Pygame是Python最经典的2D游戏开发第三方库,机巧围棋基于Pygame游戏开发引擎实现围棋游戏运行和交互逻辑,并搭建围棋游戏可视化界面。
本文不是Pygame的API文档或教程,但是本文将介绍在机巧围棋中所涉及的Pygame游戏开发引擎相关知识和方法,并详细讲解机巧围棋中基于Pygame实现的按钮控件、信息滚动显示器、音乐播放器等。
1. Pygame基本知识
1.1 Pygame游戏开发框架
Pygame游戏开发框架共包含4个部分:
- 第一部分:引入pygame和sys;
- 第二部分:初始化pygame游戏引擎,并完成Pygame游戏窗体设置;
- 第三部分:在一个无限循环中获取Pygame事件,并逐类响应;
- 第四部分:在该无限循环中不断刷新游戏屏幕。
基于Pygame进行游戏开发,必须遵循上述框架流程。在引入相关包并初始化完成之后,在一个无限循环中不断获取各类Pygame事件,对各类事件进行处理,并刷新屏幕。
Pygame游戏开发框架图如下所示:

Pygame游戏开发框架代码如下所示:
# 导入相关包
import pygame, sys
# 初始化pygame游戏引擎
pygame.init()
# 创建pygame游戏窗体,设置窗体大小和标题
screen = pygame.display.set_mode((600, 400))
pygame.display.set_caption("机巧围棋(CleverGo)")
while True:
for event in pygame.event.get():
if event.type == pygame.QUIT:
sys.exit()
else:
# 针对不同事件进行处理,完善pygame游戏运行和交互逻辑
pass
# 刷新游戏屏幕
pygame.display.update()
1.2 Pygame屏幕绘制机制
1.2.1 pygame.Surface
Surface对象是pygame的绘图层,或绘图平面,或图层,用于展示图形、文字或图像的绘制效果。在pygame中主图层和其他图层可以并列存在,每个游戏只有一个主图层,主图层可以被屏幕显示出来,其他图层不会在屏幕上显示。
主图层是由pygame.display.set_mode()方法生成的Surface对象。如果想要将其他图层上的内容绘制到主图层上,可以使用Surface对象的blit()方法。
-
surface.blit(other_surface, location)
surface: 目标图层Surface对象,如将其他图层内容绘制到主图层上,则surface为主图层
other_surface: 其他图层Surface对象
location: 一个表示绘制位置的元组 -
surface.subsurface(rect)
在surface中选择一个区域,生成一个子Surface。
rect: 一个包含四个元素的元组。第一和二个元素表示子Surface左上角在surface中的坐标位置,第三和四个元素表示子Surface的宽和高
-
surface.fill(color)
给surface填充指定颜色。
color: 是一个代表RGB的三元组,如白色为(255, 255, 255)
-
surface.get_abs_offset()
获取子 Surface 对象在顶层父对象中的偏移位置。
-
surface.get_size()
获取surface的大小,即width和height。
1.2.2 屏幕绘制重要函数
-
pygame.display.set_mode(r=(0, 0), flags=0)
用于创建pygame游戏主图层Surface对象。
r: 游戏屏幕的分辨率,采用(width, height)方式输入
flags: 显示类型,常用显示标签有pygame.RESIZEABLE(窗口大小可调)、pygame.NOFRAME(窗口没有边界显示)、pygame.FULLSCREEN(窗口全屏显示)
-
pygame.display.set_caption(title, icontitle=None)
用于设置窗口的标题内容。
title: 标题
icontitle: 图标化后的小标题
-
pygame.display.update() & pygame.display.flip()
屏幕刷新函数,flip函数将重新绘制整个窗口,update函数仅仅重新绘制窗口中有变化的区域。
update比flip执行速度更快。
1.3 Pygame事件处理机制
Pygame事件本质上是一种封装好的数据类型(对象),是Pygame的一个类,表示事件类型。事件类型只有属性,没有方法。
在Pygame中存在一个最大长度为128的缓存并派发所有事件的事件队列,当队列满时,更多事件将会被丢弃。用户按照先到先处理的原则,对事件逐一处理。
1.3.1 事件类型及属性
Pygame中共存在6种事件类型,分别是:系统事件、键盘事件、鼠标事件、游戏杆事件、窗口事件和用户自定义事件。在机巧围棋中所用到的Pygame事件如下:
系统事件:
- pygame.QUIT:游戏退出事件,该事件无属性
鼠标事件:
- pygame.MOUSEBUTTONDOWN:鼠标按下事件
event.pos:鼠标当前的坐标值
event.button:鼠标按下的键的编号,1代表左键,2代表中键,3代表右键 - pygame.MOUSEBUTTONUP:鼠标按键释放事件
event.pos:鼠标当前的坐标值
event.button:鼠标释放的键的编号,1代表左键,2代表中键,3代表右键 - pygame.MOUSEMOTION:鼠标移动事件
event.pos:鼠标当前的坐标值
event.buttons:为一个3个元素的元组,对应于鼠标的三个按键,如果相应按键处于按下状态,则值为1,否则为0
event.rel:为一个2个元素的元组,表示鼠标相对移动距离
1.3.2 对事件队列的操作
