说明
【跟月影学可视化】学习笔记。
如何用片元着色器控制局部颜色?
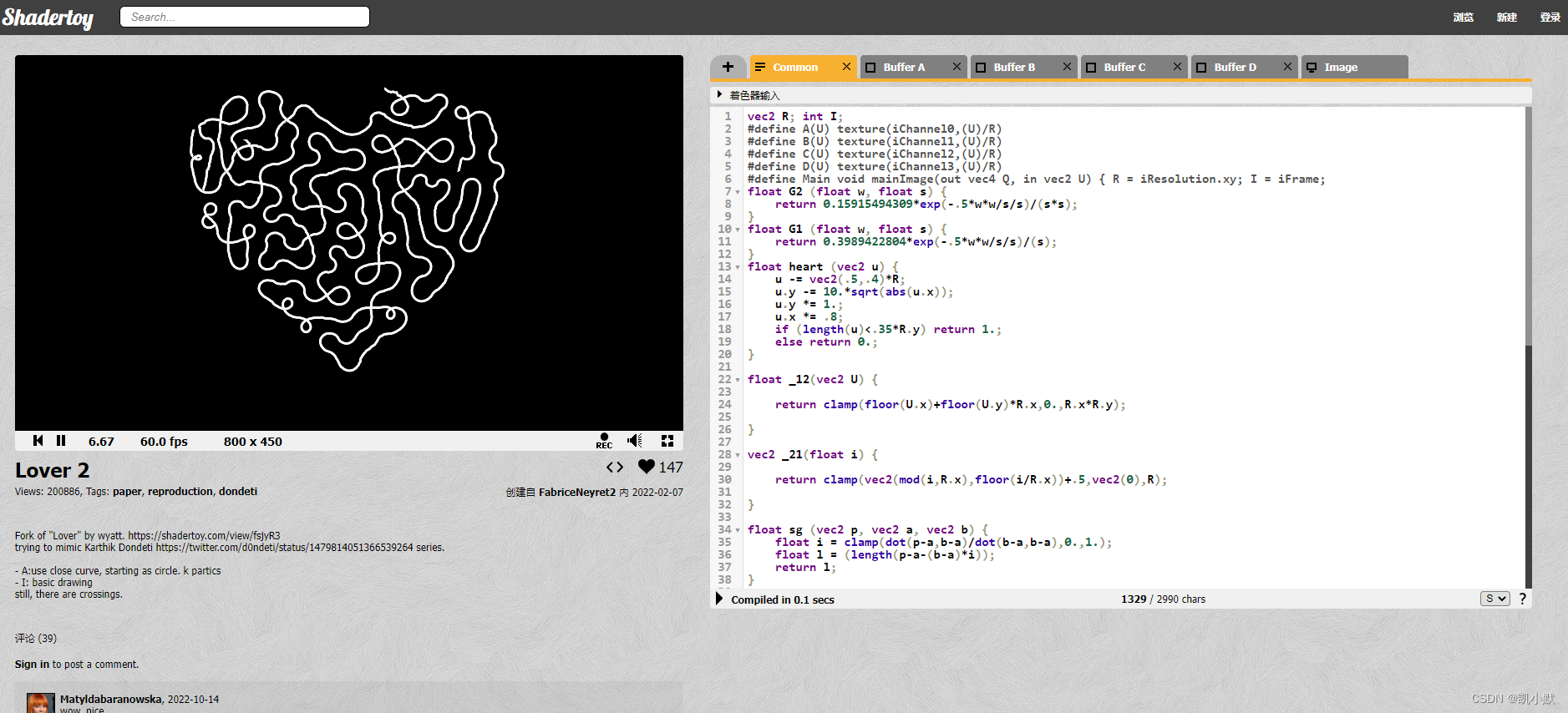
把图片绘制为纯黑色:
const fragment = `
#ifdef GL_ES
precision highp float;
#endif
varying vec2 vUv;
void main() {
gl_FragColor = vec4(0, 0, 0, 1);
}
`;
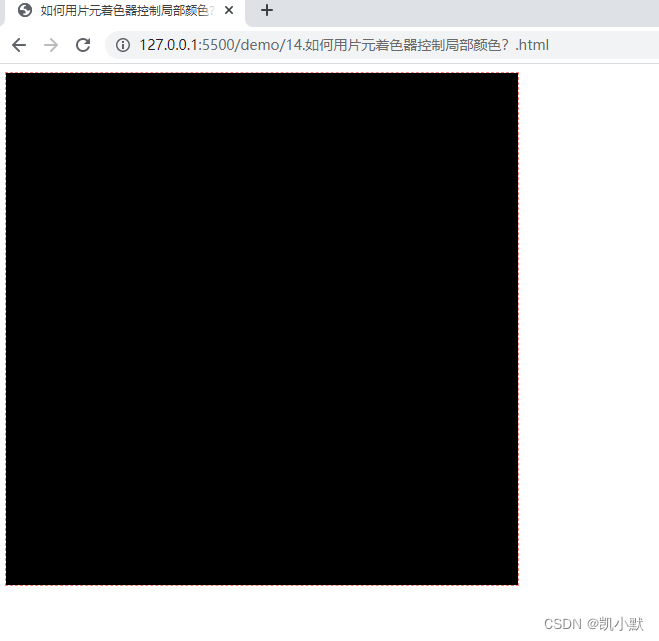
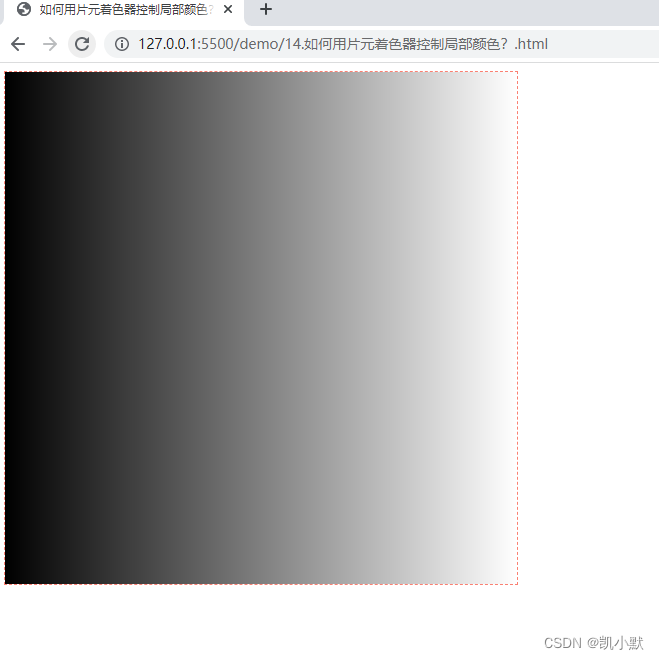
根据纹理坐标值来绘制,让某个图案的颜色,从左到右由黑向白过渡
const fragment = `
#ifdef GL_ES
precision highp float;
#endif
varying vec2 vUv;
void main() {
gl_FragColor.rgb = vec3(vUv.x);
gl_FragColor.a = 1.0;
}
`;
使用乘法创造一个 10*10 的方格,让每个格子左上角是绿色,右下角是红色,中间是过渡色。
const fragment = `
#ifdef GL_ES
precision highp float;
#endif
varying vec2 vUv;
void main() {
vec2 st = vUv * 10.0;
gl_FragColor.rgb = vec3(fract(st), 0.0);
gl_FragColor.a = 1.0;
}
`;
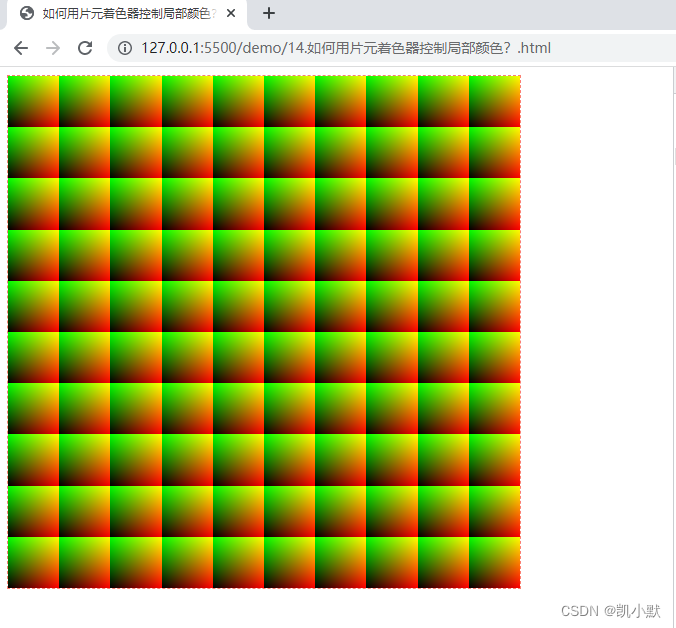
通过 idx = floor(st) 获取网格的索引,判断网格索引除以 2 的余数(奇偶性),根据它来决定是否翻转网格内的 x、y 坐标。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>如何用片元着色器控制局部颜色?</title>
<style>
canvas {
border: 1px dashed salmon;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<canvas width="512" height="512"></canvas>
<script src="./common/lib/gl-renderer.js"></script>
<script>
const vertex = `
attribute vec2 a_vertexPosition;
attribute vec2 uv;
varying vec2 vUv;
void main() {
gl_PointSize = 1.0;
vUv = uv;
gl_Position = vec4(a_vertexPosition, 1, 1);
}
`;
// // 把图片绘制为纯黑色
// const fragment = `
// #ifdef GL_ES
// precision highp float;
// #endif
// varying vec2 vUv;
// void main() {
// gl_FragColor = vec4(0, 0, 0, 1);
// }
// `;
// // 根据纹理坐标值来绘制,让某个图案的颜色,从左到右由黑向白过渡
// const fragment = `
// #ifdef GL_ES
// precision highp float;
// #endif
// varying vec2 vUv;
// void main() {
// gl_FragColor.rgb = vec3(vUv.x);
// gl_FragColor.a = 1.0;
// }
// `;
// // 使用乘法创造一个 10*10 的方格,让每个格子左上角是绿色,右下角是红色,中间是过渡色。
// const fragment = `
// #ifdef GL_ES
// precision highp float;
// #endif
// varying vec2 vUv;
// void main() {
// vec2 st = vUv * 10.0;
// gl_FragColor.rgb = vec3(fract(st), 0.0);
// gl_FragColor.a = 1.0;
// }
// `;
// 通过 idx = floor(st) 获取网格的索引,判断网格索引除以 2 的余数(奇偶性),根据它来决定是否翻转网格内的 x、y 坐标。
const fragment = `
#ifdef GL_ES
precision highp float;
#endif
varying vec2 vUv;
void main() {
vec2 st = vUv * 10.0;
vec2 idx = floor(st);
vec2 grid = fract(st);
vec2 t = mod(idx, 2.0);
if(t.x == 1.0) {
grid.x = 1.0 - grid.x;
}
if(t.y == 1.0) {
grid.y = 1.0 - grid.y;
}
gl_FragColor.rgb = vec3(grid, 0.0);
gl_FragColor.a = 1.0;
}
`;
const canvas = document.querySelector("canvas");
const renderer = new GlRenderer(canvas);
// 加载片元着色器并创建程序
const program = renderer.compileSync(fragment, vertex);
renderer.useProgram(program);
// 将顶点数据送入缓冲区
renderer.setMeshData([
{
positions: [
[-1, -1],
[-1, 1],
[1, 1],
[1, -1],
],
attributes: {
uv: [
[0, 0],
[0, 1],
