Material(材质)
一、MeshNormalMaterial(网状通用材料)
例:
const MeshBasicMaterial=new THREE.MeshNormalMaterial()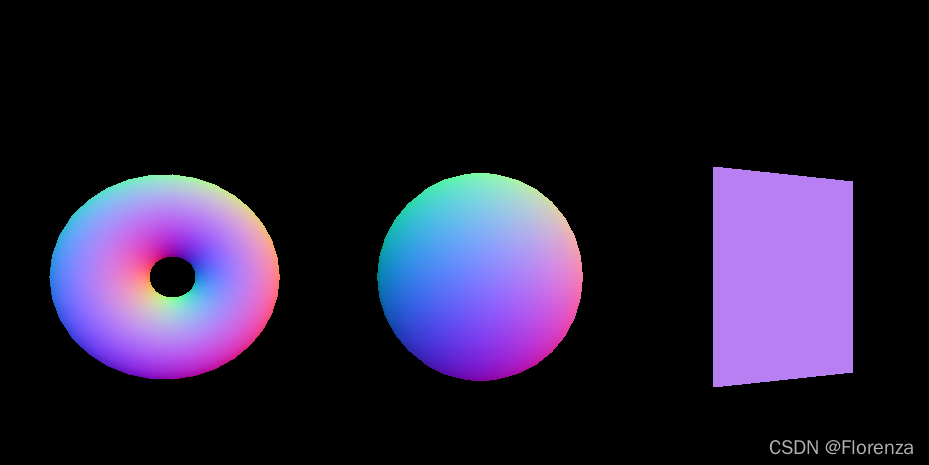
.wireframe : 线框
Boolean Render geometry as wireframe. Default is false (i.e. render as smooth shaded). .wireframeLinewidth : Float Controls wireframe thickness. Default is 1. Due to limitations of the OpenGL Core Profile with the WebGL renderer on most platforms linewidth will always be 1 regardless of the set value.
。线框:布尔型 将几何体渲染为线框。默认值为false(即渲染为平滑着色)。 。线框线宽:浮动 控制线框厚度。默认值为1。 由于大多数平台上带有WebGL渲染器的OpenGL核心配置文件的限制,无论设置值如何,线宽都将始终为1。
例:
const MeshBasicMaterial=new THREE.MeshNormalMaterial()
MeshBasicMaterial.wireframe=true; //线框显示?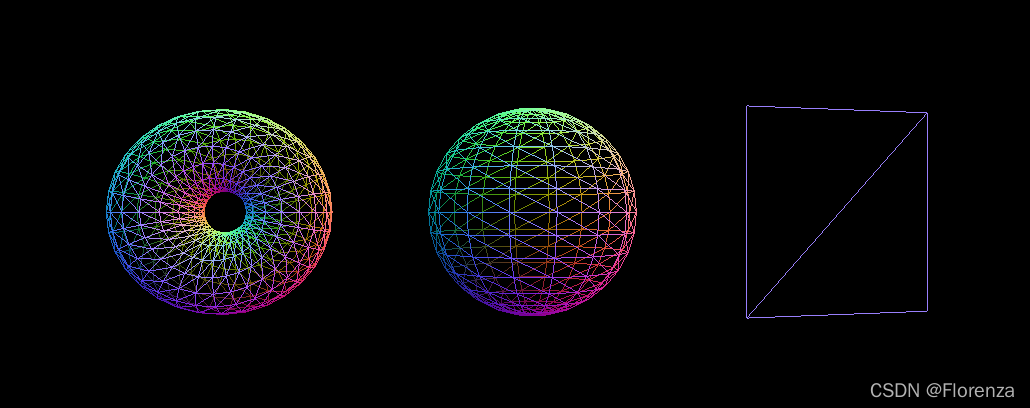
.flatShading : 平面阴影
Boolean Define whether the material is rendered with flat shading. Default is false.
