本文将使用不到百行代码,完成一个最简单的聊天室功能,单纯只是最基础的要点。
目录
为什么有websocket
????大家每天使用网络,最常见的就是http协议传输内容,感觉也可以满足需求,多个websocket协议干啥呢?这就要从http本身说起了,http(超文本传输协议),是一种无状态的,客户端发出一次请求,服务器返回一次答复的协议。它有两个问题:
① 从协议上讲,服务器不知道两次请求之间的关系。
② 一次请求,一次回复,服务器无法主动向用户传递数据。
而websokect是一种有状态的协议,当用户发起websocket连接时,服务器会维持与客户端的联系,我们往往用会话(session)来表示这个样的联系,这样以来,由于连接始终保持,服务器可以主动向客户端发送数据,这样有什么意义呢?想象一下在线游戏,对方一旦进行了操作,需要将数据上传给服务器,这时候如果服务器能主动给你发一条信息。那么,相比你每隔一段时间去请求数据,时延会低,开销会小,何乐不为呢?
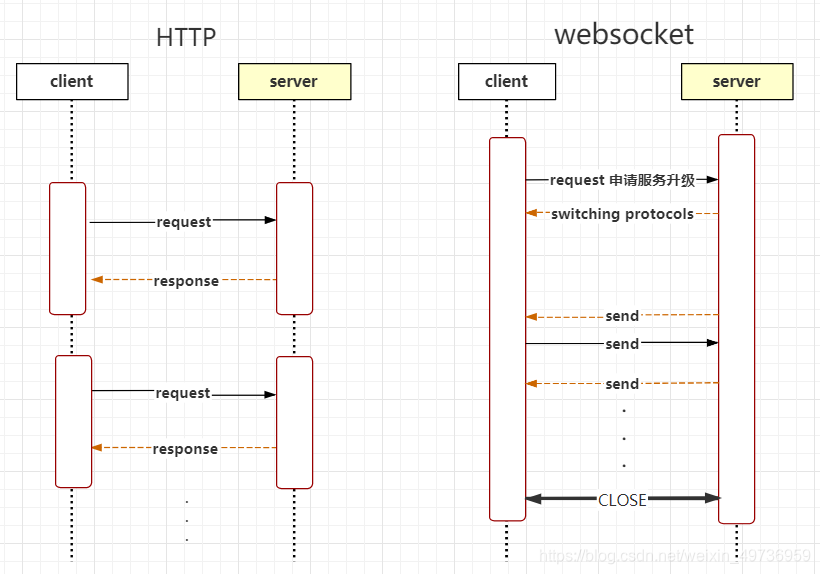
websocket 四个重要事件
打开连接事件open: 当一个连接建立时触发,对应接收函数onopen
收到消息事件message:当服务器或者客户端收到消息时触发,对应接收函数onMessage
关闭连接事件close:但连接断开时触发,对应接收函数onClose
错误事件error:连接或者端点发生错误时触发,对应接收函数onError。
无论浏览器端还是服务器端,我们在使用websocket 时,只需要去完善其对应生命周期事件下的对应方法,接下来的简单聊天室,就是对上面几个事件的实现!
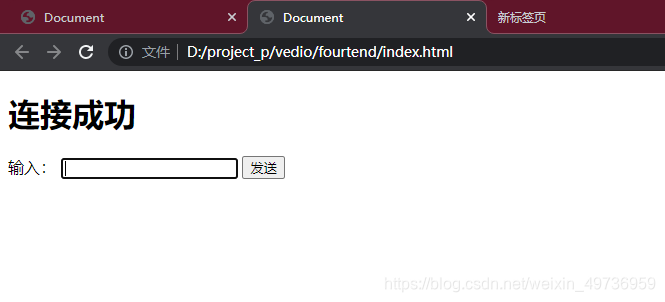
(聊天室)效果
进行连接
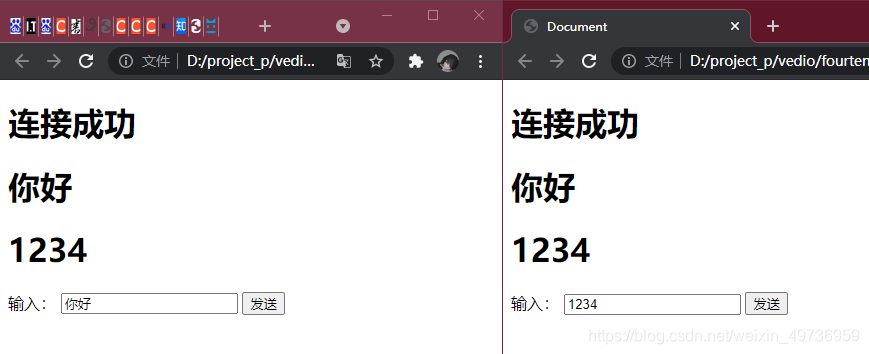
互发消息
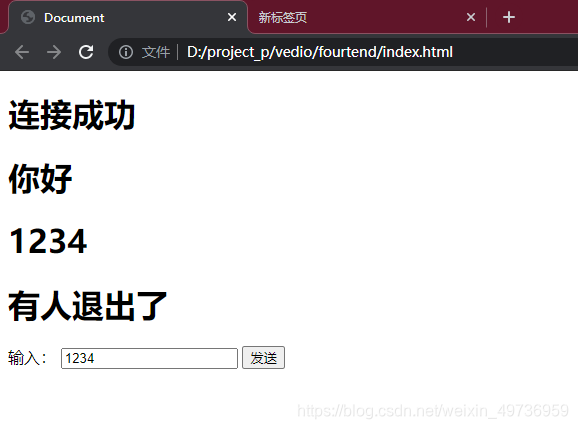
退出
(聊天室)服务器springboot端
新建一个springboot的项目,项目路径如下,首先要引入websocket 依赖到pom.xml 中, 接着要添加一个配置类,和一个websocket服务类。其他的文件都不需要修改。
添加websocket 依赖
在pom.xml 的 dependencies 标签 里添加如下内容,并更新maven依赖。
<!-- springboot websocket 启动器 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-websocket</artifactId>
</dependency>
添加配置类WebsocketConfig
在添加了这个配置类之后会去搜索你项目当中的@ServerEndpointer标签(@ServerEndpointer是websocket服务类的注解,在里面写具体的服务逻辑),之后让它像Controller一样可以被外界访问到。
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.socket.server.standard.ServerEndpointExporter;
@Configuration
public class WebsocketConfig {
@Bean
// 自动注入ServerEndpointer bean对象,自动注册使用了@ServerEndpoint的bean
public ServerEndpointExporter serverEndpointExporter() {
return new ServerEndpointExporter();
}
}
添加websocket服务类
现在聊天室实现的功能很简单:
- 当用户连接到聊天室(onOpen)就把用户和用户的连接保存到sessions中,以便向用户发送消息;
- 当服务器收到用户的一条消息时(onMessage),就把内容发送给所有用户;
- 当用户断开连接(onClose)就从sessions中把这个连接删除,再告诉其他用户,有人离开了。
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import javax.websocket.*;