[1, 1],
[1, 0],
],
},
cells: [
[0, 1, 2],
[2, 0, 3],
],
},
]);
// 渲染
renderer.render();
</script>
</body>
</html>

如何用片元着色器绘制圆、线段和几何图形
绘制圆
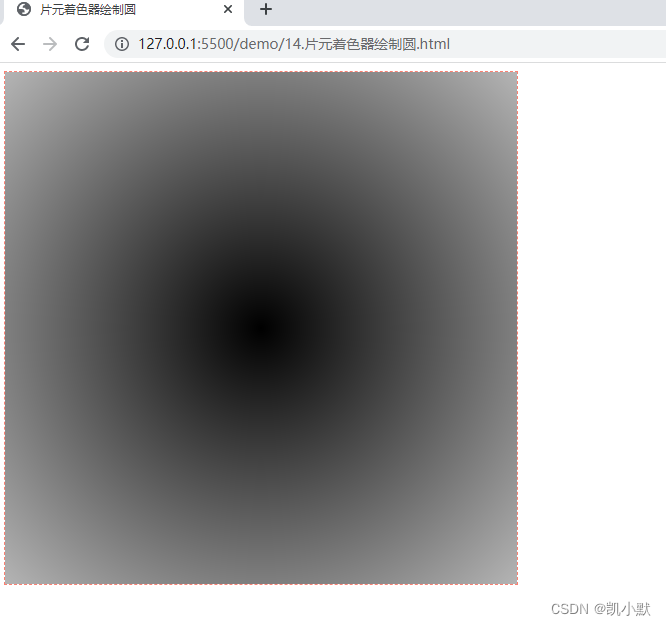
绘制一个模糊的圆
const fragment = `
#ifdef GL_ES
precision highp float;
#endif
varying vec2 vUv;
void main() {
floatd = distance(vUv, vec2(0.5));
gl_FragColor.rgb = d * vec3(1.0);
gl_FragColor.a = 1.0;
}
`;
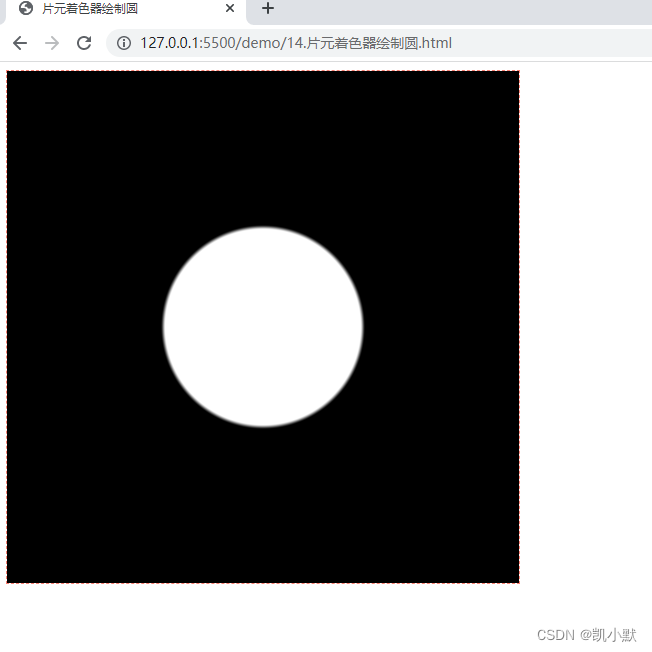
绘制一个清晰的圆
const fragment = `
#ifdef GL_ES
precision highp float;
#endif
varying vec2 vUv;
void main() {
float d = distance(vUv, vec2(0.5));
gl_FragColor.rgb = step(d, 0.2) * vec3(1.0);
gl_FragColor.a = 1.0;
}
`;
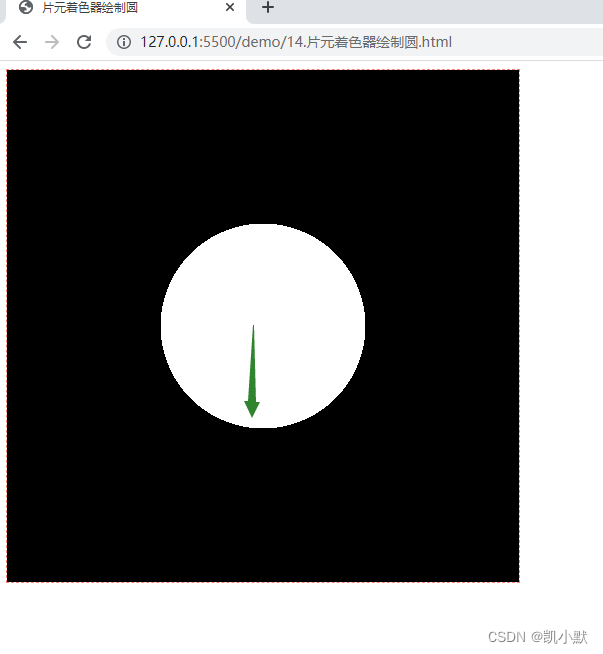
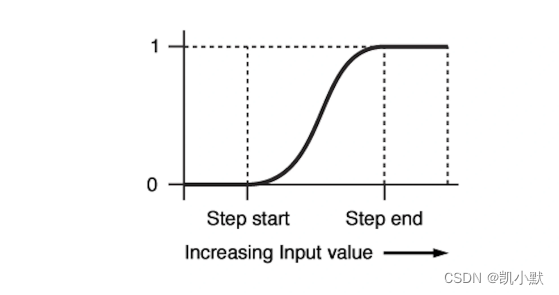
因为浮点数计算的精度导致的锯齿现象。用 smoothstep 代替 step 即可解决这种问题。smoothstep 在 step-start 和 step-end 之间有一个平滑过渡的区间。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>片元着色器绘制圆</title>
<style>
canvas {
border: 1px dashed salmon;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<canvas width="512" height="512"></canvas>
<script src="./common/lib/gl-renderer.js"></script>
<script>
const vertex = `
attribute vec2 a_vertexPosition;
attribute vec2 uv;
varying vec2 vUv;
void main() {
gl_PointSize = 1.0;
vUv = uv;
gl_Position = vec4(a_vertexPosition, 1, 1);
}
`;
// // 模糊的圆
// const fragment = `
// #ifdef GL_ES
// precision highp float;
// #endif
// varying vec2 vUv;
// void main() {
// float d = distance(vUv, vec2(0.5));
// gl_FragColor.rgb = d * vec3(1.0);
// gl_FragColor.a = 1.0;
// }
// `;
// // 清晰的圆
// const fragment = `
// #ifdef GL_ES
// precision highp float;
// #endif
// varying vec2 vUv;
// void main() {
// float d = distance(vUv, vec2(0.5));
// gl_FragColor.rgb = step(d, 0.2) * vec3(1.0);
// gl_FragColor.a = 1.0;
// }
// `;
// 清晰的圆无锯齿
const fragment = `
#ifdef GL_ES
precision highp float;
#endif
varying vec2 vUv;
void main() {
float d = distance(vUv, vec2(0.5));
gl_FragColor.rgb = smoothstep(d, d + 0.01, 0.2) * vec3(1.0);
gl_FragColor.a = 1.0;
}
`;
const canvas = document.querySelector("canvas");
const renderer = new GlRenderer(canvas);
// 加载片元着色器并创建程序
const program = renderer.compileSync(fragment, vertex);
renderer.useProgram(program);
// 将顶点数据送入缓冲区
renderer.setMeshData([
{
positions: [
[-1, -1],
[-1, 1],
[1, 1],
[1, -1],
],
attributes: {
uv: [
[0, 0],
[0, 1],
[1, 1],
[1, 0],
],
},
cells: [
[0, 1, 2],
[2, 0, 3],
],
},
]);
// 渲染
renderer.render();
</script>
</body>
</html>
实现图片的渐显渐隐效果
上一节我们实现了图片粒子化,下面利用绘制圆实现图片的渐显渐隐效果
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>片元着色器绘制圆实现图片的渐显渐隐效果</title>
<style>
canvas {
border: 1px dashed salmon;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<canvas width="1920" height="1080"></canvas>
