Cocos Creator制作一个虚拟摇杆
1. 演示
版本:v2.4.3
语言:TS
演示GIF

2. 实现过程
素材


期望效果
- 类似于王者荣耀的那种小摇杆
- 摇杆中心位置为屏幕点击的位置
- 摇杆点击部分不会出界
过程
(1)摇杆跟随触摸
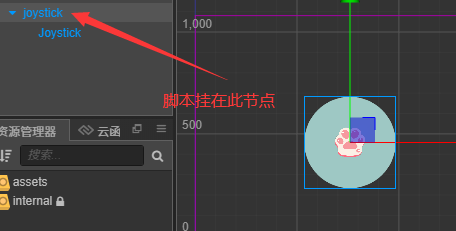
this.Joystick = this.node.getChildByName("Joystick");
// 此处监听的joystick为摇杆
this.Joystick.on(cc.Node.EventType.TOUCH_MOVE, this.onTouchMove, this);
onTouchMove(e: cc.Event.EventTouch) {
this.JoystickMove(e)
}
JoystickMove(e: cc.Event.EventTouch) {
// 移动
let delta = e.getDelta();
let moveDistance = cc.v3(delta.x / this.node.scale, delta.y / this.node.scale)
// 此处增加缩放参数为了方便,使用时可以直接缩放大小
this.Joystick.setPosition(this.Joystick.position.add(moveDistance))
}

此时可以实现触摸点跟随手指或者鼠标移动。getDelta函数是获取触点距离上一次事件移动的距离对象,返回的是一个Vec2。但此时摇杆不会自动归位。
(2)摇杆自动归位
this.Joystick.on(cc.Node.EventType.TOUCH_END, this.onTouchEnd, this);
this.Joystick.on(cc.Node.EventType.TOUCH_CANCEL, this.onTouchCancel, this);
onTouchEnd(e: cc.Event.EventTouch) {
this.JoystickReset()
}
onTouchCancel(e: cc.Event.EventTouch) {
this.JoystickReset()
}
JoystickReset() {
cc.tween(this.Joystick)
.to(0.05, {x: 0, y: 0})
.start()
}

