
一 问题背景
- 平台端购置一批裸代理,来做广告异地展现审核。从外部购置的代理,使用方式为:
- 通过给定的HTTP 的 API 提取代理 IP:PORT,返回的结果会给出代理的有效时长 3~5 分钟,以及代理所属地域;
从提取的代理中,选取指定地域,添加认证信息,请求获取结果;
本文设计实现一个通过的代理网关:
- 管理维护代理资源,并做代理的认证鉴权;
- 对外暴露统一的代理入口,而非动态变化的代理IP:PORT;
- 流量过滤及限流,比如:静态资源不走代理;
本文重点在代理网关本身的设计与实现,而非代理资源的管理与维护。
注:本文包含大量可执行的JAVA代码以解释代理相关的原理
二 技术路线
本文的技术路线。在实现代理网关之前,首先介绍下代理相关的原理及如何实现
- 透明代理;
- 非透明代理;
- 透明的上游代理;
- 非透明的上游代理;
最后,本文要构建代理网关,本质上就是一个非透明的上游代理,并给出详细的设计与实现。
1 透明代理
透明代理是代理网关的基础,本文采用JAVA原生的NIO进行详细介绍。在实现代理网关时,实际使用的为NETTY框架。原生NIO的实现对理解NETTY的实现有帮助。
透明代理设计三个交互方,客户端、代理服务、服务端,其原理是:
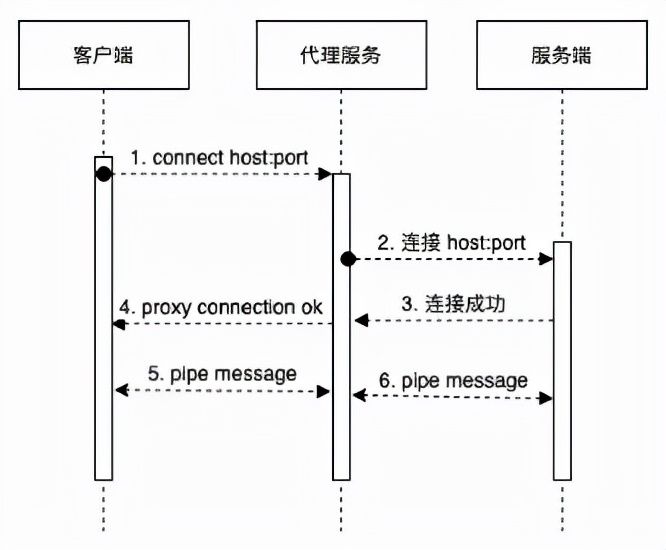
- 代理服务在收到连接请求时,判定:如果是CONNECT请求,需要回应代理连接成功消息到客户端;
- CONNECT请求回应结束后,代理服务需要连接到CONNECT指定的远程服务器,然后直接转发客户端和远程服务通信;
- 代理服务在收到非CONNECT请求时,需要解析出请求的远程服务器,然后直接转发客户端和远程服务通信;
需要注意的点是:
- 通常HTTPS请求,在通过代理前,会发送CONNECT请求;连接成功后,会在信道上进行加密通信的握手协议;因此连接远程的时机是在CONNECT请求收到时,因为此后是加密数据;
- 透明代理在收到CONNECT请求时,不需要传递到远程服务(远程服务不识别此请求);
- 透明代理在收到非CONNECT请求时,要无条件转发;
完整的透明代理的实现不到约300行代码,完整摘录如下:
@Slf4j
public class SimpleTransProxy {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
int port = 8006;
ServerSocketChannel localServer = ServerSocketChannel.open();
localServer.bind(new InetSocketAddress(port));
Reactor reactor = new Reactor();
// REACTOR线程
GlobalThreadPool.REACTOR_EXECUTOR.submit(reactor::run);
// WORKER单线程调试
while (localServer.isOpen()) {
// 此处阻塞等待连接
SocketChannel remoteClient = localServer.accept();
// 工作线程
GlobalThreadPool.WORK_EXECUTOR.submit(new Runnable() {
@SneakyThrows
@Override
public void run() {
// 代理到远程
SocketChannel remoteServer = new ProxyHandler().proxy(remoteClient);
// 透明传输
reactor.pipe(remoteClient, remoteServer)
.pipe(remoteServer, remoteClient);
}
});
}
}
}
@Data
class ProxyHandler {
private String method;
private String host;
private int port;
private SocketChannel remoteServer;
private SocketChannel remoteClient;
/**
* 原始信息
*/
private List<ByteBuffer> buffers = new ArrayList<>();
private StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
/**
* 连接到远程
* @param remoteClient
* @return
* @throws IOException
*/
public SocketChannel proxy(SocketChannel remoteClient) throws IOException {
this.remoteClient = remoteClient;
connect();
return this.remoteServer;
}
public void connect() throws IOException {
// 解析METHOD, HOST和PORT
beforeConnected();
// 链接REMOTE SERVER
createRemoteServer();
// CONNECT请求回应,其他请求WRITE THROUGH
afterConnected();
}
protected void beforeConnected() throws IOException {
// 读取HEADER
readAllHeader();
// 解析HOST和PORT
parseRemoteHostAndPort();
}
/**
* 创建远程连接
* @throws IOException
*/
protected void createRemoteServer() throws IOException {
remoteServer = SocketChannel.open(new InetSocketAddress(host, port));
}
/**
* 连接建立后预处理
* @throws IOException
*/
protected void afterConnected() throws IOException {
// 当CONNECT请求时,默认写入200到CLIENT
if ("CONNECT".equalsIgnoreCase(method)) {
// CONNECT默认为443端口,根据HOST再解析
remoteClient.write(ByteBuffer.wrap("HTTP/1.0 200 Connection Established\r\nProxy-agent: nginx\r\n\r\n".getBytes()));
} else {
writeThrouth();
}
}
protected void writeThrouth() {
buffers.forEach(byteBuffer -> {
try {
remoteServer.write(byteBuffer);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
