背景
上次看了下xxl-job,发现他的通信机制就是自己基于Netty实现了一个http服务器,然后发现自己看的不是很懂,就打算自己来实现一个简单的支持http协议和webSocket协议的服务器来帮助自己理解
依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>fastjson</artifactId>
<version>1.2.62</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>cn.hutool</groupId>
<artifactId>hutool-all</artifactId>
<version>5.7.13</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.netty</groupId>
<artifactId>netty-all</artifactId>
<version>5.0.0.Alpha1</version>
</dependency>
主要这里我的netty版本用的5.x,推荐使用4.x版本的netty,因为netty 5.x好像是被netty作者废弃掉了。5.x版本和4.x版本部分api可能不同
包结构
实现 WebSocketServer
- WebSocketServer.java
@Slf4j
public class WebSocketServer {
// /Users/weihu/Desktop/sofe/java/netty-student/netty-websocket/src/main/resources/WebSocketServer.html
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
int port = args.length > 0 ? Integer.parseInt(args[0]) : 8080;
new WebSocketServer().run(port);
}
public void run(int port) throws Exception{
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
EventLoopGroup workGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
ServerBootstrap bootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
bootstrap.group(bossGroup, workGroup)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class).childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline();
pipeline.addLast("http-codec", new HttpServerCodec()) // http 编解码处理器