。平面阴影:布尔型 定义是否使用平面着色渲染材质。默认值为false。
?例:
const MeshBasicMaterial=new THREE.MeshNormalMaterial()
MeshBasicMaterial.wireframe=true //线框
MeshBasicMaterial.flatShading=true //平面阴影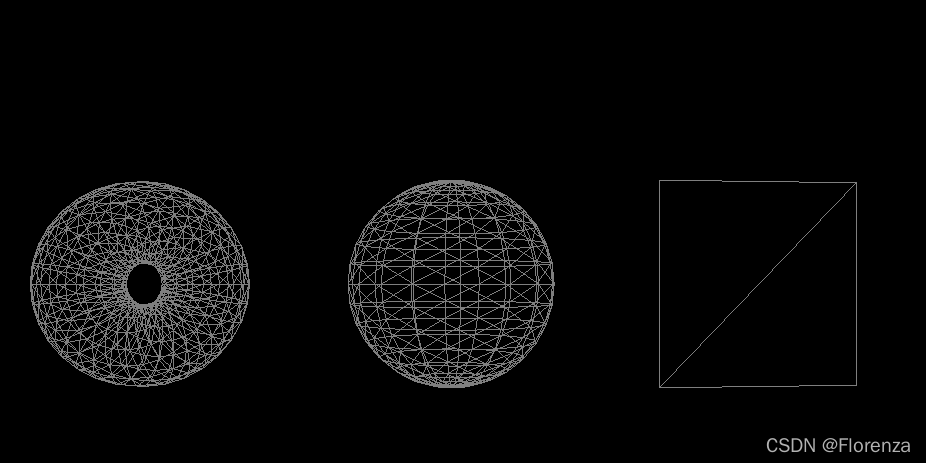
二、MeshMatcapMaterial????????(无光泽帽/泥塑
const MeshBasicMaterial=new THREE.MeshMatcapMaterial(); //泥塑材料)材质
MeshMatcapMaterial is defined by a MatCap (or Lit Sphere) texture, which encodes the material color and shading.
MeshMatcapMaterial由MatCap(或光照球体)纹理定义,它对材质颜色和明暗度进行编码。
MeshMatcapMaterial( parameters : Object ) parameters - (optional) an object with one or more properties defining the material's appearance. Any property of the material (including any property inherited from Material) can be passed in here. The exception is the property color, which can be passed in as a hexadecimal string and is 0xffffff (white) by default. Color.set( color ) is called internally.
MeshMatcapMaterial(参数:对象) 参数-(可选)具有一个或多个定义材料外观的属性的对象。材料的任何属性(包括从材料继承的任何属性)都可以在这里传入。 属性color是个例外,它可以作为十六进制字符串传入,默认情况下是0xffffff(白色)。内部调用Color.set( color)。
例:

.matcap : 纹理
Texture The matcap map. Default is null.
。matcap:纹理 马特卡普地图。默认值为null。
?例:
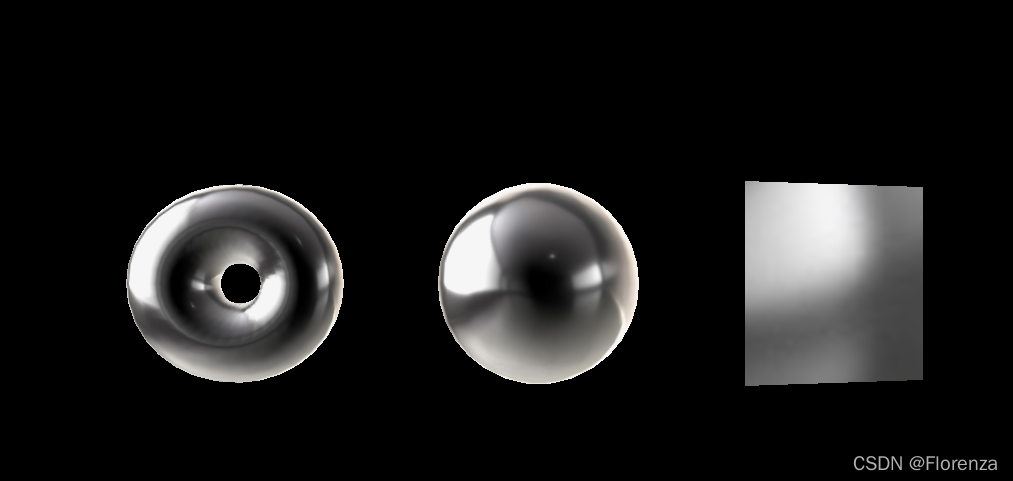
const MeshBasicMaterial=new THREE.MeshMatcapMaterial(); //泥塑材料
const matcp=texture.load('/matcaps/3.png');
MeshBasicMaterial.matcap=matcp

?材质
结果:
?