import javax.websocket.server.ServerEndpoint;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Vector;
// 必须要添加,否则spring 容器中就找不到服务类
@Component
// 和 Controller的路由一样,当用户访问 127.0.0.1:8080/live 时可以连接到websocket服务
@ServerEndpoint("/live")
public class Live {
// 存放当前所有在线用户
public static Vector<Session> sessions = new Vector<>();
@OnOpen()
public void onOpen(Session session, EndpointConfig config){
sessions.add(session);
System.out.println("连接成功");
try {
// 向该用户返回一条连接成功的消息
session.getBasicRemote().sendText("连接成功");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@OnMessage
public void onMessage(Session session, String message){
System.out.println(message);
// 所有用户发送收到的消息
for (Session s : sessions){
try {
s.getBasicRemote().sendText(message);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
@OnClose
public void onClose(Session session){
System.out.println("已退出");
sessions.remove(session);
// 所有用户发送收到的消息
for (Session s : sessions){
try {
s.getBasicRemote().sendText("有人退出了");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
(聊天室)前端
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="record"></div>
<label for="in1">输入:</label>
<input name="in1" id="in1" type="text" />
<button id="b1">发送</button>
<script>
!(function(){
// 执行这句话会建立一个websocket 连接
let ws = new WebSocket("ws://127.0.0.1:8080/live");
// 设置在连接成功后执行的方法
ws.onopen = () => {
console.log("I'm connected!");
}
// 收到服务器传来的消息,就把他添加到页面上
ws.onmessage = (messageEvent) =>{
addnew(messageEvent.data);
console.log(messageEvent.data);
}
// 发生错误时调用方法
ws.onerror = () =>{
console.log("websocket发生了错误");
}
// 当点击按钮时,就使用ws.send() 发送一条数据
document.getElementById("b1").addEventListener("click", ()=>{
ws.send(document.getElementById("in1").value);
})
// 向界面添加一条内容为s的消息
function addnew (s) {
let h1 = document.createElement("h1");
h1.innerText = s;
document.getElementById("record").appendChild(h1);
}
}())
</script>
</body>
</html>