一、RESTful简介
REST:Representational State Transfer,表现层资源状态转移。
- 资源:
资源是一种看待服务器的方式,即,将服务器看作是由很多离散的资源组成。每个资源是服务器上一个可命名的抽象概念。因为资源是一个抽象的概念,所以它不仅仅能代表服务器文件系统中的一个文件、数据库中的一张表等等具体的东西,可以将资源设计的要多抽象有多抽象,只要想象力允许而且客户端应用开发者能够理解。与面向对象设计类似,资源是以名词为核心来组织的,首先关注的是名词。一个资源可以由一个或多个URI来标识。URI既是资源的名称,也是资源在Web上的地址。对某个资源感兴趣的客户端应用,可以通过资源的URI与其进行交互。 - 资源的表述:
资源的表述是一段对于资源在某个特定时刻的状态的描述。可以在客户端-服务器端之间转移(交换)。资源的表述可以有多种格式,例如HTML/XML/JSON/纯文本/图片/视频/音频等等。资源的表述格式可以通过协商机制来确定。请求-响应方向的表述通常使用不同的格式。 - 状态转移:
状态转移说的是:在客户端和服务器端之间转移(transfer)代表资源状态的表述。通过转移和操作资源的表述,来间接实现操作资源的目的。
二、RESTful的实现
具体说,就是 HTTP 协议里面,有四个表示操作方式的动词:GET、POST、PUT、DELETE。它们分别对应四种基本操作:GET 用来获取资源,POST 用来新建资源,PUT 用来更新资源,DELETE 用来删除资源。
REST 风格提倡 URL 地址使用统一的风格设计,从前到后各个单词使用斜杠分开,不使用问号键值对方式携带请求参数,而是将要发送给服务器的数据作为 URL 地址的一部分,以保证整体风格的一致性。
| 操作 | 传统方式 | REST风格 |
|---|---|---|
| 查询操作 | getUserById?id=1 | user/1–>get请求方式 |
| 保存操作 | saveUser | user–>post请求方式 |
| 删除操作 | deleteUser?id=1 | user/1–>delete请求方式 |
| 更新操作 | updateUser | user–>put请求方式 |
通俗地说就是查询、保存、删除、更新user都是操作user这个资源,那么这四种操作在URL中的资源那一层就可以都写user,而具体不同的操作则由请求方式决定。
(一)使用RESTful风格实现get和post请求
首先,创建一个 web 模块并配置好web.xml和部署Tomcat
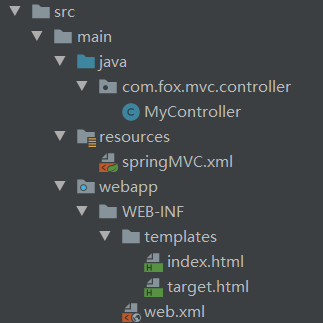
controller:
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
@Controller
public class MyController {
@RequestMapping(value = "/")
public String toIndex(){
return "index";
}
/*
* 使用RESTFul模拟用户资源的增删改查:
* /user GET 查询所有用户信息
* /user/1 GET 根据用户id查询用户信息
* /user POST 添加用户信息
*/
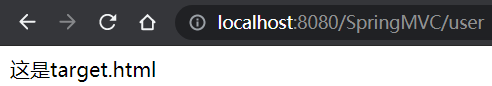
@RequestMapping(value = "/user",method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String selectUsers(){
System.out.println("查询所有用户信息");
return "target";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/user/{id}",method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String selectUserById(){
System.out.println("根据用户id查询用户信息");
return "target";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/user",method = RequestMethod.POST)
public String addUser(){
System.out.println("添加用户信息");
return "target";
}
}
index.html:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>首页</title>
</head>
<body>
这是index.html<br>
<a th:href="@{/user}">查询所有用户信息</a><br>
<a th:href="@{/user/1}">根据id查询用户信息</a><br>
<form th:action="@{/user}" method="post">
用户名:<input type="text" name="username"><br>
密码:<input type="password" name="password"><br>
<input type="submit" value="添加用户信息"><br>
</form>
</body>
</html>
target.html:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
