目录
????????? 1.1 Harris角点检测算法的基本思想
1. Harris角点检测算法
1.1 Harris角点检测算法的基本思想
????????从图像局部的小窗口观察图像特征。
????????角点定义:窗口向任意方向的移动都导致图像灰度的明显变化。
?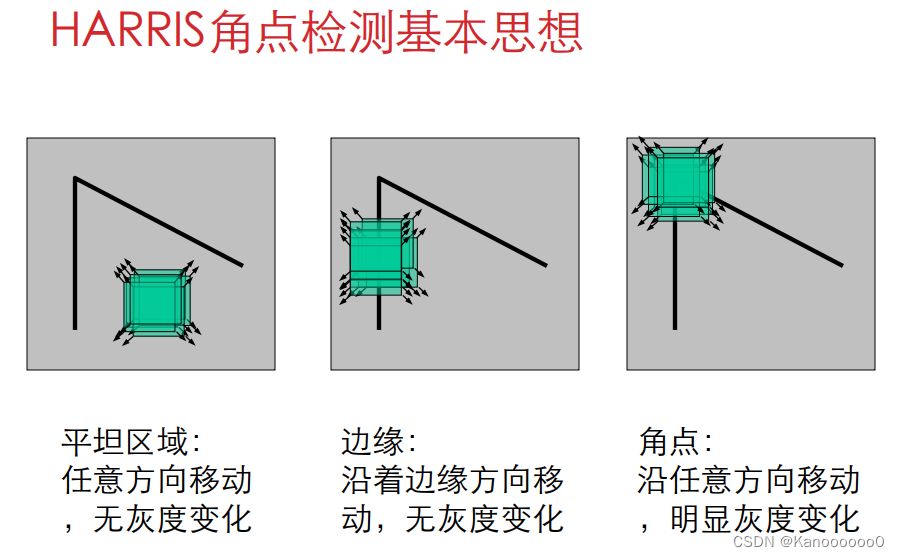 1.2 Harris角点检测算法的数学表达
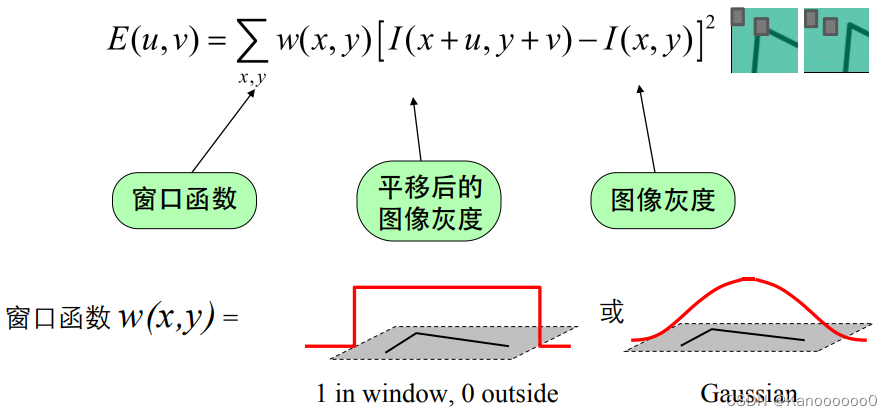
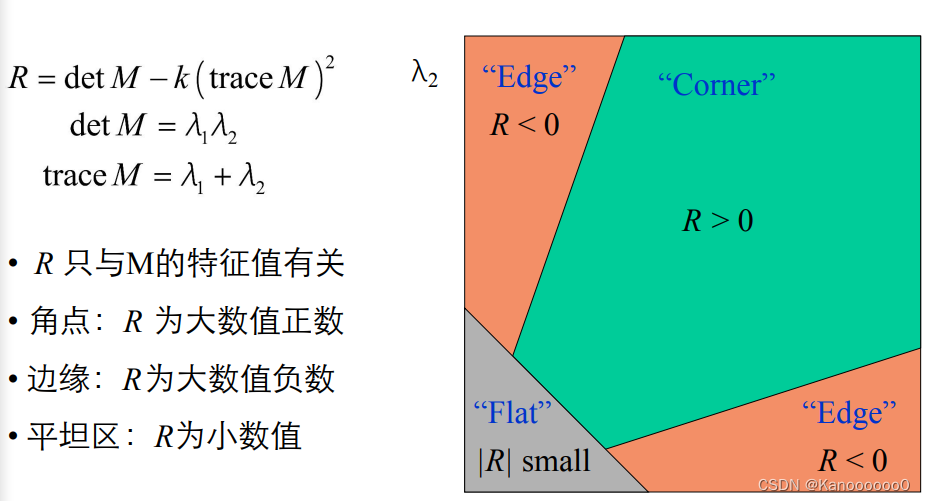
1.2 Harris角点检测算法的数学表达
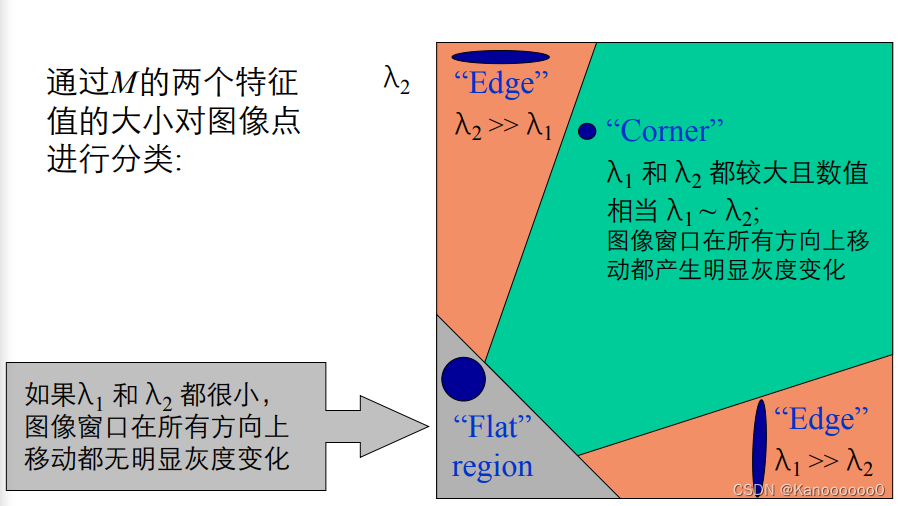
????????将图像窗口平移[u,v]产生灰度变化E(u,v)。
????????

?
 ?
?
 ?
?
?
?
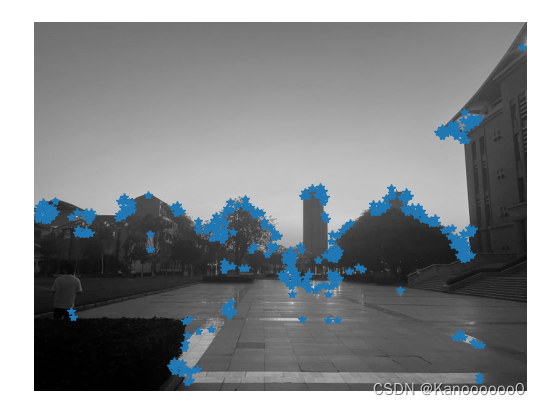
?1.3 Harris角点检测算法的代码实现
from pylab import *
from numpy import *
from scipy.ndimage import filters
from PIL import Image
def compute_harris_response(im,sigma=3):
""" Compute the Harris corner detector response function
for each pixel in a graylevel image. """
# derivatives
imx = zeros(im.shape)
filters.gaussian_filter(im, (sigma,sigma), (0,1), imx)
imy = zeros(im.shape)
filters.gaussian_filter(im, (sigma,sigma), (1,0), imy)
# compute components of the Harris matrix
Wxx = filters.gaussian_filter(imx*imx,sigma)
Wxy = filters.gaussian_filter(imx*imy,sigma)
Wyy = filters.gaussian_filter(imy*imy,sigma)
# determinant and trace
Wdet = Wxx*Wyy - Wxy**2
Wtr = Wxx + Wyy
return Wdet / Wtr
def get_harris_points(harrisim,min_dist=10,threshold=0.1):
""" Return corners from a Harris response image
min_dist is the minimum number of pixels separating
corners and image boundary. """
# find top corner candidates above a threshold
corner_threshold = harrisim.max() * threshold
harrisim_t = (harrisim > corner_threshold) * 1
# get coordinates of candidates
coords = array(harrisim_t.nonzero()).T
# ...and their values
candidate_values = [harrisim[c[0],c[1]] for c in coords]
