UnityShader入门学习笔记
本笔记对Siki学院中的UnityShader视频所学的内容作了一点笔记,方便后面查询。
-
GPU简介
- GPU包含较多的ALU
-
主要分三种语言
- OpenGL GLSL
- DirectX HLSL
- NVIDIA CG
-
OpenGL和OpengGL ES区别:OpenGL ES主要用于手机平台
-
CG语言可以编译成GLSL和HLSL语言
-
渲染流水线
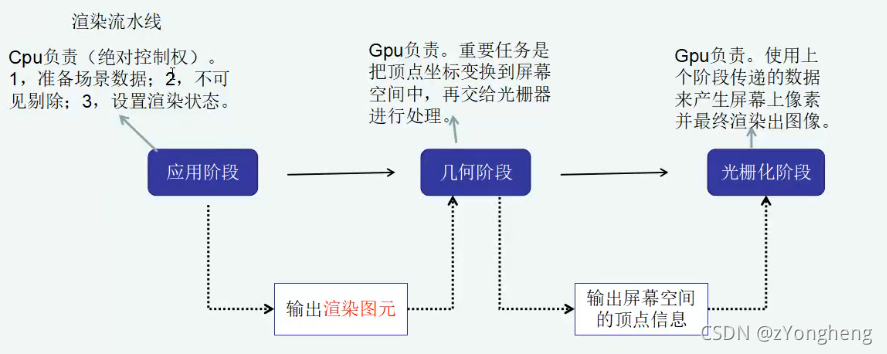
-
应用阶段:准备场景数据-渲染图元(CPU)
- 将数据加载到显存(顶点、纹理等)
- 设置渲染状态(使用哪个顶点着色器、片源着色器、光源属性、材质等)
- 调用Draw Call(渲染哪些图元列表)
- 优化点,应该尽量减少Draw Call
- 动态合并:将定点数小于多少的一组Mesh
- 静态合并:将相同的材质,Mesh合并到一起
-
几何阶段-顶点信息(顶点坐标到屏幕坐标)(GPU 流水线)
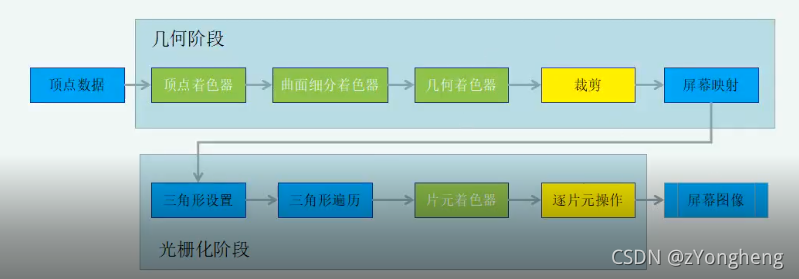
- *顶点数据*
- **顶点着色器**(顶点着色、空间变换)
- **曲面细分着色器**(细分图元)
- **几何着色器**(逐图元的着色操作)
- 裁剪(不在摄像机范围内的裁剪)
- *屏幕映射*(将图元转成屏幕坐标)
-
光栅化(GPU 流水线)
- 三角形设置
- 三角形遍历
- 片源着色器(逐片源操作,片源着色)
- 逐片元设置(修改颜色等)
- 屏幕图像
-
顶点着色器
- 作用:坐标变换、光照、顶点动画等
- 过程
- 模型空间:建模相当于模型的坐标
- 齐次裁剪空间:三个步骤:世界坐标-观察空间-齐次裁剪空间
- 长宽高为1的空间
- 计算顶点颜色:
-
裁剪
- 一个图元分成三种:完全在视野内、完全在视野外、部分在视野内(需要裁剪)
-
屏幕映射
- 将齐次坐标转屏幕坐标(-1,1)-(x1,y1),(x2,y2)
- 结果输出新的坐标系:窗口坐标系
- OpenGL和DirectX坐标不一致,OpenGL左下角为0,DirectX是左上角为0
-
三角形设置
- 根据顶点计算和标记被三角覆盖的区域
-
三角形遍历
- 检查每个像素,如果被覆盖,会产生一个片源
- 使用顶点信息对覆盖区域进行像素差值
-
片源着色器
- 纹理采样:获取纹理坐标,然后进行差值,最终计算每个片元的纹理坐标
-
逐片源操
-
片元
-
模板测试
- 模板缓冲(Stencil Buffer)、颜色缓冲
- 模板测试通过后可以通过程序可控的程序判断是否要把新的模板缓冲区
-
深度测试
- 如果片源没有通过深度测试,它就无法修改深度缓冲区的值
- 一般比较函数是小于等于,表示距离摄像机近的才能显示
-
混合
- 一个物体接着一个物体画到屏幕上
- 对于不透明的物体,一般直接进行覆盖
- 对于半透明的物体,需要进行颜色的混合
-
颜色缓冲区
-
-
总结
-
各种测试的顺序并不是唯一的,对于大多数GPU,会尽可能在片源着色器之前进行这些测试。
-
对于透明物体,是无法提前进行透明度测试,因此GPU无法进行优化。
-
GPU使用双重缓冲策略可以使画面更加连续
-
CPU和GPU使用命令缓冲区进行并行工作
-
固定渲染管线:比较旧的GPU提供的(目前已经不存在了)
-
-
Unity Shader(ShaderLab)
- Surface Shader
- Unlit Shader(顶点片源)
- Image Effect Shader(特效相关)
- Compute Shader
-
Shader Properties
Properties { _MainTex ("Texture", 2D) = "white" {} _Int("Int", int) = 2 _Float("Float", float) = 1.5 _Range("Range", Range(0.0, 2.0)) = 1.0 _Color("Color", Color) = (0, 0, 0, 0) _Vector("Vector", Vector) = (1, 4, 3, 8) _Cube("Cube", Cube) = "white" {}//天空盒 _3D("3D", 3D) = "black" {} } -
