目录
1、单个字面量类型的参数
若mapper接口中的方法参数为单个的字面量类型,此时可以使用 ${} 和 #{} 以任意的名称(最好见名识意)获取参数的值,注意 ${} 需要手动加单引号
注:单个字面量类型的参数也可以使用下面的第五种 @Param 注解来获取,但是这时就只能通过 @Param 的值来获取参数
① 在 ParameterMapper 接口添加方法
/**
* 根据用户名查询用户信息
*/
User getUserByUsername(String username);② 在?ParameterMapper.xml 添加 SQL 语句?
<!-- User getUserByUsername(String username) -->
<select id="getUserByUsername" resultType="User">
<!-- ${}和#{}中的变量名可以任取, -->
<!-- >select * from t_user where username = #{username} -->
select * from t_user where username = '${username}' <!-- 注意${}外的单引号 -->
</select>2、多个字面量类型的参数
若mapper接口中的方法参数为多个时,此时MyBatis会自动将这些参数放在一个map集合中,因此只需要通过${}和#{}访问map集合的键就可以获取相对应的值,注意${}需要手动加单引号。
使用arg或者param都行,要注意的是,arg是从arg0开始的,param是从param1开始的
1. 以arg0,arg1...为键,以参数为值;
2. 以param1,param2...为键,以参数为值;
arg 和 param 可以在同一个 SQL 语句中混合使用
① 在?ParameterMapper 接口添加方法
/**
* 验证登录
*/
User checkLogin(String username, String password);② 在?ParameterMapper.xml 添加 SQL 语句
<!-- User checkLogin(String username, String password) -->
<select id="checkLogin" resultType="User">
<!-- select * from t_user where username = #{arg0} and password = #{param2} -->
select * from t_user where username = '${arg0}' and password = '${param2}'
</select>3、map 集合类型的参数
若 mapper 接口中的方法需要的参数为多个时,此时可以手动创建 map 集合,将这些数据放在map中只需要通过 ${} 和 #{} 访问map集合的键就可以获取相对应的值,注意 ${} 需要手动加单引号
①?在?ParameterMapper 接口添加方法
/**
* 验证登录(参数为 map)
*/
User checkLoginByMap(Map<String, Object> map);②?在?ParameterMapper.xml 添加 SQL 语句
<!-- User checkLoginByMap(Map<String, Object> map) -->
<select id="checkLoginByMap" resultType="User">
<!-- select * from t_user where username = #{username} and password = #{password} -->
select * from t_user where username = '${username}' and password = '${password}'
</select>
4、实体类类型参数
若 mapper 接口中的方法参数为实体类对象时此时可以使用 ${} 和 #{},通过访问实体类对象中的属性名获取属性值,注意 ${} 需要手动加单引号
①?在?ParameterMapper 接口添加方法
/**
* 添加用户信息
*/
int insertUser(User user);②?在?ParameterMapper.xml 添加 SQL 语句
<!-- int insertUser(User user) -->
<insert id="insertUser">
insert into t_user values(null, #{username}, #{password}, #{age}, #{sex}, #{email})
</insert>5、使用 @param 表示参数(部分源码分析)
可以通过@Param注解标识mapper接口中的方法参数,此时,会将这些参数放在map集合中(以 @Param 中的值为键,参数为值 或 以param1,param2,... 为键,参数为值),只需要通过${}和#{}访问map集合的键就可以获取相对应的值,注意${}需要手动加单引号
①?在?ParameterMapper 接口添加方法
/**
* 验证登录(使用@param注解)
*/
User checkLoginByParam(@Param("username") String username, @Param("password") String password);②?在?ParameterMapper.xml 添加 SQL 语句
<!-- User checkLoginByParam(@Param("username") String username, @Param("password") String password) -->
<select id="checkLoginByParam" resultType="User">
select * from t_user where username = #{username} and password = #{password}
</select>③ 在测试类中进行测试
@Test
public void testCheckLoginByParam(){
SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtils.getSqlSession();
ParameterMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(ParameterMapper.class);
User admin = mapper.checkLogin("admin", "123456");
System.out.println(admin);
}源码分析:
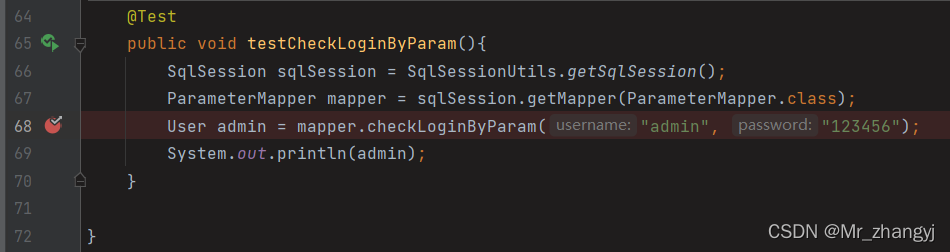
① 如图,在执行方法的那一行打上断点,并以 debug 的方式运行
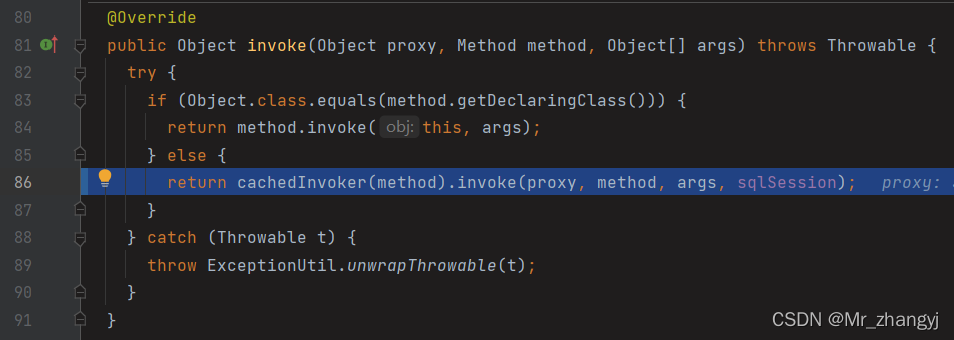
?② 调试启动后,步入,跳转到 MapperProxy类 ,可见使用的是代理模式,下一步到下图该行后,步入 invoke 方法
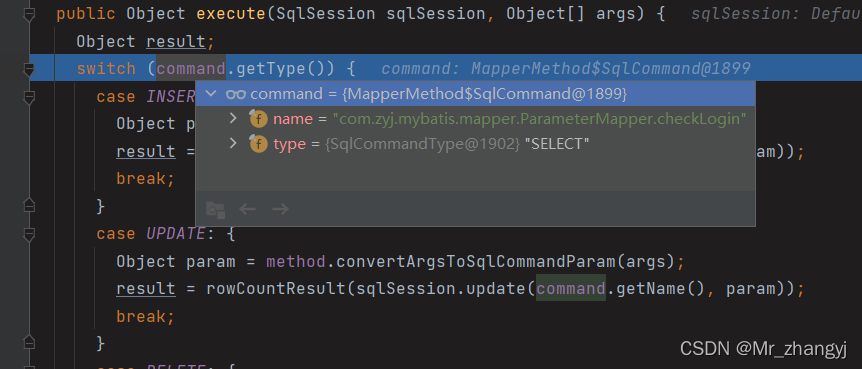
?③ 一直步入到 MapperMethod 类的 execute 方法。可以看到执行 command 的 name 存放的是要执行的 SQL 语句,type 存放的是其类型,根据不用的 SQL 语句的类型会执行不同的方法
public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {
Object result;
// 获取所要执行的SQL语句的类型,根据不同类型执行不同方法
// command的name存放的是要执行的SQL语句,type存放的是其类型
switch (command.getType()) {
case INSERT: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.insert(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case UPDATE: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.update(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case DELETE: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.delete(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case SELECT:
// method就是mapper接口的方法
if (method.returnsVoid() && method.hasResultHandler()) {
// 方法没有返回值
executeWithResultHandler(sqlSession, args);
result = null;
} else if (method.returnsMany()) {
// 方法返回多条数据
result = executeForMany(sqlSession, args);
} else if (method.returnsMap()) {
// 方法返回Map
result = executeForMap(sqlSession, args);
} else if (method.returnsCursor()) {
// 方法返回Cousor
result = executeForCursor(sqlSession, args);
} else {
// 将方法参数转换为SQL语句的参数,args存放的就是调用方法的参数
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = sqlSession.selectOne(command.getName(), param);
if (method.returnsOptional()
&& (result == null || !method.getReturnType().equals(result.getClass()))) {
result = Optional.ofNullable(result);
}
}
break;
case FLUSH:
result = sqlSession.flushStatements();
break;
default:
throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + command.getName());
}
if (result == null && method.getReturnType().isPrimitive() && !method.returnsVoid()) {
throw new BindingException("Mapper method '" + command.getName()
+ " attempted to return null from a method with a primitive return type (" + method.getReturnType() + ").");
}
return result;
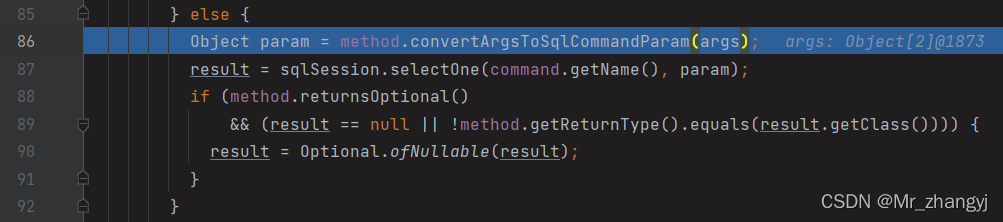
}④ 执行到下图改行时,步入
?步入后跳转到?MapperMethod 类的?convertArgsToSqlCommandParam 方法,再次步入,跳转到 ParamNameResolver类 的 getNamedParams 方法。
该方法首先获取了 names.size() 方法,而 names 的定义为?private final SortedMap<Integer, String> names; 且在该类的第90行被赋值为?names = Collections.unmodifiableSortedMap(map); 从而可知:getNamedParams 方法就是给 names 赋值的方法,部分注解如下:
public ParamNameResolver(Configuration config, Method method) {
