目录
- 前言
- 什么是多线程
- 什么是job system
- C# Job System的安全系统
- Native Container
- 创建job
- 调度jobs
- JobHandle and dependencies
- ParallelFor jobs
- An example of scheduling a ParallelFor job
- ParallelForTransform jobs
- C# Job System tips and troubleshooting
- Do not access static data from a job
- Flush scheduled batches
- Don’t try to update NativeContainer contents
- Call JobHandle.Complete to regain ownership
- Use Schedule and Complete in the control thread
- Use Schedule and Complete at the right time
- Mark NativeContainer types as read-only
- Check for data dependencies
- Debugging jobs
- Do not allocate managed memory in jobs
- Further information
前言
为什么要学:因为想要知道怎么写这些代码的GPU版本 想要看懂大佬的代码
Job System介绍地址
什么是多线程
默认情况下,一个线程在程序开始时运行。这是“主线”。主线程创建新线程来处理任务。这些新线程彼此并行运行,并且通常在完成后将其结果与主线程同步。
然而,游戏开发代码通常包含许多要一次执行的小指令。如果您为每个instruction创建一个线程,您最终会得到许多线程,每个线程的生命周期都很短。这可能会突破 CPU 和操作系统的处理能力极限。
可以通过拥有一个线程池来缓解线程生命周期的问题。但是,即使您使用线程池,您也很可能同时有大量线程处于活动状态。线程多于 CPU 内核会导致线程相互竞争 CPU 资源,从而导致频繁的上下文切换。上下文切换是在执行过程中保存线程状态的过程,然后在另一个线程上工作,然后重建第一个线程,稍后继续处理它。上下文切换是资源密集型的,因此您应该尽可能避免使用它。
什么是job system
A job system manages multithreaded code by creating jobs instead of threads.
A job system manages a group of worker threads across multiple cores. It usually has one worker thread per logical CPU core, to avoid context switching (although it may reserve some cores for the operating system or other dedicated applications).
A job system puts jobs into a job queue to execute. Worker threads in a job system take items from the job queue and execute them. A job system manages dependencies and ensures that jobs execute in the appropriate order.
什么是一个job
A job is a small unit of work that does one specific task. A job receives parameters and operates on data, similar to how a method call behaves. Jobs can be self-contained, or they can depend on other jobs to complete before they can run.
什么是job dependencies
In complex systems, like those required for game development, it is unlikely that each job is self-contained. One job is usually preparing the data for the next job. Jobs are aware of and support dependencies to make this work. If jobA has a dependency on jobB, the job system ensures that jobA does not start executing until jobB is complete.
C# Job System的安全系统
Race conditions
A race condition occurs when the output of one operation depends on the timing of another process outside of its control.
A race condition is not always a bug, but it is a source of nondeterministic behavior. When a race condition does cause a bug, it can be hard to find the source of the problem because it depends on timing, so you can only recreate the issue on rare occasions. Debugging it can cause the problem to disappear, because breakpoints and logging can change the timing of individual threads. Race conditions produce the most significant challenge in writing multithreaded code.
Safety system
the Unity C# Job System detects all potential race conditions and protects you from the bugs they can cause.
比如说,如果C# job system在一个job的control thread中从你的代码发送了一个数据的referencee,它无法确定在job正在写data的同时是否control thread也在读data。这种情况造成了一个竞争。
C# job ststem通过给每个job发送一份所需data的copy来解决这个问题,而不是control thread中的reference。这种copy和data分离,消除了race.
The way the C# Job System copies data means that a job can only access blittable data types. These types do not need conversion when passed between managed and native code.
(托管代码是什么东西)
The C# Job System can copy blittable types with memcpy and transfer the data between the managed and native parts of Unity. It uses memcpy to put data into native memory when scheduling jobs and gives the managed side access to that copy when executing jobs. For more information, see Scheduling jobs.
