网络编程
一个简单的比喻:

计算机网络
计算机网络是指将地理位置不同的具有独立功能的多台计算机及其外部设备,通过通信线路连接起来,在网络操作系统,网络管理软件及网络通信协议的管理和协调下,实现资源共享和信息传递的计算机系统。
网络编程的目的
数据交换;通信。
想要达到这个效果需要什么
1.如何准确地定位网络上的一台主机 192.168.16.124 :端口号,定位到这个计算机上的某个资源(IP地址);
2.找到了这个主机,如何传输数据?
Javaweb:网页编程 B/S架构
网络编程:tcp/ip C/S架构
网络通信的要素
如何实现网络的通信?
通信双方的地址:
·IP
·端口号
·192.168.16.124:5900
规则:网络通信的协议
http,ftp,smtp,tcp,udp等等
TCP/IP参考模型:

小结
1.网络编程中有两个主要问题
·如何准确地定位到网络上的一台或者多台主机
·找到主机后如何进行通信
2.网络编程中的要素
·IP和端口号 IP类
·网络通信协议 UDP,TCP类
3.万物皆对象(Java)
IP
ip地址:InetAddress
·唯一定位一台网络上的计算机
·127.0.0.1:本机(localhost)
·IP地址的分类
a.IPv4/IPv6
IPv4 127.0.0.1 ,4个字节组成。 0-255,42亿个;30亿在北美。4亿在亚洲。2011年就已经用尽。
IPv6 8个无符号整数,128位
b.公网(互联网)-私网(局域网)
ABCD地址
192.168.xx.xx 专门给组织内部网使用的
·域名:记忆IP问题!
代码如下(InetAddress没有构造器所以不能new ):
package lesson01;
import java.net.InetAddress;
import java.net.UnknownHostException;
//测试IP
public class TestInetAddress {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
InetAddress inetAddress1 = InetAddress.getByName("127.0.0.1");
InetAddress inetAddress2 = InetAddress.getLocalHost();
InetAddress inetAddress3 = InetAddress.getByName("localhost");
System.out.println(inetAddress1);
System.out.println(inetAddress2);
System.out.println(inetAddress3);
//查询网页地址
InetAddress inetAddress4 = InetAddress.getByName("www.baidu.com");
System.out.println(inetAddress4);
} catch (UnknownHostException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
端口

一些命令:
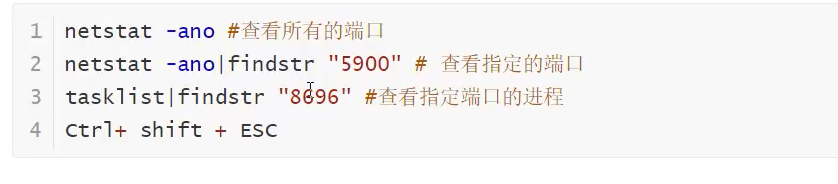
InetSocketAddress 可以new; 里面的方法和InetAddress几乎相同。
通信协议
协议:与诶定,就好比我们现在说的普通话
网络通信协议:速率,传输码率,代码结构,传输控制…
问题:非常的复杂?
大事化小:分层!
TCP/IP协议簇:实际上是一组协议
重要:
TCP:用户传输协议
UDP:用户数据报协议
出名的协议:
TCP:
IP:网络互连协议
TCP UDP 对比

三次握手,四次挥手:

官方解释:
三次握手;

四次挥手;

