Dubbo
1. Dubbo基础
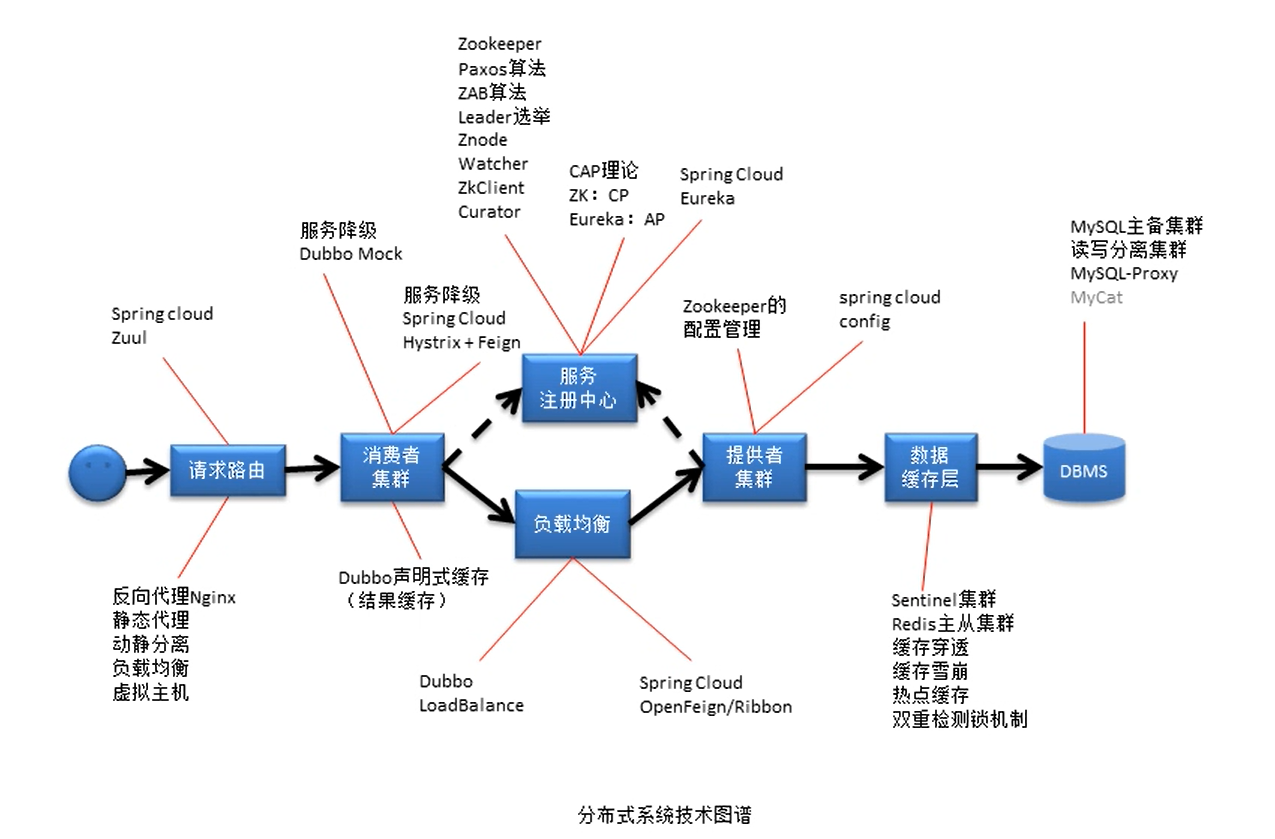
分布式系统技术图谱
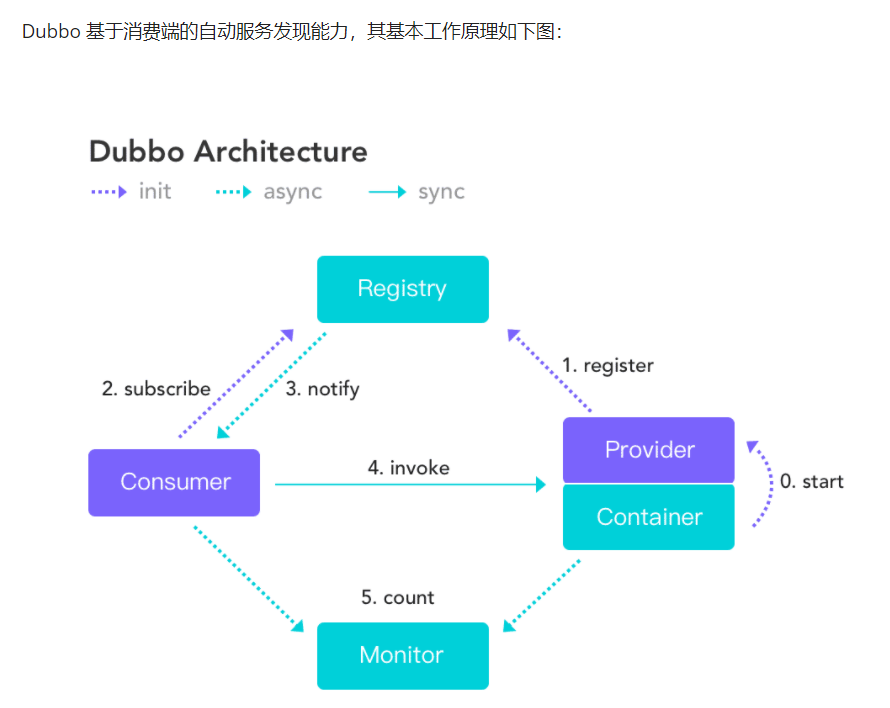
Dubbo简介
Dubbo是一个分布式服务框架,致力于提供高性能和透明化的RPC远程服务调用方案,以及SOA服务治理方案。简单的说,Dubbo就是个服务框架,如果没有分布式的需求,其实是不需要用的,只有在分布式的时候,才有Dubbo这样的分布式服务框架的需求,并且本质上是个服务调用的东东,说白了就是个远程服务调用的分布式框架(告别Web Service模式中的WSdl,以服务者与消费者的方式在Dubbo上注册)
其核心部分包含:
- 远程通讯: 提供对多种基于长连接的NIO框架抽象封装,包括多种线程模型,序列化,以及“请求-响应”模式的信息交换方式。
- 集群容错: 提供基于接口方法的透明远程过程调用,包括多协议支持,以及软负载均衡,失败容错,地址路由,动态配置等集群支持。
- 自动发现: 基于注册中心目录服务,使服务消费方能动态的查找服务提供方,使地址透明,使服务提供方可以平滑增加或减少机器。
2. Dubbo的使用
1. RPC原理
RPC(Remote Procedure Call Protocol)——远程过程调用协议,它是一种通过网络从远程计算机程序上请求服务,而不需要了解底层网络技术的协议。RPC协议假定某些传输协议的存在,如TCP/IP或UDP,为通信程序之间携带信息数据。RPC将原来的本地调用转变为调用远端的服务器上的方法,给系统的处理能力和吞吐量带来了近似于无限制提升的可能。在OSI网络通信模型中,RPC跨域了传输层和应用层。RPC使得开发包括网络分布式多程序在内的应用程序更加容易。
2. Dubbo功能

3. 环境搭建
3.1 安装Registry服务注册中心:zookeeper
在docker容器中安装zookeeper
3.2 安装Monitor监控中心
在docker容器中安装dubbo-admin
4. 入门案例 — Springboot版
4.1 项目结构

4.2 项目构建
1. 依赖
- 核心依赖
<!--DUBBO-->
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.apache.dubbo/dubbo-spring-boot-starter -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.dubbo</groupId>