// http多个消息部分组合成一条完整http消息
.addLast("aggregator", new HttpObjectAggregator(65536))
// 支持向客户端发送html5消息,主要用于支持浏览器和服务端进行websocket 通信,如果仅是http服务不需要该处理器
.addLast("http-chunked", new ChunkedWriteHandler())
// 核心业务逻辑处理器
.addLast("handler", new WebSocketServerHandler());
}
});
Channel channel = bootstrap.bind(port).sync().channel();
log.info("Web socket or http server started at port: {}", port);
log.info("open your browser and navigate to http://localhost:{}/",port);
channel.closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
workGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}
这里的代码其实就是固定的一套模板,当然如果是要优化一些网络相关的参数另说,可以看到接收和处理,核心业务逻辑都在
WebSocketServerHandler这个类中
业务handler WebSocketServerHandler
- WebSocketServerHandler.java
@Slf4j
public class WebSocketServerHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<Object> {
private WebSocketServerHandshaker handshaker;
@Override
public void messageReceived(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg)
throws Exception {
// 传统的HTTP接入
if (msg instanceof FullHttpRequest) {
handleHttpRequest(ctx, (FullHttpRequest) msg);
}
// WebSocket接入
else if (msg instanceof WebSocketFrame) {
handleWebSocketFrame(ctx, (WebSocketFrame) msg);
}
}
@Override
public void channelReadComplete(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
ctx.flush();
}