<script src="./common/lib/gl-renderer.js"></script>
<script>
const vertex = `
attribute vec2 a_vertexPosition;
attribute vec2 uv;
varying vec2 vUv;
void main() {
gl_PointSize = 1.0;
vUv = uv;
gl_Position = vec4(a_vertexPosition, 1, 1);
}
`;
const fragment = `
#ifdef GL_ES
precision highp float;
#endif
uniform sampler2D tMap;
uniform vec2 uResolution;
uniform float uTime;
varying vec2 vUv;
float random (vec2 st) {
return fract(sin(dot(st.xy, vec2(12.9898,78.233)))*43758.5453123);
}
void main() {
vec2 uv = vUv;
uv.y *= uResolution.y / uResolution.x;
vec2 st = uv * 100.0;
float d = distance(fract(st), vec2(0.5));
float p = uTime + random(floor(st));
float shading = 0.5 + 0.5 * sin(p);
d = smoothstep(d, d + 0.01, 1.0 * shading);
vec4 color = texture2D(tMap, vUv);
gl_FragColor.rgb = color.rgb * clamp(0.5, 1.3, d + 1.0 * shading);
gl_FragColor.a = color.a;
}
`;
const canvas = document.querySelector("canvas");
const renderer = new GlRenderer(canvas);
// 加载片元着色器并创建程序
const program = renderer.compileSync(fragment, vertex);
renderer.useProgram(program);
(async function () {
const texture = await renderer.loadTexture('./assets/img/flower.jpg');
renderer.uniforms.tMap = texture;
renderer.uniforms.uResolution = [canvas.width, canvas.height];
renderer.uniforms.uTime = 0;
// 将顶点数据送入缓冲区
renderer.setMeshData([{
positions: [
[-1, -1],
[-1, 1],
[1, 1],
[1, -1],
],
attributes: {
uv: [
[0, 0],
[0, 1],
[1, 1],
[1, 0],
],
},
cells: [[0, 1, 2], [2, 0, 3]],
}]);
renderer.render();
function update(t) {
renderer.uniforms.uTime = t / 500;
requestAnimationFrame(update);
}
update(0);
}());
</script>
</body>
</html>

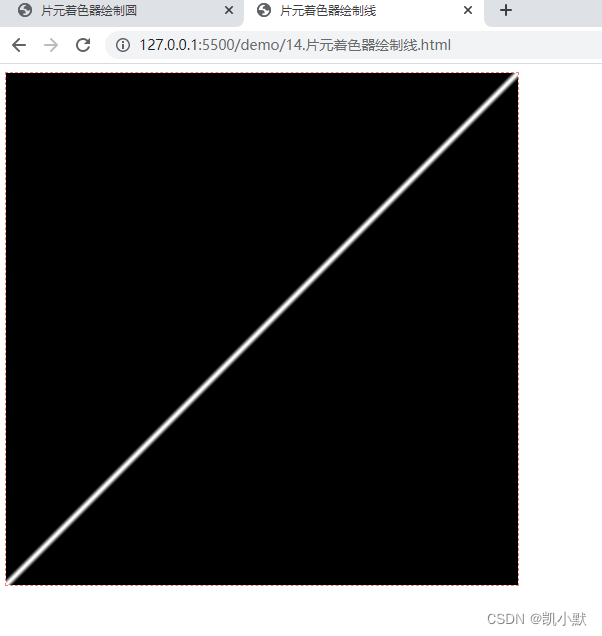
绘制线
计算点到直线(向量)的距离即可。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>片元着色器绘制圆</title>
<style>
canvas {
border: 1px dashed salmon;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<canvas width="512" height="512"></canvas>
<script src="./common/lib/gl-renderer.js"></script>
<script>
const vertex = `
attribute vec2 a_vertexPosition;
attribute vec2 uv;
varying vec2 vUv;
void main() {
gl_PointSize = 1.0;
vUv = uv;
gl_Position = vec4(a_vertexPosition, 1, 1);
}
`;
// 画出一条斜线
const fragment = `
#ifdef GL_ES
precision highp float;
#endif
varying vec2 vUv;
void main() {
vec3 line = vec3(1, 1, 0);
float d = abs(cross(vec3(vUv,0), normalize(line)).z);
gl_FragColor.rgb = (1.0 - smoothstep(0.0, 0.01, d)) * vec3(1.0);
gl_FragColor.a = 1.0;
}
`;
const canvas = document.querySelector("canvas");
const renderer = new GlRenderer(canvas);
// 加载片元着色器并创建程序
const program = renderer.compileSync(fragment, vertex);
renderer.useProgram(program);
// 将顶点数据送入缓冲区
renderer.setMeshData([
{
positions: [
[-1, -1],
[-1, 1],
