Lammps之定压比热熔计算
该文章由
D
r
.
X
i
a
n
\color{Violet} \rm Dr. Xian
Dr.Xian 撰写,主要介绍
l
a
m
m
p
s
\color{Violet} lammps
lammps 计算定压比热容方法。
?
\heartsuit
?
E
m
a
i
l
:
\rm \color{Violet}Email:
Email:Victor_Xian285@163.com
前言
比热容反映了物质储存热量的能力,是考核储能系统材料性质的关键指标之一。仿真研究过程中我们通常需要对多个体系进行比热容计算以分析相关因素对体系比热容大小的影响,难免对多体系重复计算并处理繁多复杂的数据结果。使用循环计算的方式对比热容进行计算可以大大简化计算过程,使用python方便对数据大规模数据。
提示:以下是本篇文章正文内容,下面案例以计算不同尺寸Ar体系比热容为例,可供参考。
一、定压比热容计算方法

定压比热容
C
p
Cp
Cp定义:在压强不变的情况下,单位质量的某种物质温度升高1K所需吸收的热量。
根据定义计算公式如下:
因此需要在MD计算时导出体系在温度变化过程中的总能变化、体系体积以及密度,lammps中dump命令可直接实现。
C
p
=
(
Δ
Q
Δ
T
V
ρ
)
\color{Violet} C_{p}=\left ( \frac{\Delta Q}{\Delta T V\rho} \right )
Cp?=(ΔTVρΔQ?)
二、lammps计算之In文件
本计算用到了之前博客
《
L
A
M
M
P
S
非
平
衡
分
子
动
力
学
(
N
E
M
D
)
纳
米
线
热
导
率
教
程
—
一
个
代
码
循
环
计
算
不
同
温
度
和
尺
寸
》
\color{Violet}《LAMMPS非平衡分子动力学 (NEMD) 纳米线热导率教程—一个代码循环计算不同温度和尺寸》
《LAMMPS非平衡分子动力学(NEMD)纳米线热导率教程—一个代码循环计算不同温度和尺寸》 中循环计算的技巧,在这里不过多赘述,详情可见链接: link.
in文件Ar模型建立及比热容计算部分,主要是对Ar升温过程中总能进行统计,(
V
\color{Violet}V
V×
ρ
\color{Violet}ρ
ρ)体系质量不变。
echo screen
units metal
dimension 3
boundary p p p
atom_style full
# 定义几个参数
variable T equal ${loop_file_out_name} # 温度
variable TS equal 0.01 # timestep
timestep ${TS}
variable Tdamp equal 100*${TS} # Tdamp 1
variable Pdamp equal 1000*${TS} # Pdamp 2
# 初始化坐标、势函数、速度等数据
variable A equal 5.4
variable z_length equal ${A}*${loop_file_in_name}*2
variable x_length equal ${A}*10
variable y_length equal ${A}*10
lattice fcc ${A}
region box block 0 ${x_length} &
0 ${y_length} &
0 ${z_length} units box #模型x,y长度54,z长度变化
create_box 1 box
create_atoms 1 box
mass 1 40
pair_style lj/cut 10.0 # LJ 势的截断半径取10 A
pair_coeff * * 1.032e-2 3.405 # epsilon 和 sigma
velocity all create ${T} 12345
neighbor 2 bin
neigh_modify every 5 delay 0 check no
minimize 1.0e-5 1.0e-7 1000 10000
write_data system.data
##------------------ step 4 ----------------##
#------------------循环驰豫-------------------#
#--------------------------------------------#
# loop relax system 50 ps
#--------------------------------------------#
variable 50_ps equal 50/${TS}
variable 500_ps equal 500/${TS}
variable loop_all_num equal 5
variable relax_system loop ${loop_all_num}
label loop
fix NVT all nvt temp ${T} ${T} ${Tdamp}
run ${50_ps}
unfix NVT
minimize 1.0e-5 1.0e-7 1000 10000
minimize 1.0e-5 1.0e-7 1000 10000
next relax_system
jump SELF loop
##------------------ step 5 ---------------##
#----------------比热容计算------------------#
#------------------------------------------#
thermo 500
thermo_style custom step temp vol density ke pe etotal enthalpy
fix 1 all npt temp ${T} ${T} ${Tdamp} iso 1 1 ${Pdamp}
run 100000
unfix 1