Shader SubShader
- Unity中可以包含多个SubShader,Unity会使用第一个能够运行的SubShader,可以在不同平台兼容,如果都不能运行,Unity是使用Fallback执行
- Pass通道不建议写多个
-
Shader Tag
//标签可选 key=value Tags { "Queue" = "Transparent"//渲染顺序 "RenderType"="Opaque" //渲染类型,着色器替换功能 "DisableBatching" = "True"//关闭合批(动态合并,静态合并) "ForceNoShadowCasting" = "True"//是否投射阴影 "IgnoreProjector" = "True"//受不受Projector影响,通常用于透明物体 "CanUseSpriteAltas" = "False"//是否用于图片的Shader,UI一般为TRUE "PreviewType" = "Plane"//用作Shader面板预览的类型 } -
Render 设置
//Cull off/back/front 裁剪(选择渲染哪个面,默认只渲染正面) //ZTest Always/Less Greater/LEqual/GEqual/Equal/NotEqual 深度测试(默认小于等于) //ZWrite off/on 深度写入(默认是开) //Blend ScrFactor DstFactor 混合 //LOD 100 不同情况下使用不同的LOD达到性能提升 -
Pass Name
//Name "Default" Pass通道名称,可以使用Use Pass通道名称 -
Pass Tags
Tags{ "LightMode" = "ForwardBase"//渲染流水中的角色 "RequireOptions" = "SoftVegetation"//满足某些条件时才渲染Pass通道 } -
Fallback
//Fallback "Legacy Shaders/Transparent/VertexLit" Fallback Off//当Shader运行不了的时候会显示下面的Shader -
数学知识
- 三角函数和正弦、余弦变换
- 向量的乘法和叉乘
- 行列式
- 矩阵
- 伴随矩阵(容易算错,A代数余子式组成的矩阵的转置才是伴随矩阵),建议一步一步的计算
- 逆矩阵及转置矩阵、奇异矩阵(不可逆矩阵)
- 正交矩阵与正交空间
- 齐次坐标定义
- 线性变换(原点坐标不变)、仿射变换(进行线性变换后接着进行平移)、可逆变换、等角变换
-
图形学知识
-
2D坐标轴变化α角后的(x,y)对应的坐标值
( x ‘ , y ‘ ) = ( x c o s θ + y s i n θ , y c o s θ ? x s i n θ ) (x^`,y^`) = (xcosθ+ysinθ, ycosθ-xsinθ) (x‘,y‘)=(xcosθ+ysinθ,ycosθ?xsinθ) -
2D坐标轴平移(a,b)后(x,y)对应的坐标值
( x ‘ , y ‘ ) = ( x ? a , y ? b ) (x^`,y^`) = (x-a, y-b) (x‘,y‘)=(x?a,y?b) -
2D坐标轴变化α角,后进行平移(a, b)对应的坐标
-
2D旋转矩阵推导(使用特殊值法)
M = ( c o s θ s i n θ ? s i n θ c o s θ ) M = \left( \begin{matrix} cosθ & sin θ \\ -sinθ & cosθ \end{matrix} \right) M=(cosθ?sinθ?sinθcosθ?) -
3D绕X轴、Y轴、Z轴进行旋转的旋转矩阵
沿Z旋转
Z = ( c o s θ s i n θ 0 ? s i n θ c o s θ 0 0 0 1 ) Z = \left( \begin{matrix} cosθ & sin θ & 0\\ -sinθ & cosθ & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 1 \end{matrix} \right) Z=???cosθ?sinθ0?sinθcosθ0?001????