Native Container
安全系统复制数据过程的缺点是它还会隔离每个副本中的作业结果。为了克服这个限制,您需要将结果存储在一种称为NativeContainer的共享内存中。
NativeContainer是一种托管值类型,可为本机内存提供安全的 C# wrapper 。它包含一个指向unmanaged allocation的指针。当与 Unity C# job 系统一起使用时,NativeContainer允许job访问与主线程共享的数据,而不是使用副本。
NativeContainer 的类型
Unity 附带了一个NativeContainer名为NativeArray。您还可以使用 NativeSlice 操作 aNativeArray以获取从NativeArray特定位置到特定长度的子集。
注意:实体组件系统(ECS) 包扩展了Unity.Collections命名空间以包括其他类型NativeContainer:
NativeList- 可调整大小的NativeArray.
NativeHashMap- 键值对。
NativeMultiHashMap- 每个键有多个值。
NativeQueue- 先进先出 ( FIFO ) 队列。
NativeContainer 和安全系统
NativeContainer类型中。它跟踪任何正在读取和写入的内容NativeContainer。
注意:所有类型的安全检查NativeContainer(例如越界检查、释放检查和竞争条件检查)仅在 Unity编辑器和播放模式中可用。
该安全系统的一部分是DisposeSentinel和AtomicSafetyHandle。DisposeSentinel如果您没有正确释放内存,它会检测内存泄漏并给您一个错误。触发内存泄漏错误发生在泄漏发生很久之后。
使用AtomicSafetyHandle转移NativeContainer代码中的所有权。例如,如果两个 scheduled jobs正在写入同一个NativeArray,安全系统会抛出异常,并带有明确的错误消息,解释为什么以及如何解决问题。当您schedule the offending job时,安全系统会引发此异常。
在这种情况下,您可以使用依赖. 第一个 job可以写入NativeContainer,一旦它完成执行,下一个作业就可以安全地读取和写入相同的NativeContainer . 当从主线程访问数据时,读取和写入限制也适用。安全系统确实允许多个job并行读取相同的数据。
默认情况下,当job可以访问 NativeContainer时,它同时具有读取和写入访问权限。此This configuration can slow performance. The C# Job System doesn’t allow you to schedule a job that has write access to a NativeContainer at the same time as another job that’s writing to it.
If a job doesn’t need to write to a NativeContainer, mark the NativeContainer with the [ReadOnly] attribute, like so:
[ReadOnly]
public NativeArray<int> input;
In the above example, you can execute the job at the same time as other jobs that also have read-only access to the first NativeArray.
Note: There is no protection against accessing static data from within a job. Accessing static data circumvents all safety systems and can crash Unity. For more information, see C# Job System tips and troubleshooting.
NativeContainer Allocator
When creating a NativeContainer, you must specify the memory allocation type that you need. The allocation type depends on the length of time the job runs. This way you can tailor the allocation to get the best performance possible in each situation.
There are three Allocator types for NativeContainer memory allocation and release. You must specify the appropriate one when instantiating a NativeContainer.
Allocator.Temp has the fastest allocation. Use it for allocations with a lifespan of one frame or fewer. However, you can’t use Temp to pass NativeContainer allocations to jobs.
Allocator.TempJob is a slower allocation than Temp but is faster than Persistent. Use it for thread-safe allocations within a lifespan of four frames. Important: You must Dispose of this type of allocation within four frames, or the console prints a warning, generated from the native code. Most small jobs use this NativeContainer allocation type.
Allocator.Persistent is the slowest allocation but can last as long as you need it to, and if necessary, throughout the application’s lifetime. It is a wrapper for a direct call to malloc. Longer jobs can use this NativeContainer allocation type. Don’t use Persistent where performance is essential.
For example:
NativeArray<float> result = new NativeArray<float>(1, Allocator.TempJob);
Note: The number 1 in the example above indicates the size of the NativeArray. In this case, it has only one array element because it only stores one piece of data in result.
创建job
To create a job in Unity you need to implement the IJob interface. IJob allows you to schedule a single job that runs in parallel to any other jobs that are running.
Note: A “job” is a collective term in Unity for any struct that implements the IJob interface.