暴力写法,比较低级
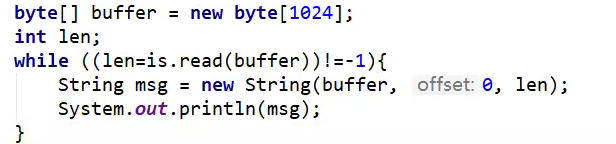
TCP实现聊天思路:
客户端:
1.连接服务器Socket
2.发送消息
服务器:
1.建立服务的端口 ServerSocket
2.等待用户的连接 accept
3.接受用户的消息
tcp实现聊天服务端代码:
package lesson02;
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
public class TcpServerDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//提升一下作用域
ServerSocket serverSocket = null;
Socket socket = null;
InputStream is = null;
ByteArrayOutputStream baos = null;
try {
//1.我得有一个地址
serverSocket = new ServerSocket(9999);
//等到客户端连接过来
socket = serverSocket.accept();
//读取客户端的消息
is = socket.getInputStream();
//管道流
baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int len;
while((len=is.read(buffer))!=-1){
baos.write(buffer,0,len);
}
System.out.println(baos.toString());
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if(baos!=null){
try {
baos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (is!=null){
try {
is.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (socket!=null){
try {
socket.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (serverSocket!=null){
try {
serverSocket.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
tcp实现聊天客户端代码:
package lesson02;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.net.InetAddress;
import java.net.Socket;
//客户端
public class TcpClientDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//提升一下作用域
Socket socket = null;
OutputStream os = null;
try {
//1.要知道服务器的地址,端口号
InetAddress serverIP = InetAddress.getByName("127.0.0.1");
int port = 9999;
//2.创建一个socket连接
socket = new Socket(serverIP,port);
//3.发送消息 IO流
os = socket.getOutputStream();
os.write("你好,欢迎学习Java".getBytes());
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if (os!=null){
try {
os.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (socket!=null){
try {
socket.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
在客户端和服务端中,socket其主要连接作用;
如果传过来是一个不认识的东西,我们需要一个管道流:
文件上传程序
ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
文件上传客户端代码如下:
package lesson02;
import java.io.*;
import java.net.InetAddress;
import java.net.Socket;
public class TcpClientDemo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//1.创建一个socket连接
Socket socket = new Socket(InetAddress.getByName("127.0.0.1"), 9000);
//2.创建一个输出流
OutputStream os = socket.getOutputStream();
//3.读取文件
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(new File("8821914_222951593000_2.jpg"));
//4.写出文件
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int len ;
while((len=fis.read(buffer))!=-1){
os.write(buffer,0,len);
}
//通知服务器,我已经结束了
socket.shutdownOutput();//我已经传输完了!
//确定服务器接受完毕,才能够断开连接
InputStream inputStream = socket.getInputStream();
//返回是一个 String byte[]
ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
byte[] buffer2 = new byte[1024];
int len2 ;
while((len2=inputStream.read(buffer2))!=-1){
baos.write(buffer2,0,len2);
}
System.out.println(baos.toString());
//5.关闭资源
baos.close();
inputStream.close();
fis.close();
os.close();
socket.close();
}
}
文件上传服务端代码如下:
package lesson02;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
public class TcpServerDemo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//1.创建服务
ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(9000);
//2.监听客户端的连接
Socket socket = serverSocket.accept();//阻塞式监听,一直等待客户端连接
//3.获取输入流
InputStream is = socket.getInputStream();//is是我们接受的图片
//文件输出
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(new File("receive.jpg"));
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int len;
while ((len= is.read(buffer))!=-1){
fos.write(buffer,0,len);//如果这里面有值就把他写出去
}
//通知客户端我接受完毕了
OutputStream os = socket.getOutputStream();
os.write("我接受完毕了".getBytes());
//关闭资源
fos.close();
is.close();
socket.close();
serverSocket.close();
}
}
Tomcat(就是别人用Java写好的客户端和服务端)
服务端:
·自定义 S
·Tomcat服务器 S:Java后台开发
客户端
·自定义 S
·浏览器 B
Tomcat bin目录下 startup.bat是Windows环境下的执行文件
startup.sh是Linux环境下的执行文件
UDP
UDP没有这个服务端和客户端这个概念,我们这里主要是为了好理解。
发送消息发送端代码:
package lesson03;
import java.net.DatagramPacket;
import java.net.DatagramSocket;
import java.net.InetAddress;
//不需要来连接服务器
public class UdpClientDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//1.建立一个socket
DatagramSocket socket = new DatagramSocket();
//2.建一个包
String msg = "你好啊,我亲爱的服务器";
//发送给谁
InetAddress localhost = InetAddress.getByName("localhost");
int port = 9090;
//数据,数据的长度起始,要发送给谁
DatagramPacket packet = new DatagramPacket(msg.getBytes(), 0, msg.getBytes().length, localhost, port);
//3.发送包
socket.send(packet);
//关闭流
socket.close();
}
}
发送消息接收端代码;
package lesson03;
import java.net.DatagramPacket;
import java.net.DatagramSocket;
//还是要等待客户端的连接
public class UdpServerDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//开放端口
DatagramSocket socket = new DatagramSocket(9090);
//接受数据包
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
DatagramPacket packet = new DatagramPacket(buffer, 0, buffer.length);
socket.receive(packet);//阻塞接收,就是一直在接收,除非收到了东西
System.out.println(packet.getAddress().getHostAddress());