}
/**
* 读取请求内容
* @throws IOException
*/
protected void readAllHeader() throws IOException {
while (true) {
ByteBuffer clientBuffer = newByteBuffer();
int read = remoteClient.read(clientBuffer);
clientBuffer.flip();
appendClientBuffer(clientBuffer);
if (read < clientBuffer.capacity()) {
break;
}
}
}
/**
* 解析出HOST和PROT
* @throws IOException
*/
protected void parseRemoteHostAndPort() throws IOException {
// 读取第一批,获取到METHOD
method = parseRequestMethod(stringBuilder.toString());
// 默认为80端口,根据HOST再解析
port = 80;
if ("CONNECT".equalsIgnoreCase(method)) {
port = 443;
}
this.host = parseHost(stringBuilder.toString());
URI remoteServerURI = URI.create(host);
host = remoteServerURI.getHost();
if (remoteServerURI.getPort() > 0) {
port = remoteServerURI.getPort();
}
}
protected void appendClientBuffer(ByteBuffer clientBuffer) {
buffers.add(clientBuffer);
stringBuilder.append(new String(clientBuffer.array(), clientBuffer.position(), clientBuffer.limit()));
}
protected static ByteBuffer newByteBuffer() {
// buffer必须大于7,保证能读到method
return ByteBuffer.allocate(128);
}
private static String parseRequestMethod(String rawContent) {
// create uri
return rawContent.split("\r\n")[0].split(" ")[0];
}
private static String parseHost(String rawContent) {
String[] headers = rawContent.split("\r\n");
String host = "host:";
for (String header : headers) {
if (header.length() > host.length()) {
String key = header.substring(0, host.length());
String value = header.substring(host.length()).trim();
if (host.equalsIgnoreCase(key)) {
if (!value.startsWith("http://") && !value.startsWith("https://")) {
value = "http://" + value;
}
return value;
}
}
}
return "";
}
}
@Slf4j
@Data
class Reactor {
private Selector selector;
private volatile boolean finish = false;
@SneakyThrows
public Reactor() {
selector = Selector.open();
}
@SneakyThrows
public Reactor pipe(SocketChannel from, SocketChannel to) {
from.configureBlocking(false);
from.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ, new SocketPipe(this, from, to));
return this;
}
@SneakyThrows
public void run() {
try {
while (!finish) {
if (selector.selectNow() > 0) {
Iterator<SelectionKey> it = selector.selectedKeys().iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey selectionKey = it.next();
if (selectionKey.isValid() && selectionKey.isReadable()) {
((SocketPipe) selectionKey.attachment()).pipe();
}
it.remove();
}
}
}
} finally {
close();
}
}
@SneakyThrows
public synchronized void close() {
if (finish) {
return;
}
finish = true;
if (!selector.isOpen()) {
return;
}
for (SelectionKey key : selector.keys()) {
closeChannel(key.channel());
key.cancel();
}
if (selector != null) {
selector.close();
}
}
public void cancel(SelectableChannel channel) {
SelectionKey key = channel.keyFor(selector);
if (Objects.isNull(key)) {
return;
}
key.cancel();
}
@SneakyThrows
public void closeChannel(Channel channel) {
SocketChannel socketChannel = (SocketChannel)channel;
if (socketChannel.isConnected() && socketChannel.isOpen()) {
socketChannel.shutdownOutput();
socketChannel.shutdownInput();
}
socketChannel.close();