沿X旋转
X = ( 1 0 0 0 c o s θ s i n θ 0 ? s i n θ c o s θ ) X = \left( \begin{matrix} 1 & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & cosθ & sinθ \\ 0 & -sinθ & cosθ \end{matrix} \right) X=???100?0cosθ?sinθ?0sinθcosθ???? -
向量v沿任意单位向量n旋转θ角后的向量v‘
- 在3D计算的过程中,要在关键的透明面上进行绘制
- 一般还有一些辅助线包含了关键投影面和投影面上的法线以及一些向量的延长
- 向量计算主要使用的向量在各个轴上分量进行叠加
v ′ ? = ( v ? ? ( v ? n ? ) n ? ) c o s θ + ( n ? × v ? ) s i n θ + ( v ? n ? ) n ? \vec{v'} = (\vec{v}-(\vec{v}\vec{n})\vec{n})cosθ + (\vec{n}\times\vec{v})sinθ+(\vec{v}\vec{n})\vec{n} v′=(v?(vn)n)cosθ+(n×v)sinθ+(vn)n
之后再进行特殊点带入,计算出旋转矩阵。
其中n向量的特殊点使用nx,ny,nz代替
-
缩放(均匀缩放、非均匀缩放)沿轴缩放kx,ky,kz
( k x 0 0 0 k y 0 0 0 k z ) \left( \begin{matrix} kx & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & ky & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & kz\end{matrix} \right) ???kx00?0ky0?00kz???? -
沿向量n对向量v进行缩放的缩放矩阵
-
2D向X轴投影的投影矩阵、2D向XY屏幕投影的投影矩阵(特殊值法带入)
-
2D沿n向量的投影矩阵
M = ( n x 2 n x n y n x n y n y 2 ) M=\left( \begin{matrix} n_x^2 & n_xn_y \\ n_xn_y & n_y^2 \end{matrix} \right) M=(nx2?nx?ny??nx?ny?ny2??) -
3D沿法线n的投影面的投影矩阵
-
透视投影的计算**(如果自己开发游戏引擎,则必须能推导处投影矩阵的表达式)**
-
不考虑进平面和远平面计算投影矩阵
( n 0 0 0 0 n 0 0 0 0 n 0 0 0 ? 1 0 ) ( x 0 y 0 z 0 1 ) = ( n x 0 n y 0 z 0 n ? z 0 ) \left( \begin{matrix} n & 0 & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & n & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & n & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & -1 & 0 \end{matrix} \right)\left( \begin{matrix} x_0 \\ y_0 \\ z_0 \\ 1 \end{matrix} \right) = \left( \begin{matrix} nx_0 \\ ny_0 \\ z_0n \\ -z_0 \end{matrix} \right) ?????n000?0n00?00n?1?0000???????????x0?y0?z0?1??????=?????nx0?ny0?z0?n?z0??????? -
考虑CVV规则观察体
M = ( 2 n / w 0 0 0 0 2 n / h 0 0 0 0 ? ( f + n ) / ( f ? n ) ? 2 n f / ( f ? n ) 0 0 ? 1 0 ) M=\left( \begin{matrix} 2n/w & 0 & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & 2n/h & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & -(f+n)/(f-n) & -2nf/(f-n) \\ 0 & 0 & -1 & 0 \end{matrix} \right) M=?????2n/w000?02n/h00?00?(f+n)/(f?n)?1?00?2nf/(f?n)0??????
将矩阵(x,y,z,1)转化为(x2, y2, z2, -z0) -
考虑Fov视角大小
M = ( c o t ( F o v / 2 ) / A s p e c t 0 0 0 0 c o t ( F o v / 2 ) 0 0 0 0 ? ( f + n ) / ( f ? n ) ? 2 n f / ( f ? n ) 0 0 ? 1 0 ) M=\left( \begin{matrix} cot(Fov/2)/Aspect & 0 & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & cot(Fov/2) & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & -(f+n)/(f-n) & -2nf/(f-n) \\ 0 & 0 & -1 & 0 \end{matrix} \right) M=?????cot(Fov/2)/Aspect000?0cot(Fov/2)00?00?(f+n)/(f?n)?1?00?2nf/(f?n)0??????
-
-
正交投影的计算(同上面的运算,不再推导)
-
漫反射
-
lambert公式
-
已知入射光颜色c,入射光向量l,法线向量n,材质颜色m,求光的漫反射强度Cdiffuse
-
漫反射只和摄像机位置无关,只和入射角度有关
C d i f f u s e = C 光 m 物 体 m a x ( 0 , n ? l ? ) C_{diffuse}=C_光m_{物体}max(0, \vec{n}\vec{l}) Cdiffuse?=C光?m物体?max(0,nl)
-
-
-
高光反射
-
Phone模型
- 已知入射光颜色c,入射光向量l,法线向量n,材质颜色m,摄像机位置向量v,求高光反射强度
C 反 射 = C 光 M m a x ( 0 , ( 2 l ? n ? n ? ? l ? ) v ? ) C_{反射}=C_光Mmax(0, (2\vec{l}\vec{n}\vec{n}-\vec{l})\vec{v}) C反射?=C光?Mmax(0,(2lnn?l)v)
- 已知入射光颜色c,入射光向量l,法线向量n,材质颜色m,摄像机位置向量v,求高光反射强度
-
BlinePhone模型
- bline模型使用半角向量和法线向量计算光照强度
C 反 射 = C 光 M m a x ( 0 , n ? ( l ? + v ? ) / ( ∣ l ? + v ? ∣ ) ) C_{反射}=C_光Mmax(0, \vec{n}(\vec{l}+\vec{v})/(|\vec{l}+\vec{v}|)) C反射?=C光?Mmax(0,n(l+v)/(∣l+v∣))
-
-
法线贴图
-
首先需要计算物体坐标和法线坐标的转换矩阵。
一致法线向量n,切线向量t(从法线贴图中获取),计算旋转矩阵
要求旋转矩阵的z轴和n方向相同,x轴和t方向相同,y轴和b(副切线)方向相同。
R = ( t ? b ? n ? ) R=\left( \begin{matrix} \vec{t} \\ \vec{b} \\ \vec{n} \end{matrix} \right) R=???tbn????