三、MeshDepthMaterial?(网格深度材料)
MeshDepthMaterial A material for drawing geometry by depth. Depth is based off of the camera near and far plane. White is nearest, black is farthest.
网格深度材料 一种按深度画几何图形的材料。深度是基于相机的近平面和远平面。白色最近,黑色最远。?
?const MeshBasicMaterial=new THREE.MeshDepthMaterial() ? //景深材料????????例:

?四、MeshLambertMaterial无光泽表面的材质
A material for non-shiny surfaces, without specular highlights. The material uses a non-physically based Lambertian model for calculating reflectance. This can simulate some surfaces (such as untreated wood or stone) well, but cannot simulate shiny surfaces with specular highlights (such as varnished wood). Shading is calculated using a Gouraud shading model. This calculates shading per vertex (i.e. in the vertex shader) and interpolates the results over the polygon's faces. Due to the simplicity of the reflectance and illumination models, performance will be greater when using this material over the MeshPhongMaterial, MeshStandardMaterial or MeshPhysicalMaterial, at the cost of some graphical accuracy.
无光泽表面的材质,没有镜面高光。 该材质使用基于非物理的朗伯模型来计算反射率。这可以很好地模拟某些表面(如未经处理的木材或石头),但不能模拟具有镜面高光的闪亮表面(如涂漆木材)。 使用Gouraud着色模型计算着色。这将计算每个顶点的着色(即在顶点着色器中)并将结果插值到多边形的面上。 由于反射和照明模型的简单性,当在MeshPhongMaterial、MeshStandardMaterial或MeshPhysicalMaterial上使用该材质时,性能会更好,但会损失一些图形精度。
****需要灯光辅助才能看到形状
例:
const MeshBasicMaterial=new THREE.MeshLambertMaterial() //反射材料
const ambientLight=new THREE.AmbientLight(0xffffff,0.5) //环境光
sence.add(ambientLight)
const pointLinght=new THREE.PointLight(0xffffff,0.5)
pointLinght.position.x=2;
pointLinght.position.y=3;
pointLinght.position.z=4;
sence.add(pointLinght)
colorTexture.minFilter=THREE.NearestFilter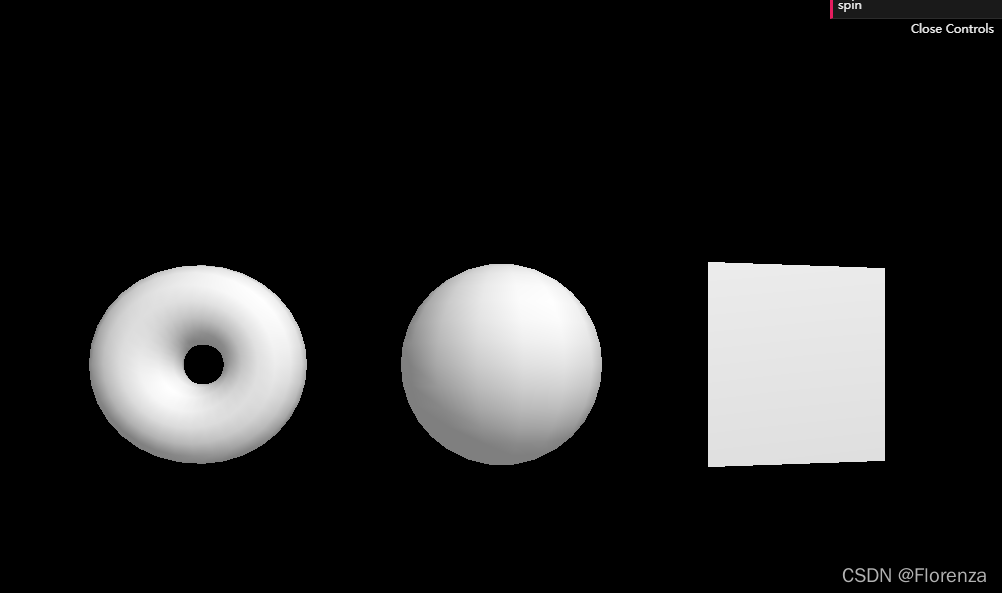
五、MeshPhongMaterial?镜面高光材质
MeshPhongMaterial A material for shiny surfaces with specular highlights. The material uses a non-physically based Blinn-Phong model for calculating reflectance. Unlike the Lambertian model used in the MeshLambertMaterial this can simulate shiny surfaces with specular highlights (such as varnished wood). Shading is calculated using a Phong shading model. This calculates shading per pixel (i.e. in the fragment shader, AKA pixel shader) which gives more accurate results than the Gouraud model used by MeshLambertMaterial, at the cost of some performance. The MeshStandardMaterial and MeshPhysicalMaterial also use this shading model. Performance will generally be greater when using this material over the MeshStandardMaterial or MeshPhysicalMaterial, at the cost of some graphical accuracy.
