物理引擎是纯粹的物理运算库,如力、加速度等(纯数据运算与图形绘制无关)。
3d物理引擎:bullet
2d物理引擎有两种:1.box2d 2.chipmunk
2d物理引擎会改变物体的位置和旋转,比如物理碰撞会引发物体的旋转
cocos中用到的物理引擎:
cocos2dx中的Node自带物理引擎的参数(基于chipmunk封装的):
//Physics:remaining backwardly compatible
#if CC_USE_PHYSICS
PhysicsBody* _physicsBody;
public:
void setPhysicsBody(PhysicsBody* physicsBody)
{
if (_physicsBody != nullptr)
{
removeComponent(_physicsBody);
}
addComponent(physicsBody);
}
PhysicsBody* getPhysicsBody() const { return _physicsBody; }
friend class PhysicsBody;
#endif简单理解:
在特定的物理环境下,拥有不同物理参数的刚体会产生不同的物理运动:
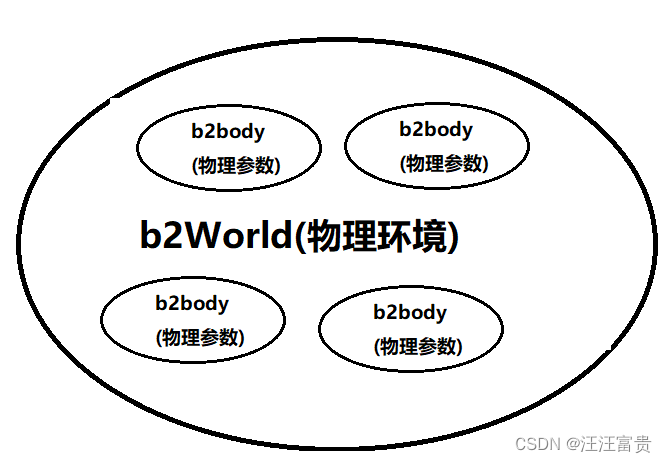
cocos封装的b2World类:
/// The world class manages all physics entities, dynamic simulation,
/// and asynchronous queries. The world also contains efficient memory
/// management facilities.
class b2World
{
public:
/// Construct a world object.
/// @param gravity the world gravity vector.
b2World(const b2Vec2& gravity);
~b2World();
b2Draw* m_debugDraw;
b2Body* m_bodyList;
/// Register a routine for debug drawing. The debug draw functions are called
/// inside with b2World::DrawDebugData method. The debug draw object is owned
/// by you and must remain in scope.
void SetDebugDraw(b2Draw* debugDraw);
/// Call this to draw shapes and other debug draw data. This is intentionally non-const.
void DrawDebugData();
/**
其他代码省略
**/
}
//用m_debugDraw绘制m_bodyList中的body
void b2World::DrawDebugData()
{
if (m_debugDraw == NULL)
{
return;
}
uint32 flags = m_debugDraw->GetFlags();
if (flags & b2Draw::e_shapeBit)
{
for (b2Body* b = m_bodyList; b; b = b->GetNext())
{
const b2Transform& xf = b->GetTransform();
for (b2Fixture* f = b->GetFixtureList(); f; f = f->GetNext())
{
if (b->IsActive() == false)
{
DrawShape(f, xf, b2Color(0.5f, 0.5f, 0.3f));
}
else if (b->GetType() == b2_staticBody)
{
DrawShape(f, xf, b2Color(0.5f, 0.9f, 0.5f));
}
//后面省略
}
}
}
//后面省略
}
void b2World::DrawShape(b2Fixture* fixture, const b2Transform& xf, const b2Color& color)
{
switch (fixture->GetType())
{
case b2Shape::e_circle:
{
b2CircleShape* circle = (b2CircleShape*)fixture->GetShape();
b2Vec2 center = b2Mul(xf, circle->m_p);
float32 radius = circle->m_radius;
b2Vec2 axis = b2Mul(xf.q, b2Vec2(1.0f, 0.0f));
//debugDraw绘制
m_debugDraw->DrawSolidCircle(center, radius, axis, color);
}
break;
//后面省略
}
}b2dWorld需要一个DebugDraw对象(继承于b2Draw),用来绘制body,使body的形状显示出来,用于调试。
cocos自带的DebugDraw类:
// This class implements debug drawing callbacks that are invoked
// inside b2World::Step.
class GLESDebugDraw : public b2Draw
{
float32 mRatio;//一米等于多少像素
cocos2d::GLProgram* mShaderProgram;
GLint mColorLocation;
void initShader( void );
public:
GLESDebugDraw();
GLESDebugDraw( float32 ratio );
virtual void DrawPolygon(const b2Vec2* vertices, int vertexCount, const b2Color& color);
virtual void DrawSolidPolygon(const b2Vec2* vertices, int vertexCount, const b2Color& color);
virtual void DrawCircle(const b2Vec2& center, float32 radius, const b2Color& color);
virtual void DrawSolidCircle(const b2Vec2& center, float32 radius, const b2Vec2& axis, const b2Color& color);
virtual void DrawSegment(const b2Vec2& p1, const b2Vec2& p2, const b2Color& color);
virtual void DrawTransform(const b2Transform& xf);
virtual void DrawPoint(const b2Vec2& p, float32 size, const b2Color& color);
virtual void DrawString(int x, int y, const char* string, ...);
virtual void DrawAABB(b2AABB* aabb, const b2Color& color);
};创建物理世界代码:
void b2d_world::init_b2d_world(float g) {
b2Vec2 phy_g;
phy_g.x = 0;
phy_g.y = g;
//创建一个b2World物理世界
this->phy_world = new b2World(phy_g);
// 提高我们的计算的性能。
this->phy_world->SetAllowSleeping(true);
// 为这个世界配置一个debugDraw对象,让这个debugDraw来完成我们的调试区域的绘制。
this->debug_draw = new GLESDebugDraw(b2d_world::PTM_RADIO);
this->phy_world->SetDebugDraw(this->debug_draw);
// test 动态圆形
b2Body* body = b2d_create_circle(this->phy_world, 100 / b2d_world::PTM_RADIO, b2BodyType::b2_dynamicBody);
body->SetTransform(b2Vec2(480 / b2d_world::PTM_RADIO, 320 / b2d_world::PTM_RADIO), 0);
body->SetLinearVelocity(b2Vec2(100 / b2d_world::PTM_RADIO, 0));
// 启动游戏的update,来迭代我们的物理世界
this->scheduleUpdateWithPriority(0);
}