在打包原生包的时候js层想调用c++层,但是没有对应的实现需要自己扩展自己的jsb,官方有两种绑定方式:手动绑定和自动绑定,这里着重介绍手动绑定:
首先找到cocos creator自带的c++层的源码,复制出来然后自定义引擎,这里我也不细讲了,感兴趣的可以去看看官网的文档。
将c++层的jswrap 主要的目录如下:
?找到手动manual文件夹下在这里创建自己的c++文件就可以了
?这里作为测试我创建了文件 jsb_test.hpp jsb_test.cpp
test.hpp:
#pragma once
namespace se
{
class Object;
}
bool register_all_testio(se::Object* obj);
test.cpp:
#include "jsb_test.hpp"
#include "cocos/scripting/js-bindings/manual/jsb_conversions.hpp"
#include "cocos/scripting/js-bindings/jswrapper/SeApi.h"
#include "stdio.h"
#include "test.hpp"
#include<iostream>
/**
* 整形:
* short 2字节 -2^15 ~ 2^15 - 1 -32768 ~ 32767 short a = 32768 => a = -32768;
* int 4字节
* long 4字节
* long long 8字节
*
* 实型
* float 4字节
* double 8字节
*
* 字符型
* char 1字节
*
*
*/
using namespace std;
static se::Object* __jsb_test_proto = nullptr;
static se::Class* __jsb_test_class = nullptr;
static bool jsb_Test(se::State &s) {
// char* a = "ads";
CC_UNUSED std::string ok = "";
std::string result = "测试指令";
ok = std_string_to_seval(result,&s.rval());
return true;
}
SE_BIND_FUNC(jsb_Test);
static bool jsb_Console(se::State &s) {
cout << s.args()[0].toString() << endl;
return true;
}
SE_BIND_FUNC(jsb_Console);
// 析构函数
static bool jsb_finalize(se::State& s) {
cout << "析构函数调用" << endl;
ns::TestJsb* obj = (ns::TestJsb*)s.nativeThisObject();
delete obj;
return true;
}
// 绑定析构函数
SE_BIND_FINALIZE_FUNC(jsb_finalize);
// 构造函数
static bool jsb_constructor(se::State& s) {
cout << "构造函数调用" << endl;
ns::TestJsb* obj = new ns::TestJsb();
s.thisObject()->setPrivateData(obj);
return true;
}
// 绑定构造函数
SE_BIND_CTOR(jsb_constructor, __jsb_test_class,jsb_finalize);
// get方法
static bool jsb_getName(se::State& s) {
// 拿到nativeObject 的属性name值
ns::TestJsb* obj = (ns::TestJsb*)s.nativeThisObject();
cout << "name is " << obj->getName() << endl;
s.rval().setString(obj->getName());
return true;
}
SE_BIND_PROP_GET(jsb_getName);
// set方法
static bool jsb_setName(se::State& s) {
std::cout << "设置名字" << std::endl;
cout << "参数是:" << s.args()[0].toString() << endl;
ns::TestJsb* obj = (ns::TestJsb*)s.nativeThisObject();
const std::string& a0 = s.args()[0].toString();
obj->setName(a0.c_str());
cout << "设置名字完毕" << endl;
return true;
}
SE_BIND_PROP_SET(jsb_setName);
static bool jsb_staticFunction(se::State& s) {
ns::TestJsb::goHome();
return true;
}
SE_BIND_FUNC(jsb_staticFunction);
// 回调函数
static bool jsb_callback(se::State& s) {
const auto& args = s.args();
int argc = (int)args.size();
if(argc == 0) {
cout << "参数个数错误" << endl;
return false;
}
ns::TestJsb* cobj = (ns::TestJsb*)s.nativeThisObject();