# sort candidates (reverse to get descending order)
index = argsort(candidate_values)[::-1]
# store allowed point locations in array
allowed_locations = zeros(harrisim.shape)
allowed_locations[min_dist:-min_dist,min_dist:-min_dist] = 1
# select the best points taking min_distance into account
filtered_coords = []
for i in index:
if allowed_locations[coords[i,0],coords[i,1]] == 1:
filtered_coords.append(coords[i])
allowed_locations[(coords[i,0]-min_dist):(coords[i,0]+min_dist),
(coords[i,1]-min_dist):(coords[i,1]+min_dist)] = 0
return filtered_coords
def plot_harris_points(image,filtered_coords):
""" Plots corners found in image. """
figure()
gray()
imshow(image)
plot([p[1] for p in filtered_coords],
[p[0] for p in filtered_coords],'*')
axis('off')
show()
def get_descriptors(image,filtered_coords,wid=5):
""" For each point return pixel values around the point
using a neighbourhood of width 2*wid+1. (Assume points are
extracted with min_distance > wid). """
desc = []
for coords in filtered_coords:
patch = image[coords[0]-wid:coords[0]+wid+1,
coords[1]-wid:coords[1]+wid+1].flatten()
desc.append(patch)
return desc
def match(desc1,desc2,threshold=0.5):
""" For each corner point descriptor in the first image,
select its match to second image using
normalized cross correlation. """
n = len(desc1[0])
# pair-wise distances
d = -ones((len(desc1),len(desc2)))
for i in range(len(desc1)):
for j in range(len(desc2)):
d1 = (desc1[i] - mean(desc1[i])) / std(desc1[i])
d2 = (desc2[j] - mean(desc2[j])) / std(desc2[j])
ncc_value = sum(d1 * d2) / (n-1)
if ncc_value > threshold:
d[i,j] = ncc_value