}
}
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
class SocketPipe {
private Reactor reactor;
private SocketChannel from;
private SocketChannel to;
@SneakyThrows
public void pipe() {
// 取消监听
clearInterestOps();
GlobalThreadPool.PIPE_EXECUTOR.submit(new Runnable() {
@SneakyThrows
@Override
public void run() {
int totalBytesRead = 0;
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
while (valid(from) && valid(to)) {
byteBuffer.clear();
int bytesRead = from.read(byteBuffer);
totalBytesRead = totalBytesRead + bytesRead;
byteBuffer.flip();
to.write(byteBuffer);
if (bytesRead < byteBuffer.capacity()) {
break;
}
}
if (totalBytesRead < 0) {
reactor.closeChannel(from);
reactor.cancel(from);
} else {
// 重置监听
resetInterestOps();
}
}
});
}
protected void clearInterestOps() {
from.keyFor(reactor.getSelector()).interestOps(0);
to.keyFor(reactor.getSelector()).interestOps(0);
}
protected void resetInterestOps() {
from.keyFor(reactor.getSelector()).interestOps(SelectionKey.OP_READ);
to.keyFor(reactor.getSelector()).interestOps(SelectionKey.OP_READ);
}
private boolean valid(SocketChannel channel) {
return channel.isConnected() && channel.isRegistered() && channel.isOpen();
}
}以上,借鉴NETTY:
- 首先初始化REACTOR线程,然后开启代理监听,当收到代理请求时处理。
- 代理服务在收到代理请求时,首先做代理的预处理,然后又SocketPipe做客户端和远程服务端双向转发。
- 代理预处理,首先读取第一个HTTP请求,解析出METHOD, HOST, PORT。
- 如果是CONNECT请求,发送回应Connection Established,然后连接远程服务端,并返回SocketChannel
- 如果是非CONNECT请求,连接远程服务端,写入原始请求,并返回SocketChannel
- SocketPipe在客户端和远程服务端,做双向的转发;其本身是将客户端和服务端的SocketChannel注册到REACTOR
- REACTOR在监测到READABLE的CHANNEL,派发给SocketPipe做双向转发。
测试
代理的测试比较简单,指向代码后,代理服务监听8006端口,此时:
curl -x 'localhost:8006'?http://httpbin.org/get测试HTTP请求
curl -x 'localhost:8006'?https://httpbin.org/get测试HTTPS请求
注意,此时代理服务代理了HTTPS请求,但是并不需要-k选项,指示非安全的代理。因为代理服务本身并没有作为一个中间人,并没有解析出客户端和远程服务端通信的内容。在非透明代理时,需要解决这个问题。
2 非透明代理
非透明代理,需要解析出客户端和远程服务端传输的内容,并做相应的处理。
当传输为HTTP协议时,SocketPipe传输的数据即为明文的数据,可以拦截后直接做处理。
当传输为HTTPS协议时,SocketPipe传输的有效数据为加密数据,并不能透明处理。
另外,无论是传输的HTTP协议还是HTTPS协议,SocketPipe读到的都为非完整的数据,需要做聚批的处理。
- SocketPipe聚批问题,可以采用类似BufferedInputStream对InputStream做Decorate的模式来实现,相对比较简单;详细可以参考NETTY的HttpObjectAggregator;
- HTTPS原始请求和结果数据的加密和解密的处理,需要实现的NIO的SOCKET CHANNEL;
SslSocketChannel封装原理
考虑到目前JDK自带的NIO的SocketChannel并不支持SSL;已有的SSLSocket是阻塞的OIO。如图:
可以看出
- 每次入站数据和出站数据都需要 SSL SESSION 做握手;
- 入站数据做解密,出站数据做加密;
- 握手,数据加密和数据解密是统一的一套状态机;
以下,代码实现 SslSocketChannel
public class SslSocketChannel {
/**
* 握手加解密需要的四个存储
*/
protected ByteBuffer myAppData; // 明文
protected ByteBuffer myNetData; // 密文
protected ByteBuffer peerAppData; // 明文
protected ByteBuffer peerNetData; // 密文
/**
* 握手加解密过程中用到的异步执行器
*/
protected ExecutorService executor = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
/**
* 原NIO 的 CHANNEL
*/
protected SocketChannel socketChannel;
/**
* SSL 引擎
*/
protected SSLEngine engine;
public SslSocketChannel(SSLContext context, SocketChannel socketChannel, boolean clientMode) throws Exception {
// 原始的NIO SOCKET
this.socketChannel = socketChannel;
// 初始化BUFFER
SSLSession dummySession = context.createSSLEngine().getSession();
myAppData = ByteBuffer.allocate(dummySession.getApplicationBufferSize());