TOUCH_END, TOUCH_CANCEL代表的状态为当手指在目标节点区域内离开屏幕时,当手指在目标节点区域外离开屏幕时。使用缓动使动画更流畅。
(3)限制摇杆不出界
原理:
此处思路来源于CSDN章鱼仔,通过三角形的相似等比。
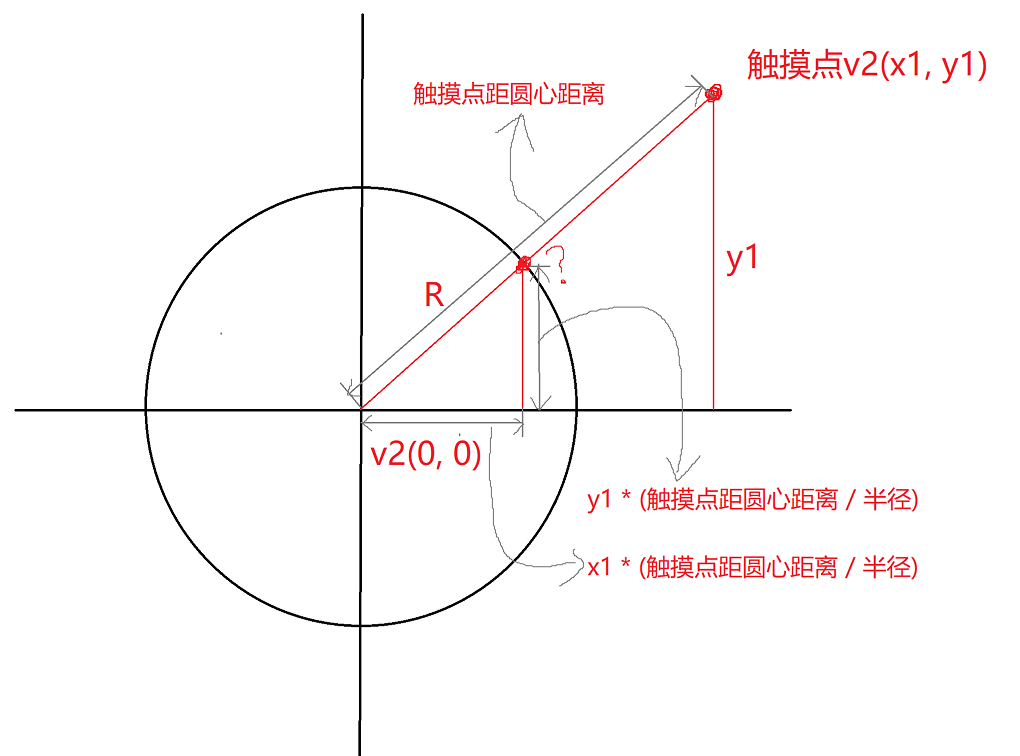
完善JoystickMove代码
JoystickMove(e: cc.Event.EventTouch) {
// 移动
let delta = e.getDelta();
let moveDistance = cc.v3(delta.x / this.node.scale, delta.y / this.node.scale)
// 加上缩放参数,更加方便实用
this.Joystick.setPosition(this.Joystick.position.add(moveDistance))
// 转换坐标
let touchPos = e.getLocation(); // 以当前屏幕左下角为坐标系原点所获得的的位置
let touchPosInNode = this.node.convertToNodeSpaceAR(touchPos)
let distanceBetweenTouchPosToJoystick = touchPosInNode.mag() * this.node.scale; // 此处缩放参数作用与前边同理
// 限制移动 < 半径
if (distanceBetweenTouchPosToJoystick > this.radius) {
let lengthScale = this.radius / distanceBetweenTouchPosToJoystick;
this.Joystick.x = touchPosInNode.x * lengthScale;
this.Joystick.y = touchPosInNode.y * lengthScale;
}
}

此时移动不会出界,而且可以任意调整缩放倍数都可以保持不出界状态!
注意getLocation()函数返回的坐标是以屏幕左下角为坐标中心的坐标,并不是世界坐标!
节点.convertToNodeSpaceAR(位置)返回的是这个位置在这个节点下的位置。
(4)添加箭头
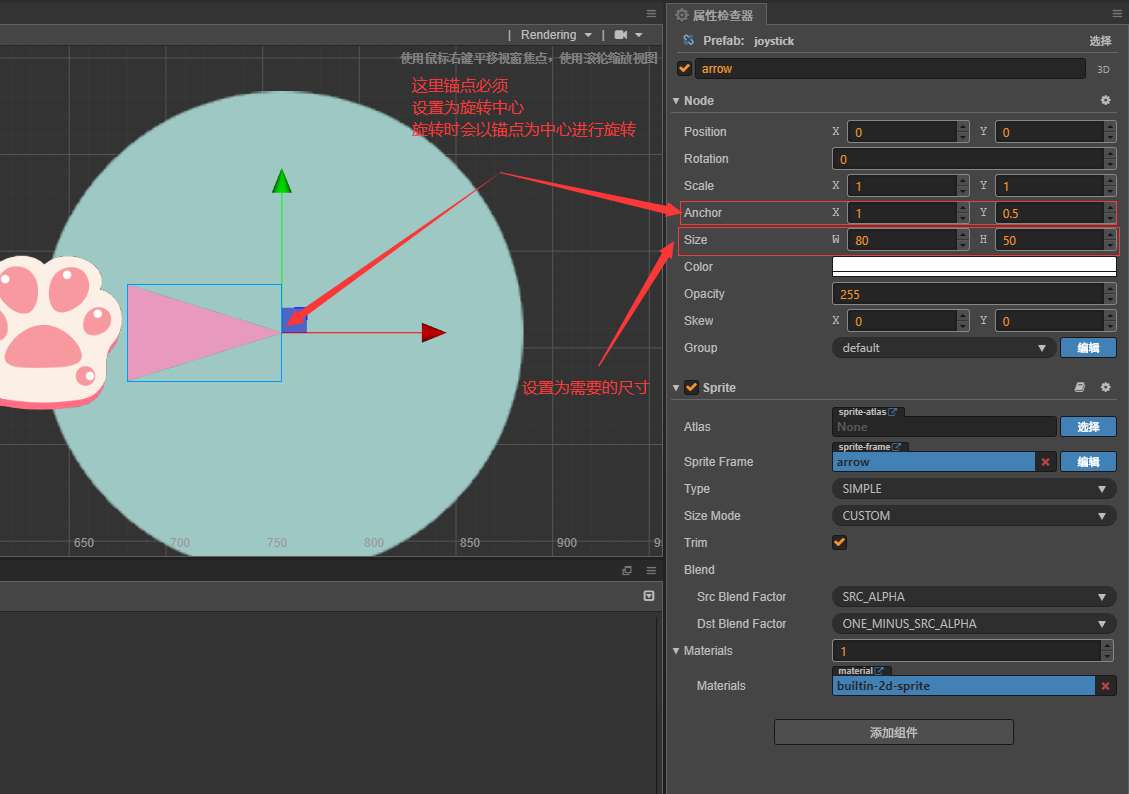
完善代码
onTouchMove(e: cc.Event.EventTouch) {
this.JoystickMove(e)