ndx = argsort(-d)
matchscores = ndx[:,0]
return matchscores
def match_twosided(desc1,desc2,threshold=0.5):
""" Two-sided symmetric version of match(). """
matches_12 = match(desc1,desc2,threshold)
matches_21 = match(desc2,desc1,threshold)
ndx_12 = where(matches_12 >= 0)[0]
# remove matches that are not symmetric
for n in ndx_12:
if matches_21[matches_12[n]] != n:
matches_12[n] = -1
return matches_12
def appendimages(im1,im2):
""" Return a new image that appends the two images side-by-side. """
# select the image with the fewest rows and fill in enough empty rows
rows1 = im1.shape[0]
rows2 = im2.shape[0]
if rows1 < rows2:
im1 = concatenate((im1,zeros((rows2-rows1,im1.shape[1]))),axis=0)
elif rows1 > rows2:
im2 = concatenate((im2,zeros((rows1-rows2,im2.shape[1]))),axis=0)
# if none of these cases they are equal, no filling needed.
return concatenate((im1,im2), axis=1)
def plot_matches(im1,im2,locs1,locs2,matchscores,show_below=True):
""" Show a figure with lines joining the accepted matches
input: im1,im2 (images as arrays), locs1,locs2 (feature locations),
matchscores (as output from 'match()'),
show_below (if images should be shown below matches). """
im3 = appendimages(im1,im2)
if show_below:
im3 = vstack((im3,im3))
imshow(im3)
cols1 = im1.shape[1]
for i,m in enumerate(matchscores):
if m>0:
plot([locs1[i][1],locs2[m][1]+cols1],[locs1[i][0],locs2[m][0]],'c')
axis('off')
if __name__ == '__main__':
im = array(Image.open('C:\\Users\\Kano\\Desktop\\1.jpg').convert('L'))
harrisim = compute_harris_response(im)
filtered_coords = get_harris_points(harrisim,6)
plot_harris_points(im, filtered_coords)
?

