本文目录
一、背景描述
在代码开发的过程中,总想看自己写的代码执行效率如何,每个方法的执行耗时是多少,但是在每个方法里添加耗时打印太麻烦,也不现实。不过幸好有 Spring 的面向切面编程。有了这个面向切面编程之后,那么,想要实现上述功能,一切就变得简单明了。
二、AOP实例
下面就上代码,其实很简单的一个类,代码没有几行:
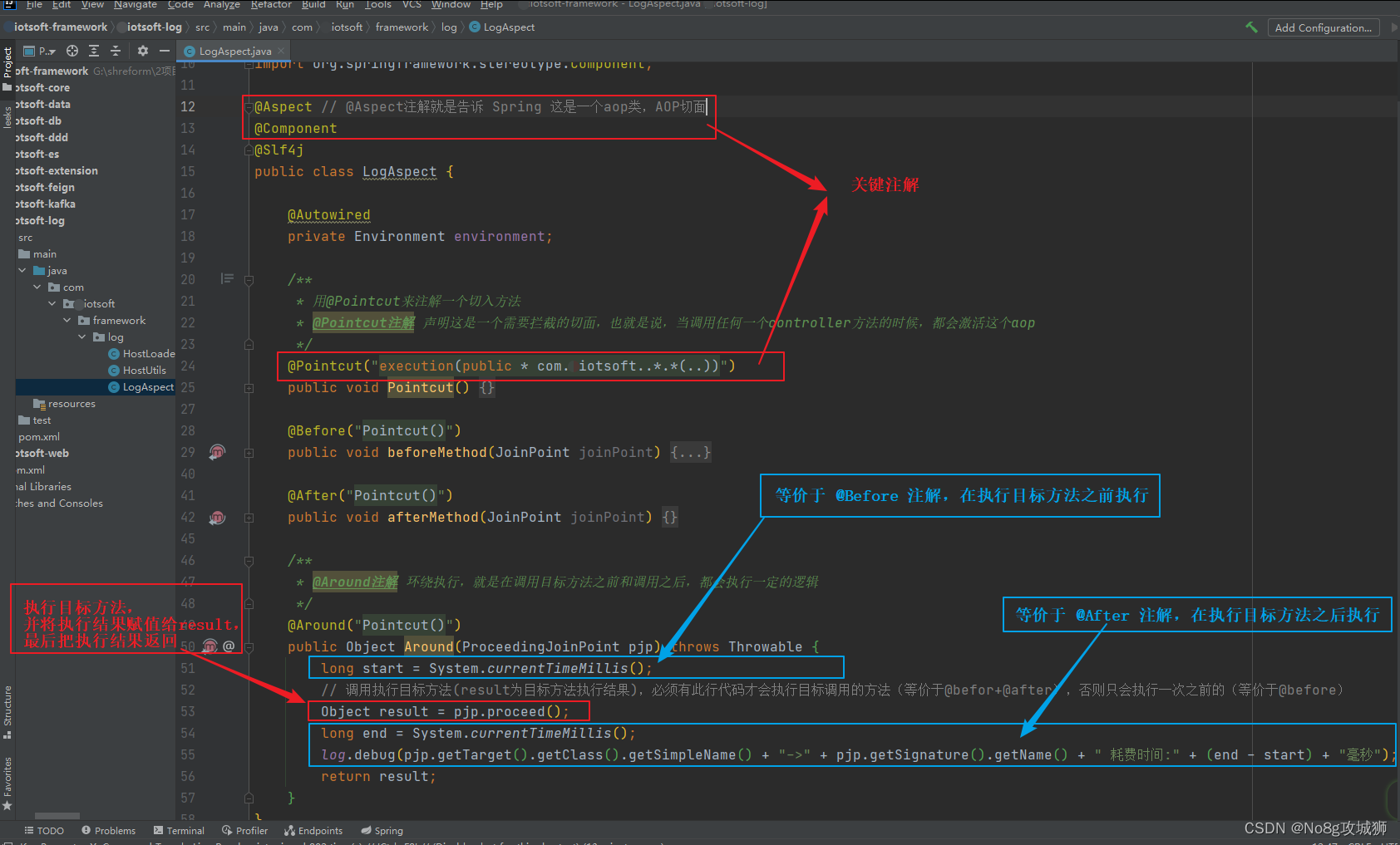
package com.iotsoft.framework.log;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*;
import org.slf4j.MDC;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.core.env.Environment;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Aspect // @Aspect注解就是告诉 Spring 这是一个aop类,AOP切面
@Component
@Slf4j
public class LogAspect {
@Autowired
private Environment environment;
/**
* 用@Pointcut来注解一个切入方法
* @Pointcut注解 声明这是一个需要拦截的切面,也就是说,当调用任何一个controller方法的时候,都会激活这个aop
*/
@Pointcut("execution(public * com.iotsoft..*.*(..))")
public void Pointcut() {
}
@Before("Pointcut()")
public void beforeMethod(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
String system = environment.getProperty("spring.application.system");
String name = environment.getProperty("spring.application.name");
if (system == null || "".equals(system)) {
system = name;
}
MDC.put("system", system);
MDC.put("app", name);
MDC.put("host", HostUtils.getHostName());
MDC.put("port", String.valueOf(HostUtils.getServerPort()));
}
@After("Pointcut()")
public void afterMethod(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
//MDC.clear();
}
/**
* @Around注解 环绕执行,就是在调用目标方法之前和调用之后,都会执行一定的逻辑
*/
@Around("Pointcut()")
public Object Around(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 调用执行目标方法(result为目标方法执行结果),必须有此行代码才会执行目标调用的方法(等价于@befor+@after),否则只会执行一次之前的(等价于@before)
Object result = pjp.proceed();
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
log.debug(pjp.getTarget().getClass().getSimpleName() + "->" + pjp.getSignature().getName() + " 耗费时间:" + (end - start) + "毫秒");
return result;
}
}三、@Around注解图文介绍
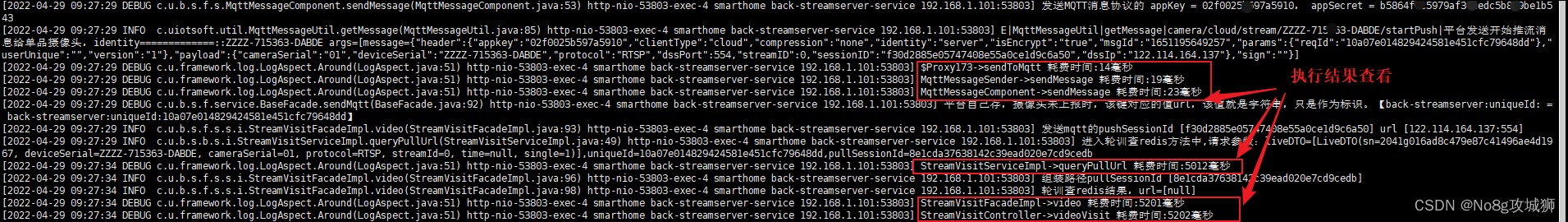
执行结果查看
?
@After 和 @Before 的解释可以看图片中,用法跟 @Around 一样。
完结!