[1, 1],
[1, -1],
],
attributes: {
uv: [
[0, 0],
[0, 1],
[1, 1],
[1, 0],
],
},
cells: [
[0, 1, 2],
[2, 0, 3],
],
},
]);
// 渲染
renderer.render();
</script>
</body>
</html>
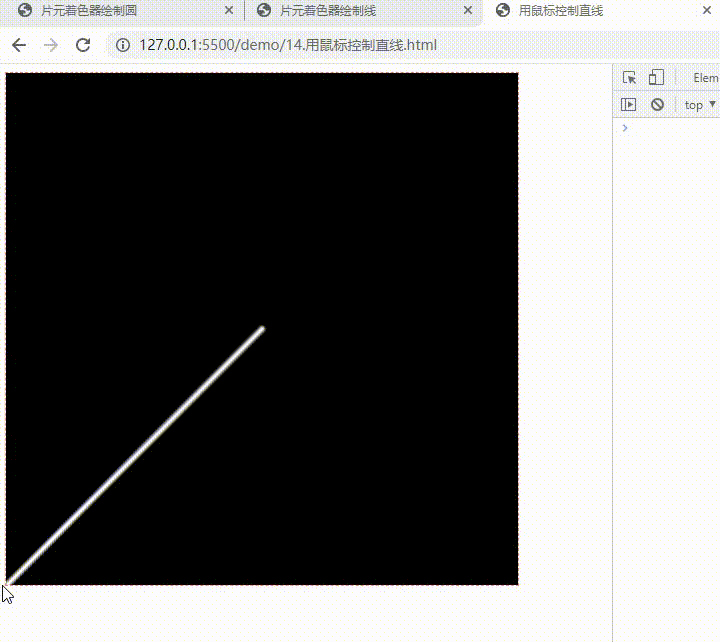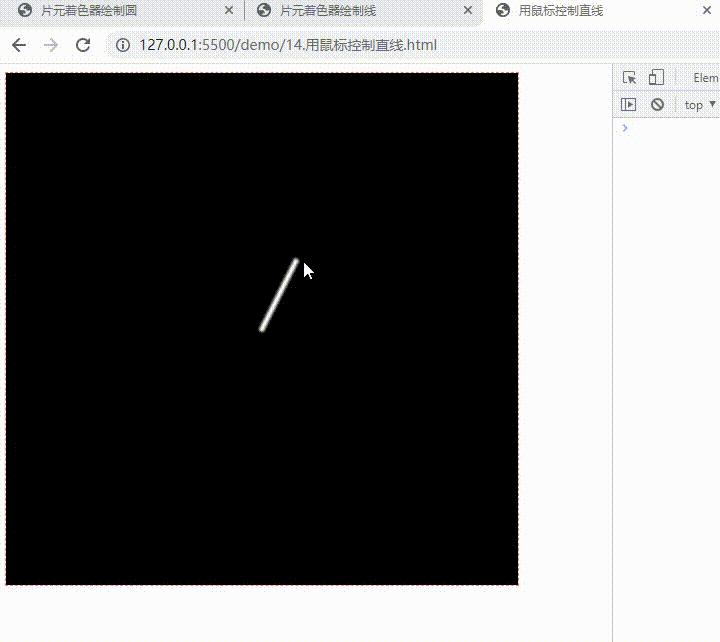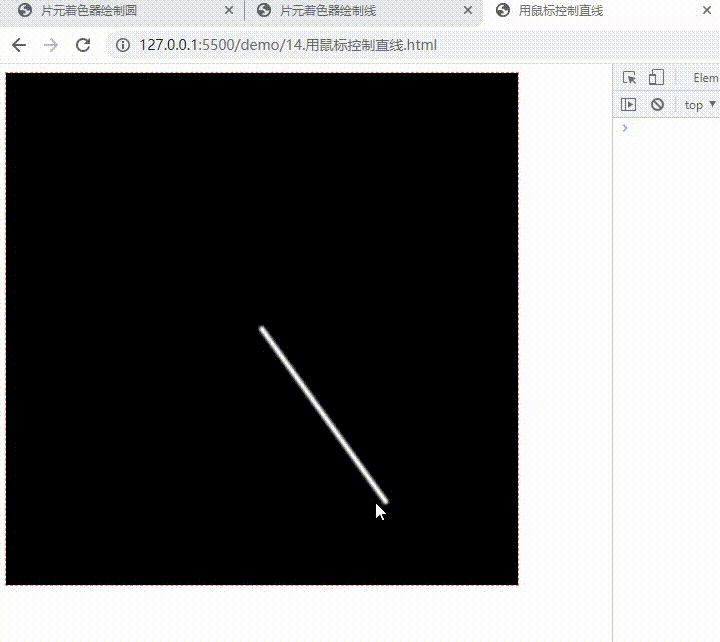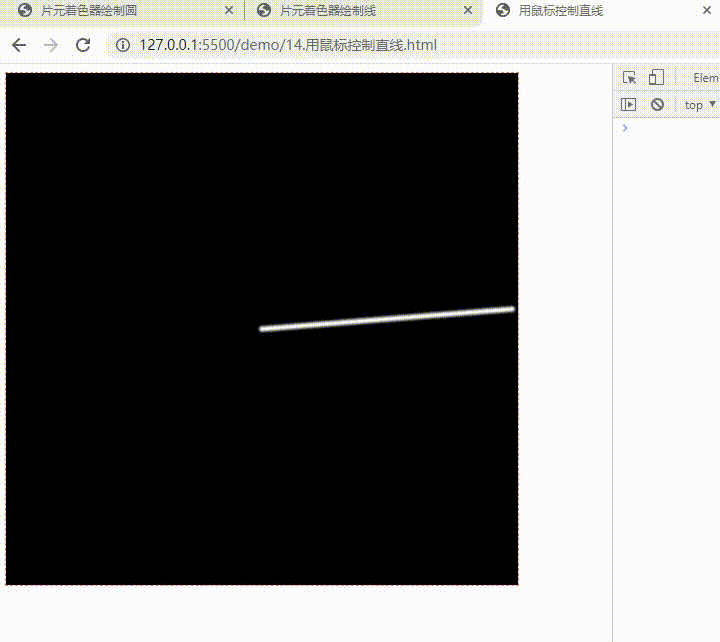
用鼠标控制直线
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>用鼠标控制直线</title>
<style>
canvas {
border: 1px dashed salmon;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<canvas width="512" height="512"></canvas>
<script src="./common/lib/gl-renderer.js"></script>
<script>
const vertex = `
attribute vec2 a_vertexPosition;
attribute vec2 uv;
varying vec2 vUv;
void main() {
gl_PointSize = 1.0;
vUv = uv;
gl_Position = vec4(a_vertexPosition, 1, 1);
}
`;
const fragment = `
#ifdef GL_ES
precision highp float;
#endif
varying vec2 vUv;
uniform vec2 uMouse;
uniform vec2 uOrigin;
// 返回点到线段的距离
float seg_distance(in vec2 st, in vec2 a, in vec2 b) {
vec3 ab = vec3(b - a, 0);
vec3 p = vec3(st - a, 0);
float l = length(ab);
float d = abs(cross(p, normalize(ab)).z);
float proj = dot(p, ab) / l;
if(proj >= 0.0 && proj <= l) return d;
return min(distance(st, a), distance(st, b));
}
void main() {
float d = seg_distance(vUv, uMouse, uOrigin);
gl_FragColor.rgb = (1.0 - smoothstep(0.0, 0.01, d)) * vec3(1.0);
gl_FragColor.a = 1.0;
}
`;
const canvas = document.querySelector("canvas");
const renderer = new GlRenderer(canvas);
// 加载片元着色器并创建程序
const program = renderer.compileSync(fragment, vertex);
renderer.useProgram(program);
renderer.uniforms.uMouse = [-1, -1];
// 直线经过的固定点
renderer.uniforms.uOrigin = [0.5, 0.5];
canvas.addEventListener("mousemove", (e) => {
const { x, y, width, height } =
e.target.getBoundingClientRect();
renderer.uniforms.uMouse = [
(e.x - x) / width,
1.0 - (e.y - y) / height,
];
}
);
// 将顶点数据送入缓冲区
renderer.setMeshData([
{
positions: [
[-1, -1],
[-1, 1],
[1, 1],
[1, -1],
],
attributes: {
uv: [
[0, 0],
[0, 1],
[1, 1],
[1, 0],
],
},
cells: [
[0, 1, 2],
[2, 0, 3],
],
},
]);
// 渲染
renderer.render();
</script>
</body>
</html>
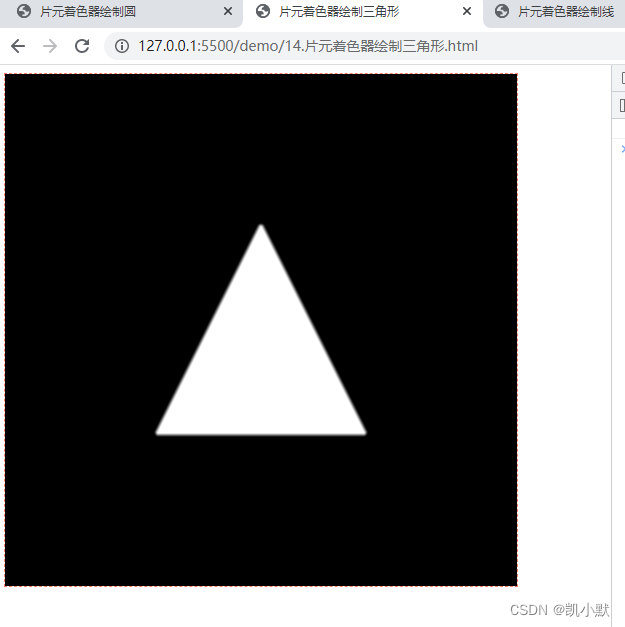
绘制三角形
点到三角形三条边的距离有三个,只要这三个距离的符号都相同,我们就能确定点在三角形内。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>片元着色器绘制三角形</title>
<style>
canvas {
border: 1px dashed salmon;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<canvas width="512" height="512"></canvas>
<script src="./common/lib/gl-renderer.js"></script>
<script>
const vertex = `
attribute vec2 a_vertexPosition;
attribute vec2 uv;
varying vec2 vUv;
void main() {
gl_PointSize = 1.0;
vUv = uv;
gl_Position = vec4(a_vertexPosition, 1, 1);
}
`;
const fragment = `
#ifdef GL_ES
precision highp float;