在pygame中通过pygame.event.get()方法获得所有添加到事件队列中的事件,返回一个事件列表,同时在事件队列中删除这些事件。
在1.1所述开发框架中,在while循环中不断使用pygame.event.get()方法,从事件队列中取出事件,并分别对各类事件进行处理。
1.4 Pygame图形绘制机制
在Pygame中通过pygame.draw中相关方法绘制矩形、直线、多边形、圆形等各种常见图形。
-
pygame.draw.rect(surface, color, rect, width=0)
绘制矩形。
surface: 矩形绘制的屏幕
color: 矩形颜色
rect: 为一个4元组,表示矩形的绘制区域
width: 绘制的矩形边缘宽度,默认为0,表示填充图形
-
pygame.draw.line(surface, color, start_pos, end_pos, width=1)
绘制直线。
surface: 直线绘制的屏幕
color: 直线颜色
start_pos: 直线绘制起始点
end_pos: 直线绘制结束点
width: 直线的宽度,默认为1,即1个像素宽
-
pygame.draw.circle(surface, color, pos, radius, width=0)
绘制圆形。
surface: 圆形绘制的屏幕
color: 圆形的颜色
pos: 圆心位置
radius: 圆的半径
width: 绘制的圆形边缘宽度,默认为0,表示填充圆形
1.5 Pygame文字绘制机制
Pygame中通过pygame.font.Font()创建字体对象,调用一个字体对象的render()方法可以生成文本Surface对象,通过Surface对象的blit()方法,可讲相应文本绘制到指定屏幕上。
-
font = pygame.font.Font(font_path, size)
生成字体对象。
font_path: 字体文件路径,如果设置为None,则会使用系统默认字体(好像不支持中文)
size: 字体的大小
-
font.render(text, antialias, color)
渲染文本对象,生成一个Surfae对象。
text: 文本内容
antialias: 是否抗锯齿,设置为True会将文本的锯齿形边缘变得光滑
color: 文本的颜色
1.6 Pygame图片绘制机制
Pygame中通过pygame.image.load(image_path)方法加载图片,生成一个Surface对象。
在加载图片时调用convert_alpha()方法可以保留图片的alpha通道,如此当生成的Surface对象被blit到主图层时,可以保留载入图片中的透明效果。
1.7 Pygame音乐控制机制
Pygame中通过pygame.mixer.Sound(music_path)方法加载音乐,生成一个Sound对象。
-
pygame.mixer.get_busy()
检测当前是否有音乐正在播放。
-
sound.play()
播放sound音乐。
-
sound.stop()
停止播放sound音乐。
2. Pygame按钮及信息滚动显示器
Pygame是一个比较底层的游戏引擎,原生Pygame库没有封装按钮等常见控件。在机巧围棋中,封装了Pygame按钮控件及信息滚动显示器工具,并且构造了一个良好的Pygame控件和工具管理机制。
定义由Pygame事件驱动的对象为Pygame控件(如按钮),创建CtBase类为所有Pygame控件的基类,所有自定义控件必须继承CtBase类,并实现update()方法。在CtBase类中定义了active属性记录控件是否被激活,并通过enable()和disable()方法激活或冻结控件。控件基类代码如下:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# @Time : 2021/10/7 10:56
# @Author : He Ruizhi
# @File : ctbase.py
# @Software: PyCharm
import pygame
class CtBase:
"""pygame控件基类,所有自定义控件均需继承CtBase"""
def __init__(self):
# 控件是否被激活
self.active = False
def enable(self):
"""激活控件"""
self.active = True
def disable(self):
"""冻结控件"""
self.active = False
def update(self, event: pygame.event) -> ...:
"""
根据pygame.event对控件状态进行更新
所有控件类均需重写该方法
"""
raise NotImplementedError
定义由自身状态驱动的对象为Pygame工具(如信息滚动显示器),创建ToolBase类为所有Pygame工具的基类,所有自定义工具必须继承ToolBase类,并实现update()方法。在ToolBase类中同样定义了active属性记录工具是否被激活,并可以使用enable()方法和disable()方法修改工具激活状态。工具基类代码如下:
class ToolBase:
"""pygame工具基类,所有自定义工具均需继承ToolBase"""
def __init__(self):
# 工具是否被激活
self.active = False
def enable(self):
"""激活工具"""
self.active = True
def disable(self):
"""冻结工具"""
self.active = False
def update(self):
"""
对工具状态进行更新
所有工具类均需重写该方法
"""
raise NotImplementedError
2.1 按钮控件