myNetData = ByteBuffer.allocate(dummySession.getPacketBufferSize());
peerAppData = ByteBuffer.allocate(dummySession.getApplicationBufferSize());
peerNetData = ByteBuffer.allocate(dummySession.getPacketBufferSize());
dummySession.invalidate();
engine = context.createSSLEngine();
engine.setUseClientMode(clientMode);
engine.beginHandshake();
}
/**
* 参考 https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/technotes/guides/security/jsse/JSSERefGuide.html
* 实现的 SSL 的握手协议
* @return
* @throws IOException
*/
protected boolean doHandshake() throws IOException {
SSLEngineResult result;
HandshakeStatus handshakeStatus;
int appBufferSize = engine.getSession().getApplicationBufferSize();
ByteBuffer myAppData = ByteBuffer.allocate(appBufferSize);
ByteBuffer peerAppData = ByteBuffer.allocate(appBufferSize);
myNetData.clear();
peerNetData.clear();
handshakeStatus = engine.getHandshakeStatus();
while (handshakeStatus != HandshakeStatus.FINISHED && handshakeStatus != HandshakeStatus.NOT_HANDSHAKING) {
switch (handshakeStatus) {
case NEED_UNWRAP:
if (socketChannel.read(peerNetData) < 0) {
if (engine.isInboundDone() && engine.isOutboundDone()) {
return false;
}
try {
engine.closeInbound();
} catch (SSLException e) {
log.debug("收到END OF STREAM,关闭连接.", e);
}
engine.closeOutbound();
handshakeStatus = engine.getHandshakeStatus();
break;
}
peerNetData.flip();
try {
result = engine.unwrap(peerNetData, peerAppData);
peerNetData.compact();
handshakeStatus = result.getHandshakeStatus();
} catch (SSLException sslException) {
engine.closeOutbound();
handshakeStatus = engine.getHandshakeStatus();
break;
}
switch (result.getStatus()) {
case OK:
break;
case BUFFER_OVERFLOW:
peerAppData = enlargeApplicationBuffer(engine, peerAppData);
break;
case BUFFER_UNDERFLOW:
peerNetData = handleBufferUnderflow(engine, peerNetData);
break;
case CLOSED:
if (engine.isOutboundDone()) {
return false;
} else {
engine.closeOutbound();
handshakeStatus = engine.getHandshakeStatus();
break;
}
default:
throw new IllegalStateException("无效的握手状态: " + result.getStatus());
}
break;
case NEED_WRAP:
myNetData.clear();
try {
result = engine.wrap(myAppData, myNetData);
handshakeStatus = result.getHandshakeStatus();
} catch (SSLException sslException) {
engine.closeOutbound();
handshakeStatus = engine.getHandshakeStatus();
break;
}
switch (result.getStatus()) {
case OK :
myNetData.flip();
while (myNetData.hasRemaining()) {
socketChannel.write(myNetData);
}
break;
case BUFFER_OVERFLOW:
myNetData = enlargePacketBuffer(engine, myNetData);
break;
case BUFFER_UNDERFLOW:
throw new SSLException("加密后消息内容为空,报错");
case CLOSED:
try {
myNetData.flip();
while (myNetData.hasRemaining()) {
socketChannel.write(myNetData);
}
peerNetData.clear();
} catch (Exception e) {
handshakeStatus = engine.getHandshakeStatus();
}
break;
default:
throw new IllegalStateException("无效的握手状态: " + result.getStatus());
}
break;
case NEED_TASK:
Runnable task;
while ((task = engine.getDelegatedTask()) != null) {
executor.execute(task);
}
handshakeStatus = engine.getHandshakeStatus();
break;
case FINISHED:
break;