this.useActualParamName = config.isUseActualParamName();
// 获取调用的方法的所有参数的类型,即class对象
final Class<?>[] paramTypes = method.getParameterTypes();
// 获取参数的注解,使用二维数组的原因是方法可能有多个参数,而一个参数也可能有多个注解
final Annotation[][] paramAnnotations = method.getParameterAnnotations();
final SortedMap<Integer, String> map = new TreeMap<>();
// 获取参数的个数
int paramCount = paramAnnotations.length;
// get names from @Param annotations
for (int paramIndex = 0; paramIndex < paramCount; paramIndex++) {
// 判断参数类型是否是特殊参数,不用管
if (isSpecialParameter(paramTypes[paramIndex])) {
// skip special parameters
continue;
}
String name = null;
// 只要检测到有一个注解是Param类型,则直接跳出这个for循环
for (Annotation annotation : paramAnnotations[paramIndex]) {
if (annotation instanceof Param) {
// 若任一注解是Param类型,则将hasParamAnnotation设置为true
hasParamAnnotation = true;
// 获取在方法里@Param注解的value值
name = ((Param) annotation).value();
break;
}
}
if (name == null) {
// @Param was not specified.
if (useActualParamName) {
name = getActualParamName(method, paramIndex);
}
if (name == null) {
// use the parameter index as the name ("0", "1", ...)
// gcode issue #71
name = String.valueOf(map.size());
}
}
// 以参数的索引为键,以@Param注解的值为值,存储到map中
map.put(paramIndex, name);
}
names = Collections.unmodifiableSortedMap(map);
}最后 names 的值如下:
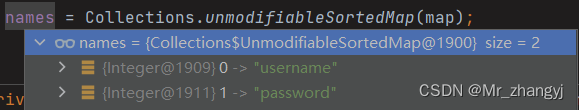
?接下来回到?getNamedParams 方法,其实就是将获取参数的两种方式存放到 map(以 @Param 中的值为键,参数为值 或 以param1,param2,... 为键,参数为值),部分注解如下:
public Object getNamedParams(Object[] args) {
final int paramCount = names.size();
if (args == null || paramCount == 0) {
return null;
// hasParamAnnotation在上面的ParamNameResolver方法被赋值,当参数有@Param注解时为true
} else if (!hasParamAnnotation && paramCount == 1) {
Object value = args[names.firstKey()];
return wrapToMapIfCollection(value, useActualParamName ? names.get(0) : null);
} else {
final Map<String, Object> param = new ParamMap<>();
int i = 0;
for (Map.Entry<Integer, String> entry : names.entrySet()) {
// 向新建的map集合中存放,以@Param注解的值为键,传入方法的真实参数为值
// 也就是以@Param注解的值来获取参数值
param.put(entry.getValue(), args[entry.getKey()]);
// add generic param names (param1, param2, ...)
// 生成用来获取参数的param1, param2 ... (GENERIC_NAME_PREFIX = "param")
final String genericParamName = GENERIC_NAME_PREFIX + (i + 1);
// ensure not to overwrite parameter named with @Param
if (!names.containsValue(genericParamName)) {
// 若names里没有和genericParamName相等的value值,则存入以paramX为键,传入方法的真实参数为值
// 也就是以param1, param2 ... 来获取参数值
param.put(genericParamName, args[entry.getKey()]);
}
i++;
}
return param;
}
}执行完后 param 的内容如下:
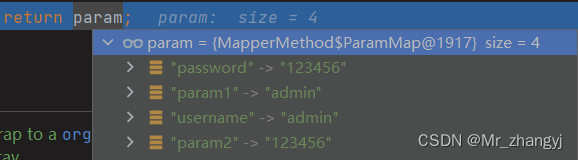
6、总结
在使用过程中最好使用 实体类型的参数 和 @Param注解 来获取参数值?
-
MyBatis获取参数值的两种方式:${}和#{}
-
${}的本质就是字符串拼接,#{}的本质就是占位符赋值
-
${} 使用字符串拼接的方式拼接 sql,需要手动加单引号;但是使用 #{} 占位符赋值的方式拼接sql,会自动添加单引号