptor = (MappedInterceptor) interceptor;
if (mappedInterceptor.matches(lookupPath, this.pathMatcher)) {
chain.addInterceptor(mappedInterceptor.getInterceptor());
}
}
然后去找合适的处理器适配器HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());
// 遍历handlerAdapters找到支持handler的处理器适配器
for (HandlerAdapter ha : this.handlerAdapters) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Testing handler adapter [" + ha + "]");
}
if (ha.supports(handler)) {
return ha;
}
}
然后就是去调用处理器得到modelandview mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
public ModelAndView handle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler)
throws Exception {
((HttpRequestHandler) handler).handleRequest(request, response);
return null;
}
具体流程下一篇在搞,我还没有看完。。。。。