fix 2 all npt temp ${T} 150 ${Tdamp} iso 1 1 ${Pdamp}
run 100000
unfix 2
fix 3 all npt temp ${T} ${T} ${Tdamp} iso 1 1 ${Pdamp}
run 100000
unfix 3
二、数据处理之热熔计算-Python脚本拟合
使用总能与温度的斜率进行计算可提高结果准确度,计算代码如下:

"""
Created on Mon Nov 9 22:46 2021
#-------------------------------#
@author: Dr.Xian
Email: Victor_Xian285@163.com
#-------------------------------#
"""
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import pylab
import matplotlib.ticker as plticker
from matplotlib.pyplot import MultipleLocator
import xlrd
from matplotlib.lines import Line2D
import math
from scipy import optimize
def f_1(x, A, B):
return A * x + B
plt.style.use('science')
def setup(ax,x_label,y_label):
# 边框线的线宽设置
width = 1.5
ax.spines['top'].set_linewidth(width)
ax.spines['bottom'].set_linewidth(width)
ax.spines['left'].set_linewidth(width)
ax.spines['right'].set_linewidth(width) #
# 边框上的刻度的出现
ax.tick_params(top='on', bottom='on', left='on', right='on', direction='in')
# 边框上的ticks对应的lable,即数字的尺寸
ax.tick_params(labelsize=20,pad=6)
#ax.yaxis.set_ticks_position('right')
ax.tick_params(which='major', width=1.50, length=6)
ax.tick_params(which='minor', width=0.75, length=0)
# 边框上的ticks的出现的间隔
locx = plticker.MultipleLocator(base=10)
ax.xaxis.set_major_locator(locx)
locy = plticker.MultipleLocator(base=200)
ax.yaxis.set_major_locator(locy)
# 边框上的注释labels
labels = ax.get_xticklabels() + ax.get_yticklabels()
[label.set_fontname('Times New Roman') for label in labels]
# 边框上的注释labels距离坐标轴的距离
xAxisLable = x_label
yAxisLable = y_label
ax.set_xlabel(xAxisLable, font1, labelpad=5)
ax.set_ylabel(yAxisLable, font1, labelpad=5)
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------#
# 读取excel
excel_path = r"Ar_Cp.xlsx"
work_sheet = xlrd.open_workbook(excel_path);
# sheet的数量
sheet_num = work_sheet.nsheets;
# 获取sheet name
sheet_name = []
for sheet in work_sheet.sheets():
sheet_name.append(sheet.name)
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------#
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------#
for sheet_num in range(1):
# 选取sheet
now_sheet = work_sheet.sheets()[0]
#now_sheet_ref = work_sheet.sheets()[3]
# sheet的行
row = now_sheet.nrows
# sheet的列
ncol = now_sheet.ncols
#----------------------------------------------------------------------#
#----------------------------------------------------------------------#
font1 = {'family': 'Times New Roman',
'weight': 'bold',
'size': 18,
}
font2 = {'family': 'Times New Roman',
'weight': 'normal',
'size': 11,
}
#----------------------------------------------------------------------#
# Total energy
y10 = now_sheet.col_values(1)