#endif
varying vec2 vUv;
float line_distance(in vec2 st, in vec2 a, in vec2 b) {
vec3 ab = vec3(b - a, 0);
vec3 p = vec3(st - a, 0);
float l = length(ab);
return cross(p, normalize(ab)).z;
}
float seg_distance(in vec2 st, in vec2 a, in vec2 b) {
vec3 ab = vec3(b - a, 0);
vec3 p = vec3(st - a, 0);
float l = length(ab);
float d = abs(cross(p, normalize(ab)).z);
float proj = dot(p, ab) / l;
if(proj >= 0.0 && proj <= l) return d;
return min(distance(st, a), distance(st, b));
}
float triangle_distance(in vec2 st, in vec2 a, in vec2 b, in vec2 c) {
float d1 = line_distance(st, a, b);
float d2 = line_distance(st, b, c);
float d3 = line_distance(st, c, a);
if(d1 >= 0.0 && d2 >= 0.0 && d3 >= 0.0 || d1 <= 0.0 && d2 <= 0.0 && d3 <= 0.0) {
return -min(abs(d1), min(abs(d2), abs(d3))); // 内部距离为负
}
return min(seg_distance(st, a, b), min(seg_distance(st, b, c), seg_distance(st, c, a))); // 外部为正
}
void main() {
float d = triangle_distance(vUv, vec2(0.3), vec2(0.5, 0.7), vec2(0.7, 0.3));
gl_FragColor.rgb = (1.0 - smoothstep(0.0, 0.01, d)) * vec3(1.0);
gl_FragColor.a = 1.0;
}
`;
const canvas = document.querySelector("canvas");
const renderer = new GlRenderer(canvas);
// 加载片元着色器并创建程序
const program = renderer.compileSync(fragment, vertex);
renderer.useProgram(program);
// 将顶点数据送入缓冲区
renderer.setMeshData([
{
positions: [
[-1, -1],
[-1, 1],
[1, 1],
[1, -1],
],
attributes: {
uv: [
[0, 0],
[0, 1],
[1, 1],
[1, 0],
],
},
cells: [
[0, 1, 2],
[2, 0, 3],
],
},
]);
// 渲染
renderer.render();
</script>
</body>
</html>
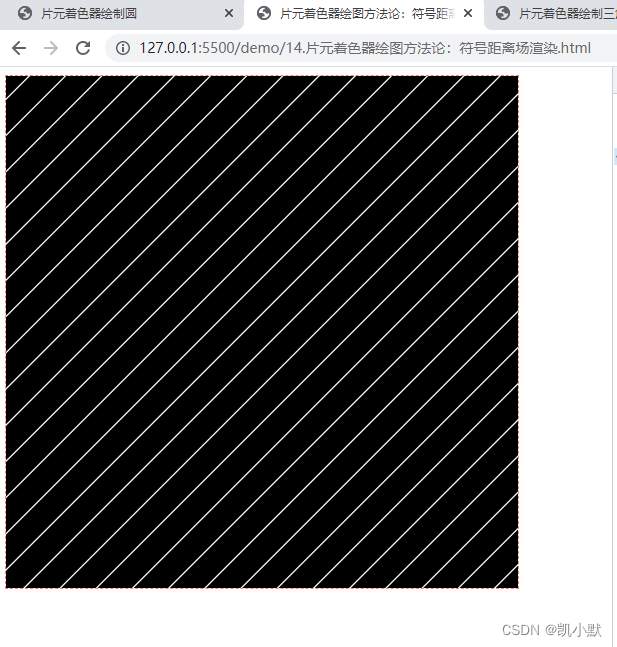
片元着色器绘图方法论:符号距离场渲染
在图形渲染中有一个专有的名称叫做符号距离场渲染(Signed Distance Fields Rendering)。它本质上就是利用空间中的距离分布来着色的。
- 第一步:定义距离。
- 第二步:根据距离着色。
绘制平面分割线
constfragment = `
#ifdef GL_ES
precision highp float;
#endif
varying vec2 vUv;
void main() {
vec3 line = vec3(1, 1, 0);
float d = abs(cross(vec3(vUv,0), normalize(line)).z);
d = fract(20.0 * d);
gl_FragColor.rgb = (smoothstep(0.45, 0.5, d) - smoothstep(0.5, 0.55, d)) * vec3(1.0);
gl_FragColor.a = 1.0;
}
`;
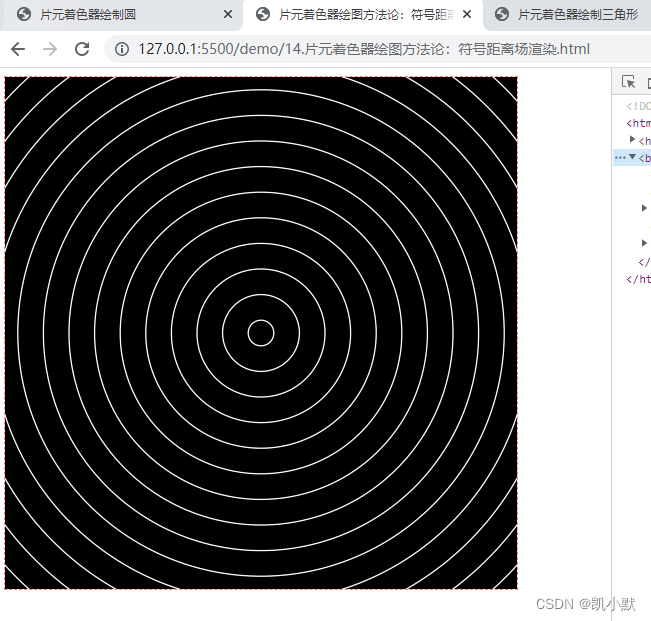
绘制圆环
const fragment = `
#ifdef GL_ES
precision highp float;
#endif
varying vec2 vUv;
void main() {
float d = distance(vUv, vec2(0.5));
d = fract(20.0 * d);
gl_FragColor.rgb = (smoothstep(0.45, 0.5, d) - smoothstep(0.5, 0.55, d)) * vec3(1.0);
gl_FragColor.a = 1.0;
}
`;
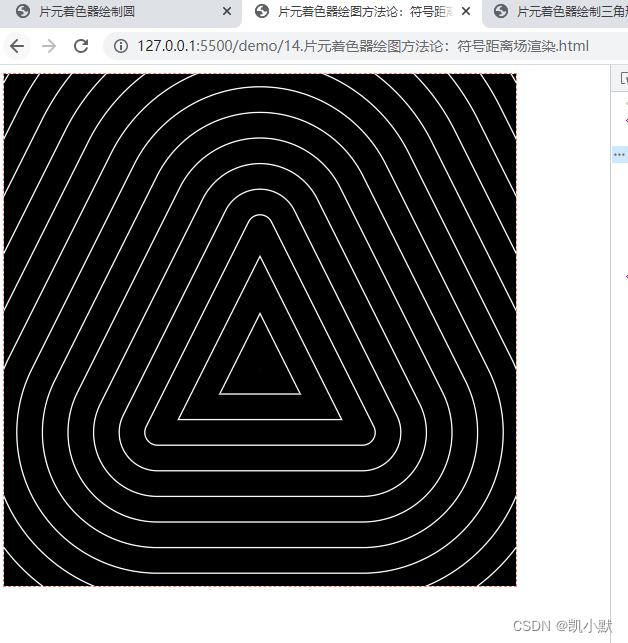
绘制三角环
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>片元着色器绘图方法论:符号距离场渲染</title>
<style>
canvas {
border: 1px dashed salmon;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<canvas width="512" height="512"></canvas>
<script src="./common/lib/gl-renderer.js"></script>
<script>
const vertex = `
