标题# 网络字节序问题以及大端小端
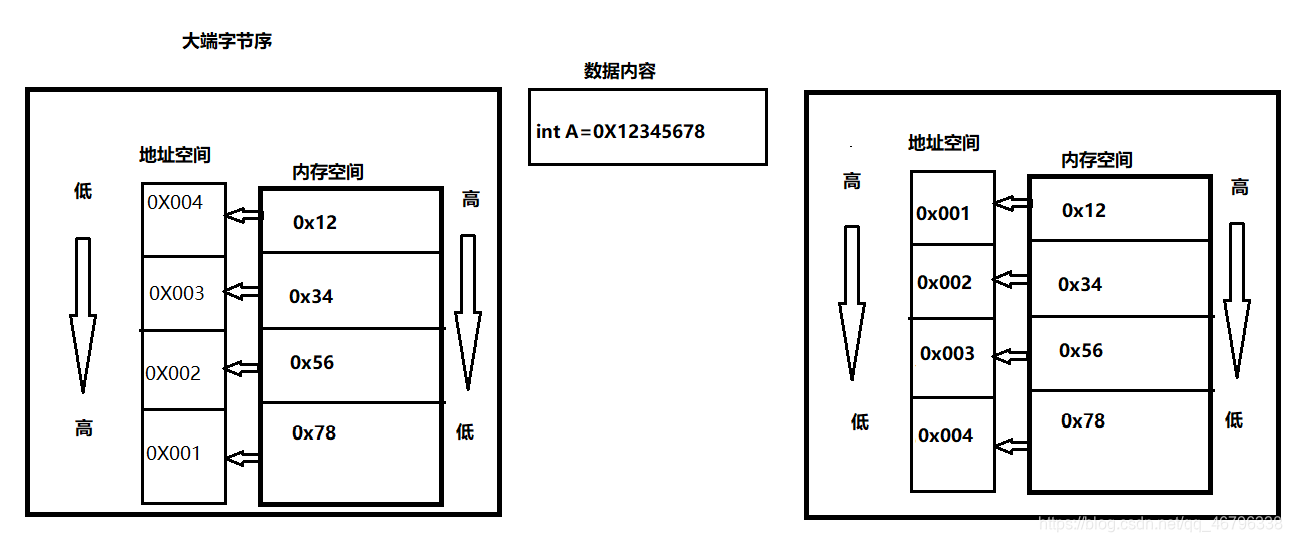
一、什么是大端和小端?
大端字节序: 最高位存放最低地址位,最低位存放最低地址位。
小端字节序: 顺口溜(小小大大),最高位存放最高地址位,最低位存放最低地址位。
图解:
二、判断本地电脑的字节序
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
/*在测试程序中,使用联合体的原因是:union型数据的每个成员所占的空间等于其最大的成员所占的空间。对union型成员的
存取都是相对于该联合体基地址的偏移量为0处开始,也就是联合体的访问不论对哪个变量的存取都是从union的首
地址开始的。通过检测第一个字节存放的数据即可得出结果。*/
union MyUnion
{
char ch;
int i;
}tMyUnion;
int main()
{
//验证本地电脑字节序的大小端1
tMyUnion.i = 0x12345678;
if (tMyUnion.ch==0x12)
{
printf("is big endian\n");
}
else
{
printf("is small endian\n");
}
//验证本地电脑字节序的大小端2
int a = 0x12345678;
char* p = (char*)&a;
printf("0x%x\n", p[0]);
printf("0x%x\n", p[1]);
printf("0x%x\n", p[2]);
printf("0x%x\n", p[3]);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行的结果:

由运行结果可以看出是小端字节序
网络字节序
UDP/TCP/IP协议规定:把接收到的第一个字节当作高位字节看待,这就要求发送端发送的第一个字节是高位字节;而在发送端发送数据时,发送的第一个字节是该数值在内存中的起始地址处对应的那个字节,也就是说,该数值在内存中的起始地址处对应的那个字节就是要发送的第一个高位字节(即:高位字节存放在低地址处);由此可见,多字节数值在发送之前,在内存中因该是以大端法存放的;
2.本地与网络字节序的转换函数
//h -----host;n----network ;s------short;l----long。
#include <arpa/inet.h>
//将主机字节序转换为网络字节序
unit32_t htonl (unit32_t hostlong);
unit16_t htons (unit16_t hostshort);
//将网络字节序转换为主机字节序
unit32_t ntohl (unit32_t netlong);
unit16_t ntohs (unit16_t netshort);
3ip地址转换函数
典分十进制本地Ip地址:127.0.0.1------------------->网络字节序ip地址
网络字节序ip地址--------------------------->典分十进制本地Ip地址
#include <arpa/inet.h>
int inet_pton(int af,const char*src,void *dst);
const char *inet_ntop(int af,const void *src,char *dst,socklen_t size);
//inet_addr的参数是一个:点分十进制字符串,返回的值为一个32位的二进制网络字节序的IPv4地址。
unsigned long addr = inet_addr(const char *str);
struct in_addr tAddr;
memcpy(&tAddr, &addr , sizeof(addr ));
//将32位的二进制网络字节序转换回本地的典分十进制的字符串函数
char *str = inet_ntoa(tAddr);```
最后制作不易,本文为原创文章如需装载,请标明出处,欢迎私信评了交流。