MeshPhongMaterial一种用于具有镜面高光的闪亮曲面的材质。该材质使用基于非物理的Blinn-Phong模型来计算反射率。与MeshLambertMaterial中使用的Lambertian模型不同,这可以模拟具有镜面高光的闪亮曲面(如涂漆木材)。使用Phong着色模型计算着色。这将计算每个像素的着色(即在片段着色器中,也称为像素着色器),其结果比MeshLambertMaterial使用的Gouraud模型更精确,但会牺牲一些性能。MeshStandardMaterial和MeshPhysicalMaterial也使用这种着色模型。与MeshStandardMaterial或MeshPhysicalMaterial相比,使用此材质时,性能通常会更好,但会牺牲一些图形精度。
***需要灯光辅助才能看到?
例:
const MeshBasicMaterial=new THREE.MeshPhongMaterial() //镜面反射材料
//光
const ambientLight=new THREE.AmbientLight(0xffffff,0.5) //环境光
sence.add(ambientLight)
const pointLinght=new THREE.PointLight(0xffffff,0.5)
pointLinght.position.x=2;
pointLinght.position.y=3;
pointLinght.position.z=4;
sence.add(pointLinght)
colorTexture.minFilter=THREE.NearestFilter?六、MeshToonMaterial卡通材质
Constructor MeshToonMaterial( parameters : Object ) parameters - (optional) an object with one or more properties defining the material's appearance. Any property of the material (including any property inherited from Material) can be passed in here. The exception is the property color, which can be passed in as a hexadecimal string and is 0xffffff (white) by default. Color.set( color ) is called internally.
构造器 MeshToonMaterial(参数:对象) 参数-(可选)具有一个或多个定义材料外观的属性的对象。材料的任何属性(包括从材料继承的任何属性)都可以在这里传入。 属性color是个例外,它可以作为十六进制字符串传入,默认情况下是0xffffff(白色)。内部调用Color.set( color)。
***需要灯光辅助?
例:
const MeshBasicMaterial=new THREE.MeshToonMaterial() //卡通材料?//添加灯光
const ambientLight=new THREE.AmbientLight(0xffffff,0.5) //环境光
sence.add(ambientLight)
const pointLinght=new THREE.PointLight(0xffffff,0.5)
pointLinght.position.x=2;
pointLinght.position.y=3;
pointLinght.position.z=4;
sence.add(pointLinght)
colorTexture.minFilter=THREE.NearestFilter
.gradientMap : 梯度纹理贴图
Texture Gradient map for toon shading. It's required to set Texture.minFilter and Texture.magFilter to THREE.NearestFilter when using this type of texture. Default is null.