case NOT_HANDSHAKING:
break;
default:
throw new IllegalStateException("无效的握手状态: " + handshakeStatus);
}
}
return true;
}
/**
* 参考 https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/technotes/guides/security/jsse/JSSERefGuide.html
* 实现的 SSL 的传输读取协议
* @param consumer
* @throws IOException
*/
public void read(Consumer<ByteBuffer> consumer) throws IOException {
// BUFFER初始化
peerNetData.clear();
int bytesRead = socketChannel.read(peerNetData);
if (bytesRead > 0) {
peerNetData.flip();
while (peerNetData.hasRemaining()) {
peerAppData.clear();
SSLEngineResult result = engine.unwrap(peerNetData, peerAppData);
switch (result.getStatus()) {
case OK:
log.debug("收到远程的返回结果消息为:" + new String(peerAppData.array(), 0, peerAppData.position()));
consumer.accept(peerAppData);
peerAppData.flip();
break;
case BUFFER_OVERFLOW:
peerAppData = enlargeApplicationBuffer(engine, peerAppData);
break;
case BUFFER_UNDERFLOW:
peerNetData = handleBufferUnderflow(engine, peerNetData);
break;
case CLOSED:
log.debug("收到远程连接关闭消息.");
closeConnection();
return;
default:
throw new IllegalStateException("无效的握手状态: " + result.getStatus());
}
}
} else if (bytesRead < 0) {
log.debug("收到END OF STREAM,关闭连接.");
handleEndOfStream();
}
}
public void write(String message) throws IOException {
write(ByteBuffer.wrap(message.getBytes()));
}
/**
* 参考 https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/technotes/guides/security/jsse/JSSERefGuide.html
* 实现的 SSL 的传输写入协议
* @param message
* @throws IOException
*/
public void write(ByteBuffer message) throws IOException {
myAppData.clear();
myAppData.put(message);
myAppData.flip();
while (myAppData.hasRemaining()) {
myNetData.clear();
SSLEngineResult result = engine.wrap(myAppData, myNetData);
switch (result.getStatus()) {
case OK:
myNetData.flip();
while (myNetData.hasRemaining()) {
socketChannel.write(myNetData);
}
log.debug("写入远程的消息为: {}", message);
break;
case BUFFER_OVERFLOW:
myNetData = enlargePacketBuffer(engine, myNetData);
break;
case BUFFER_UNDERFLOW:
throw new SSLException("加密后消息内容为空.");
case CLOSED:
closeConnection();
return;
default:
throw new IllegalStateException("无效的握手状态: " + result.getStatus());
}
}
}
/**
* 关闭连接
* @throws IOException
*/
public void closeConnection() throws IOException {
engine.closeOutbound();
doHandshake();
socketChannel.close();
executor.shutdown();
}
/**
* END OF STREAM(-1)默认是关闭连接
* @throws IOException
*/
protected void handleEndOfStream() throws IOException {
try {
engine.closeInbound();
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("END OF STREAM 关闭失败.", e);
}
closeConnection();
}
}以上:
- 基于 SSL 协议,实现统一的握手动作;
- 分别实现读取的解密,和写入的加密方法;
- 将 SslSocketChannel 实现为 SocketChannel的Decorator;
SslSocketChannel测试服务端
基于以上封装,简单测试服务端如下
@Slf4j
public class NioSslServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
NioSslServer sslServer = new NioSslServer("127.0.0.1", 8006);
sslServer.start();
// 使用 curl -vv -k 'https://localhost:8006' 连接
}
private SSLContext context;
private Selector selector;
public NioSslServer(String hostAddress, int port) throws Exception {
// 初始化SSL Context
context = serverSSLContext();