这是target.html<br>
</body>
</html>
运行Tomcat:
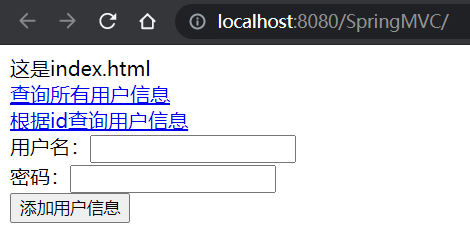
点击第一个链接:
IDEA输出:
点击第二个链接:
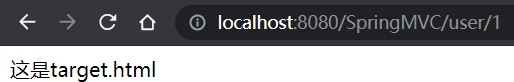
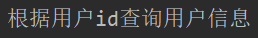
IDEA输出:
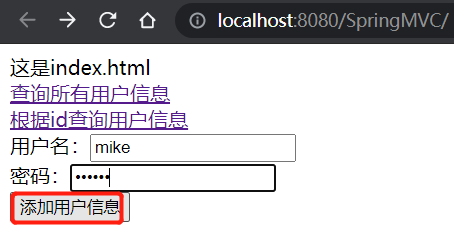
填写表单:
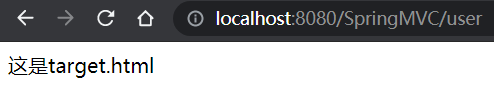
IDEA输出:
(二)使用RESTful风格实现put和delete请求
1.HiddenHttpMethodFilter
由于浏览器只支持发送get和post方式的请求,即使在form表单的method写上"put"或"delete",也会被视为get请求,那么该如何发送put和delete请求呢?
SpringMVC 提供了 HiddenHttpMethodFilter 帮助我们将 POST 请求转换为 DELETE 或 PUT 请求。
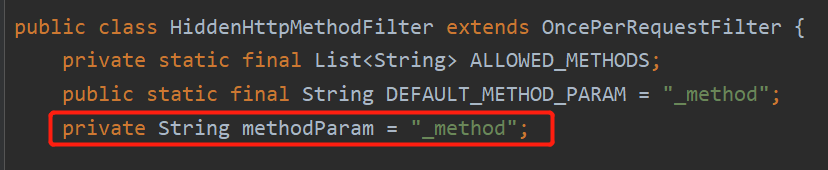
我们来看一下HiddenHttpMethodFilter的源码:
下面是HiddenHttpMethodFilter真正执行过滤的方法:
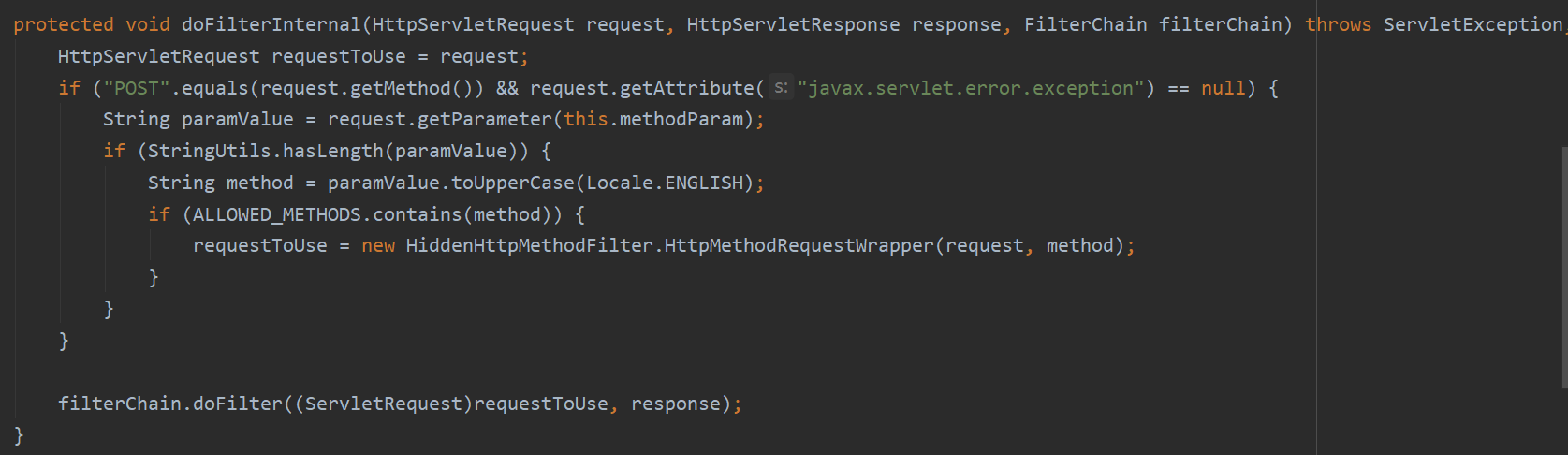
它会首先将我们的请求拦截,并将请求对象赋值给requestToUse,如果"POST".equals(request.getMethod()) && request.getAttribute("javax.servlet.error.exception") == null成立就会执行下面的代码,后面那一部分是成立的不用纠结,我们只需要管前面的"POST".equals(request.getMethod()),因此要想发送put或delete请求,我们需要先把请求设置为post请求。接着String paramValue = request.getParameter(this.methodParam);,this.methodParam即前面一张图看到的"_method",也就是将请求对象里名为"_method"的参数值传给paramValue。如果想接着执行下面的代码就必须满足StringUtils.hasLength(paramValue),它的意思是paramValue有长度就往下执行。所以我们要想发送put或delete请求还要做一件事就是在请求里设置一个名为"_method"的参数并赋值。接着String method = paramValue.toUpperCase(Locale.ENGLISH);意思是将这个paramValue的值全部大写传给method这个字符串对象,接着ALLOWED_METHODS.contains(method),如果ALLOWED_METHODS这个集合包含method表示的字符串,才会往下执行。我们来看一下ALLOWED_METHODS:
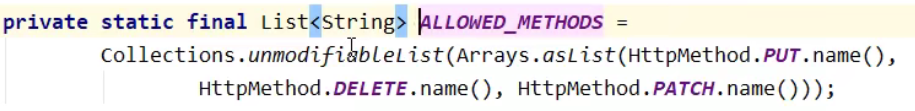
它包含了三种请求的名字:PUT、DELETE、PATCH。如果满足,requestToUse = new HiddenHttpMethodFilter.HttpMethodRequestWrapper(request, method);就会创建一个新的请求对象重新赋值给requestToUse,我们来看这个HttpMethodRequestWrapper类的源码:
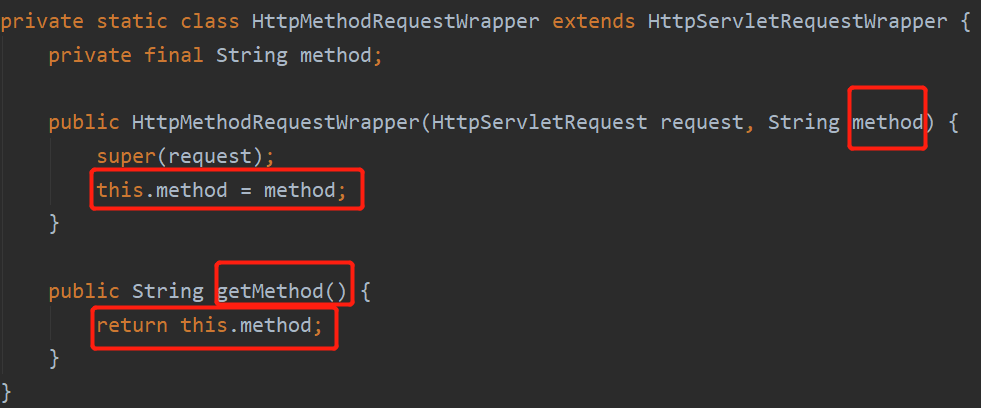
它会创建一个封装了我们传入的请求方式的请求对象,最后filterChain.doFilter((ServletRequest)requestToUse, response);由fileterChain放行我们这个请求对象,这样我们就可以往下执行访问目标资源了,至此就实现了发送put或delete请求。
总结:
HiddenHttpMethodFilter 要想处理put和delete请求的条件:
- 当前请求的请求方式必须为post
- 当前请求必须传输请求参数
_method,参数值为put或delete
满足以上条件,HiddenHttpMethodFilter 过滤器就会将当前请求的请求方式转换为请求参数_method的值,因此请求参数_method的值才是最终的请求方式。
2.发送put请求
案例:发送put请求
在web.xml中注册HiddenHttpMethodFilter:
<!--注册过滤器HiddenHttpMethodFilter-->
<filter>
<filter-name>HiddenHttpMethodFilter</filter-name>
<filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.HiddenHttpMethodFilter</filter-class>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>HiddenHttpMethodFilter</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>
controller:
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
@Controller
public class MyController {
//访问首页
@RequestMapping(value = "/")
public String toIndex(){
return "index";
}
// /user PUT 修改用户信息
@RequestMapping(value = "/user",method = RequestMethod.PUT)
public String updateUser(){
System.out.println("修改用户信息");
return "target";
}
}
index.html:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>首页</title>
</head>
<body>
这是index.html<br>
<form th:action="@{/user}" method="post">
<input type="hidden" name="_method" value="put"><!--设置参数_method的值为put。这一项用户不需要了解,因此hidden-->
用户名:<input type="text" name="username"><br>
密码:<input type="password" name="password"><br>
<input type="submit" value="修改用户信息"><br>
</form>
</body>
</html>
启动Tomcat:
IDEA输出:
注意:目前为止,SpringMVC中提供了两个过滤器:CharacterEncodingFilter和HiddenHttpMethodFilter。在web.xml中注册时,必须先注册CharacterEncodingFilter,再注册HiddenHttpMethodFilter,不然还是会出现乱码问题。
原因:
在 CharacterEncodingFilter 中通过 request.setCharacterEncoding(encoding) 方法设置字符集,而request.setCharacterEncoding(encoding) 方法要求前面不能有任何获取请求参数的操作,而 HiddenHttpMethodFilter 恰恰有一个获取请求方式的操作:String paramValue = request.getParameter(this.methodParam);。而在多个Filter过滤器在执行的时候,它们执行的优先顺序是由它们在web.xml中从上到下配置的顺序决定。如果HiddenHttpMethodFilter配置在前,那么就会出现乱码问题。
3.发送delete请求
具体不举例子,看下面的完整案例。
三、RESTful案例
(一)准备工作
首先,创建一个 web 模块并配置好web.xml和部署Tomcat
准备实体类:
public class Employee {
private Integer id;
private String lastName;
private String email;
//1 男, 0 女
private Integer gender;
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getLastName() {
return lastName;
}
public void setLastName(String lastName) {
this.lastName = lastName;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
public Integer getGender() {
return gender;
}
public void setGender(Integer gender) {
this.gender = gender;
}
public Employee(Integer id, String lastName, String email, Integer gender) {
super();
this.id = id;
this.lastName = lastName;
this.email = email;
this.gender = gender;
}
public Employee() {
}
}
准备dao用于模拟数据以及操作数据:
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import com.atguigu.mvc.bean.Employee;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
@Repository
public class EmployeeDao {
private static Map<Integer, Employee> employees = null;
static{
employees = new HashMap<Integer, Employee>();
employees.put(1001, new Employee(1001, "E-AA", "aa@163.com", 1));
employees.put(1002, new Employee(1002, "E-BB", "bb@163.com", 1));