副切线方向为t向量和n向量的叉乘 -
在shaderlab中,cross计算得到的值为标量,必须要再成w才能成为向量(易错点)
-
对于贴图来说,xy为贴图的uv值,z轴的方向总是正方向,需要自己去推导。
-
-
透明
- 不需要自己去计算透明效果,只需要在片源着色器中返回alpha值,然后做配置即可。
-
-
投影变换
- 局部空间
- 世界空间
- 观察空间
- 裁剪空间
- 屏幕空间
-
摄像机投影
- 正交投影
- 透视投影
-
编写第一个shader
-
输出一个彩色的球
CGPROGRAM //定义顶点着色器和片源着色器的名称 #pragma vertex vert #pragma fragment frag //输入结构体 application to vert struct a2v { //用模型顶点填充v变量 float4 vertex: POSITION; //用模型法线填充n变量 float3 normal: NORMAL; //用模型的第一套uv填充texcoord float4 texcoord: TEXCOORD0; }; //输出结构体 vert to frag struct v2f { //pos为裁剪空间的位置信息 float4 pos: SV_POSITION; //color 语义可以储存颜色信息 fixed3 color: COLOR0; }; //POSITION SV_POSITION 语义,不能省略 //POSITION 模型顶点信息 //SV_POSITION 裁剪空间的顶点信息 //sv_TARGET Rendertaget 默认的帧缓存中 v2f vert(a2v v) { v2f o; o.pos = UnityObjectToClipPos(v.vertex); //将-1,1区间变幻成0,1区间 o.color = v.normal * 0.5 + fixed3(0.5, 0.5, 0.5); return o; } fixed4 frag(v2f i):sv_TARGET { return fixed4(i.color, 1); } ENDCG
-
-
常见语义
顶点着色器输入结构体
- POSITION:顶点位置 float4
- NORMAL:定点法线 float3
- TARGENT:顶点切线 float4
- TEXTCOORDn:顶点为例坐标 float2\float4
- COLOR:顶点颜色 fixed4或float
顶点着色器输出结构体
- SV_POSITION:裁剪空间顶点坐标
- COLOR0:常用于输出颜色信息,不是必须
- COLOR1:常用于输出颜色信息,不是必须
- TEXCOORD0-TEXCOORD7:常用于输出纹理坐标
片源着色器 输出语义
- SV_Target:渲染目标
-
调试方法
-
使用color进行调试
o.color = v.normal * 0.5 + fixed3(0.5, 0.5, 0.5); o.color = v.tangent.xyz*0.5 + fixed3(0.5,0.5,0.5); o.color = fixed4(v.texcoord.xy, 0, 1); o.color = v.color;这种方法需要自己判断颜色对应的数据。
-
使用窗口-帧调试器调试
-
使用第三方工具 Inter Gpa,Snapdragon Profiler等
-
Opengl和DirectX,当开启Anti Aliasing,并同时处理多张图片,需要手动翻转
#if UNITY_UV_STARTS_AT_TOP if(_Maintext_TexelSize.y < 0) uv.y = 1-yv.y; #endif
-
-
CG
-
CG编译方式为动态(也可以支持静态)
-
CG基本数据类型
float 32 half 16 int 32 一般当float计算 fixed 12位(PC上一般将当做float计算) bool simpler 纹理,分为sampler1D,sampler2D string(一般不被支持) -
数组
-
结构体
-
-
Unity支持Shader Target
- #prama target 2.0 D3D9 2.0不支持LOD纹理
- #prama target 2.0 D3D9 3.0支持顶点纹理采样
- #prama target 2.0 D3D10 4.0支持几何着色器
- #prama target 2.0 D3D11 5.0
-
使用ShaderLab编写简单的漫反射
CGPROGRAM #include "UnityCG.cginc" #include "UnityLightingCommon.cginc" #pragma vertex vert #pragma fragment frag //只有在CGPROGRAM再次定义一个与属性块内名字与类型相同的变量,属性块对应的变量才能起作用 fixed4 _Diffuse; struct v2f { float4 vertex: SV_POSITION; fixed3 color: Color; }; v2f vert(appdata_base v) { v2f o; o.vertex = UnityObjectToClipPos(v.vertex); fixed3 worldNormal = UnityObjectToWorldNormal(v.normal); fixed3 worldLight = normalize(_WorldSpaceLightPos0.xyz); fixed3 diffuse = _LightColor0.rgb * _Diffuse.rgb * saturate(dot(worldNormal, worldLight)); o.color = diffuse; return o; } fixed4 frag(v2f i):sv_TARGET { return fixed4(i.color, 1); } ENDCG -
基本函数
abs acos all &&运算 any ||运算 asin atan atan2(y,x) 计算y/x的反正切 ceil 向上取整 clamp x小于a,则返回a,x大于b,则返回b,否则返回x cos cosh cross(A,B) 计算另个三元向量的叉积 degrees 弧度转角度 determinant 计算矩阵的行列式因子 dot 点积 exp 计算e为底的指数函数 exp2 floor 向下取整 fmod x/y的余数 frac 返回标量或矢量的小数 frexp(x, out i) 将浮点x分解为尾数和指数 isfinite 判断标量或向量每个数据是否是有限数 isinf 判断是否是无限数 isnan 判断是否是非数据 Idexp Ierp(a,b,f) 在a和b之间进行插值,f表示权值 lit(NdotL, NdotH, m) log log2 log10 max min modf(x, out ip) 将x分解成整数和分数,整数保存在ip,分数部分由函数返回 mul(M, N) mul(v, M) mul(v, M) noise(x) 噪音函数 radians(x) 将角度转成弧度 round(x) 返回四舍五入的值 rsqrt(x) x平方的倒数,x必须大于0 saturate(x) 把x限制在0,1之间 sign(x) sin sincos(float x, out s, out c) 通过计算sin和cos,分别返回s和c sinh(x) smoothstep(min, max, x) step(a, x) sqrt(x) tan(x) tanh(x) transpose(M) M的转置 -