System.out.println(new String(packet.getData(),0, packet.getLength()));
//关闭连接
socket.close();
}
}
循环发送消息接收端
package chat;
import java.net.DatagramPacket;
import java.net.DatagramSocket;
public class UdpReceiveDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
DatagramSocket socket = new DatagramSocket(6666);
while (true){
//准备接收包裹
byte[] container = new byte[1024];
DatagramPacket packet = new DatagramPacket(container,0,container.length);
socket.receive(packet);//阻塞式接收包裹
//断开连接 bye
byte[] data = packet.getData();
String receiveData = new String(data, 0, data.length);
System.out.println(receiveData);
if (receiveData.equals("bye")){
break;
}
}
socket.close();
}
}
循环发送消息发送端
package chat;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.net.DatagramPacket;
import java.net.DatagramSocket;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
public class UdpSenderDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
DatagramSocket socket = new DatagramSocket(8888);
//准备数据:控制台读取System.in
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
while (true){
String data = reader.readLine();
byte[] datas = data.getBytes();
DatagramPacket packet = new DatagramPacket(datas, 0, datas.length, new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 6666));
socket.send(packet);
if (data.equals("bye")){
break;
}
}
socket.close();
}
}
多线程实例(在线咨询:两个人都可以是发送方,也都可以是接收方,双方可以在线聊天)
发送端:
package chat;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.net.DatagramPacket;
import java.net.DatagramSocket;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
public class TalkSend implements Runnable {
DatagramSocket socket = null;
BufferedReader reader = null;//这里这个是从控制端读取
private int fromPort;
private String toIP;
private int toPort;
public TalkSend(int fromPort, String toIP, int toPort) {
this.fromPort = fromPort;
this.toIP = toIP;
this.toPort = toPort;
try {
socket = new DatagramSocket(fromPort);
reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public void run() {
//DatagramSocket socket = new DatagramSocket(8888);
//准备数据:控制台读取System.in
//BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
while (true) {
try {
String data = reader.readLine();
byte[] datas = data.getBytes();
DatagramPacket packet = new DatagramPacket(datas, 0, datas.length, new InetSocketAddress(this.toIP, this.toPort));
socket.send(packet);
if (data.equals("bye")) {
break;
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
/* String data = reader.readLine();
byte[] datas = data.getBytes();
DatagramPacket packet = new DatagramPacket(datas, 0, datas.length, new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 6666));
socket.send(packet);
if (data.equals("bye")){
break;
}
}
socket.close();*/
}
socket.close();
}
}
接收端:
package chat;
import java.net.DatagramPacket;
import java.net.DatagramSocket;
import java.net.SocketException;
public class TalkReceive implements Runnable{
DatagramSocket socket = null;
private int port;
private String msgFrom;
public TalkReceive(int port, String msgFrom) {
this.port = port;
this.msgFrom = msgFrom;
try {
socket = new DatagramSocket(port);
} catch (SocketException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public void run() {
//DatagramSocket socket = new DatagramSocket(6666);
try {
while (true){
//准备接收包裹
byte[] container = new byte[1024];
DatagramPacket packet = new DatagramPacket(container,0,container.length);
socket.receive(packet);//阻塞式接收包裹
//断开连接 bye
byte[] data = packet.getData();
String receiveData = new String(data, 0, data.length);
System.out.println(msgFrom+":"+receiveData);
if (receiveData.equals("bye")){
break;
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
socket.close();
}
}
学生线程:
package chat;
public class TalkStudent {
//开启两个线程
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Thread(new TalkSend(7777,"localhost",9999)).start();
new Thread(new TalkReceive(8888,"teacher")).start();
}
}
老师线程:
package chat;
public class TalkTeacher {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Thread(new TalkSend(5555,"localhost",8888)).start();
new Thread(new TalkReceive(9999,"student")).start();
}
}
URL
url:统一资源定位符,定位资源的,定位互联网上的某一个资源。

大概就是这个模式,可以少但不可以多。
URL类:

网上下载代码:
package lesson04;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.net.HttpURLConnection;
import java.net.MalformedURLException;
import java.net.URL;
public class URLDownDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//1.下载地址
URL url = new URL("http://localhost:8090/konglingcai/SecurityFile.txt");
//2.连接到这个资源 HTTP
HttpURLConnection urlConnection = (HttpURLConnection) url.openConnection();
InputStream inputStream = urlConnection.getInputStream();
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("SecurityFile.txt");//把文件下载下来的名字
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int len;
while((len=inputStream.read(buffer))!=-1){
fos.write(buffer,0,len);
}
fos.close();
inputStream.close();
urlConnection.disconnect();
}
}