y10_matrix = list(filter(None, y10[1:]))
y15 = now_sheet.col_values(3)
y15_matrix = list(filter(None, y15[1:]))
y20 = now_sheet.col_values(5)
y20_matrix = list(filter(None, y20[1:]))
y25 = now_sheet.col_values(7)
y25_matrix = list(filter(None, y25[1:]))
# temp
x10 = now_sheet.col_values(0)
x10_matrix = list(filter(None, x10[1:]))
x15 = now_sheet.col_values(2)
x15_matrix = list(filter(None, x15[1:]))
x20 = now_sheet.col_values(4)
x20_matrix = list(filter(None, x20[1:]))
x25 = now_sheet.col_values(6)
x25_matrix = list(filter(None, x25[1:]))
markersize = 10
linewidth = 3
markevery =1
alpha =1
p_1 = dict(marker='o',color = 'k',linestyle = 'none',markevery=markevery,markerfacecolor='none',markersize=markersize,linewidth=linewidth,alpha=alpha)
p_2 = dict(marker='s',color = 'b',linestyle = 'none',markevery=markevery,markerfacecolor='none',markersize=markersize,linewidth=linewidth,alpha=alpha)
p_3 = dict(marker='<',color = 'g',linestyle = 'none',markevery=markevery,markerfacecolor='none',markersize=markersize,linewidth=linewidth,alpha=alpha)
p_4 = dict(marker='>',color = 'y',linestyle = 'none',markevery=markevery,markerfacecolor='none',markersize=markersize,linewidth=linewidth,alpha=alpha)
p_5 = dict(marker='o',color = 'm',linestyle = 'none',markevery=markevery,markerfacecolor='none',markersize=markersize,linewidth=linewidth,alpha=alpha)
p_6 = dict(marker='^',color = 'c',linestyle = 'none',markevery=markevery,markerfacecolor='none',markersize=markersize,linewidth=linewidth,alpha=alpha)
p_7 = dict(marker='p',color = 'r',linestyle = 'none',markevery=markevery,markerfacecolor='none',markersize=markersize,linewidth=linewidth,alpha=alpha)
alpha=1
p_11 = dict(color = 'r',linestyle = '--',linewidth=linewidth,alpha=alpha)
p_22 = dict(color = 'b',linestyle = '--',linewidth=linewidth,alpha=alpha)
p_33 = dict(color = 'g',linestyle = '--',linewidth=linewidth,alpha=alpha)
p_44 = dict(color = 'y',linestyle = '--',linewidth=linewidth,alpha=alpha)
p_55 = dict(color = 'm',linestyle = '--',linewidth=linewidth,alpha=alpha)
p_66 = dict(color = 'c',linestyle = '--',linewidth=linewidth,alpha=alpha)
p_77 = dict(color = 'r',linestyle = '--',linewidth=linewidth,alpha=alpha)
p_s_1 =dict(marker='o',markersize=10,ecolor='darkorange',color='darkorange',\
elinewidth=2, ls='none', alpha=1,capsize=8)
#----------------------------------------------------------------------#
fig, axe = plt.subplots(1, 1, figsize=(5,5))
xxx = np.arange(20)
axe.plot(x10_matrix, y10_matrix,**p_1,label='10.8 nm')
axe.plot(x15_matrix, y15_matrix,**p_2,label='16.2 nm')
axe.plot(x20_matrix, y20_matrix,**p_3,label='21.6 nm')