几何函数
distance faceforward length reflect Tex1D Tex2D -
使用逐片源绘制漫反射
CGPROGRAM #include "UnityCG.cginc" #include "UnityLightingCommon.cginc" #pragma vertex vert #pragma fragment frag //只有在CGPROGRAM再次定义一个与属性块内名字与类型相同的变量,属性块对应的变量才能起作用 fixed4 _Diffuse; struct v2f { float4 vertex: SV_POSITION; fixed3 worldNormal: TEXCOORD0; }; v2f vert(appdata_base v) { v2f o; o.vertex = UnityObjectToClipPos(v.vertex); fixed3 worldNormal = UnityObjectToWorldNormal(v.normal); o.worldNormal = worldNormal; return o; } fixed4 frag(v2f i):sv_TARGET { fixed3 ambient = UNITY_LIGHTMODEL_AMBIENT.xyz; fixed3 worldLightDir = normalize(_WorldSpaceLightPos0.xyz); fixed3 diffuse = _LightColor0.rgb * _Diffuse.rgb * saturate(dot(worldLightDir, i.worldNormal)); fixed3 color = ambient + diffuse; return fixed4(color, 1); } ENDCG -
在顶点着色器实现高光
_Diffuse("Diffuse", Color) = (1,1,1,1) _Specular("Specular", Color) = (1,1,1,1) _Gloss("Gloss", Range(0, 256)) = 5 CGPROGRAM #include "UnityCG.cginc" #include "UnityLightingCommon.cginc" #pragma vertex vert #pragma fragment frag //只有在CGPROGRAM再次定义一个与属性块内名字与类型相同的变量,属性块对应的变量才能起作用 fixed4 _Diffuse; fixed4 _Specular; float _Gloss; struct v2f { float4 vertex: SV_POSITION; fixed3 color: Color; }; v2f vert(appdata_base v) { v2f o; o.vertex = UnityObjectToClipPos(v.vertex); fixed3 ambient = UNITY_LIGHTMODEL_AMBIENT; fixed3 worldNormal = UnityObjectToWorldNormal(v.normal); fixed3 worldLight = normalize(_WorldSpaceLightPos0.xyz); fixed3 diffuse = _LightColor0.rgb * _Diffuse.rgb * saturate(dot(worldNormal, worldLight)); fixed3 reflectDir = normalize(reflect(-worldLight,worldNormal)); fixed3 viewDir = normalize(_WorldSpaceCameraPos.xyz - UnityObjectToWorldDir(v.vertex)); fixed3 specular = _LightColor0.rgb * _Specular.rgb * pow(max(0, dot(reflectDir, viewDir)), _Gloss); o.color = diffuse + specular + ambient; return o; } fixed4 frag(v2f i):sv_TARGET { return fixed4(i.color, 1); } ENDCG -
使用片源着色器绘制
CGPROGRAM #include "UnityCG.cginc" #include "UnityLightingCommon.cginc" #pragma vertex vert #pragma fragment frag //只有在CGPROGRAM再次定义一个与属性块内名字与类型相同的变量,属性块对应的变量才能起作用 fixed4 _Diffuse; float4 _Specular; float _Gloss; struct v2f { float4 vertex: SV_POSITION; fixed3 worldNormal: TEXCOORD0; float3 worldPos: TEXCOORD1; }; v2f vert(appdata_base v) { v2f o; o.vertex = UnityObjectToClipPos(v.vertex); fixed3 worldNormal = UnityObjectToWorldNormal(v.normal); o.worldNormal = worldNormal; o.worldPos = UnityObjectToWorldDir(v.vertex); return o; } fixed4 frag(v2f i):sv_TARGET { fixed3 ambient = UNITY_LIGHTMODEL_AMBIENT.xyz; fixed3 worldLightDir = normalize(_WorldSpaceLightPos0.xyz); fixed3 diffuse = _LightColor0.rgb * _Diffuse.rgb * max(0, dot(worldLightDir, i.worldNormal)); fixed3 reflectDir = normalize(reflect(-worldLightDir, i.worldNormal)); fixed3 viewDir = normalize(_WorldSpaceCameraPos.xyz - i.worldPos.xyz); fixed3 specular = _LightColor0.rgb * _Specular.rgb * pow(saturate(dot(reflectDir, viewDir)), _Gloss); fixed3 color = diffuse + specular; return fixed4(color, 1); } ENDCG在实际测试中发现,该版本的高光位置并不正确。
-
使用BinnPhong高光反射方法