this.arrowDirection()
}
arrowDirection() {
// 设置箭头大小
this.setArrowLength()
// 计算夹角
this.setArrow(cc.v2(this.Joystick.position))
}
setArrowLength() {
let arrowParamScale = this.Joystick.position.mag() * this.node.scale / this.radius;
this.arrow.width = this.arrowMaxLenth * arrowParamScale; // 箭头长度
this.arrow.opacity = 255 * arrowParamScale; // 箭头透明度
}
/**
*
* @param JoystickPos 摇杆节点坐标
*/
setArrow(JoystickPos: cc.Vec2) {
let dir = JoystickPos.sub(cc.v2(0, 0))
let vec = cc.v2(0, 1); // 水平向右的对比向量
let radian = dir.signAngle(vec); // 求方向向量与对比向量间的弧度
let rotate = cc.misc.radiansToDegrees(radian); // 将弧度转换为角度
this.arrow.angle = -rotate - 90; // ***此处rotate正负值以及减去的角度根据自己的图片去修改***
}
再完善一下摇杆回弹时的动画,让箭头可以复原!
JoystickReset() {
let time: number = 0.05;
let arrowReset = cc.tween(this.arrow).to(time, {width: 0, opacity: 0})
cc.tween(this.Joystick)
.call(() => {
arrowReset.start()
})
.to(time, {x: 0, y: 0})
.start()
}
原理:
首先dir是摇杆的向量与摇杆中心的一个带方向的向量差,若是求向量夹角必须有另外一个参考向量,此处定义为(0, 1),求出的值为弧度所以需要将弧度转换为我们要的角度。
弧度转角度公式: 角度 = 弧度 * 180 / PI
cocos中可以直接使用cc.misc.radiansToDegrees()