To create a job, you need to:
- Create a struct that implements IJob.
- Add the member variables that the job uses (either blittable types or NativeContainer types).
- Create a method in your struct called Execute with the implementation of the job inside it.
When executing the job, the Execute method runs once on a single core.
Note: When designing your job, remember that they operate on copies of data, except in the case of NativeContainer. So, the only way to access data from a job in the control thread is by writing to a NativeContainer.
An example of a simple job definition
// Job adding two floating point values together
public struct MyJob : IJob
{
public float a;
public float b;
public NativeArray<float> result;
public void Execute()
{
result[0] = a + b;
}
}
调度jobs
To schedule a job, you must:
- Instantiate the job.
- Populate the job’s data.
- Call the Schedule method.
Calling Schedule puts the job into the job queue for execution at the appropriate time. Once scheduled, you cannot interrupt a job.
Note: You can not call Schedule from within jobs.
An example of scheduling a job
// Create a native array of a single float to store the result. This example waits for the job to complete for illustration purposes
NativeArray<float> result = new NativeArray<float>(1, Allocator.TempJob);
// Set up the job data
MyJob jobData = new MyJob();
jobData.a = 10;
jobData.b = 10;
jobData.result = result;
// Schedule the job
JobHandle handle = jobData.Schedule();
// Wait for the job to complete
handle.Complete();
// All copies of the NativeArray point to the same memory, you can access the result in "your" copy of the NativeArray
float aPlusB = result[0];
// Free the memory allocated by the result array
result.Dispose();
我应该什么时候dispose这些变量
JobHandle and dependencies
When you call the Schedule method of a job it returns a JobHandle. You can use a JobHandle in your code as a dependency for other jobs. If a job depends on the results of another job, you can pass the first job’s JobHandle as a parameter to the second job’s Schedule method, like so:
JobHandle firstJobHandle = firstJob.Schedule();
secondJob.Schedule(firstJobHandle);
Note: All of a job’s dependencies must be scheduled on the same control thread as the job itself.
control thread具体体现在代码的哪里
Combining dependencies
If a job has many dependencies, you can use the method JobHandle.CombineDependencies to merge them. CombineDependencies allows you to pass them onto the Schedule method.
NativeArray<JobHandle> handles = new NativeArray<JobHandle>(numJobs, Allocator.TempJob);
// Populate `handles` with `JobHandles` from multiple scheduled jobs...
JobHandle jh = JobHandle.CombineDependencies(handles);
Waiting for jobs in the control thread
Use JobHandle to force your code to wait in the control thread for your job to finish executing. To do this, call the method Complete on the JobHandle. At this point, you know the control thread can safely access the NativeContainer that the job was using.
Note: Jobs do not start executing when you schedule them. If you are waiting for the job in the control thread, and you need access to the NativeContainer data that the job is using, you can call the method JobHandle.Complete. This method flushes the jobs from the memory cache and starts the process of execution. Calling Complete on a JobHandle returns ownership of that job’s NativeContainer types to the control thread. You need to call Complete on a JobHandle to safely access those NativeContainer types from the control thread again. It is also possible to return ownership to the control thread by calling Complete on a JobHandle that is from a job dependency. For example, you can call Complete on jobA, or you can call Complete on jobB which depends on jobA. Both result in the NativeContainer types that are used by jobA being safe to access on the control thread after the call to Complete.
Otherwise, if you don’t need access to the data, you need to explicity flush the batch. To do this, call the static method JobHandle.ScheduleBatchedJobs. Note that calling this method can negatively impact performance.