attribute vec2 a_vertexPosition;
attribute vec2 uv;
varying vec2 vUv;
void main() {
gl_PointSize = 1.0;
vUv = uv;
gl_Position = vec4(a_vertexPosition, 1, 1);
}
`;
// // 绘制平面分割线
// const fragment = `
// #ifdef GL_ES
// precision highp float;
// #endif
// varying vec2 vUv;
// void main() {
// vec3 line = vec3(1, 1, 0);
// float d = abs(cross(vec3(vUv,0), normalize(line)).z);
// d = fract(20.0 * d);
// gl_FragColor.rgb = (smoothstep(0.45, 0.5, d) - smoothstep(0.5, 0.55, d)) * vec3(1.0);
// gl_FragColor.a = 1.0;
// }
// `;
// // 绘制圆环
// const fragment = `
// #ifdef GL_ES
// precision highp float;
// #endif
// varying vec2 vUv;
// void main() {
// float d = distance(vUv, vec2(0.5));
// d = fract(20.0 * d);
// gl_FragColor.rgb = (smoothstep(0.45, 0.5, d) - smoothstep(0.5, 0.55, d)) * vec3(1.0);
// gl_FragColor.a = 1.0;
// }
// `;
// 绘制三角环
const fragment = `
#ifdef GL_ES
precision highp float;
#endif
varying vec2 vUv;
float line_distance(in vec2 st, in vec2 a, in vec2 b) {
vec3 ab = vec3(b - a, 0);
vec3 p = vec3(st - a, 0);
float l = length(ab);
return cross(p, normalize(ab)).z;
}
float seg_distance(in vec2 st, in vec2 a, in vec2 b) {
vec3 ab = vec3(b - a, 0);
vec3 p = vec3(st - a, 0);
float l = length(ab);
float d = abs(cross(p, normalize(ab)).z);
float proj = dot(p, ab) / l;
if(proj >= 0.0 && proj <= l) return d;
return min(distance(st, a), distance(st, b));
}
float triangle_distance(in vec2 st, in vec2 a, in vec2 b, in vec2 c) {
float d1 = line_distance(st, a, b);
float d2 = line_distance(st, b, c);
float d3 = line_distance(st, c, a);
if(d1 >= 0.0 && d2 >= 0.0 && d3 >= 0.0 || d1 <= 0.0 && d2 <= 0.0 && d3 <= 0.0) {
return -min(abs(d1), min(abs(d2), abs(d3))); // 内部距离为负
}
return min(seg_distance(st, a, b), min(seg_distance(st, b, c), seg_distance(st, c, a))); // 外部为正
}
void main() {
float d = triangle_distance(vUv, vec2(0.3), vec2(0.5, 0.7), vec2(0.7, 0.3));
d = fract(20.0 * abs(d));
// gl_FragColor.rgb = vec3(d); // vec3(d) 来渲染颜色
gl_FragColor.rgb = (smoothstep(0.45, 0.5, d) - smoothstep(0.5, 0.55, d)) * vec3(1.0);
gl_FragColor.a = 1.0;
}
`;
const canvas = document.querySelector("canvas");
const renderer = new GlRenderer(canvas);
// 加载片元着色器并创建程序
const program = renderer.compileSync(fragment, vertex);
renderer.useProgram(program);
// 将顶点数据送入缓冲区
renderer.setMeshData([
{
positions: [
[-1, -1],
[-1, 1],
[1, 1],
[1, -1],
],
attributes: {
uv: [
[0, 0],
[0, 1],
[1, 1],
[1, 0],
],
},
cells: [
[0, 1, 2],
[2, 0, 3],
],
},
]);
// 渲染
renderer.render();
</script>
</body>
</html>
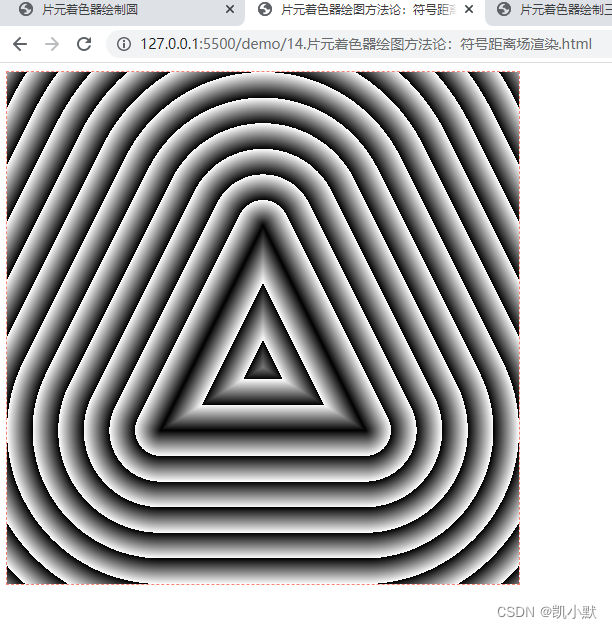
vec3(d) 来渲染颜色
着色器绘制几何图形的用途
- 实现图像的剪裁
- 实现对图像的动态修饰
- 可以在一些 3D 场景中修饰几何体
实现图像的剪裁
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>着色器造型实现图像的剪裁</title>