singAngle()函数源码部分如下,如果对向量的叉乘、点乘的几何意义不熟悉可以看一下:
/*
* 带方向的夹角的弧度。该方法仅用做兼容 2D 计算。
*/
signAngle (vector) {
cc.warnID(1408, 'vec3.signAngle', 'v2.1', 'cc.v2(selfVector).signAngle(vector)');
let vec1 = new Vec2(this.x, this.y);
let vec2 = new Vec2(vector.x, vector.y);
return vec1.signAngle(vec2);
}
/*
* 带方向的夹角的弧度。
*/
signAngle (vector: Vec2): number {
let angle = this.angle(vector);
return this.cross(vector) < 0 ? -angle : angle;
}
/*
* 夹角的弧度。
*/
angle (vector: Vec2): number {
var magSqr1 = this.magSqr();
var magSqr2 = vector.magSqr();
if (magSqr1 === 0 || magSqr2 === 0) {
console.warn("Can't get angle between zero vector");
return 0.0;
}
var dot = this.dot(vector);
var theta = dot / (Math.sqrt(magSqr1 * magSqr2));
theta = misc.clampf(theta, -1.0, 1.0);
return Math.acos(theta); // 反余弦函数
}
/*
* 当前向量与指定向量进行叉乘。
*/
cross (vector: Vec2): number {
return this.x * vector.y - this.y * vector.x;
}
/**
*当前向量与指定向量进行点乘。
*/
dot (vector: Vec2): number {
return this.x * vector.x + this.y * vector.y;
}
/*
* 限定浮点数的最大最小值。
* 数值大于 max_inclusive 则返回 max_inclusive。
* 数值小于 min_inclusive 则返回 min_inclusive。