An example of multiple jobs and dependencies
Job code:
// Job adding two floating point values together
public struct MyJob : IJob
{
public float a;
public float b;
public NativeArray<float> result;
public void Execute()
{
result[0] = a + b;
}
}
// Job adding one to a value
public struct AddOneJob : IJob
{
public NativeArray<float> result;
public void Execute()
{
result[0] = result[0] + 1;
}
}
Main thread code:
// Create a native array of a single float to store the result in. This example waits for the job to complete
NativeArray<float> result = new NativeArray<float>(1, Allocator.TempJob);
// Setup the data for job #1
MyJob jobData = new MyJob();
jobData.a = 10;
jobData.b = 10;
jobData.result = result;//这是在干嘛 是把control thread的参数地址传递给job吗
// Schedule job #1
JobHandle firstHandle = jobData.Schedule();
// Setup the data for job #2
AddOneJob incJobData = new AddOneJob();
incJobData.result = result;//又做了这种事
// Schedule job #2
JobHandle secondHandle = incJobData.Schedule(firstHandle);//是不是因为这里用了dependency 就不用给first handle调用complete
// Wait for job #2 to complete
secondHandle.Complete();
// All copies of the NativeArray point to the same memory, you can access the result in "your" copy of the NativeArray
float aPlusB = result[0];
// Free the memory allocated by the result array
result.Dispose();
ParallelFor jobs
When scheduling jobs, there can only be one job doing one task. In a game, it is common to want to perform the same operation on a large number of objects. There is a separate job type called IJobParallelFor to handle this.
Note: A “ParallelFor” job is a collective term in Unity for any struct that implements the IJobParallelFor interface.
A ParallelFor job uses a NativeArray of data to act on as its data source. ParallelFor jobs run across multiple cores. There is one job per core, each handling a subset of the workload. IJobParallelFor behaves like IJob, but instead of a single Execute method, it invokes the Execute method once per item in the data source. There is an integer parameter in the Execute method. This index is to access and operate on a single element of the data source within the job implementation.
An example of a ParallelFor job definition:
struct IncrementByDeltaTimeJob: IJobParallelFor
{
public NativeArray<float> values;//这个就是被并行执行的array
public float deltaTime;
public void Execute (int index)//看 这里有个index 这个就是用来并行执行的index吧
{
float temp = values[index];
temp += deltaTime;
values[index] = temp;
}
}
Scheduling ParallelFor jobs