。梯度贴图:纹理 卡通阴影的渐变贴图。需要将Texture.minFilter和Texture.magFilter设置为三个。使用这种类型的纹理时使用NearestFilter。默认值为null
例:
纹理贴图

const MeshBasicMaterial=new THREE.MeshToonMaterial() //卡通材料
const gradientsMesh=texture.load('/gradients/3.jpg')
gradientsMesh.minFilter=THREE.NearestFilter
gradientsMesh.magFilter=THREE.NearestFilter
MeshBasicMaterial.gradientMap=gradientsMesh
七、MeshStandardMaterial?标准材质
?A standard physically based material, using Metallic-Roughness workflow.
Physically based rendering (PBR) has recently become the standard in many 3D applications, such as Unity, Unreal and 3D Studio Max.
This approach differs from older approaches in that instead of using approximations for the way in which light?? ?interacts with a surface, a physically correct model is used. The idea is that, instead of tweaking materials to look good under specific lighting, a material can?? ?be created that will react 'correctly' under all lighting scenarios.
In practice this gives a more?? ?accurate and realistic looking result than the MeshLambertMaterial or MeshPhongMaterial, at the cost of being somewhat more computationally expensive.
Shading is calculated in the same way as for the MeshPhongMaterial, using a Phong shading model. This calculates shading per pixel (i.e. in the fragment shader, AKA pixel shader) which gives more accurate results than the Gouraud model used by MeshLambertMaterial, at the cost of some performance.
Note that for best results you should always specify an environment map when using this material.
For a non-technical introduction to the concept of PBR and how to set up a PBR material, check out these articles by the people at marmoset:
Basic Theory of Physically Based Rendering
Physically Based Rendering and You Can Too
Technical details of the approach used in three.js (and most other PBR systems) can be found is this paper from Disney (pdf), by Brent Burley一种基于物理的标准材料,使用金属粗糙度工作流。
基于物理的渲染(PBR)最近已成为许多3D应用程序的标准,如Unity、Unreal和3D Studio Max。
这种方法与旧方法的不同之处在于,它使用了一个物理上正确的模型,而不是对光与曲面的相互作用方式使用近似值。其想法是,可以创建一种在所有照明场景下都能“正确”反应的材质,而不是调整材质以使其在特定照明下看起来很好。
在实践中,与MeshLambertMaterial或MeshPhongMaterial相比,这会提供更精确、更逼真的结果,但代价是计算成本更高。
着色的计算方法与网格PhongMaterial相同,使用Phong着色模型。这会计算每像素的着色(即在片段着色器中,也称为像素着色器),这比MeshLambertMaterial使用的Gouraud模型提供更精确的结果,但会牺牲一些性能。
请注意,为了获得最佳效果,在使用此材质时应始终指定环境贴图。
要了解PBR概念的非技术性介绍以及如何建立PBR材料,请查看marmoset的人员撰写的以下文章:
基于物理绘制的基本理论
基于物理的渲染,您也可以
三个项目中使用的方法的技术细节。js(以及大多数其他PBR系统)是由Brent Burley从迪士尼(pdf)撰写的这篇论文
****需要灯光辅助才能看到形状?
例:
const MeshBasicMaterial=new THREE.MeshStandardMaterial(); //标准网格材质?
.metalness : 金属光泽
Float How much the material is like a metal. Non-metallic materials such as wood or stone use 0.0, metallic use 1.0, with nothing (usually) in between. Default is 0.0. A value between 0.0 and 1.0 could be used for a rusty metal look. If metalnessMap is also provided, both values are multiplied.
。金属性:浮动 这种材料有多像金属。木材或石头等非金属材料使用0.0,金属材料使用1.0,中间(通常)没有任何东西。默认值为0.0。介于0.0和1.0之间的值可用于生锈的金属外观。如果还提供了metalnessMap,则两个值相乘。
.roughness : 粗糙度
Float How rough the material appears. 0.0 means a smooth mirror reflection, 1.0 means fully diffuse. Default is 1.0. If roughnessMap is also provided, both values are multiplied.
。粗糙度:浮动 材料看起来有多粗糙。0.0表示平滑的镜面反射,1.0表示完全漫反射。默认值为1.0。如果还提供了roughnessMap,则两个值相乘。