</head>
<body>
<canvas width="1920" height="1080"></canvas>
<script src="./common/lib/gl-renderer.js"></script>
<script>
const vertex = `
attribute vec2 a_vertexPosition;
attribute vec2 uv;
varying vec2 vUv;
void main() {
gl_PointSize = 1.0;
vUv = uv;
gl_Position = vec4(a_vertexPosition, 1, 1);
}
`;
const fragment = `
#ifdef GL_ES
precision highp float;
#endif
varying vec2 vUv;
uniform sampler2D tMap;
uniform float uTime;
float line_distance(in vec2 st, in vec2 a, in vec2 b) {
vec3 ab = vec3(b - a, 0);
vec3 p = vec3(st - a, 0);
float l = length(ab);
return cross(p, normalize(ab)).z;
}
float seg_distance(in vec2 st, in vec2 a, in vec2 b) {
vec3 ab = vec3(b - a, 0);
vec3 p = vec3(st - a, 0);
float l = length(ab);
float d = abs(cross(p, normalize(ab)).z);
float proj = dot(p, ab) / l;
if(proj >= 0.0 && proj <= l) return d;
return min(distance(st, a), distance(st, b));
}
float triangle_distance(in vec2 st, in vec2 a, in vec2 b, in vec2 c) {
float d1 = line_distance(st, a, b);
float d2 = line_distance(st, b, c);
float d3 = line_distance(st, c, a);
if(d1 >= 0.0 && d2 >= 0.0 && d3 >= 0.0 || d1 <= 0.0 && d2 <= 0.0 && d3 <= 0.0) {
return -min(abs(d1), min(abs(d2), abs(d3))); // 内部距离为负
}
return min(seg_distance(st, a, b), min(seg_distance(st, b, c), seg_distance(st, c, a))); // 外部为正
}
void main() {
vec4 color = texture2D(tMap, vUv);
vec2 uv = vUv - vec2(0.5);
vec2 a = vec2(-0.577, 0) - vec2(0.5);
vec2 b = vec2(0.5, 1.866) - vec2(0.5);
vec2 c = vec2(1.577, 0) - vec2(0.5);
float scale = min(1.0, 0.0005 * uTime);
float d = triangle_distance(uv, scale * a, scale * b, scale * c);
gl_FragColor.rgb = (1.0 - smoothstep(0.0, 0.01, d)) * color.rgb;
gl_FragColor.a = 1.0;
}
`;
const canvas = document.querySelector('canvas');
const renderer = new GlRenderer(canvas);
// load fragment shader and createProgram
const program = renderer.compileSync(fragment, vertex);
renderer.useProgram(program);
(async function () {
const texture = await renderer.loadTexture('./assets/img/flower.jpg');
renderer.uniforms.tMap = texture;
renderer.uniforms.uTime = 0;
renderer.setMeshData([{
positions: [
[-1, -1],
[-1, 1],
[1, 1],
[1, -1],
],
attributes: {
uv: [
[0, 0],
[0, 1],
[1, 1],
[1, 0],
],
},
cells: [[0, 1, 2], [2, 0, 3]],
}]);
renderer.render();
function update(t) {
renderer.uniforms.uTime = t / 2;
requestAnimationFrame(update);
}
update(0);
}());
</script>
</script>
</body>
</html>
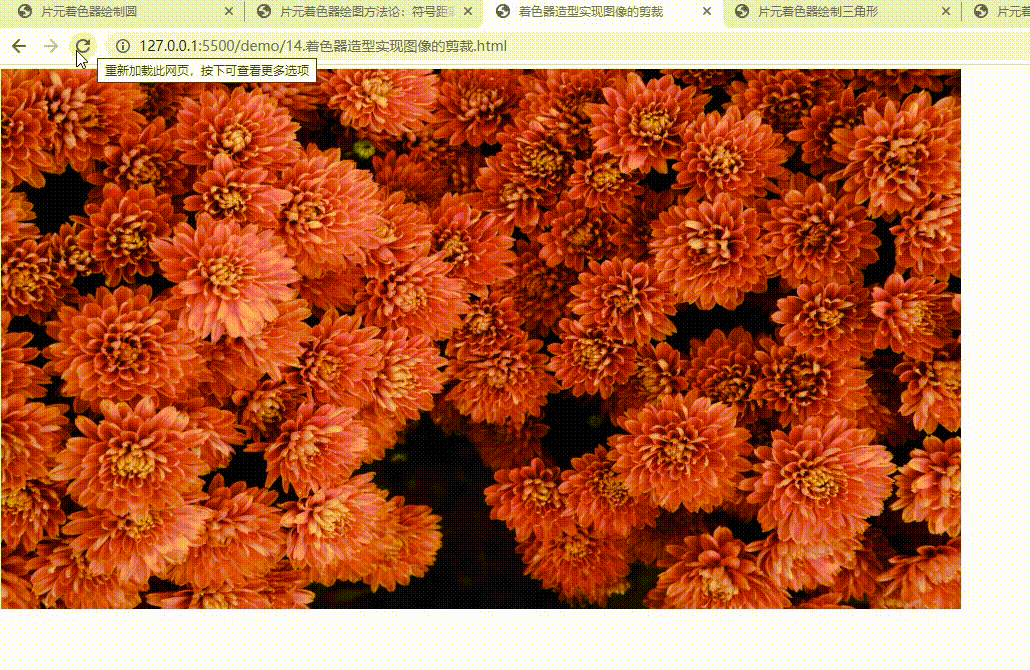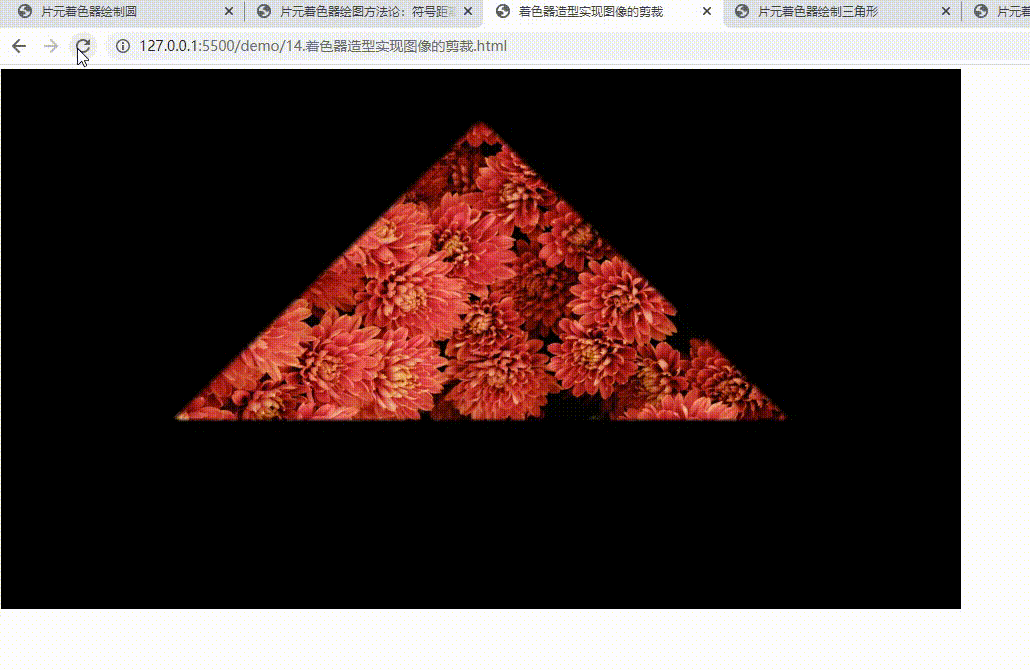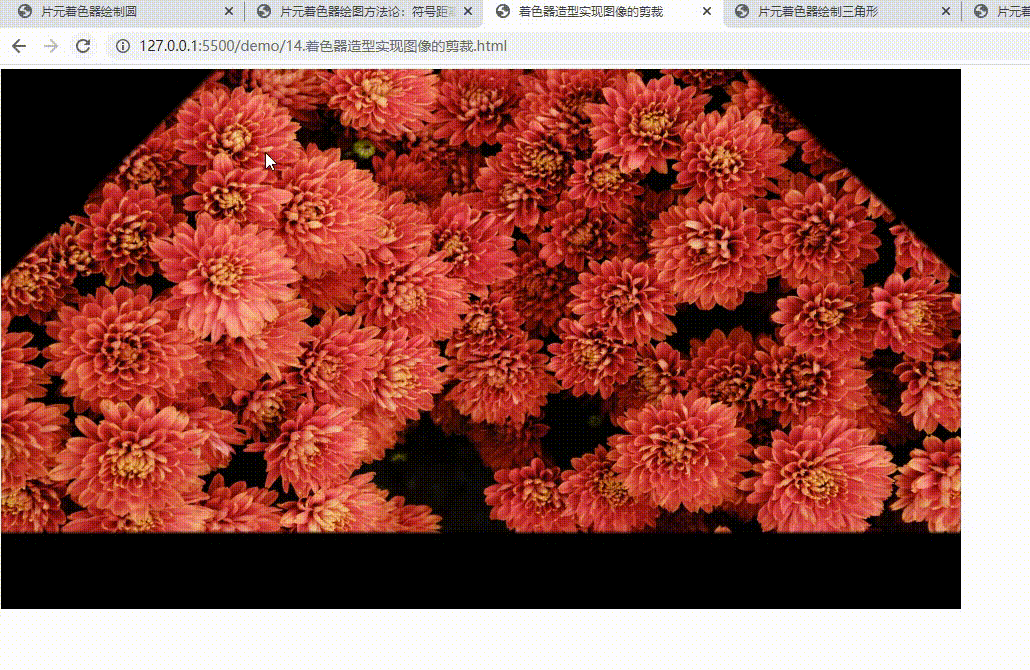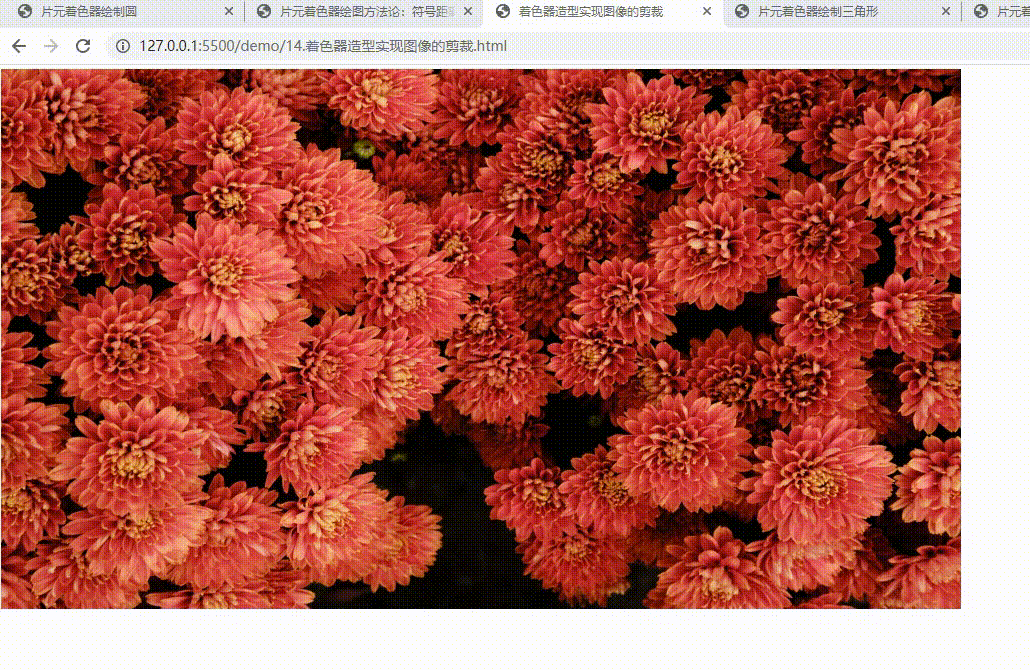
实现对图像的动态修饰
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>实现对图像的动态修饰</title>
</head>
<body>