* 否则返回自身。
*/
misc.clampf = function (value, min_inclusive, max_inclusive) {
if (min_inclusive > max_inclusive) {
var temp = min_inclusive;
min_inclusive = max_inclusive;
max_inclusive = temp;
}
return value < min_inclusive ? min_inclusive : value < max_inclusive ? value : max_inclusive;
};
主脚本编写
(1)主脚本部分实现功能
- 更改触摸范围为全屏
- 跨脚本调用摇杆
- 移动物体
(2)演示
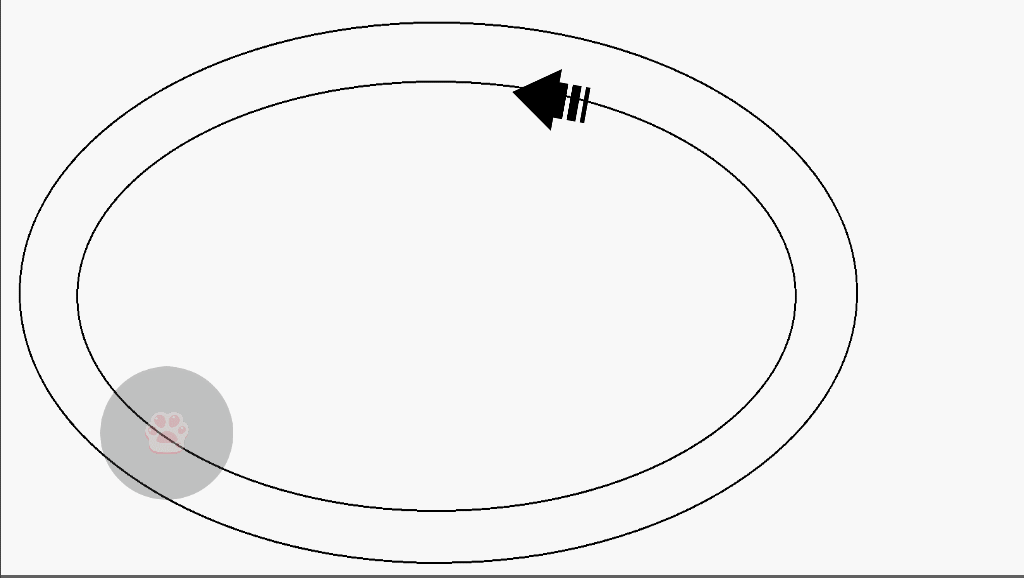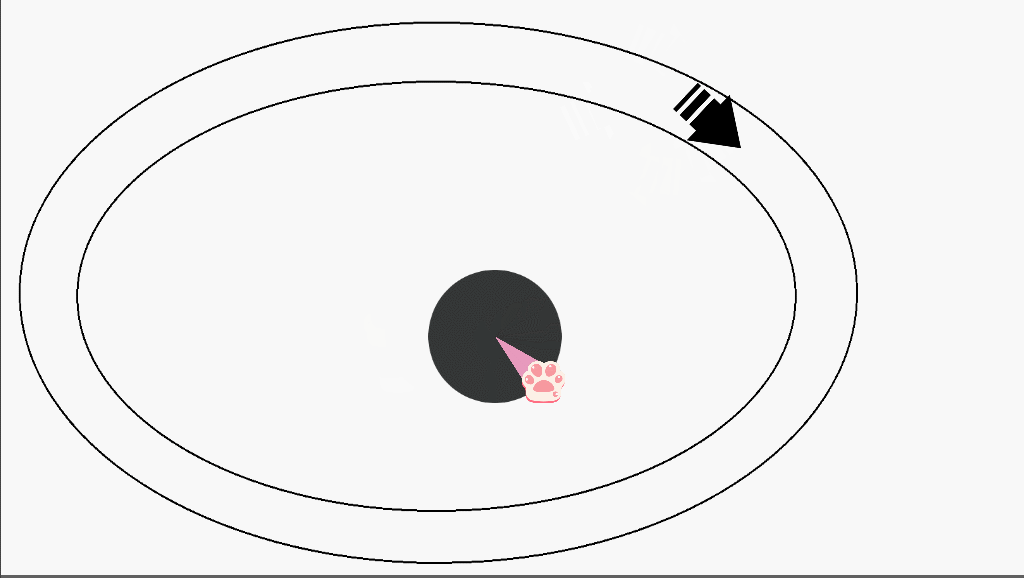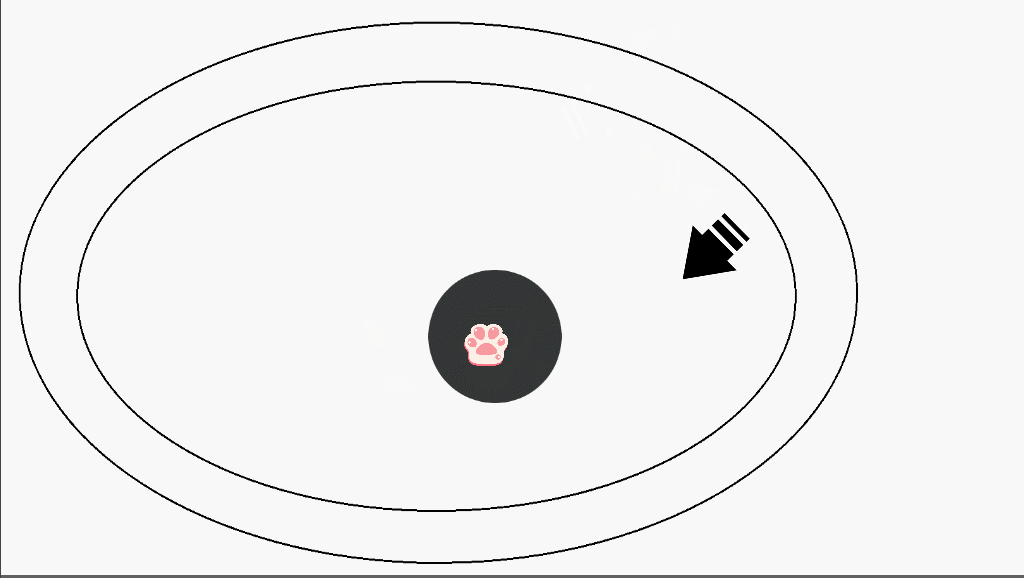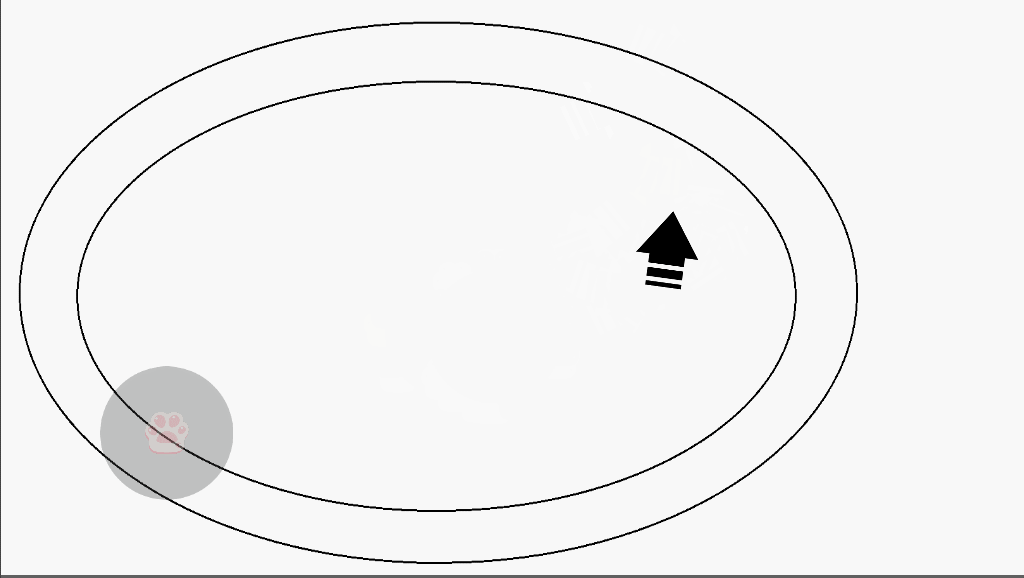
(3)实现
摇杆脚本部分
// 返回给调用者需要用到的参数
returnArrowAngle() {
let radin = cc.misc.degreesToRadians(-this.arrow.angle - 90);
cc.log(this.arrow.angle)
let vec = cc.v2(0, 1);
let targetVec = vec.rotate(-radin);
let data = {
angle: this.arrow.angle, // 角度
vec: targetVec,
speedScale: this.arrow.width / this.arrowMaxLenth,
moveState: this.Joystick.x != 0 && this.Joystick.y != 0 ? true : false,
}
return data;
}
原理与计算朝向原理差不多,只是这次将角度转为弧度,再通过将参考的向量旋转指定弧度(radin)后,即可得出指定已知角度的向量!
主脚本部分
@property({type: cc.Node, displayName: "可点击区域"})
touchArea: cc.Node = null;
@property({type: cc.Node, displayName: "摇杆"})