fixed4 frag(v2f i):sv_TARGET { fixed3 ambient = UNITY_LIGHTMODEL_AMBIENT.xyz; fixed3 worldLightDir = normalize(_WorldSpaceLightPos0.xyz); fixed3 diffuse = _LightColor0.rgb * _Diffuse.rgb * max(0, dot(worldLightDir, i.worldNormal)); //fixed3 reflectDir = normalize(reflect(-worldLightDir, i.worldNormal)); fixed3 viewDir = normalize(_WorldSpaceCameraPos.xyz - i.worldPos.xyz); fixed3 halfDir = normalize(worldLightDir + viewDir); fixed3 specular = _LightColor0.rgb * _Specular.rgb * pow(saturate(dot(i.worldNormal, halfDir)), _Gloss); fixed3 color = diffuse + specular; return fixed4(color, 1); } -
使用纹理
_MainTex("MainTex", 2D) = "white" {} _Diffuse("Diffuse", Color) = (1,1,1,1) _Specular("Specular", Color) = (1,1,1,1) _Gloss("Gloss", Range(0, 256)) = 5 CGPROGRAM #include "UnityCG.cginc" #include "UnityLightingCommon.cginc" #pragma vertex vert #pragma fragment frag fixed4 _Diffuse; float4 _Specular; float _Gloss; sampler2D _MainTex; float4 _MainTex_ST; struct v2f { float4 vertex: SV_POSITION; fixed3 worldNormal: TEXCOORD0; float3 worldPos: TEXCOORD1; float2 uv: TEXCOORD2; }; v2f vert(appdata_base v) { v2f o; o.vertex = UnityObjectToClipPos(v.vertex); fixed3 worldNormal = UnityObjectToWorldNormal(v.normal); o.worldNormal = worldNormal; o.worldPos = mul(unity_ObjectToWorld, v.vertex); o.uv = v.texcoord.xy * _MainTex_ST.xy + _MainTex_ST.zw; return o; } fixed4 frag(v2f i):sv_TARGET { fixed3 ambient = UNITY_LIGHTMODEL_AMBIENT.xyz; fixed3 albedo = tex2D(_MainTex, i.uv).rgb; //漫反射 fixed3 worldLightDir = UnityWorldSpaceLightDir(i.worldPos); fixed3 diffuse = _LightColor0.rgb * albedo * _Diffuse.rgb * max(0, dot(worldLightDir, i.worldNormal)); //高光反射 //fixed3 reflectDir = normalize(reflect(-worldLightDir, i.worldNormal)); fixed3 viewDir = normalize(UnityWorldSpaceViewDir(i.worldPos)); fixed3 halfDir = normalize(worldLightDir + viewDir); fixed3 specular = _LightColor0.rgb * _Specular.rgb * pow(saturate(dot(i.worldNormal, halfDir)), _Gloss); fixed3 color = ambient + diffuse + specular; return fixed4(color, 1); } ENDCG -
法线贴图
_MainTex("MainTex", 2D) = "white" {} _BumpMap("Normal Map", 2D) = "bump" {} _BumpMapScale("Bump Sclse", float) = 1 _Diffuse("Diffuse", Color) = (1,1,1,1) _Specular("Specular", Color) = (1,1,1,1) _Gloss("Gloss", Range(0, 256)) = 5 CGPROGRAM #include "UnityCG.cginc" #include "UnityLightingCommon.cginc" #pragma vertex vert #pragma fragment frag fixed4 _Diffuse; float4 _Specular; float _Gloss; sampler2D _MainTex; float4 _MainTex_ST; sampler2D _BumpMap; float4 _BumpMap_ST; float _BumpMapScale; struct v2f { float4 vertex: SV_POSITION; fixed3 lightDir: TEXCOORD0; float3 viewDir: TEXCOORD1; float2 uv: TEXCOORD2; float2 normalUv: TEXCOORD3; }; v2f vert(appdata_tan v) { v2f o; o.vertex = UnityObjectToClipPos(v.vertex); o.uv = TRANSFORM_TEX(v.texcoord, _MainTex); o.normalUv = TRANSFORM_TEX(v.texcoord, _BumpMap); //求副切向向量 // flaot3 binormal = cross(normalize(v.normal), normalize(v.tangent.xyz)) * v.tangent.w; // float3x3 rotation = float3(v.tangent.xyz, binormal, v.normal); TANGENT_SPACE_ROTATION; //求切线空间光源方向及视角方向 o.lightDir = mul(rotation, ObjSpaceLightDir(v.vertex)).xyz; o.viewDir = mul(rotation, ObjSpaceViewDir(v.vertex)).xyz; return o; } fixed4 frag(v2f i):sv_TARGET { fixed3 tangentLightDir = normalize(i.lightDir); fixed3 tangentviewDir = normalize(i.viewDir); fixed4 packedNormal = tex2D(_BumpMap, i.normalUv); fixed3 