按钮是最常见的控件,一般通过鼠标按键按下、鼠标按键弹起和鼠标移动事件驱动按钮控件状态更新。
创建按钮控件必须继承CtBase类,同时指定绘制按钮的Surface对象、按钮上的文本内容以及按钮绘制的位置(同时也支持自定义修改按钮底色、边框颜色、文本颜色、文字大小等等)。在重写的update()方法中,监控鼠标左键按下、鼠标移动和鼠标左键弹起事件。当鼠标左键在按钮上按下,将按钮绘制成按下时颜色;当鼠标移动时,监控鼠标位置,若鼠标移出按钮区域,则将按钮绘制成弹起时颜色;当鼠标左键在按钮上弹起时,会将按钮绘制成弹起时颜色,并调用相关方法以及播放按钮点击音效。
按钮控件实现代码如下:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# @Time : 2021/9/25 20:45
# @Author : He Ruizhi
# @File : button.py
# @Software: PyCharm
import pygame
import os
import copy
from pgutils.text import draw_text
from pgutils.position import pos_in_surface
from pgutils.pgcontrols.ctbase import CtBase
from typing import Tuple, List, Union, Callable, Optional
current_path = os.path.dirname(__file__)
class Button(CtBase):
"""每一个Button均为一个pygame.surface.subsurface"""
def __init__(self, surface: pygame.Surface,
text: str,
pos: Union[Tuple[str or int], List[str or int]],
call_function: Optional[Callable] = None,
click_sound: Union[str, pygame.mixer.Sound] = current_path + "/../../assets/audios/Button.wav",
font_path: str = current_path + "/../../assets/fonts/msyh.ttc",
font_size: int = 14,
size: Union[Tuple[int], List[int]] = (87, 27),
text_color: Union[Tuple[int], List[int]] = (0, 0, 0),
up_color: Union[Tuple[int], List[int]] = (225, 225, 225),
down_color: Union[Tuple[int], List[int]] = (190, 190, 190),
outer_edge_color: Union[Tuple[int], List[int]] = (240, 240, 240),
inner_edge_color: Union[Tuple[int], List[int]] = (173, 173, 173)):
"""
pygame按钮控件,用于在给定pygame.surface上绘制一个按钮
:param surface: 绘制按钮的pygame.surface
:param text: 按钮上的文本
:param pos: 按钮绘制位置
:param call_function: 点击按钮调用的方法
:param click_sound: 按钮的点击音效
:param font_path: 按钮上的文本字体路径
:param text_color: 按钮上的文本颜色
:param font_size: 文本大小
:param size: 按钮大小
:param up_color: 按钮弹起时的颜色
:param down_color: 按钮按下时的颜色
:param outer_edge_color: 按钮外边框颜色
:param inner_edge_color: 按钮内边框颜色
"""
super(Button, self).__init__()
pos = copy.copy(list(pos))
if isinstance(pos[0], str):
assert pos[0] == "center"
pos[0] = (surface.get_width() - size[0]) // 2
if isinstance(pos[1], str):
assert pos[1] == "center"
pos[1] = (surface.get_height() - size[1]) // 2
if isinstance(click_sound, str):
click_sound = pygame.mixer.Sound(click_sound)
# 按钮surface
self.button_surface = surface.subsurface(pos[0], pos[1], size[0], size[1])
# 外边框
self.outer_rect = 0, 0, size[0], size[1]
# 内边框
self.inner_rect = self.outer_rect[0] + 1, self.outer_rect[1] + 1, self.outer_rect[2] - 2, self.outer_rect[3] - 2
self.font = pygame.font.Font(font_path, font_size)
self.text = self.font.render(text, True, text_color)
self.text_color = text_color