// 注册监听器
selector = SelectorProvider.provider().openSelector();
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
serverSocketChannel.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(hostAddress, port));
serverSocketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
}
public void start() throws Exception {
log.debug("等待连接中.");
while (true) {
selector.select();
Iterator<SelectionKey> selectedKeys = selector.selectedKeys().iterator();
while (selectedKeys.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey key = selectedKeys.next();
selectedKeys.remove();
if (!key.isValid()) {
continue;
}
if (key.isAcceptable()) {
accept(key);
} else if (key.isReadable()) {
((SslSocketChannel)key.attachment()).read(buf->{});
// 直接回应一个OK
((SslSocketChannel)key.attachment()).write("HTTP/1.1 200 OK\r\nContent-Type: text/plain\r\n\r\nOK\r\n\r\n");
((SslSocketChannel)key.attachment()).closeConnection();
}
}
}
}
private void accept(SelectionKey key) throws Exception {
log.debug("接收新的请求.");
SocketChannel socketChannel = ((ServerSocketChannel)key.channel()).accept();
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
SslSocketChannel sslSocketChannel = new SslSocketChannel(context, socketChannel, false);
if (sslSocketChannel.doHandshake()) {
socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ, sslSocketChannel);
} else {
socketChannel.close();
log.debug("握手失败,关闭连接.");
}
}
}以上:
- 由于是NIO,简单的测试需要用到NIO的基础组件Selector进行测试;
- 首先初始化ServerSocketChannel,监听8006端口;
- 接收到请求后,将SocketChannel封装为SslSocketChannel,注册到Selector
- 接收到数据后,通过SslSocketChannel做read和write;
SslSocketChannel测试客户端
基于以上服务端封装,简单测试客户端如下
@Slf4j
public class NioSslClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
NioSslClient sslClient = new NioSslClient("httpbin.org", 443);
sslClient.connect();
// 请求 'https://httpbin.org/get'
}
private String remoteAddress;
private int port;
private SSLEngine engine;
private SocketChannel socketChannel;
private SSLContext context;
/**
* 需要远程的HOST和PORT
* @param remoteAddress
* @param port
* @throws Exception
*/
public NioSslClient(String remoteAddress, int port) throws Exception {
this.remoteAddress = remoteAddress;
this.port = port;
context = clientSSLContext();
engine = context.createSSLEngine(remoteAddress, port);
engine.setUseClientMode(true);
}
public boolean connect() throws Exception {
socketChannel = SocketChannel.open();
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
socketChannel.connect(new InetSocketAddress(remoteAddress, port));
while (!socketChannel.finishConnect()) {
// 通过REACTOR,不会出现等待情况
//log.debug("连接中..");
}
SslSocketChannel sslSocketChannel = new SslSocketChannel(context, socketChannel, true);
sslSocketChannel.doHandshake();
// 握手完成后,开启SELECTOR
Selector selector = SelectorProvider.provider().openSelector();
socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ, sslSocketChannel);
// 写入请求
sslSocketChannel.write("GET /get HTTP/1.1\r\n"
+ "Host: httpbin.org:443\r\n"
+ "User-Agent: curl/7.62.0\r\n"
+ "Accept: */*\r\n"
+ "\r\n");
// 读取结果
while (true) {
selector.select();
Iterator<SelectionKey> selectedKeys = selector.selectedKeys().iterator();