<artifactId>dubbo-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>2.7.3</version>
</dependency>
<!--Curator是Netflix公司开源的一套Zookeeper客户端框架-->
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.apache.curator/curator-framework -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.curator</groupId>
<artifactId>curator-framework</artifactId>
<version>4.0.1</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.apache.curator/curator-recipes -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.curator</groupId>
<artifactId>curator-recipes</artifactId>
<version>4.0.1</version>
</dependency>
- 项目其他依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!--公共模块依赖 dubbo-common-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.ning</groupId>
<artifactId>dubbo-common</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
</dependency>
2. 公共暴露的接口模块 – dubbo-common
-
项目结构
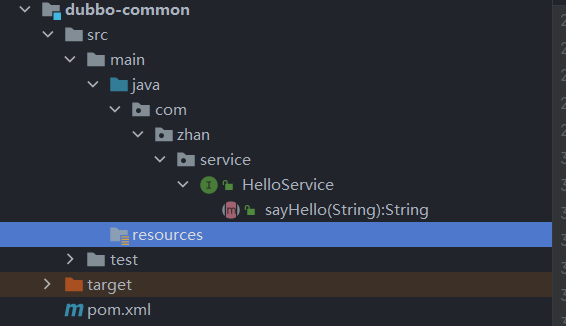 \
\ -
对外暴露接口
package com.zhan.service; public interface HelloService { public String sayHello(String name); }
3. provider模块
- 模块结构
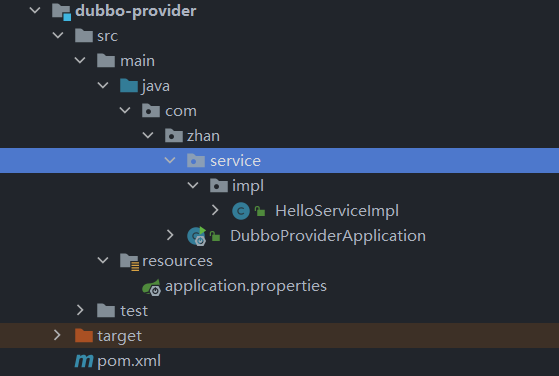
-
暴露接口服务实现类
这里的@service注解是dubbo的注解,不是springboot的注解,用于暴露接口服务