axe.plot(x25_matrix, y25_matrix,**p_4,label='27.0 nm')
#A25单位eV/K; V单位A3; rou单位g/cm3
cmdim2mdim = 1e-6
Adim2mdim = 1e-30
g2Kg = 1e-3
ev2kJ = 1.6*1e-22
convert = ev2kJ*cmdim2mdim/Adim2mdim/g2Kg
#----------------------------------------------------------------------#
# 25
#----------------------------------------------------------------------#
A25, B25 = optimize.curve_fit(f_1, x25_matrix, y25_matrix)[0]
x_25_1 = np.arange(198,260,2)
y25 = A25 * x_25_1 + B25
axe.plot(x_25_1, y25 , "y",ls='--',lw=2,label='Linear fitting 27.0 nm')
rouV_25 = 1.33*1e+6
Cp_25 = A25/(rouV_25)*convert
print('27nm体系能量温度斜率为:',A25)
print('27nm体系Cp=',Cp_25)
#----------------------------------------------------------------------#
# 20
#----------------------------------------------------------------------#
A20, B20 = optimize.curve_fit(f_1, x20_matrix, y20_matrix)[0]
x_20_1 = np.arange(198,260,2)
y20 = A20 * x_20_1 + B20
axe.plot(x_20_1, y20 , "g",ls='--',lw=2,label='Linear fitting 21.6 nm')
rouV_20 = 1.06*1e+6
Cp_20 = A20/(rouV_20)*convert
print('21.6nm体系能量温度斜率为:',A20)
print('21.6nm体系Cp=',Cp_20)
#----------------------------------------------------------------------#
# 15
#----------------------------------------------------------------------#
A15, B15 = optimize.curve_fit(f_1, x15_matrix, y15_matrix)[0]
x_15_1 = np.arange(198,260,2)
y15 = A15 * x_15_1 + B15
axe.plot(x_15_1, y15 , "b",ls='--',lw=2,label='Linear fitting 21.6 nm')
rouV_15 = 7.97*1e+5
Cp_15 = A15/(rouV_15)*convert
print('16.2nm体系能量温度斜率为:',A15)
print('16.2nm体系Cp=',Cp_15)
#----------------------------------------------------------------------#
# 10
#----------------------------------------------------------------------#
A10, B10 = optimize.curve_fit(f_1, x10_matrix, y10_matrix)[0]
x_10_1 = np.arange(198,260,2)
y10 = A10 * x_10_1 + B10
axe.plot(x_10_1, y10 , "k",ls='--',lw=2,label='Linear fitting 21.6 nm')
rouV_10 = 5.31*1e+5
Cp_10 = A10/(rouV_10)*convert
print('10.8nm体系能量温度斜率为:',A10)
print('10.8nm体系Cp=',Cp_10)
setup(axe,r'$\rm Temperature\ /K$',r'$\rm Total\ energy\ /eV$')
axe.legend(loc='best', frameon=False, \
labelspacing=0.3)
axe.legend(bbox_to_anchor=(1.10, 1), \
loc='upper left', borderaxespad=0,fontsize='xx-large')
plt.show()
三、结果分析
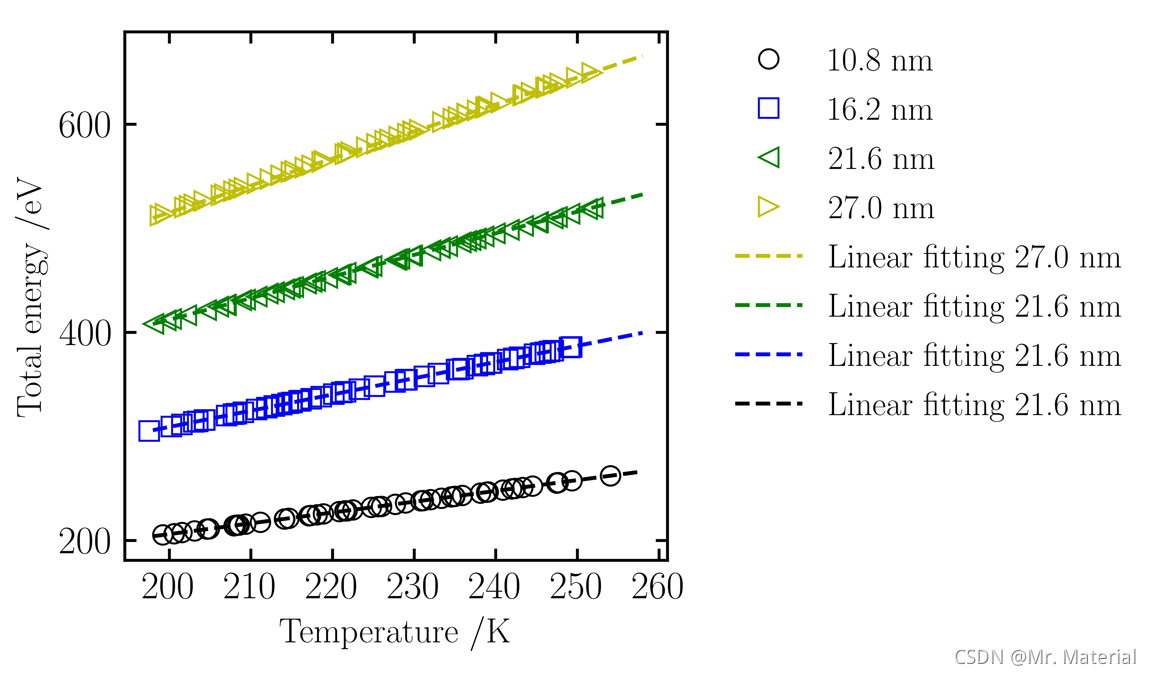
27.0 nm 体系能量温度斜率为: 2.5954295597954276
27.0 nm 体系Cp= 0.3122321274941868 kJ/kg/K
21.6 nm 体系能量温度斜率为: 2.0759228010947757
21.6 nm 体系Cp= 0.31334683790109824 kJ/kg/K
16.2 nm 体系能量温度斜率为: 1.5593179432373265
16.2 nm 体系Cp= 0.3130374791944445 kJ/kg/K
10.8 nm 体系能量温度斜率为: 1.0379864745097611
10.8 nm 体系Cp= 0.31276428610463614 kJ/kg/K
四、总结
以上就是所分享内容,本文仅仅简单介绍了如何计算Cp,原理简单,欢迎各位小伙伴交流~