首先,需要创建一个订单表
在创建模型的时候再创建数据库迁移文件
php artisan make:model Order -m
完善数据库字段
public function up()
{
Schema::create('orders', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->id();
$table->integer('user_id')->comment('下单的用户');
$table->string('order_on')->comment('订单单号');
$table->decimal('amount')->comment('总金额');
$table->tinyInteger('status')->default(1)->comment('订单状态 1下单 2支付 3发货 4收货');
$table->integer('address_id')->comment('收货地址');
$table->string('express_type')->comment('快递类型 SF YT YD');
$table->string('express_no')->comment('快递单号');
$table->timestamp('pay_time')->nullable()->comment('支付时间');
$table->string('pay_type')->nullable()->comment('支付类型:支付宝 微信');
$table->string('trade_no')->nullable()->comment('支付单号');
$table->timestamps();
});
}
由于一个订单可能会包含多个商品,使用,需要一个从表
创建订单详情模型并创建数据库迁移文件
php artisan make:model OrderDetails -m
完善数据库字段
public function up()
{
Schema::create('order_details', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->id();
$table->integer('order_id')->comment('所属订单');
$table->integer('goods_id')->comment('商品');
//为什么要设置订单价格,因为要以用户支付时的价格为准,不得去以商品的价格为准
$table->integer('price')->comment('商品的价格');
$table->integer('num')->comment('商品数量');
$table->timestamps();
});
}
现在可以创建订单的控制器了
在订单控制器中
/*
* 订单列表
*/
public function index(Request $request)
{
//查询条件
//订单号
$order_no = $request->input('order_no');
//支付单号
$trade_no = $request->input('trade_no');
//订单状态
$status = $request->input('status');
$orders = Order::when($order_no,function ($query) use ($order_no){
$query->where('order_no',$order_no);
})->when($trade_no,function ($query) use ($trade_no){
$query->where('trade_no',$trade_no);
})->when($status,function ($query) use ($status){
$query->where('status',$status);
})->paginate();
return $this->response->paginator($orders, new OrderTransformer());
}
然后再去创建订单的Transformer文件
需要返回的数据字段
public function transform(Order $order)
{
return [
'id' => $order->id,
'order_no' => $order->order_on,
'user_id' => $order->user_id,
'amount' => $order->amount,
'status' => $order->status,
'address_id' => $order->address_id,
'express_type' => $order->express_type,
'express_no' => $order->express_no,
'pay_time' => $order->pay_time,
'pay_type' => $order->pay_type,
'trade_no' => $order->trade_no,
'created_at' => $order->created_at,
'updated_at' => $order->updated_at,
];
}
然后数据就可以正常返回了,但是,有没有感觉数据有点简单?
比如,那不可能再去根据user_id再去写一遍查询吧?