self.size = size
self.call_function = call_function
self.click_sound = click_sound
self.up_color = up_color
self.down_color = down_color
self.outer_edge_color = outer_edge_color
self.inner_edge_color = inner_edge_color
# 按钮是否被按下
self.is_down = False
def draw_up(self):
"""绘制未被点击的按钮"""
self.is_down = False
self.draw(self.up_color)
def draw_down(self):
"""绘制已被点击的按钮"""
self.is_down = True
self.draw(self.down_color)
def draw(self, base_color: Union[Tuple[int], List[int]]):
"""根据传入的颜色,对按钮显示效果进行更新"""
# 填充按钮底色
self.button_surface.fill(base_color)
# 绘制外框
pygame.draw.rect(self.button_surface, self.outer_edge_color, self.outer_rect, width=1)
# 绘制内框
pygame.draw.rect(self.button_surface, self.inner_edge_color, self.inner_rect, width=1)
# 绘制按钮文本
draw_text(self.button_surface, self.text, ["center", "center"])
def set_text(self, text: str, draw_update: bool = True):
"""设置按钮文本"""
self.text = self.font.render(text, True, self.text_color)
if draw_update:
self.draw_up()
def enable(self):
"""激活按钮"""
self.active = True
self.draw_up()
def disable(self):
"""冻结按钮"""
self.active = False
self.draw_down()
def update(self, event: pygame.event):
"""根据pygame.event对按钮进行状态更新和方法调用"""
if event.type == pygame.MOUSEBUTTONDOWN and event.button == 1:
# 鼠标左键按下
if pos_in_surface(event.pos, self.button_surface):
self.draw_down()
self.is_down = True
elif event.type == pygame.MOUSEMOTION:
# 鼠标移动事件,用来检测按钮是否应该弹起
if not pos_in_surface(event.pos, self.button_surface) and self.is_down:
self.draw_up()
self.is_down = False
elif event.type == pygame.MOUSEBUTTONUP and event.button == 1:
# 鼠标左键弹起事件
if pos_in_surface(event.pos, self.button_surface) and self.is_down:
self.draw_up()
# 播放按钮点击音效
self.click_sound.play()
# 调用相应方法
if self.call_function is not None:
self.call_function()
按钮显示效果如下:

2.2 信息滚动显示器
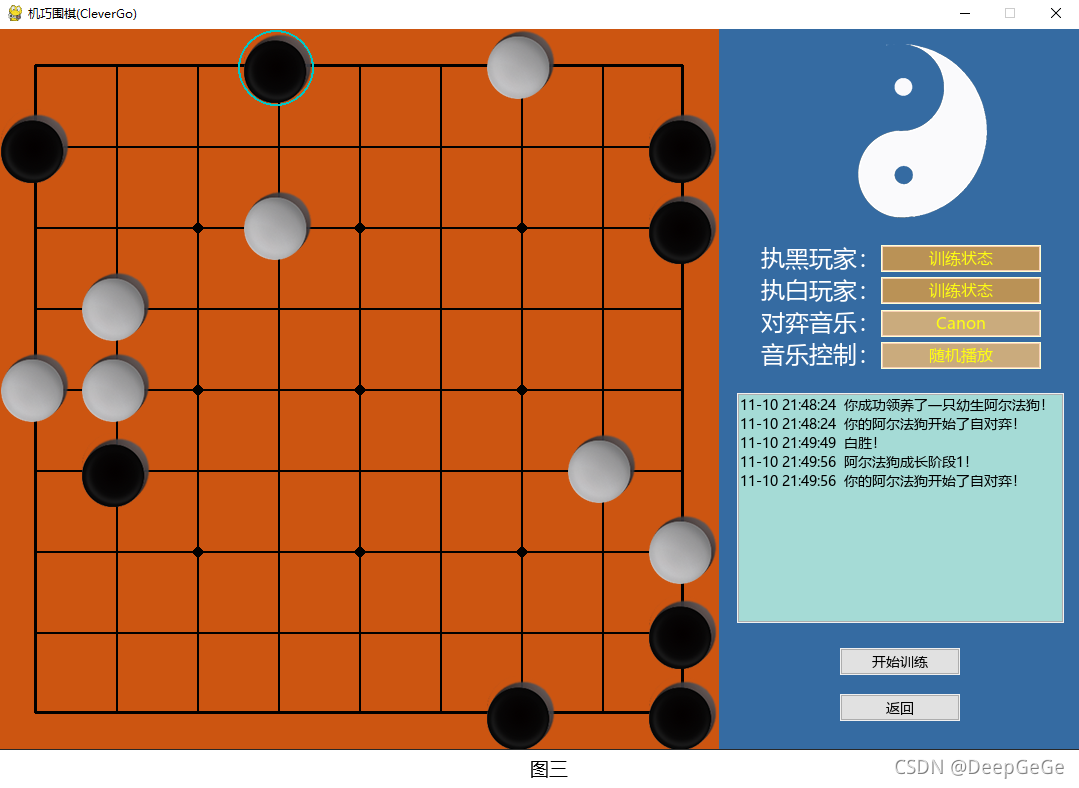
在机巧围棋中,使用信息滚动显示器展示下图所示的幼生阿尔法狗训练过程中的状态提示信息。
创建信息滚动显示器必须继承ToolBase类,同时指定绘制信息滚动显示器的Surface对象(同时也支持修改边框颜色、底色、文本颜色、文字大小等等)。在重写的update()方法中,将信息滚动显示器对象中定义的information_container属性中记录的文本绘制到屏幕上。
信息滚动显示器实现代码如下:
class InformationDisplay(ToolBase):
def __init__(self, surface: pygame.Surface,
display_pos: Optional[List[str or float or int]] = None,
display_size: Optional[List[int or float]] = None,
max_show: int = 5,
bg_color: Tuple[int, int, int] = (165, 219, 214),
outer_rect_color: Tuple[int, int, int] = (240, 240, 240),
inner_rect_color: Tuple[int, int, int] = (173, 173, 173),
font_size: int = 14,
font_color: Tuple[int, int, int] = (0, 0, 0),
font_path: str = current_path + "/../../assets/fonts/msyh.ttc"):
"""
在指定pygame.surface上滚动显示信息