package com.zhan.service.impl; import com.zhan.service.HelloService; import org.apache.dubbo.config.annotation.Service; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component @Service public class HelloServiceImpl implements HelloService { @Override public String sayHello(String name) { return "provider向"+name+"say Hello"; } } -
dobbo配置
# dubbo配置 # 服务模块的名称 dubbo.application.name=dubbo-provider # 扫描服务所在的包 dubbo.scan.base-packages=com.zhan.service # 传输协议的名称 dubbo.protocol.name=dubbo # 传输协议的端口 dubbo.protocol.port=20880 # 服务注册地址 dubbo.registry.address=zookeeper://39.108.184.64:2181 -
其他配置
# 端口配置 server.port=8010 #服务名配置 spring.application.name=dubbo-provider
4. consumer模块
-
模块结构
-
访问入口控制类
@Reference注解:用于dubbo消费者服务指明引用哪个提供者接口服务
package com.zhan.controller; import com.zhan.service.HelloService; import org.apache.dubbo.config.annotation.Reference; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody; @Controller public class HelloController { @Reference private HelloService helloService; @GetMapping("/hello/{name}") @ResponseBody public String sayHello(@PathVariable("name") String name){ return helloService.sayHello(name); } } -
dubbo配置
# dubbo配置 dubbo.application.name=dubbo-consumer dubbo.registry.address=zookeeper://39.108.184.64:2181 -
其他配置
# 端口配置 server.port=8080 #服务名 spring.application.name=dubbo-consumer
5. 服务启动
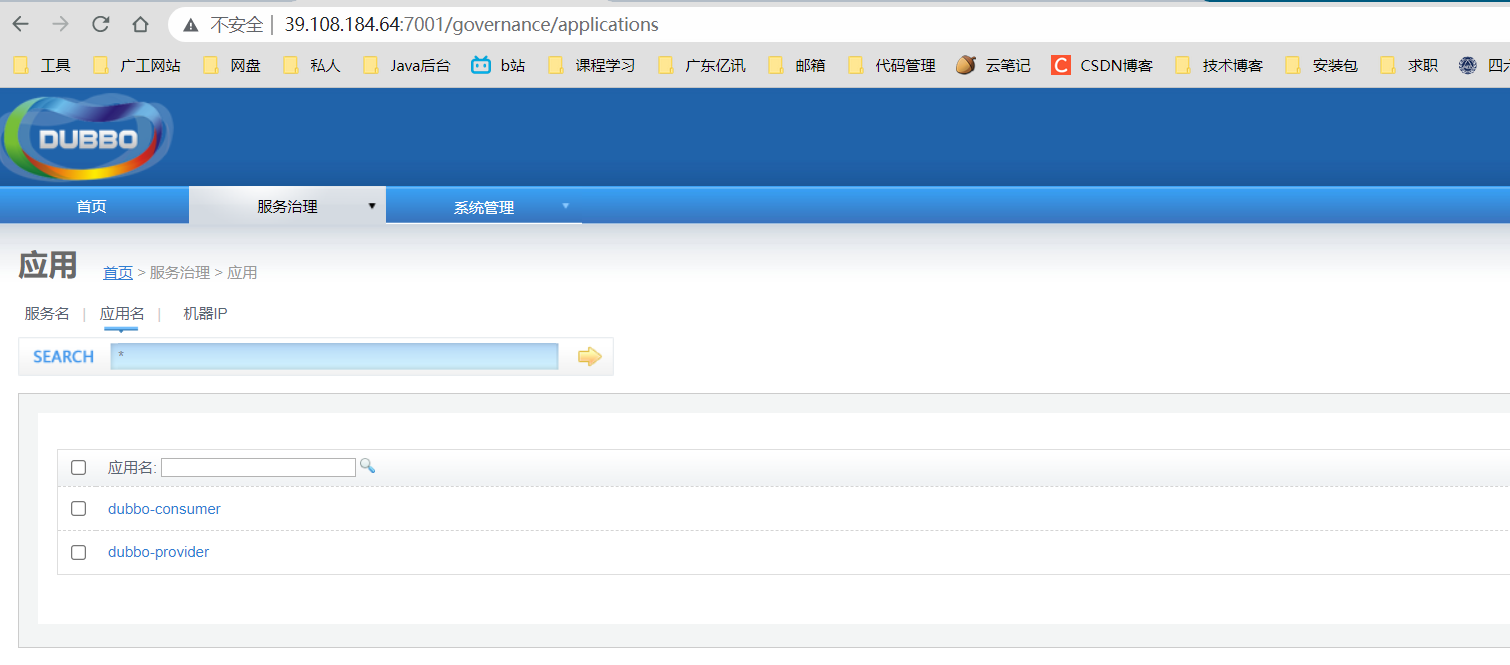
-
启动提供者和消费者:访问dubbo-admin(http://39.108.184.64:7001/),可以看到两个应用
-
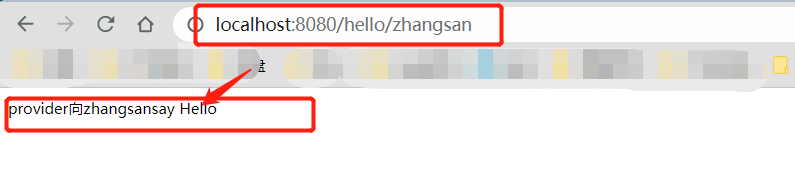
访问 http://localhost:8080/hello/zhangsan 入门案例搭建成功!
5. dubbo配置
配置详解
https://dubbo.apache.org/zh/docs/references/configuration/properties/
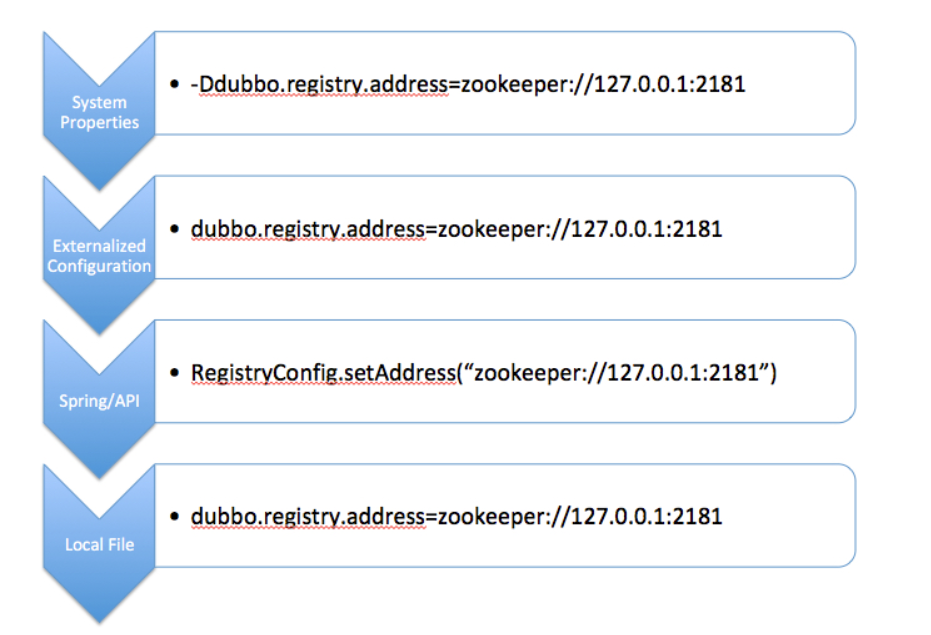
配置来源
从Dubbo支持的配置来源说起,默认有6种配置来源:
- JVM System Properties,JVM -D 参数
- System environment,JVM进程的环境变量
- Externalized Configuration,外部化配置,从配置中心读取
- Application Configuration,应用的属性配置,从Spring应用的Environment中提取"dubbo"打头的属性集
- API / XML /注解等编程接口采集的配置可以被理解成配置来源的一种,是直接面向用户编程的配置采集方式
- 从classpath读取配置文件 dubbo.properties
关于dubbo.properties属性:
- 如果在 classpath 下有超过一个 dubbo.properties 文件,比如,两个 jar 包都各自包含了 dubbo.properties,dubbo 将随机选择一个加载,并且打印错误日志。
- Dubbo 可以自动加载 classpath 根目录下的 dubbo.properties,但是你同样可以使用 JVM 参数来指定路径:
-Ddubbo.properties.file=xxx.properties
覆盖关系
下图展示了配置覆盖关系的优先级,从上到下优先级依次降低:
1. xml文件配置方式
基本配置
-
provider.xml