se::Value jsFunc = args[0];
se::Value jsTarget = argc > 1 ? args[1] : se::Value::Undefined;
if(jsFunc.isNullOrUndefined()) {
cobj->setCallback(nullptr);
} else {
assert(jsFunc.isObject() && jsFunc.toObject()->isFunction());
s.thisObject()->attachObject(jsFunc.toObject());
s.thisObject()->attachObject(jsTarget.toObject());
cobj->setCallback([jsFunc,jsTarget](int counter) {
cout << "回调函数调用了: counter is " << endl;
char* a = "sd";
printf("counter is %d",counter);
se::ScriptEngine::getInstance()->clearException();
se::AutoHandleScope hs;
se::ValueArray args;
args.push_back(se::Value(counter));
se::Object* target = jsTarget.isObject() ? jsTarget.toObject(): nullptr;
jsFunc.toObject()->call(args,target);
});
}
return true;
}
SE_BIND_FUNC(jsb_callback);
bool register_all_testio(se::Object* obj) {
se::Value nsVal;
if(!obj->getProperty("ns", &nsVal)) {
// 不存在则创建一个js对象,相当于 let ns = {}
se::HandleObject jsObj(se::Object::createPlainObject());
// 给一个js对象设置一个全局对象
nsVal.setObject(jsObj);
// 将ns对象挂载到global对象上 名称为ns
obj->setProperty("ns", nsVal);
}
se::Object* nsObj = nsVal.toObject();
// 如果最后一个参数传入nullptr 则这个类在js中无法被new出来
se::Class* cls = se::Class::create("TestJsb",nsObj,nullptr,_SE(jsb_constructor));
cls->defineProperty("name",_SE(jsb_getName),_SE(jsb_setName));
/** 设置jsObject 对象方法名称 */
cls->defineFunction("test",_SE(jsb_Test));
cls->defineFunction("console",_SE(jsb_Console));
// 定义析构函数
cls->defineFinalizeFunction(_SE(jsb_finalize));
/** Install into jsvm*/
cls->install();
JSBClassType::registerClass<ns::TestJsb>(cls);
__jsb_test_proto = cls->getProto();
__jsb_test_class = cls;
__jsb_test_proto->setProperty("id",se::Value("test1"));
se::Value ctorVal;
// 定义静态成员和静态函数
if(nsObj->getProperty("TestJsb",&ctorVal) && ctorVal.isObject()) {
cout << "构造函数存在" << endl;
ctorVal.toObject()->setProperty("age", se::Value(22));
ctorVal.toObject()->defineFunction("goHome", _SE(jsb_staticFunction));
}
// ctorVal.toObject();
// cout << ctorVal.toObject()->getProperty("age",se::Value(22)) << endl;
se::ScriptEngine::getInstance()->clearException();
return true;
}
注意这些方法的操作对应的有个类支撑: TestJsb可以理解成mode,对应的是文件 test.hpp test.cpp
test.hpp:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
namespace ns {
class TestJsb {
private:
std::string name;
std::function<void(int)> _cb;
public:
void test();
void console(const std::string& msg);
void setName(const char* nameStr);
string& getName();
void setCallback(const std::function<void(int)>& cb);
static void goHome() {
cout << "静态函数goHome" << endl;