private void handleHttpRequest(ChannelHandlerContext ctx,
FullHttpRequest req) throws Exception {
log.info("这里再处理http请求");
// 如果 http解码失败 返回错误
if (!req.getDecoderResult().isSuccess()) {
sendHttpResponse(ctx, req, new DefaultFullHttpResponse(HttpVersion.HTTP_1_1,
HttpResponseStatus.BAD_REQUEST));
return;
}
// 如果是 websocket 握手
if (("websocket".equals(req.headers().get("Upgrade")))) {
WebSocketServerHandshakerFactory wsFactory = new WebSocketServerHandshakerFactory(
"ws://localhost:8080/websocket", null, false);
handshaker = wsFactory.newHandshaker(req);
if (handshaker == null) {
WebSocketServerHandshakerFactory
.sendUnsupportedWebSocketVersionResponse(ctx.channel());
} else {
handshaker.handshake(ctx.channel(), req);
}
return;
}
// http请求
String uri = req.getUri();
Map<String,String> resMap = new HashMap<>();
resMap.put("method",req.getMethod().name());
resMap.put("uri",uri);
String msg = "<html><head><title>test</title></head><body>你的请求为:" + JSON.toJSONString(resMap) +"</body></html>";
// 创建http响应
FullHttpResponse response = new DefaultFullHttpResponse(
HttpVersion.HTTP_1_1,
HttpResponseStatus.OK,
Unpooled.copiedBuffer(msg, CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
// 设置头信息
response.headers().set(HttpHeaders.Names.CONTENT_TYPE, "text/html; charset=UTF-8");
// 将html write到客户端
ctx.writeAndFlush(response).addListener(ChannelFutureListener.CLOSE);