<beans xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:dubbo="http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo" xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo/dubbo.xsd"> <dubbo:application name="demo-provider"/> <dubbo:registry address="zookeeper://127.0.0.1:2181"/> <dubbo:protocol name="dubbo" port="20890"/> <bean id="demoService" class="org.apache.dubbo.samples.basic.impl.DemoServiceImpl"/> <dubbo:service interface="org.apache.dubbo.samples.basic.api.DemoService" ref="demoService"/> </beans> -
consumer.xml
<beans xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:dubbo="http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo" xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo/dubbo.xsd"> <dubbo:application name="demo-consumer"/> <dubbo:registry group="aaa" address="zookeeper://127.0.0.1:2181"/> <dubbo:reference id="demoService" check="false" interface="org.apache.dubbo.samples.basic.api.DemoService"/> </beans>
配置详解
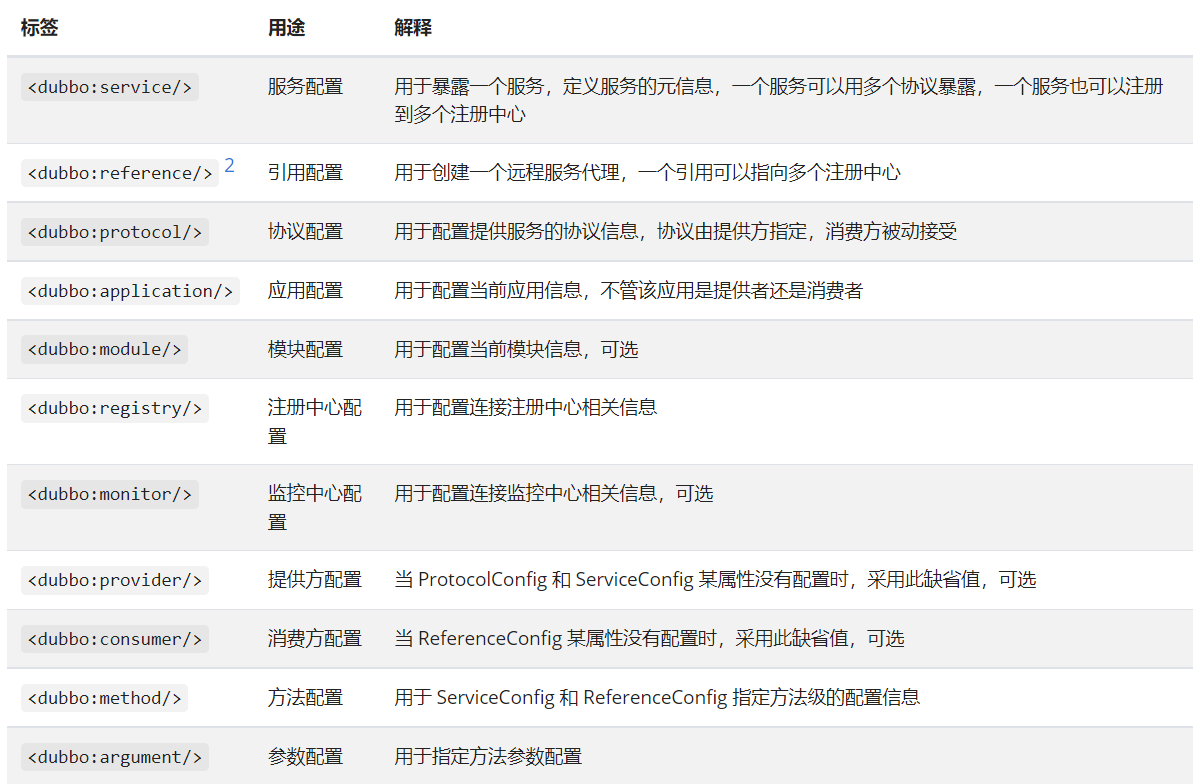
配置的覆盖关系
以 timeout 为例,下图显示了配置的查找顺序,其它 retries, loadbalance, actives 等类似
- 方法级优先,接口级次之,全局配置再次之。
- 如果级别一样,则消费方优先,提供方次之。
其中,服务提供方配置,通过 URL 经由注册中心传递给消费方。