2. SIFT算法
2.1 SIFT算法的基本原理
? ? ? ? SIFT算法是在图像尺度空间的基础上,提出了对图像缩放、旋转保持不变形的图像局部特征描述算子—SIFT(尺度不变特征变换)。
? ? ? ? SIFT算法可以解决的问题
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? 1.目标的旋转、缩放、平移(RST)
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? 2.图像仿射、投影变换(视点viewpoint)
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? 3.弱光照影响(illumination)
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? 4.部分目标遮挡(occlusion)
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? 5.杂物场景(clutter)
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? 6.噪声(noise)
? ? ? ? SIFT算法实现步骤简述:
????????实质可以归为在不同尺度空间上查找特征点(关键点)的问题。SIFT算法实现特征匹配主要有三个流程,1、提取关键点;2、对关键点附加 详细的信息(局部特征),即描述符;3、通过特征点(附带上特征向量的关 键点)的两两比较找出相互匹配的若干对特征点,建立景物间的对应关系。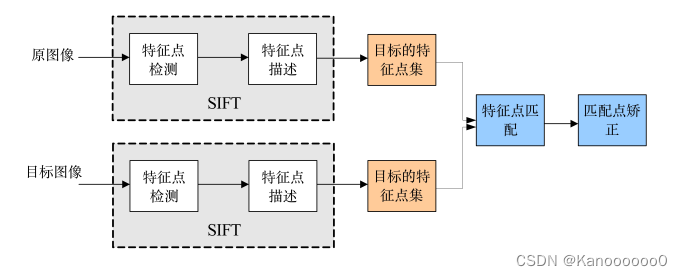
?2.2 关键点检测的相关概念
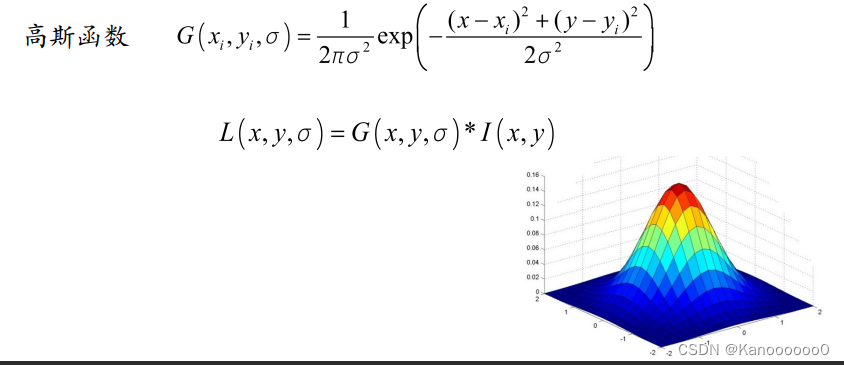
????????根据文献《Scale-space theory: A basic tool for analysing structures at different scales》可知,高斯核可以产生 多尺度空间的核,一个图像的 尺度空间,L(x, y, σ) ,定义为原始图像 I(x, y)与一个可变尺度的2维高斯 函数G(x, y, σ) 卷积运算。
????????