while (selectedKeys.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey key = selectedKeys.next();
selectedKeys.remove();
if (key.isValid() && key.isReadable()) {
((SslSocketChannel)key.attachment()).read(buf->{
log.info("{}", new String(buf.array(), 0, buf.position()));
});
((SslSocketChannel)key.attachment()).closeConnection();
return true;
}
}
}
}
}以上:
- 客户端的封装测试,是为了验证封装 SSL 协议双向都是OK的,
- 在后文的非透明上游代理中,会同时使用 SslSocketChannel做服务端和客户端
- 以上封装与服务端封装类似,不同的是初始化 SocketChannel,做connect而非bind
总结
以上:
- 非透明代理需要拿到完整的请求数据,可以通过 Decorator模式,聚批实现;
- 非透明代理需要拿到解密后的HTTPS请求数据,可以通过SslSocketChannel对原始的SocketChannel做封装实现;
- 最后,拿到请求后,做相应的处理,最终实现非透明的代理。
3 透明上游代理
透明上游代理相比透明代理要简单,区别是
- 透明代理需要响应 CONNECT请求,透明上游代理不需要,直接转发即可;
- 透明代理需要解析CONNECT请求中的HOST和PORT,并连接服务端;透明上游代理只需要连接下游代理的IP:PORT,直接转发请求即可;
- 透明的上游代理,只是一个简单的SocketChannel管道;确定下游的代理服务端,连接转发请求;
只需要对透明代理做以上简单的修改,即可实现透明的上游代理。
4 非透明上游代理
非透明的上游代理,相比非透明的代理要复杂一些
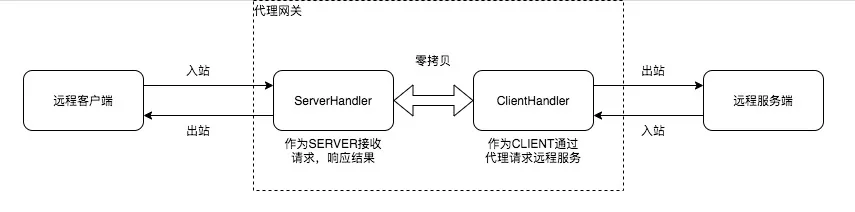
以上,分为四个组件:客户端,代理服务(ServerHandler),代理服务(ClientHandler),服务端
- 如果是HTTP的请求,数据直接通过 客户端<->ServerHandler<->ClientHandler<->服务端,代理网关只需要做简单的请求聚批,就可以应用相应的管理策略;
- 如果是HTTPS请求,代理作为客户端和服务端的中间人,只能拿到加密的数据;因此,代理网关需要作为HTTPS的服务方与客户端通信;然后作为HTTPS的客户端与服务端通信;
- 代理作为HTTPS服务方时,需要考虑到其本身是个非透明的代理,需要实现非透明代理相关的协议;
- 代理作为HTTPS客户端时,需要考虑到其下游是个透明的代理,真正的服务方是客户端请求的服务方;
三 设计与实现
本文需要构建的是非透明上游代理,以下采用NETTY框架给出详细的设计实现。上文将统一代理网关分为两大部分,ServerHandler和ClientHandler,以下
- 介绍代理网关服务端相关实现;
- 介绍代理网关客户端相关实现;
1 代理网关服务端
主要包括
- 初始化代理网关服务端
- 初始化服务端处理器
- 服务端协议升级与处理
初始化代理网关服务
public void start() {
HookedExecutors.newSingleThreadExecutor().submit(() ->{
log.info("开始启动代理服务器,监听端口:{}", auditProxyConfig.getProxyServerPort());
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(auditProxyConfig.getBossThreadCount());
EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(auditProxyConfig.getWorkThreadCount());
try {
ServerBootstrap b = new ServerBootstrap();
b.group(bossGroup, workerGroup)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.handler(new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.DEBUG))
.childHandler(new ServerChannelInitializer(auditProxyConfig))
.bind(auditProxyConfig.getProxyServerPort()).sync().channel().closeFuture().sync();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
log.error("代理服务器被中断.", e);
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
} finally {
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
});
}代理网关初始化相对简单,
- bossGroup线程组,负责接收请求
- workerGroup线程组,负责处理接收的请求数据,具体处理逻辑封装在ServerChannelInitializer中。
代理网关服务的请求处理器在 ServerChannelInitializer中定义为
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline()
.addLast(new HttpRequestDecoder())
.addLast(new HttpObjectAggregator(auditProxyConfig.getMaxRequestSize()))
.addLast(new ServerChannelHandler(auditProxyConfig));
}首先解析HTTP请求,然后做聚批的处理,最后ServerChannelHandler实现代理网关协议;
代理网关协议:
- 判定是否是CONNECT请求,如果是,会存储CONNECT请求;暂停读取,发送代理成功的响应,并在回应成功后,升级协议;
- 升级引擎,本质上是采用SslSocketChannel对原SocketChannel做透明的封装;
- 最后根据CONNECT请求连接远程服务端;
详细实现为:
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
FullHttpRequest request = (FullHttpRequest)msg;
try {
if (isConnectRequest(request)) {
// CONNECT 请求,存储待处理