}
private void handleWebSocketFrame(ChannelHandlerContext ctx,
WebSocketFrame frame) {
// 判断是否是关闭链路的指令
if (frame instanceof CloseWebSocketFrame) {
handshaker.close(ctx.channel(),
(CloseWebSocketFrame) frame.retain());
return;
}
// 判断是否是Ping消息
if (frame instanceof PingWebSocketFrame) {
ctx.channel().write(
new PongWebSocketFrame(frame.content().retain()));
return;
}
// 本例程仅支持文本消息,不支持二进制消息
if (!(frame instanceof TextWebSocketFrame)) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException(String.format(
"%s frame types not supported", frame.getClass().getName()));
}
// 返回应答消息
String request = ((TextWebSocketFrame) frame).text();
log.info("{} receiver {}", ctx.channel(), request);
ctx.channel().write(
new TextWebSocketFrame(request
+ " , 欢迎使用Netty WebSocket服务,现在时刻:"
+ DateUtil.now()));
}
private static void sendHttpResponse(ChannelHandlerContext ctx,
FullHttpRequest req, FullHttpResponse res) {
// 返回应答给客户端
if (res.getStatus().code() != 200) {
ByteBuf buf = Unpooled.copiedBuffer(res.getStatus().toString(),
CharsetUtil.UTF_8);
res.content().writeBytes(buf);
buf.release();
HttpHeaders.setContentLength(res, res.content().readableBytes());
}
// 如果是非Keep-Alive,关闭连接
ChannelFuture f = ctx.channel().writeAndFlush(res);
if (!HttpHeaders.isKeepAlive(req) || res.getStatus().code() != 200) {
f.addListener(ChannelFutureListener.CLOSE);