tangentNormal; tangentNormal.xy = (packedNormal.xy * 2 - 1) * _BumpMapScale; tangentNormal.z = sqrt(1 - saturate(dot(tangentNormal.xy, tangentNormal.xy))); //环境光 fixed3 ambient = UNITY_LIGHTMODEL_AMBIENT.xyz; fixed3 albedo = tex2D(_MainTex, i.uv).rgb; //漫反射 fixed3 diffuse = _LightColor0.rgb * albedo * _Diffuse.rgb * max(0, dot(tangentLightDir, tangentNormal)*0.5 + 0.5); //高光反射 fixed3 halfDir = normalize(tangentLightDir + tangentviewDir); fixed3 specular = _LightColor0.rgb * _Specular.rgb * pow(saturate(dot(tangentNormal, halfDir)), _Gloss); fixed3 color = ambient + diffuse + specular; return fixed4(color, 1); } ENDCG当将贴图设置成法线贴图时,可以省略一些计算
fixed3 tangentNormal = UnpackNormal(packedNormal); tangentNormal.xy *= _BumpMapScale; //tangentNormal.z = sqrt(1 - saturate(dot(tangentNormal.xy, tangentNormal.xy))); -
在顶点着色器中计算法线贴图
CGPROGRAM #include "UnityCG.cginc" #include "UnityLightingCommon.cginc" #pragma vertex vert #pragma fragment frag fixed4 _Diffuse; float4 _Specular; float _Gloss; sampler2D _MainTex; float4 _MainTex_ST; sampler2D _BumpMap; float4 _BumpMap_ST; float _BumpMapScale; struct v2f { float4 vertex: SV_POSITION; float4 uv: TEXCOORD0; float4 TtiW0: TEXCOORD1; float4 TtiW1: TEXCOORD2; float4 TtiW2: TEXCOORD3; }; v2f vert(appdata_tan v) { v2f o; o.vertex = UnityObjectToClipPos(v.vertex); o.uv.xy = TRANSFORM_TEX(v.texcoord, _MainTex); o.uv.zw = TRANSFORM_TEX(v.texcoord, _BumpMap); //计算世界坐标下蹲顶点,法线,切线,副法线 float3 worldPos = mul(unity_ObjectToWorld, v.vertex).xyz; fixed3 worldNormal = UnityObjectToWorldNormal(v.normal); fixed3 worldTangent = UnityObjectToWorldDir(v.tangent.xyz); fixed3 worldBinormal = cross(worldNormal, worldTangent) * v.tangent.w; //按列摆放得到从切线空间到世界空间的变换矩阵 o.TtiW0 = float4(worldTangent.x, worldBinormal.x, worldNormal.x, worldPos.x); o.TtiW1 = float4(worldTangent.y, worldBinormal.y, worldNormal.y, worldPos.y); o.TtiW2 = float4(worldTangent.z, worldBinormal.z, worldNormal.z, worldPos.z); return o; } fixed4 frag(v2f i):sv_TARGET { //求世界坐标 float3 worldPos = float3(i.TtiW0.w, i.TtiW1.w, i.TtiW2.w); //计算时间空间下的光照和视角 fixed3 lightDir = normalize(UnityWorldSpaceLightDir(worldPos)); fixed3 viewDir = normalize(UnityWorldSpaceViewDir(worldPos)); //获得法线纹理 fixed4 packedNormal = tex2D(_BumpMap, i.uv.zw); fixed3 tangentNormal = UnpackNormal(packedNormal); //切线空间法线转换到世界坐标 fixed3 worldNormal = normalize(float3(dot(i.TtiW0.xyz, tangentNormal), dot(i.TtiW1.xyz, tangentNormal), dot(i.TtiW2.xyz, tangentNormal))); //环境光 fixed3 ambient = UNITY_LIGHTMODEL_AMBIENT.xyz; fixed3 albedo = tex2D(_MainTex, i.uv.xy).rgb; //漫反射 fixed3 diffuse = _LightColor0.rgb * albedo * _Diffuse.rgb * max(0, dot(lightDir, worldNormal)*0.5 + 0.5); //高光反射 fixed3 halfDir = normalize(lightDir + viewDir); fixed3 specular = _LightColor0.rgb * _Specular.rgb * pow(saturate(dot(worldNormal, halfDir)), _Gloss); fixed3 color = ambient + diffuse + specular; return fixed4(color, 1); } ENDCG -
渐变纹理
- 用于制作类似卡通模型的效果
-
遮罩纹理
- 用于遮罩一些高光
-
透明效果
- Unity渲染顺序
- Background 1000 背景
- Geometry 2000 不透明物体
- AlphaTest 2450 需要透明测试的物体
- Transparent 3000 透明物体
- Overlay 4000 堆叠效果
- Unity渲染顺序
-
使用半透明图像+AlphaTest实现半透明物体