saveConnectRequest(ctx, request);
// 禁止读取
ctx.channel().config().setAutoRead(false);
// 发送回应
connectionEstablished(ctx, ctx.newPromise().addListener(future -> {
if (future.isSuccess()) {
// 升级
if (isSslRequest(request) && !isUpgraded(ctx)) {
upgrade(ctx);
}
// 开放消息读取
ctx.channel().config().setAutoRead(true);
ctx.read();
}
}));
} else {
// 其他请求,判定是否已升级
if (!isUpgraded(ctx)) {
// 升级引擎
upgrade(ctx);
}
// 连接远程
connectRemote(ctx, request);
}
} finally {
ctx.fireChannelRead(msg);
}
}2 代理网关客户端
代理网关服务端需要连接远程服务,进入代理网关客户端部分。
代理网关客户端初始化:
/**
* 初始化远程连接
* @param ctx
* @param httpRequest
*/
protected void connectRemote(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, FullHttpRequest httpRequest) {
Bootstrap b = new Bootstrap();
b.group(ctx.channel().eventLoop()) // use the same EventLoop
.channel(ctx.channel().getClass())
.handler(new ClientChannelInitializer(auditProxyConfig, ctx, safeCopy(httpRequest)));
// 动态连接代理
FullHttpRequest originRequest = ctx.channel().attr(CONNECT_REQUEST).get();
if (originRequest == null) {
originRequest = httpRequest;
}
ChannelFuture cf = b.connect(new InetSocketAddress(calculateHost(originRequest), calculatePort(originRequest)));
Channel cch = cf.channel();
ctx.channel().attr(CLIENT_CHANNEL).set(cch);
}以上:
- 复用代理网关服务端的workerGroup线程组;
- 请求和结果的处理封装在ClientChannelInitializer;
- 连接的远程服务端的HOST和PORT在服务端收到的请求中可以解析到。
代理网关客户端的处理器的初始化逻辑:
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
SocketAddress socketAddress = calculateProxy();
if (!Objects.isNull(socketAddress)) {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new HttpProxyHandler(calculateProxy(), auditProxyConfig.getUserName(), auditProxyConfig
.getPassword()));
}
if (isSslRequest()) {
String host = host();
int port = port();
if (StringUtils.isNoneBlank(host) && port > 0) {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new SslHandler(sslEngine(host, port)));
}
}
ch.pipeline().addLast(new ClientChannelHandler(clientContext, httpRequest));
}以上:
- 如果下游是代理,那么会采用HttpProxyHandler,经由下游代理与远程服务端通信;
- 如果当前需要升级为SSL协议,会对SocketChannel做透明的封装,实现SSL通信。
- 最后,ClientChannelHandler只是简单消息的转发;唯一的不同是,由于代理网关拦截了第一个请求,此时需要将拦截的请求,转发到服务端。
四 其他问题
代理网关实现可能面临的问题:
1 内存问题
代理通常面临的问题是OOM。本文在实现代理网关时保证内存中缓存时当前正在处理的HTTP/HTTPS请求体。内存使用的上限理论上为实时处理的请求数量*请求体的平均大小,HTTP/HTTPS的请求结果,直接使用堆外内存,零拷贝转发。
2 性能问题
性能问题不应提早考虑。本文使用NETTY框架实现的代理网关,内部大量使用堆外内存,零拷贝转发,避免了性能问题。
代理网关一期上线后曾面临一个长连接导致的性能问题,
- CLIENT和SERVER建立TCP长连接后(比如,TCP心跳检测),通常要么是CLIENT关闭TCP连接,或者是SERVER关闭;
- 如果双方长时间占用TCP连接资源而不关闭,就会导致SOCKET资源泄漏;现象是:CPU资源爆满,处理空闲连接;新连接无法建立;
使用IdleStateHandler定时监控空闲的TCP连接,强制关闭;解决了该问题。
五 总结
本文聚焦于统一代理网关的核心,详细介绍了代理相关的技术原理。
代理网关的管理部分,可以在ServerHandler部分维护,也可以在ClientHandler部分维护;
- ServerHandler可以拦截转换请求
- ClientHanlder可控制请求的出口
注:本文使用Netty的零拷贝;存储请求以解析处理;但并未实现对RESPONSE的处理;也就是RESPONSE是直接通过网关,此方面避免了常见的代理实现,内存泄漏OOM相关问题;
最后,本文实现代理网关后,针对代理的资源和流经代理网关的请求做了相应的控制,主要包括:
- 当遇到静态资源的请求时,代理网关会直接请求远程服务端,不会通过下游代理
- 当请求HEADER中包含地域标识时,代理网关会尽力保证请求打入指定的地域代理,经由地域代理访问远程服务端
本文参考https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/technotes/guides/security/jsse/JSSERefGuide.html实现 SslSocketChannel,以透明处理HTTP和HTTPS协议。
作者 | 新然
原文链接
本文为阿里云原创内容,未经允许不得转载。