employees.put(1003, new Employee(1003, "E-CC", "cc@163.com", 0));
employees.put(1004, new Employee(1004, "E-DD", "dd@163.com", 0));
employees.put(1005, new Employee(1005, "E-EE", "ee@163.com", 1));
}
private static Integer initId = 1006;
public void save(Employee employee){
if(employee.getId() == null){
employee.setId(initId++);
}
employees.put(employee.getId(), employee);
}
public Collection<Employee> getAll(){
return employees.values();
}
public Employee get(Integer id){
return employees.get(id);
}
public void delete(Integer id){
employees.remove(id);
}
}
controller:
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
@Controller
public class EmployeeController {
@Autowired
private EmployeeDao employeeDao;
}
web.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_4_0.xsd"
version="4.0">
<!--在多个Filter过滤器在执行的时候,它们执行的优先顺序是由它们在web.xml中从上到下配置的顺序决定-->
<!--注册过滤器CharacterEncodingFilter-->
<filter>
<filter-name>CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-name>
<filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-class>
<!--为了设置请求的编码为UTF-8-->
<init-param>
<param-name>encoding</param-name>
<param-value>UTF-8</param-value>
</init-param>
<!--为了设置响应的编码为UTF-8-->
<init-param>
<param-name>forceResponseEncoding</param-name>
<param-value>true</param-value>
</init-param>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>
<!--注册过滤器HiddenHttpMethodFilter-->
<filter>
<filter-name>HiddenHttpMethodFilter</filter-name>
<filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.HiddenHttpMethodFilter</filter-class>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>HiddenHttpMethodFilter</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>
<!-- 配置SpringMVC的前端控制器,对浏览器发送的请求统一进行处理 -->
<servlet>
<servlet-name>springMVC</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<!-- 通过初始化参数指定SpringMVC配置文件的位置和名称 -->
<init-param>
<!-- contextConfigLocation为固定值 -->
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<!-- 使用classpath:表示从类路径查找配置文件,例如maven工程中的 src/main/resources -->
<param-value>classpath:springMVC.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
<!--作为框架的核心组件,在启动过程中有大量的初始化操作要做
而这些操作放在第一次请求时才执行会严重影响访问速度
因此需要通过此标签将启动控制DispatcherServlet的初始化时间提前到服务器启动时 -->
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>springMVC</servlet-name>
<!--设置springMVC的核心控制器所能处理的请求的请求路径
/所匹配的请求可以是/login或.html或.js或.css方式的请求路径
但是/不能匹配.jsp请求路径的请求 -->
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