<canvas width="1920" height="1080"></canvas>
<script src="./common/lib/gl-renderer.js"></script>
<script>
const vertex = `
attribute vec2 a_vertexPosition;
attribute vec2 uv;
varying vec2 vUv;
void main() {
gl_PointSize = 1.0;
vUv = uv;
gl_Position = vec4(a_vertexPosition, 1, 1);
}
`;
const fragment = `
#ifdef GL_ES
precision highp float;
#endif
varying vec2 vUv;
uniform sampler2D tMap;
uniform float uTime;
float line_distance(in vec2 st, in vec2 a, in vec2 b) {
vec3 ab = vec3(b - a, 0);
vec3 p = vec3(st - a, 0);
float l = length(ab);
return cross(p, normalize(ab)).z;
}
float seg_distance(in vec2 st, in vec2 a, in vec2 b) {
vec3 ab = vec3(b - a, 0);
vec3 p = vec3(st - a, 0);
float l = length(ab);
float d = abs(cross(p, normalize(ab)).z);
float proj = dot(p, ab) / l;
if(proj >= 0.0 && proj <= l) return d;
return min(distance(st, a), distance(st, b));
}
float triangle_distance(in vec2 st, in vec2 a, in vec2 b, in vec2 c) {
float d1 = line_distance(st, a, b);
float d2 = line_distance(st, b, c);
float d3 = line_distance(st, c, a);
if(d1 >= 0.0 && d2 >= 0.0 && d3 >= 0.0 || d1 <= 0.0 && d2 <= 0.0 && d3 <= 0.0) {
return -min(abs(d1), min(abs(d2), abs(d3))); // 内部距离为负
}
return min(seg_distance(st, a, b), min(seg_distance(st, b, c), seg_distance(st, c, a))); // 外部为正
}
void main() {
vec4 color = texture2D(tMap, vUv);
vec2 uv = vUv - vec2(0.5);
vec2 a = vec2(0, 1);
float time = 0.0005 * uTime;
vec2 b = vec2(sin(time), cos(time));
float d = 0.0;
float c0 = cross(vec3(b, 0.0), vec3(a, 0.0)).z;
float c1 = cross(vec3(uv, 0.0), vec3(a, 0.0)).z;
float c2 = cross(vec3(uv, 0.0), vec3(b, 0.0)).z;
if(c0 > 0.0 && c1 > 0.0 && c2 < 0.0) {
d = 1.0;
}
if(c0 < 0.0 && (c1 >= 0.0 || c2 <= 0.0)) {
d = 1.0;
}
gl_FragColor.rgb = color.rgb;
gl_FragColor.r *= mix(0.3, 1.0, d);
gl_FragColor.a = mix(0.9, 1.0, d);
}
`;
const canvas = document.querySelector('canvas');
const renderer = new GlRenderer(canvas);
// load fragment shader and createProgram
const program = renderer.compileSync(fragment, vertex);
renderer.useProgram(program);
(async function () {
const texture = await renderer.loadTexture('./assets/img/flower.jpg');
renderer.uniforms.tMap = texture;
renderer.uniforms.uTime = 0;
renderer.setMeshData([{
positions: [
[-1, -1],
[-1, 1],
[1, 1],
[1, -1],
],
attributes: {
uv: [
[0, 0],
[0, 1],
[1, 1],
[1, 0],
],
},
cells: [[0, 1, 2], [2, 0, 3]],
}]);
renderer.render();
function update(t) {
renderer.uniforms.uTime = 2*t;
requestAnimationFrame(update);
}
update(0);
}());
</script>
</script>
</body>
</html>
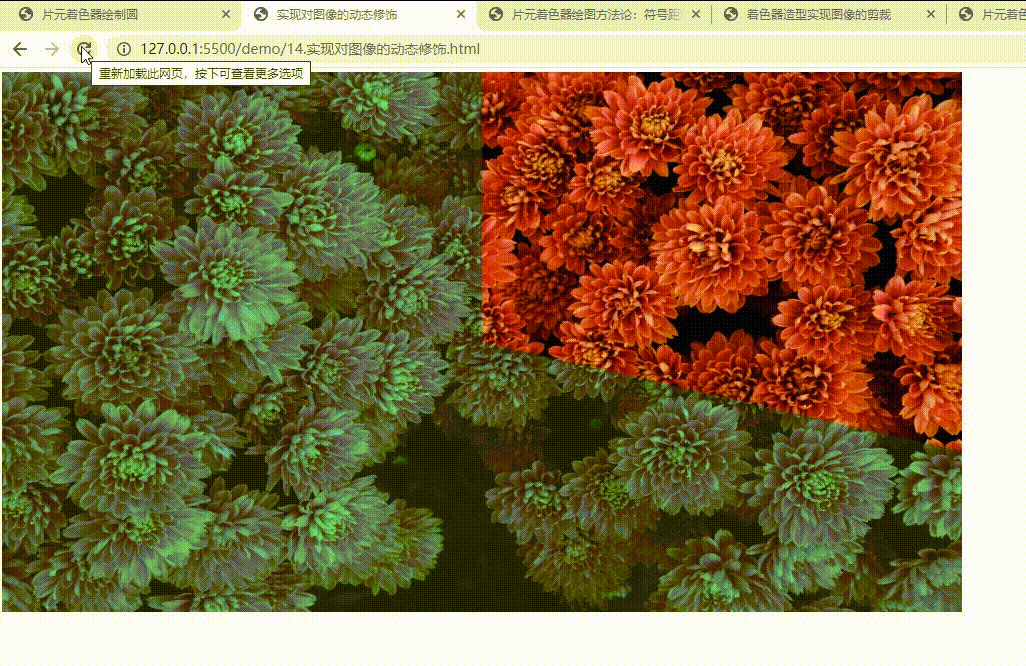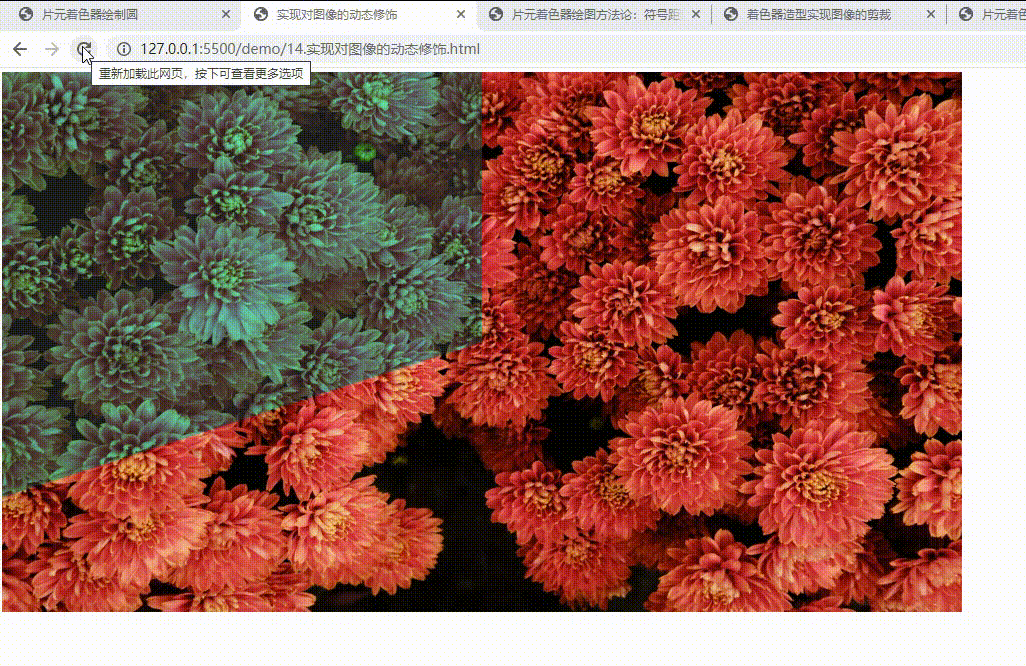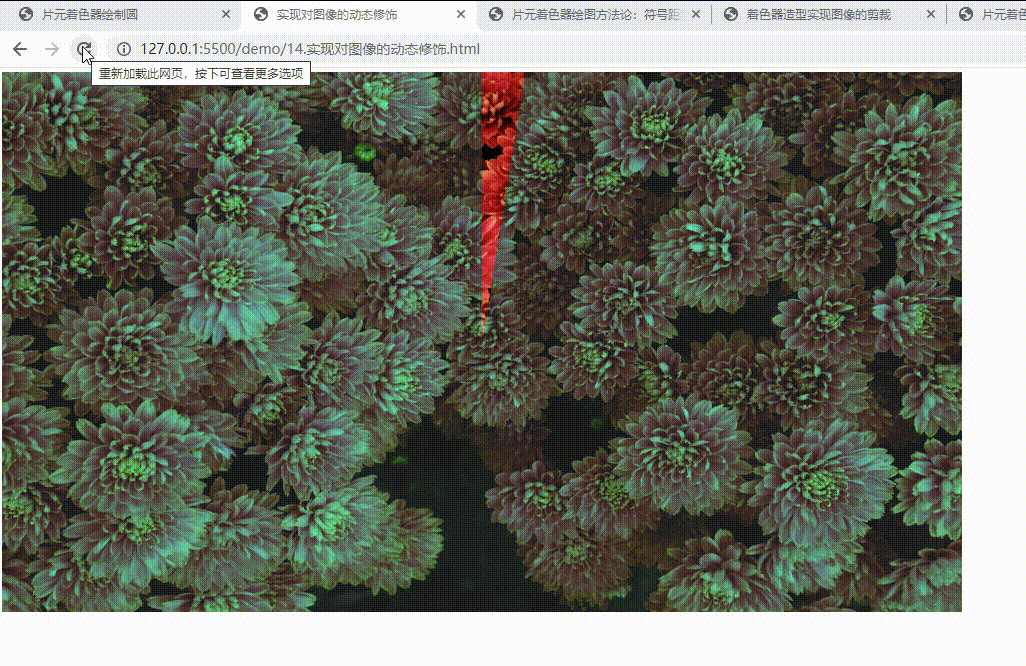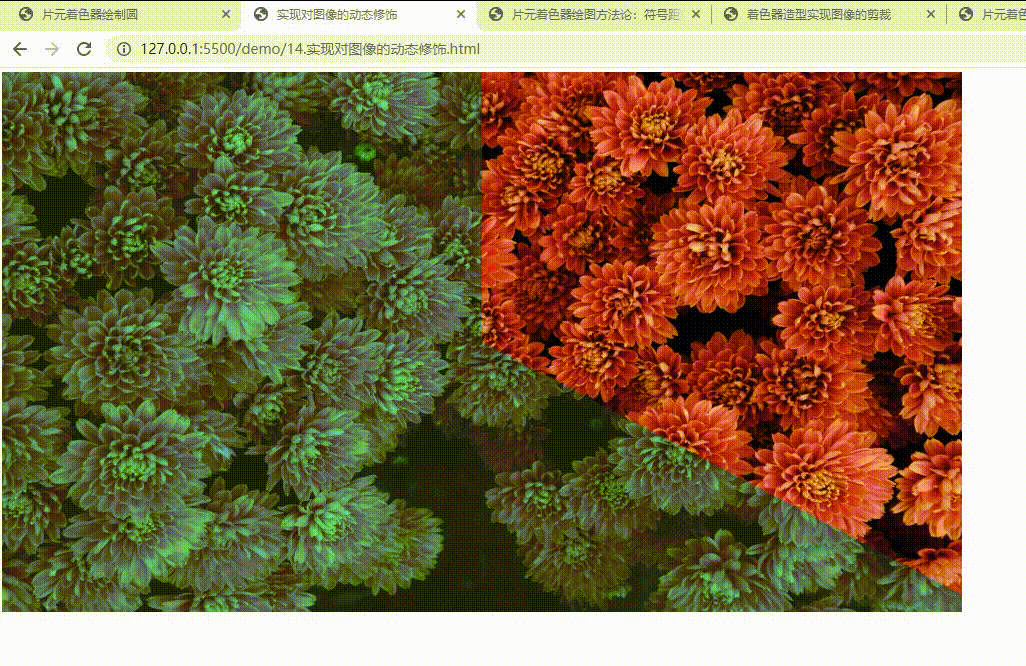
推荐网址