:param surface: 绘制屏幕
:param display_pos: 绘制位置
:param display_size: display大小
:param max_show: 信息滚动显示数
:param bg_color: 背景颜色
:param font_size: 字体大小
:param font_color: 字体颜色
:param font_path: 字体文件路径
"""
super(InformationDisplay, self).__init__()
if display_pos is None:
display_pos = [20, 20]
if display_size is None:
surface_width, surface_height = surface.get_width(), surface.get_height()
display_size = [surface_width - display_pos[0] * 2, surface_height - display_pos[1] * 2]
# 创建subsurface
self.display_surface = surface.subsurface((*display_pos, *display_size))
# 内外边框绘制位置
self.outer_rect = 0, 0, self.display_surface.get_width(), self.display_surface.get_height()
self.inner_rect = self.outer_rect[0] + 1, self.outer_rect[1] + 1, self.outer_rect[2] - 2, self.outer_rect[3] - 2
# 生成字体对象
self.font = pygame.font.Font(font_path, font_size)
# 生成信息存储器
self.information_container = deque(maxlen=max_show)
self.display_pos = display_pos
self.display_size = display_size
self.bg_color = bg_color
self.font_color = font_color
self.outer_rect_color = outer_rect_color
self.inner_rect_color = inner_rect_color
def push_text(self, text: str, update=False):
self.information_container.append(text)
if update:
self.enable()
def update(self):
self.display_surface.fill(self.bg_color)
# 绘制外框
pygame.draw.rect(self.display_surface, self.outer_rect_color, self.outer_rect, width=1)
# 绘制内框
pygame.draw.rect(self.display_surface, self.inner_rect_color, self.inner_rect, width=1)
# 绘制文本
next_pos = [3, 2]
for line in self.information_container:
line = self.font.render(line, True, self.font_color)
next_pos = draw_text(self.display_surface, line, next_pos)
2.3 控件及工具管理
在机巧围棋中,通过一个Manager对象统一管理所有控件及工具。Manager类中定义了controls和tools两个属性,每创建一个控件或工具必须使用相关方法注册到Manager对象中,并在程序主循环中调用Manager对象的control_update(event)方法和tool_update()方法对所有控件和工具状态进行监测和更新。
Manager类的实现如下:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# @Time : 2021/10/7 10:57
# @Author : He Ruizhi
# @File : manager.py
# @Software: PyCharm
from pgutils.pgcontrols.ctbase import CtBase
from pgutils.pgtools.toolbase import ToolBase
import pygame
from typing import List, Union
class Manager:
def __init__(self):
self.controls = []
self.tools = []
def control_register(self, controls: Union[List[CtBase], CtBase]):
"""
控件注册
:param controls: pygame控件或控件数组
:return:
"""
if isinstance(controls, CtBase):
self.controls.append(controls)
else:
for control in controls:
self.controls.append(control)
def tool_register(self, tools: Union[List[ToolBase], ToolBase]):
"""
工具注册
:param tools: pygame工具或工具数组
:return:
"""