joystick: cc.Node = null;
@property({type: cc.Node, displayName: "移动物体"})
thing: cc.Node = null;
// 此脚本脚本全局函数区
joystickCom: joystick;
moveSpeed = 0.5;
moveRotate: number;
// 设置点击区域监听
onLoad () {
this.joystickCom = this.joystick.getComponent(joystick);
this.touchArea.on(cc.Node.EventType.TOUCH_START, this.onTouchStart, this);
this.touchArea.on(cc.Node.EventType.TOUCH_MOVE, this.onTouchMove, this);
this.touchArea.on(cc.Node.EventType.TOUCH_END, this.onTouchEnd, this);
}
onTouchStart(e: cc.Event.EventTouch) {
this.joystickCom.onTouchStart(e);
}
onTouchMove(e: cc.Event.EventTouch) {
this.joystickCom.onTouchMove(e);
}
onTouchEnd(e: cc.Event.EventTouch) {
this.joystickCom.onTouchEnd(e);
}
// 移动实现
thingMove() {
let joystickFun = this.joystickCom.returnArrowAngle()
this.thing.angle = joystickFun.angle + 90; // 自行调整
if (joystickFun.moveState) {
this.thing.setPosition(this.thing.position.add(
cc.v3(
joystickFun.vec.x * 5 * joystickFun.speedScale,
joystickFun.vec.y * 5 * joystickFun.speedScale
)
))
}
}
update (dt) {
this.thingMove();
}
}
第一次发文章,若有错误望大佬们指正。
源码
密码: agzg