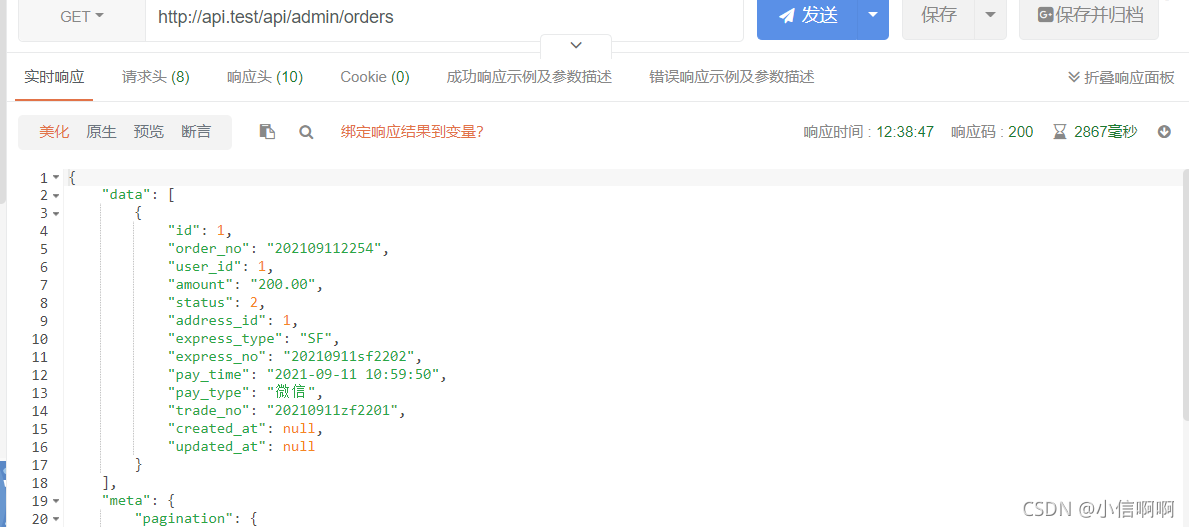
所以,laravel的dingoApi提供了可以返回额外的数据的方法,这都是laravel-dingoApi封装好的方法了
在Transformer文件中定义一个受保护的方法
//该方法提供返回额外的数据
protected $availableIncludes = ['user', 'orderDetails'];
然后对应路由中的非必填参数query
键:include 值:是定义availableIncludes 数据里面的值
例如,我想在额外返回用户数据
那么就include:user
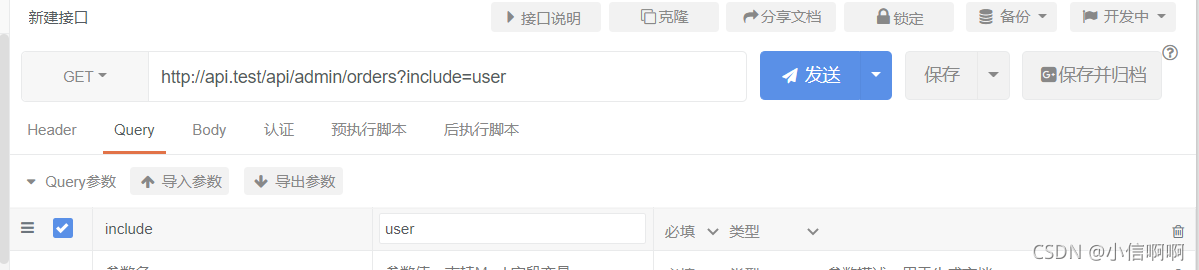
返回多个额外数据使用,分隔
如果想要进一层的获取数据,使用.号
例如
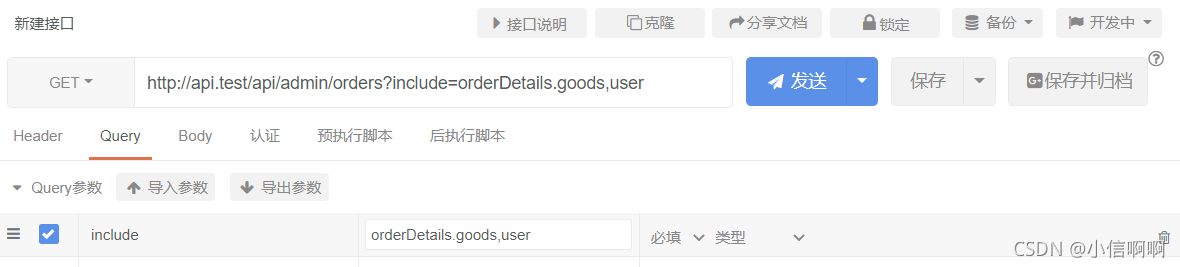
当然,需要获取额外的数据,只定义了$availableIncludes 是不够的,还需要定义相对应的关联
例如:
注:还是在Transformer中定义的方法
/*
* 额外的用户数据
*/
public function includeUser(Order $order)
{
return $this->item($order->user, new UserTransformer());
}
/*
* 额外的订单数据
*/
public function includeorderDetails(Order $order)
{
return $this->collection($order->orderDetails, new OrderDetailsTransformer());
}
其中,includeUser(Order $order)这样的写法laravel会默认分解为从当前模型中定义的模型关联去获取的数据