}
};
};
test.cpp:
#include "test.hpp"
void ns::TestJsb::setName(const char* nameStr) {
cout << "setName 里面的名字 " << nameStr << endl;
this->name = nameStr;
}
void ns::TestJsb::setCallback(const std::function<void (int)> &cb) {
_cb = cb;
if(cb !== nullptr) {
cout << "设置了回调函数" << endl;
} else {
cout << "回调函数是空的" << endl;
}
}
string& ns::TestJsb::getName() {
return this->name;
}
void ns::TestJsb::test() {
}
void ns::TestJsb::console(const std::string& msg) {
cout << "msg is " << msg << endl;
}
js层:
onLoad() {
if (typeof jsb === 'undefined') return;
if(typeof ns !== 'undefined' && ns.TestJsb) {
const jsbTestObj = new ns.TestJsb();
console.log('jsbTestObj is ',jsbTestObj);
jsbTestObj.console("hello my baby");
// jsbTestObj.name = "nb";
console.log('name is ',jsbTestObj.name);
jsbTestObj.name = "lck";
console.log('After set name,name is ',jsbTestObj.name);
console.log('age is ',jsbTestObj.age);
console.log('id is ',jsbTestObj.id);
// 静态函数调用
if(ns.TestJsb.goHome) {
ns.TestJsb.goHome();
}
if(ns.TestJsb.age) {
console.log(ns.TestJsb.age);
}
} else {
console.log('testJsb is not founded');
console.log('ns is ',ns);
}
}?打包原生工程之后会发现cocos2d_libs.xcodeproj里面没有刚刚写好的c++文件,我的做法是复制进去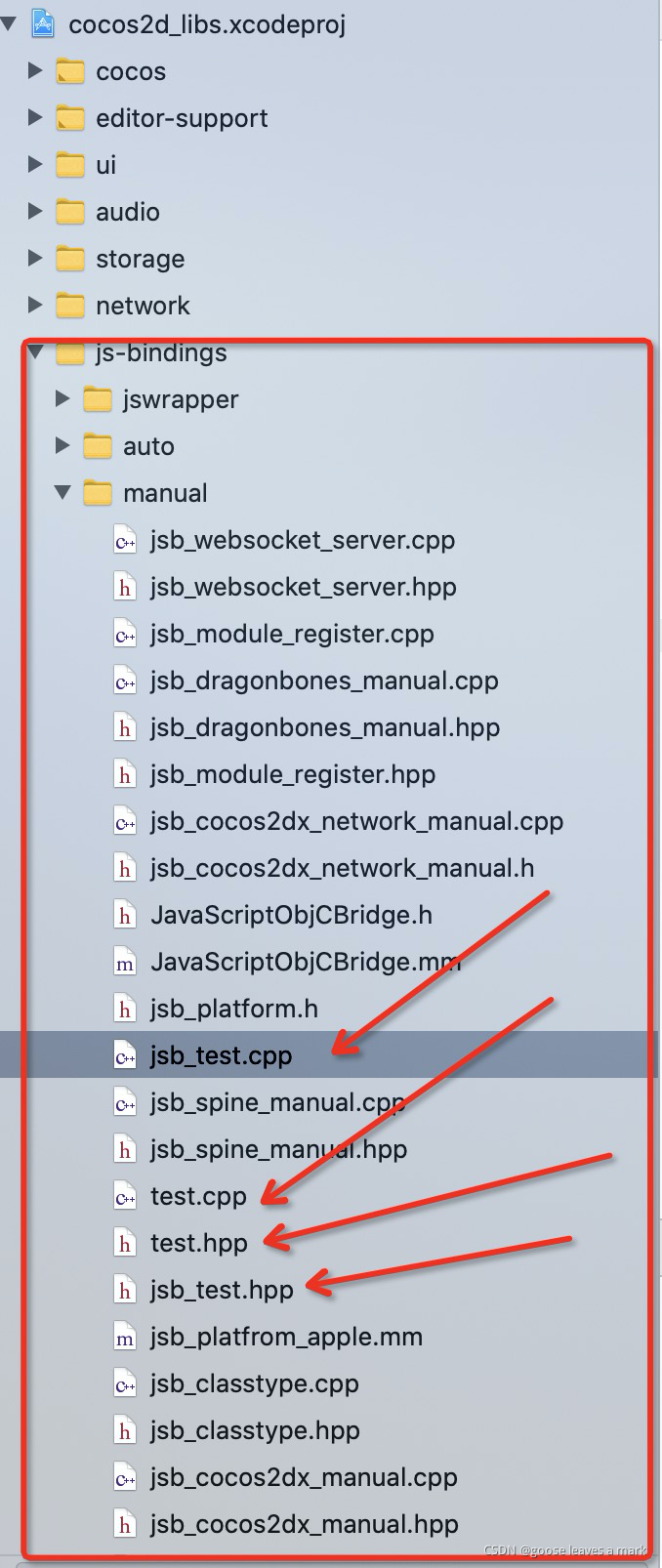
最后别忘记手动注册你写的模块,在jsb_module_register.cpp里面引入你自己的文件:比如:
#include "jsb_test.hpp"
#include<iostream>
#endif // (CC_TARGET_PLATFORM == CC_PLATFORM_IOS || CC_TARGET_PLATFORM == CC_PLATFORM_ANDROID)
using namespace cocos2d;
using namespace std;
bool jsb_register_all_modules()
{
se::ScriptEngine* se = se::ScriptEngine::getInstance();
se->addBeforeInitHook([](){
JSBClassType::init();
});
se->addBeforeCleanupHook([se](){
se->garbageCollect();
PoolManager::getInstance()->getCurrentPool()->clear();
se->garbageCollect();
PoolManager::getInstance()->getCurrentPool()->clear();
});
se->addRegisterCallback(jsb_register_global_variables);
se->addRegisterCallback(JSB_register_opengl);
se->addRegisterCallback(register_all_engine);
se->addRegisterCallback(register_all_cocos2dx_manual);
se->addRegisterCallback(register_platform_bindings);
se->addRegisterCallback(register_all_network);
se->addRegisterCallback(register_all_cocos2dx_network_manual);
se->addRegisterCallback(register_all_xmlhttprequest);
// extension depend on network
se->addRegisterCallback(register_all_extension);
cout << "注册自己的模块" << endl;
se->addRegisterCallback(register_all_testio);
这就是jsb2.0手动绑定的全过程,是不是很简单?
?
总结下来就是js想调用c++层的方法,对应着c++层有对应的类对象方法和属性,只有这样js ,c++ 才能交互,内部原理就是c++层暴露出static方法给v8(js的底层实现),这样js就可以调用这些接口从而实现交互