(二)功能清单
| 功能 | URL 地址 | 请求方式 |
|---|---|---|
| 访问首页√ | / | GET |
| 查询全部数据√ | /employee | GET |
| 删除√ | /employee/2 | DELETE |
| 跳转到添加数据页面√ | /toAdd | GET |
| 执行保存√ | /employee | POST |
| 跳转到更新数据页面√ | /employee/2 | GET |
| 执行更新√ | /employee | PUT |
(三)访问首页
在springMVC.xml中添加(在此之前要先引入mvc命名空间):
<!--配置视图控制器-->
<mvc:view-controller path="/" view-name="index"/>
<!--开启mvc注解驱动-->
<mvc:annotation-driven />
index.html:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>首页</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>首页</h1>
<a th:href="@{/employee}">查看所有员工信息</a>
</body>
</html>
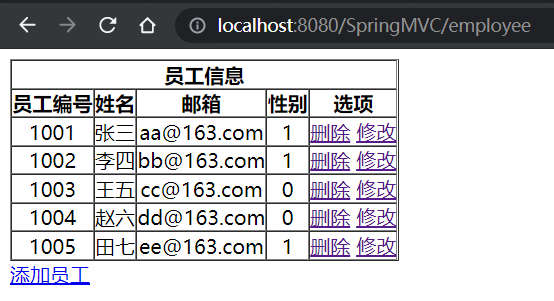
(四)查询所有员工数据
controller:
@RequestMapping(value = "/employee",method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String selectAllEmployees(Model model){
Collection<Employee> employeeList = employeeDao.getAll();
model.addAttribute("employeeList",employeeList);
return "employee_list";
}
employee_list.html:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<table border="1" cellpadding="0" cellspacing="0" style="text-align: center">
<tr>
<th colspan="5">员工信息</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<th>员工编号</th>
<th>姓名</th>
<th>邮箱</th>
<th>性别</th>
<th>选项</th>
</tr>
<tr th:each="employee:${employeeList}">
<td th:text="${employee.id}"></td>
<td th:text="${employee.lastName}"></td>
<td th:text="${employee.email}"></td>
<td th:text="${employee.gender}"></td>
<td>
<a href="">删除</a>
<a href="">修改</a>
</td>
</tr>
</table>
<a href="">添加员工</a>
</body>
</html>
(五)删除功能
在employee_list.html中创建处理delete请求方式的表单:
<!-- 作用:通过超链接控制表单的提交,将post请求转换为delete请求 -->
<form id="delete_form" method="post">
<!-- HiddenHttpMethodFilter要求:必须传输_method请求参数,并且值为最终的请求方式 -->
<input type="hidden" name="_method" value="delete"/>
</form>
接着,下载vue.js并复制到webapp/static/js/下
employee_list.html中用于删除的超链接:
<a class="deleteA" @click="deleteEmployee" th:href="@{'/employee/'+${employee.id}}">删除</a>
employee_list.html用于删除的超链接绑定点击事件:
<!--引入vue.js,通过vue处理删除链接点击事件-->
<script type="text/javascript" th:src="@{/static/js/vue.js}"></script>
<script type="text/javascript">
var vue = new Vue({
el:"#dataTable",
methods:{
//event表示当前事件
deleteEmployee:function (event) {
//根据id获取表单元素
var deleteForm = document.getElementById("deleteForm");
//将触发点击事件的超链接的href属性赋值给表单的action
deleteForm.action = event.target.href;
//提交表单
deleteForm.submit();
//阻止超链接的默认跳转行为
event.preventDefault();
}
}
});
</script>
controller:
@RequestMapping(value = "/employee/{id}",method = RequestMethod.DELETE)
public String deleteEmployeeById(@PathVariable("id") Integer id){
employeeDao.delete(id);
return "redirect:/employee";
}
springMVC.xml:
<!--开放对静态资源的访问-->
<!--所有请求都被DispatcherServlet处理,控制器没有访问静态资源的映射
我们就要用DefaultServlet处理-->
<mvc:default-servlet-handler />
在此之前工程已经运行过了,之后添加的静态资源vue.js不存在打包的结果里,重新打包(点击IDEA中Maven界面的Lifecycle中的packing)
(六)跳转到添加数据页面
springMVC.xml:
<mvc:view-controller path="/toAdd" view-name="employee_add"></mvc:view-controller>
创建employee_add.html:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>add employee</title>
</head>
<body>
<form th:action="@{/employee}" method="post">
姓名:<input type="text" name="lastName"><br>
邮箱:<input type="text" name="email"><br>
性别:<input type="radio" name="gender" value="1">男
<input type="radio" name="gender" value="0">女<br>
<input type="submit" value="添加"><br>
</form>
</body>
</html>
(七)执行保存
controller:
@RequestMapping(value = "/employee", method = RequestMethod.POST)
public String addEmployee(Employee employee){
employeeDao.save(employee);
return "redirect:/employee";
}
(八)跳转到更新数据页面
employee_list.html中用于修改的超链接:
<a th:href="@{'/employee/'+${employee.id}}">修改</a>
controller:
@RequestMapping(value = "/employee/{id}", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String getEmployeeById(@PathVariable("id") Integer id, Model model){
Employee employee = employeeDao.get(id);
model.addAttribute("employee", employee);
return "employee_update";
}
创建employee_update.html:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Update Employee</title>
</head>
<body>
<form th:action="@{/employee}" method="post">
<input type="hidden" name="_method" value="put">
<input type="hidden" name="id" th:value="${employee.id}">
姓名:<input type="text" name="lastName" th:value="${employee.lastName}"><br>
邮箱:<input type="text" name="email" th:value="${employee.email}"><br>
<!--
th:field="${employee.gender}"可用于单选框或复选框的回显
若单选框的value和employee.gender的值一致,则添加checked="checked"属性
-->
性别:<input type="radio" name="gender" value="1" th:field="${employee.gender}">男
<input type="radio" name="gender" value="0" th:field="${employee.gender}">女<br>
<input type="submit" value="更新"><br>
</form>
</body>
</html>
(九)执行更新
controller:
@RequestMapping(value = "/employee", method = RequestMethod.PUT)
public String updateEmployee(Employee employee){
employeeDao.save(employee);
return "redirect:/employee";
}