}
}
}
这里为了方便测试websock,这里再写一个简单的html页面
- WebSocketServer.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
Netty WebSocket 时间服务器
</head>
<br>
<body>
<br>
<script type="text/javascript">
var socket;
if (!window.WebSocket)
{
window.WebSocket = window.MozWebSocket;
}
if (window.WebSocket) {
socket = new WebSocket("ws://localhost:8080/websocket");
socket.onmessage = function(event) {
var ta = document.getElementById('responseText');
ta.value="";
ta.value = event.data
};
socket.onopen = function(event) {
var ta = document.getElementById('responseText');
ta.value = "打开WebSocket服务正常,浏览器支持WebSocket!";
};
socket.onclose = function(event) {
var ta = document.getElementById('responseText');
ta.value = "";
ta.value = "WebSocket 关闭!";
};
}
else
{
alert("抱歉,您的浏览器不支持WebSocket协议!");
}
function send(message) {
if (!window.WebSocket) { return; }
if (socket.readyState == WebSocket.OPEN) {
socket.send(message);
}
else
{
alert("WebSocket连接没有建立成功!");
}
}
</script>
<form onsubmit="return false;">
<input type="text" name="message" value="Netty最佳实践"/>
<br><br>
<input type="button" value="发送WebSocket请求消息" onclick="send(this.form.message.value)"/>
<hr color="blue"/>
<h3>服务端返回的应答消息</h3>
<textarea id="responseText" style="width:500px;height:300px;"></textarea>
</form>
</body>
</html>
测试
我们直接运行WebSocketServer的main方法,不传入端口号默认8080
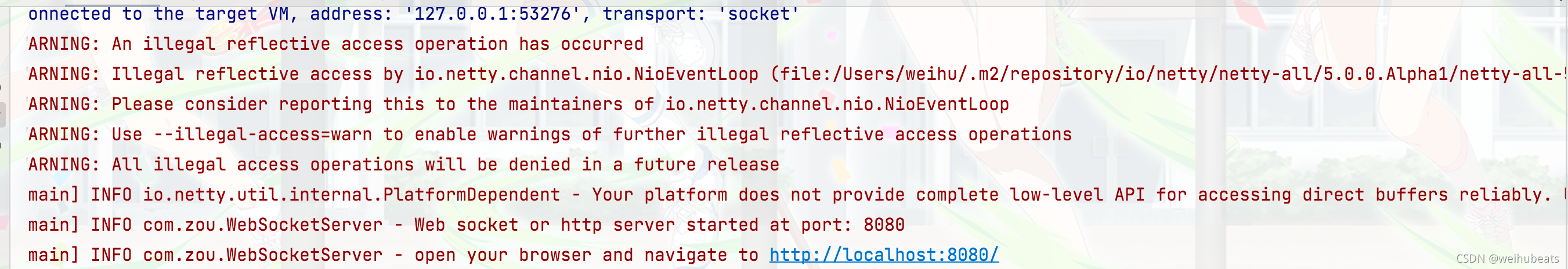