includeUser(Order $order)这个就是说从Order模型中去获取User关联,来,我们来看看order模型中的关联
果然,order模型中是包含user关联的

我定义的两个关联是
/**
* 所属用户
*/
public function user()
{
return $this->belongsTo(User::class, 'user_id', 'id');
}
/*
* 订单拥有的订单细节
*/
public function orderDetails(){
return $this->hasMany(OrderDetails::class,'order_id','id');
}
这样定义就可以实现使用Transformer返回额外的数据了,但是,我在上面有提到过还可以获取更深层的数据,是使用.号来使用,
比如:orderDetails.goods是说在OrderTransformer中的includeorderDetails找到与之对应的goods关联
来,看看有没有关联
果然
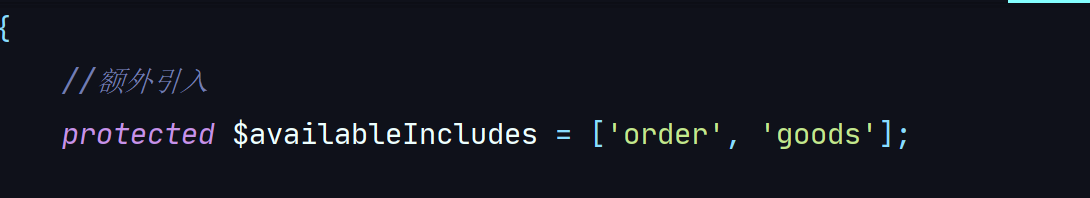
可以发现,是有goods的
/*
* 额外的商品
*/
public function includeGoods(OrderDetails $orderDetails)
{
return $this->item($orderDetails->goods, new GoodTransformer());
}
所以,这样是可以获取数据了,
其实,也不推荐获取更多层的数据了,一般两次就够用了,再多了会造成我思路的混乱
补充:需要使用dingoapi的话,
是需要去引入的,像我自己的话,是去引入到controller中,
首先,创建一个BaseController控制器,
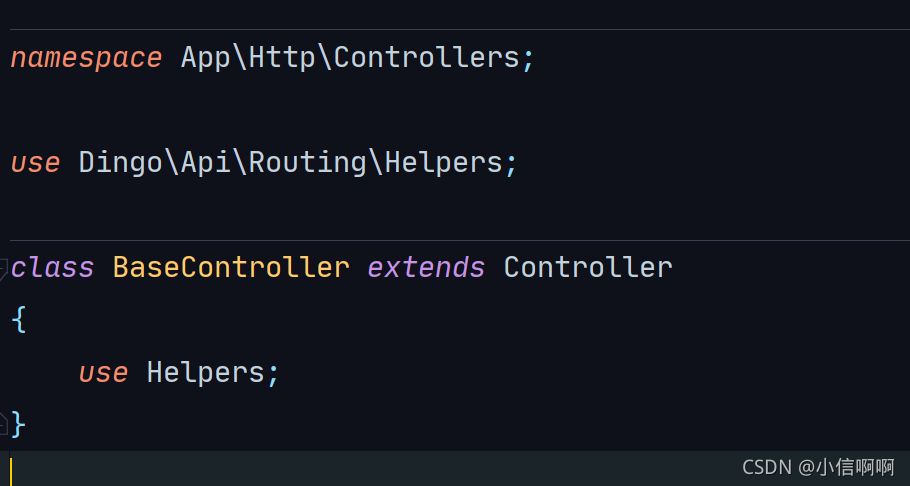
是引入Helpers才可以使用的,
引入之后,就直接继承BaseController就可以使用了