When scheduling ParallelFor jobs, you must specify the length of the NativeArray data source that you are splitting. The Unity C# Job System cannot know which NativeArray you want to use as the data source if there are several in the struct. The length also tells the C# Job System how many Execute methods to expect.
Behind the scenes, the scheduling of ParallelFor jobs is more complicated. When scheduling ParallelFor jobs, the C# Job System divides the work into batches to distribute between cores. Each batch contains a subset of Execute methods. The C# Job System then schedules up to one job in Unity’s native job system per CPU core and passes that native job some batches to complete.
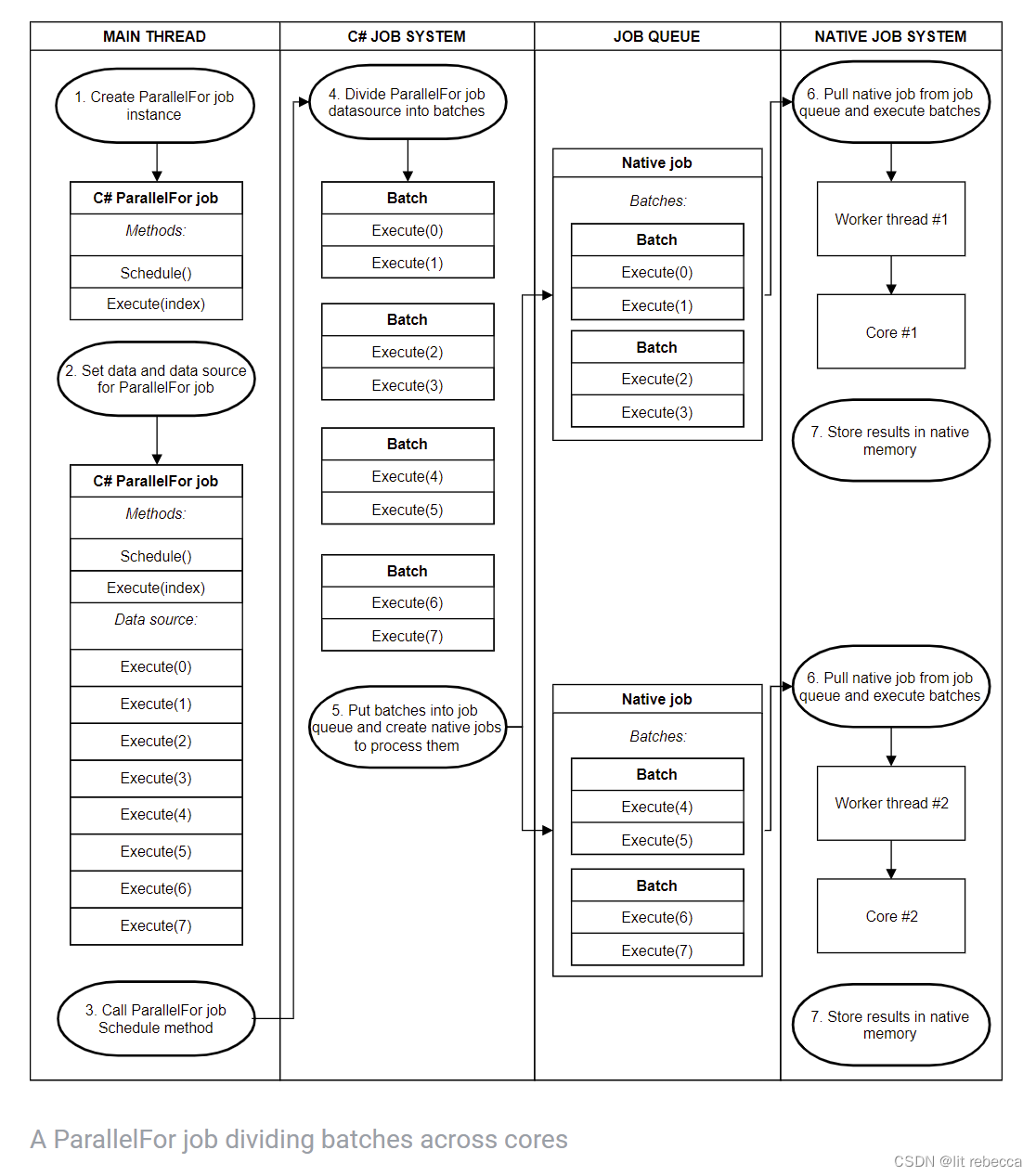
When a native job completes its batches before others, it steals remaining batches from the other native jobs. It only steals half of a native job’s remaining batches at a time, to ensure cache locality.
To optimize the process, you need to specify a batch count. The batch count controls how many jobs you get, and how fine-grained the redistribution of work between threads is. Having a low batch count, such as 1, gives you a more even distribution of work between threads. It does come with some overhead, so sometimes it is better to increase the batch count. Starting at 1 and increasing the batch count until there are negligible performance gains is a valid strategy.
An example of scheduling a ParallelFor job
Job code:
// Job adding two floating point values together
public struct MyParallelJob : IJobParallelFor
{
[ReadOnly]
public NativeArray<float> a;
[ReadOnly]
public NativeArray<float> b;
public NativeArray<float> result;
public void Execute(int i)
{
result[i] = a[i] + b[i];
}
}
Control thread code:
NativeArray<float> a = new NativeArray<float>(2, Allocator.TempJob);
NativeArray<float> b = new NativeArray<float>(2, Allocator.TempJob);
NativeArray<float> result = new NativeArray<float>(2, Allocator.TempJob);
a[0] = 1.1;
b[0] = 2.2;
a[1] = 3.3;
b[1] = 4.4;
MyParallelJob jobData = new MyParallelJob();
jobData.a = a;
jobData.b = b;
jobData.result = result;
// Schedule the job with one Execute per index in the results array and only 1 item per processing batch
JobHandle handle = jobData.Schedule(result.Length, 1);
// Wait for the job to complete
handle.Complete();
// Free the memory allocated by the arrays
a.Dispose();
b.Dispose();
result.Dispose();
ParallelForTransform jobs
A ParallelForTransform job is another type of ParallelFor job; designed specifically for operating on Transforms.