if isinstance(tools, ToolBase):
self.tools.append(tools)
else:
for tool in tools:
self.tools.append(tool)
def control_update(self, event: pygame.event):
"""
对所有注册的激活控件进行更新
:param event: pygame事件
:return:
"""
for control in self.controls:
if control.active:
control.update(event)
def tool_update(self):
"""对所有激活的工具进行更新"""
for tool in self.tools:
if tool.active:
tool.update()
# pgtool会在更新后冻结
tool.disable()
3. Pygame音乐播放器
为了在围棋对弈和围棋AI训练过程中不至于太多单调,机巧围棋基于Pygame实现了一个音乐播放器,音乐播放器支持随机播放、顺序播放和单曲循环三种模式。
在机巧围棋启动时会加载assets/musics/目录下的全部音乐资源,并用music_id和music_control_id两个属性记录播放的音乐以及音乐控制类别。
点击对弈音乐按钮即可切换播放的音乐,点击音乐控制按钮即可更改音乐播放模式。对音乐的控制均通过按钮点击时的回调函数实现,具体代码如下:
def fct_for_music_choose(self):
MUSICS[self.music_id][1].stop()
if self.music_control_id == 0: # 随机播放
rand_int = np.random.randint(len(MUSICS)) # 随机获取一首歌
if len(MUSICS) > 1:
while rand_int == self.music_id:
rand_int = np.random.randint(len(MUSICS))
self.music_id = rand_int
else:
self.music_id += 1
self.music_id %= len(MUSICS)
self.pmc_buttons[2].set_text(MUSICS[self.music_id][0])
MUSICS[self.music_id][1].play()
def fct_for_music_control(self):
self.music_control_id += 1
self.music_control_id %= len(self.music_control_name)
self.pmc_buttons[3].set_text(self.music_control_name[self.music_control_id])
# 说明音乐控制按钮上一次为音乐关
if self.music_control_id == 0:
# 须直接将音乐打开
MUSICS[self.music_id][1].play()
定义music_control()方法,监测音乐播放状态,并根据音乐控制模式在一首音乐播放完成后自动按照相关规则播放下一首音乐。同时检测音乐控制模式,实现音乐的停止和播放。通过在游戏主循环中调用music_control()方法,实现音乐播放实时控制。music_control()方法具体实现如下:
def music_control(self):
# 音乐控制
if not pygame.mixer.get_busy() and self.music_control_id != 3: # 当歌曲没在播放,且音乐没关掉
if self.music_control_id == 0: # 随机播放
rand_int = np.random.randint(len(MUSICS)) # 随机获取一首歌
if len(MUSICS) > 1:
while rand_int == self.music_id:
rand_int = np.random.randint(len(MUSICS))
self.music_id = rand_int
MUSICS[self.music_id][1].play()
elif self.music_control_id == 1: # 顺序播放
self.music_id += 1
self.music_id %= len(MUSICS)
MUSICS[self.music_id][1].play()
elif self.music_control_id == 2: # 单曲循环
MUSICS[self.music_id][1].play()
self.pmc_buttons[2].set_text(MUSICS[self.music_id][0])
self.pmc_buttons[2].draw_up()
elif pygame.mixer.get_busy() and self.music_control_id == 3: # 音乐关
MUSICS[self.music_id][1].stop()
4. 结束语
本文用约5000多字介绍了游戏开发引擎(Pygame)的核心方法,同时详细讲解了机巧围棋中的Pygame按钮、信息滚动显示器以及音乐播放器的实现形式以及管理方式。Pygame是一个偏底层的游戏开发引擎,我相信很多小伙伴在使用Pygame开发自己的小游戏时候,苦于其对按钮不支持,难以做到令自己满意的效果。
本文中的按钮控件及信息显示器等的实现具有普适性,相信读者在阅读完本文之后,可以清晰第了解到机巧围棋的运行、控制、可视化及交互逻辑。此外,本文讲解的机巧围棋中的按钮控件等实现,相信在各位小伙伴自己的Pygame项目开发中会具有相当大而参考价值。
最后,期待您能够给本文点个赞,同时去GitHub上给机巧围棋项目点个Star呀~