Shader "Unlit/001" { Properties { _MainTex("MainTex", 2D) = "white" {} _Diffuse("Diffuse", Color) = (1,1,1,1) _Cutoff("Alpha Cutoff", Range(0, 1)) = 0.5 } SubShader { Tags {"Queue" = "AlphaTest" "IgnoreProjector"="True"} LOD 100 Pass { CGPROGRAM #include "UnityCG.cginc" #include "UnityLightingCommon.cginc" #pragma vertex vert #pragma fragment frag fixed4 _Diffuse; sampler2D _MainTex; float4 _MainTex_ST; float _Cutoff; struct v2f { float4 vertex: SV_POSITION; fixed3 worldNormal: TEXCOORD0; float3 worldPos: TEXCOORD1; float2 uv: TEXCOORD2; }; v2f vert(appdata_base v) { v2f o; o.vertex = UnityObjectToClipPos(v.vertex); fixed3 worldNormal = UnityObjectToWorldNormal(v.normal); o.worldNormal = worldNormal; o.worldPos = mul(unity_ObjectToWorld, v.vertex); o.uv = v.texcoord.xy * _MainTex_ST.xy + _MainTex_ST.zw; return o; } fixed4 frag(v2f i):sv_TARGET { fixed3 ambient = UNITY_LIGHTMODEL_AMBIENT.xyz; fixed4 texColor = tex2D(_MainTex, i.uv); if((texColor.a - _Cutoff) < 0) { discard; } //漫反射 fixed3 worldLightDir = UnityWorldSpaceLightDir(i.worldPos); fixed3 diffuse = _LightColor0.rgb * texColor.rgb * _Diffuse.rgb * max(0, dot(worldLightDir, i.worldNormal) * 0.5 + 0.5); fixed3 color = ambient + diffuse; return fixed4(color, 1); } ENDCG } } //Fallback "Legacy Shaders/Transparent/VertexLit" Fallback Off//当Shader运行不了的时候会显示下面的Shader } -
Blend混合
-
命令
- Blend Srcfactor DstFactor 开启混合,使用源颜色混合因子和目标颜色混合因子
- Blend SrcFactor DstFactor,SrcFactorA DstFactorA 开启混合,但单独使用另外的混合因子混合Alpha通道
-
混合因子
One
Zero
SrcColor
SrcAlpha
DstColor
DstAlpha
OneMinusSrcColor
OneMinusSrcAlpha
OneMinusDstColor
OneMinusDstAlpha
-
混合操作
Add
Sub
RevSub
Min
Max
-
常用的混合类型
- 正常 Blend SrcAlpha OneMinusSrcAlpha
- 柔和相加 Blend OneMinusDstColor One
- 正片叠底 Blend DstColor Zero
- 两倍相乘 Blend DstColor SrcColor
- 变暗 BlendOp min/Blend One One
- 变量 Blend OneMinusDstColor One/Blend One OneMinusSrcColor
- 线性减淡 Blend One One
-
-
实现半透明效果
Shader "Unlit/001" { Properties { _MainTex("MainTex", 2D) = "white" {} _Diffuse("Diffuse", Color) = (1,1,1,1) _AlphaScale("Alpha Scale", Range(0, 1)) = 1 } SubShader { Tags {"Queue" = "Transparent" "IgnoreProjector"="True" "RenderType" = "Transparent"} LOD 100 ZWrite Off Blend SrcAlpha OneMinusSrcAlpha Pass { Tags{"LightMode" = "ForwardBase"} CGPROGRAM #include "UnityCG.cginc" #include "UnityLightingCommon.cginc" #pragma vertex vert #pragma fragment frag fixed4 _Diffuse; sampler2D _MainTex; float4 _MainTex_ST; float _AlphaScale; struct v2f { float4 vertex: SV_POSITION; fixed3 worldNormal: TEXCOORD0; float3 worldPos: TEXCOORD1; float2 uv: TEXCOORD2; }; v2f vert(appdata_base v) { v2f o; o.vertex = UnityObjectToClipPos(v.vertex); fixed3 worldNormal = UnityObjectToWorldNormal(v.normal); o.worldNormal = worldNormal; o.worldPos = mul(unity_ObjectToWorld, v.vertex); o.uv = v.texcoord.xy * _MainTex_ST.xy + _MainTex_ST.zw; return o; } fixed4 frag(v2f i):sv_TARGET { fixed3 ambient = UNITY_LIGHTMODEL_AMBIENT.xyz; fixed4 texColor = tex2D(_MainTex, i.uv); //漫反射 fixed3 worldLightDir = UnityWorldSpaceLightDir(i.worldPos); fixed3 diffuse = _LightColor0.rgb * texColor.rgb * _Diffuse.rgb * (dot(worldLightDir, i.worldNormal) * 0.5 + 0.5); fixed3 color = ambient + diffuse; return fixed4(color, texColor.a * _AlphaScale); } ENDCG } } Fallback "Transparent/VertexLit" } -
针对同一个物体复杂形状
在上节的基础上,新增加一个Pass通道,只写入深度值
Pass { ZWrite On //意味着不写入任何颜色通道 ColorMask 0 }