Note: A ParallelForTransform job is a collective term in Unity for any job that implements the IJobParallelForTransform interface.
C# Job System tips and troubleshooting
When using the Unity C# Job System, make sure you adhere to the following:
Do not access static data from a job
Accessing static data from a job circumvents all safety systems. If you access the wrong data, you might crash Unity, often in unexpected ways. For example, accessing MonoBehaviour can cause crashes on domain reloads.
Note: Because of this risk, future versions of Unity will prevent global variable access from jobs using static analysis. If you do access static data inside a job, you should expect your code to break in future versions of Unity.
Flush scheduled batches
When you want your jobs to start executing, then you can flush the scheduled batch with JobHandle.ScheduleBatchedJobs. Note that calling this method can negatively impact performance. Not flushing the batch delays the scheduling until the control thread waits for the result. In all other cases use JobHandle.Complete to start the execution process.
Note: In the Entity Component System (ECS) the batch is implicitly flushed for you, so calling JobHandle.ScheduleBatchedJobs is not necessary.
Don’t try to update NativeContainer contents
Due to the lack of ref returns, it is not possible to directly change the content of a NativeContainer. For example, nativeArray[0]++; is the same as writing var temp = nativeArray[0]; temp++; which does not update the value in nativeArray.
Instead, you must copy the data from the index into a local temporary copy, modify that copy, and save it back, like so:
MyStruct temp = myNativeArray[i];
temp.memberVariable = 0;
myNativeArray[i] = temp;
Call JobHandle.Complete to regain ownership
Tracing data ownership requires dependencies
to complete before the control thread can use them again. It is not enough to check JobHandle.IsCompleted. You must call the method JobHandle.Complete to regain ownership of the NativeContainer types to the control thread. Calling Complete also cleans up the state in the safety system. Not doing so introduces a memory leak. This process also applies if you schedule new jobs every frame that has a dependency on the previous frame’s job.
Use Schedule and Complete in the control thread
您只能从同一个控制线程调用Schedule和Complete.如果一个作业依赖于另一个作业,请使用它JobHandle来管理依赖关系,而不是尝试在作业中安排作业。
Use Schedule and Complete at the right time
Call Schedule on a job as soon as you have the data it needs, and don’t call Complete on it until you need the results. It is good practice to schedule a job that you do not need to wait for when it is not competing with any other jobs that are running. For example, if you have a period between the end of one frame and the beginning of the next frame where no jobs are running, and a one frame latency is acceptable, you can schedule the job towards the end of a frame and use its results in the following frame. Alternatively, if your game is saturating that changeover period with other jobs, and there is a big under-utilized period somewhere else in the frame, it is more efficient to schedule your job there instead.
Mark NativeContainer types as read-only
Remember that jobs have read and write access to NativeContainer types by default. Use the [ReadOnly] attribute when appropriate to improve performance.
Check for data dependencies
In the Unity Profiler window, the marker “WaitForJobGroup” on the control thread indicates that Unity is waiting for a job on a worker thread to complete. This marker could mean that you have introduced a data dependency somewhere that you should resolve. Look for JobHandle.Complete to track down where you have data dependencies that are forcing the control thread to wait.
Debugging jobs
Jobs have a Run function that you can use in place of Schedule to immediately execute the job on the control thread. You can use this for debugging purposes.
Do not allocate managed memory in jobs
在作业中分配托管内存非常慢,并且作业无法利用 Unity Burst 编译器来提高性能。Burst 是一种新的基于LLVM的后端编译器技术,可让您更轻松地完成工作。它采用 C# 作业并利用平台的特定功能生成高度优化的机器代码。
Further information
Watch the Unity GDC 2018: C# Job System playlist of talks.
For more advanced information on how the C# Job System relates to ECS, see the ECS package documentation.
For further discussion and troubleshooting, see Data Oriented Technology Stack forum.