我们先测试http请求的处理,直接访问
http://localhost:8080/index?query=1

可以看到处理成功了
然后我们试试WebSocket的测试
我们直接在浏览器输入我们WebSocketServer.html的绝对路径


可以看到WebSocket连接是正常的,接下来我们试试发送消息试试

可以看到客户端成功接收到了服务端返回的数据
我们看看服务端的log

可以看到也是接收成功到了客户端发来的消息
xxl-job 源码中基于netty实现的http
上面我们简单的实现一个http、WebSocket的demo,我们下面来简单看看在xxl-job源码中是如何实现的
核心入口在EmbedServer这个类中,我们简单的分析下
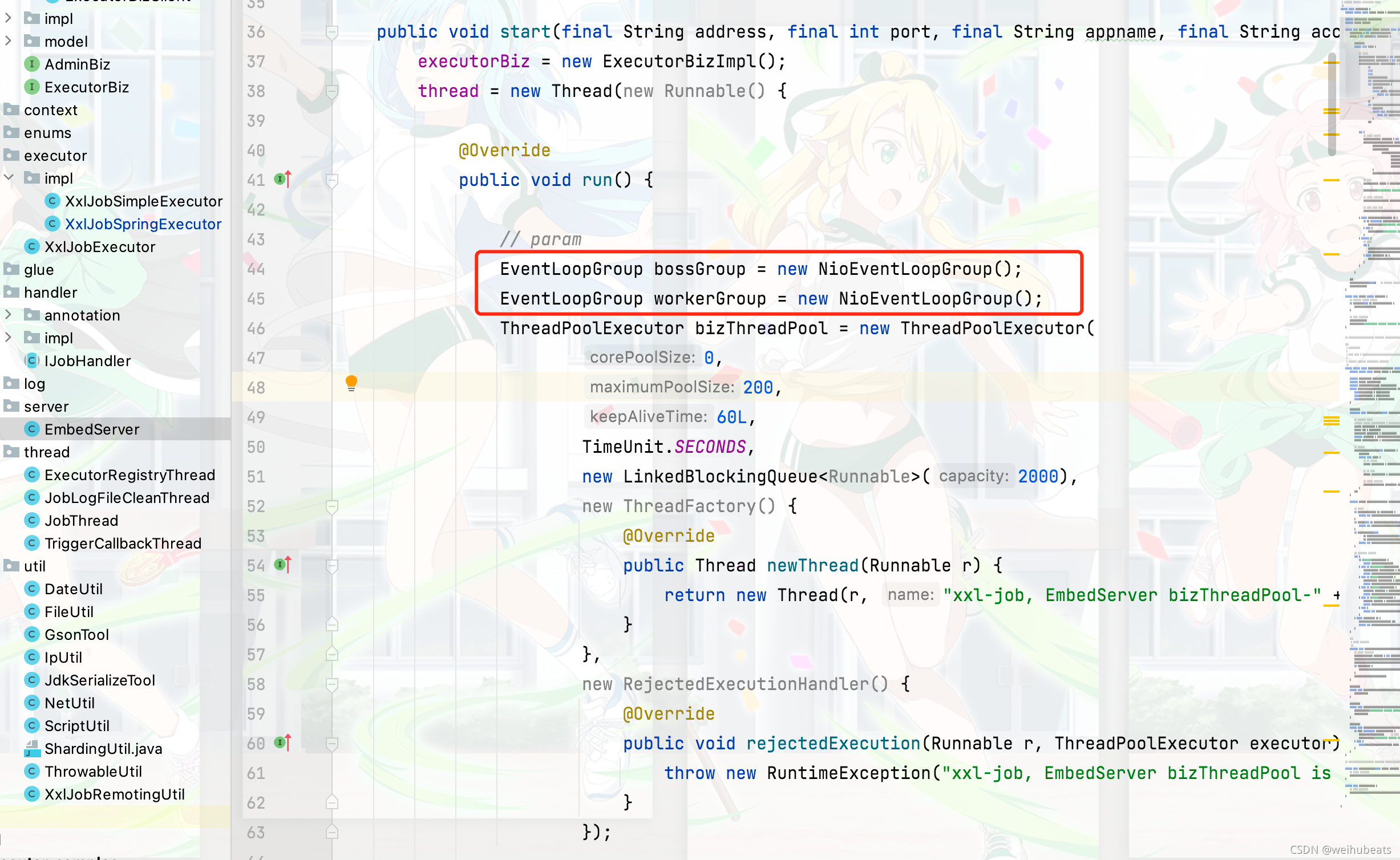
可以看到首先标准的两个EventLoopGroup

然后可以看到添加handler和我们上面实现的demo类似,不同的是因为他只是支持http所以没有
ChunkedWriteHandler这个handler,但是他多了一个IdleStateHandler,Netty的IdleStateHandler主要用于心跳机制,用来检测远端是否存活,如果不存活或活跃则对空闲Socket连接进行处理避免资源的浪费
这里他的http请求核心实现都放在了EmbedHttpServerHandler这个类,我们看看这个类吧
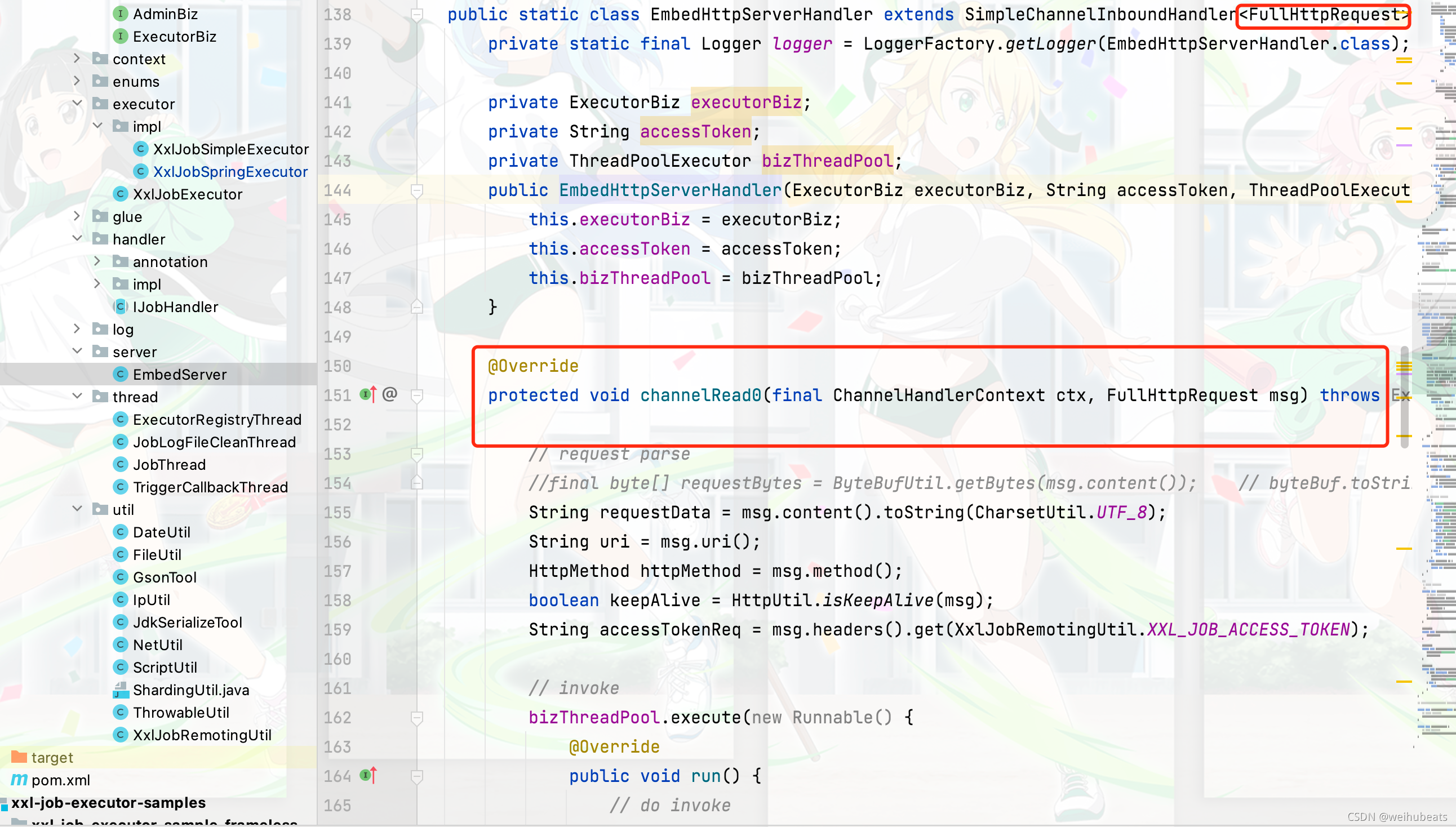
EmbedHttpServerHandler是EmbedServer的一个静态内部类。和我们实现的WebSocketServerHandler类似,不同的首先他在继承SimpleChannelInboundHandler指定了泛型为FullHttpRequest代表仅处理http,其次由于xxl-job使用的netty版本为4.x,所以它需要实现的抽象方法也变为了
protected void channelRead0(final ChannelHandlerContext ctx, FullHttpRequest msg) throws Exception {
}
我们看看 channelRead0方法的实现
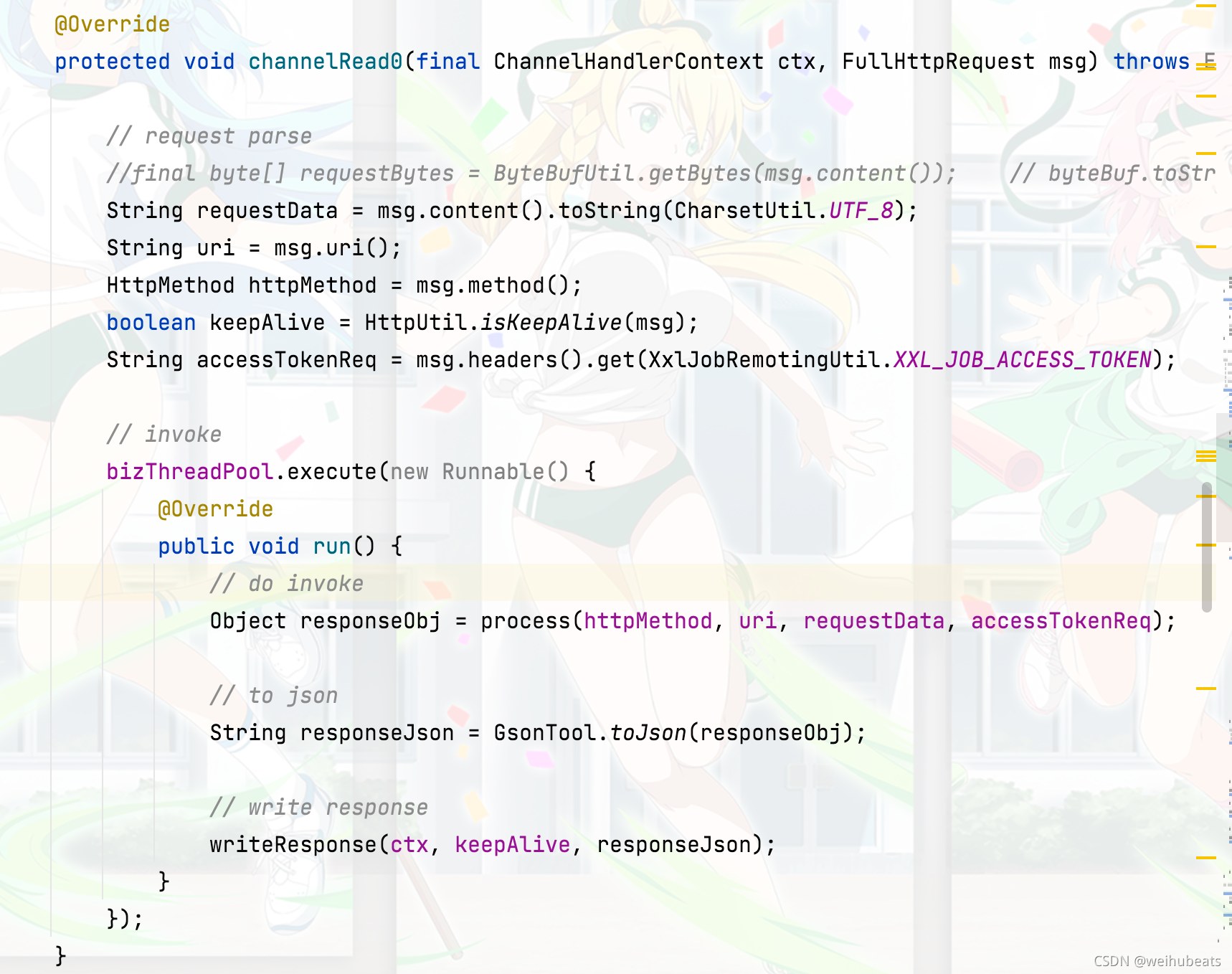
可以看到和我们实现没啥区别,不同的是处理请求又开了一个线程池,核心处理逻辑在process中

可以看到也很简单,如果为post请求直接不支持,然后加了一些token验证,然后将请求数据转换为java类作一些业务逻辑处理然后返回
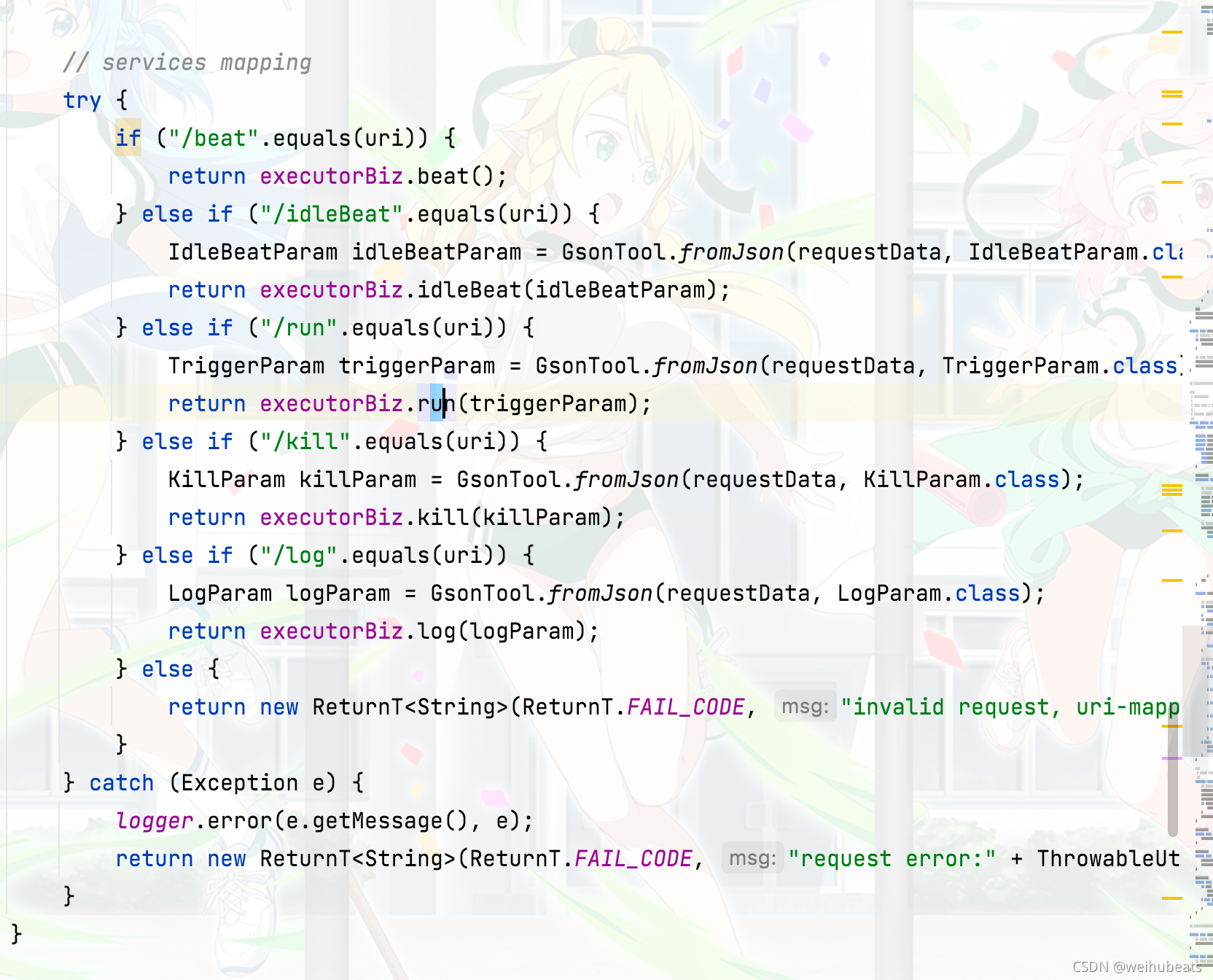
至此 xxl-job的通信源码大致就分析完了
总结
可以看到如果我们不需要自定义协议,整体基于netty的开箱即用实现起来还是非常方便的,让我们更专注于业务逻辑的处理,如果要自定义消息体,加一些编解码,半包的处理等,还是比较麻烦的,实现简单的http请求还是比较容易的
参考
- Netty权威指南
- xxl-job源码