2.3 SIFT算法特征的代码实现
?
import cv2 as cv
from cv2 import waitKey
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
if __name__ == '__main__':
box = cv.imread("C:\\Users\\19835\\Desktop\\opencv\\task2\\task_1.jpg")
# 压缩图片以便显示
box=cv.resize(box,(960,540))
box_in_sence = cv.imread("C:\\Users\\19835\\Desktop\\opencv\\task2\\task_2.jpg")
box_in_sence=cv.resize(box_in_sence,(960,540))
cv.imshow("box", box)
cv.imshow("box_in_sence", box_in_sence)
# 创建SIFT特征检测器
sift = cv.SIFT_create()
# 特征点提取与描述子生成
kp1, des1 = sift.detectAndCompute(box,None)
kp2, des2 = sift.detectAndCompute(box_in_sence,None)
# 暴力匹配
bf = cv.DescriptorMatcher_create(cv.DescriptorMatcher_BRUTEFORCE)
matches = bf.match(des1,des2)
# 绘制最佳匹配
matches = sorted(matches, key = lambda x:x.distance)
result = cv.drawMatches(box, kp1, box_in_sence, kp2, matches[:15], None)
cv.imshow("-match", result)
cv.waitKey(0)
cv.destroyAllWindows()
?

?2.4 SIFT匹配地理标记图像
from pylab import *
from PIL import Image
from PCV.localdescriptors import sift
from PCV.tools import imtools
import pydot
#download_path = "panoimages" # set this to the path where you downloaded the panoramio images
#path = "/FULLPATH/panoimages/" # path to save thumbnails (pydot needs the full system path)
download_path = "C:\\Users\\Kano\\Desktop\\Study\\computer vision\\Test2" # set this to the path where you downloaded the panoramio images
path = "C:\\Users\\Kano\\Desktop\\Study\\computer vision\\Test2" # path to save thumbnails (pydot needs the full system path)
# list of downloaded filenames
imlist = imtools.get_imlist(download_path)
nbr_images = len(imlist)
# extract features
featlist = [imname[:-3] + 'sift' for imname in imlist]
for i, imname in enumerate(imlist):
sift.process_image(imname, featlist[i])
matchscores = zeros((nbr_images, nbr_images))
for i in range(nbr_images):
for j in range(i, nbr_images): # only compute upper triangle
print ('comparing ', imlist[i], imlist[j])
l1, d1 = sift.read_features_from_file(featlist[i])
l2, d2 = sift.read_features_from_file(featlist[j])
matches = sift.match_twosided(d1, d2)
nbr_matches = sum(matches > 0)
print ('number of matches = ', nbr_matches)
matchscores[i, j] = nbr_matches
print ("The match scores is: \n", matchscores)
# copy values
for i in range(nbr_images):
for j in range(i + 1, nbr_images): # no need to copy diagonal
matchscores[j, i] = matchscores[i, j]
#可视化
threshold = 2 # min number of matches needed to create link
g = pydot.Dot(graph_type='graph') # don't want the default directed graph
for i in range(nbr_images):
for j in range(i + 1, nbr_images):
if matchscores[i, j] > threshold:
# first image in pair
im = Image.open(imlist[i])
im.thumbnail((100, 100))
filename = path + str(i) + '.png'
im.save(filename) # need temporary files of the right size
g.add_node(pydot.Node(str(i), fontcolor='transparent', shape='rectangle', image=filename))
# second image in pair
im = Image.open(imlist[j])
im.thumbnail((100, 100))
filename = path + str(j) + '.png'
im.save(filename) # need temporary files of the right size
g.add_node(pydot.Node(str(j), fontcolor='transparent', shape='rectangle', image=filename))
g.add_edge(pydot.Edge(str(i), str(j)))
g.write_png('test.png')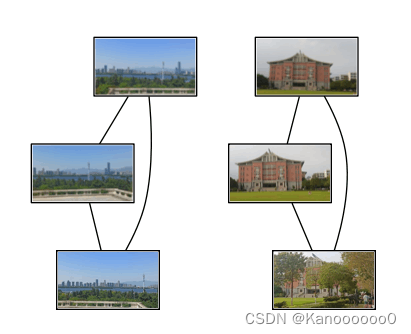
?