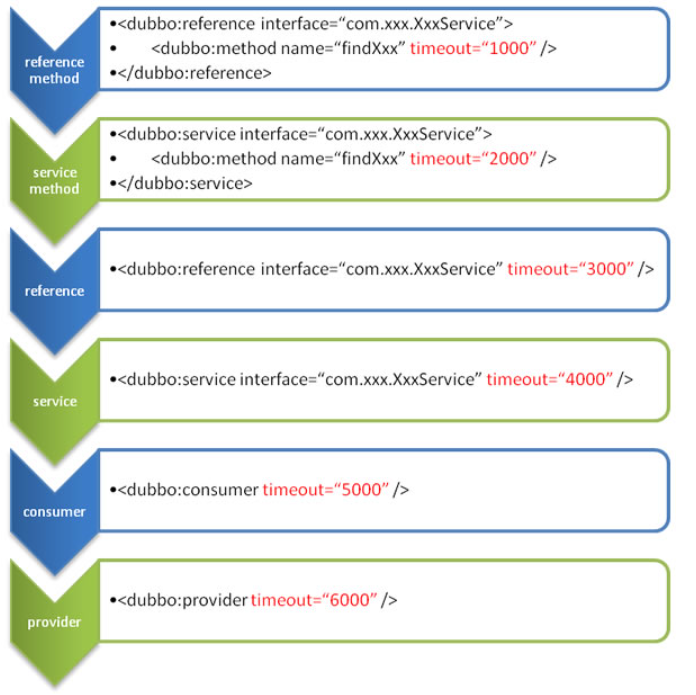
建议由服务提供方设置超时,因为一个方法需要执行多长时间,服务提供方更清楚,如果一个消费方同时引用多个服务,就不需要关心每个服务的超时设置)。
理论上 ReferenceConfig 中除了interface这一项,其他所有配置项都可以不配置,框架会自动使用ConsumerConfig,ServiceConfig, ProviderConfig等提供的默认配置。
注意:
引用缺省是延迟初始化的,只有引用被注入到其它 Bean,或被 getBean() 获取,才会初始化。如果需要饥饿加载,即没有人引用也立即生成动态代理,可以配置:<dubbo:reference … init=“true” />
2. properties(yaml、yml))配置文件方式
Dubbo 可以自动加载 classpath 根目录下的 dubbo.properties,但是你同样可以使用 JVM 参数来指定路径:-Ddubbo.properties.file=xxx.properties。
映射规则
将 xml 的 tag 名和属性名组合起来,用 ‘.’ 分隔。每行一个属性
例子:
dubbo.application.name=foo相当于<dubbo:application name="foo" />dubbo.registry.address=10.20.153.10:9090相当于<dubbo:registry address="10.20.153.10:9090" />
配置格式
# 应用级配置(无id)
dubbo.{config-type}.{config-item}={config-item-value}
# 实例级配置(指定id或name)
dubbo.{config-type}s.{config-id}.{config-item}={config-item-value}
dubbo.{config-type}s.{config-name}.{config-item}={config-item-value}
# 服务接口配置
dubbo.service.{interface-name}.{config-item}={config-item-value}
dubbo.reference.{interface-name}.{config-item}={config-item-value}
# 方法配置
dubbo.service.{interface-name}.{method-name}.{config-item}={config-item-value}
dubbo.reference.{interface-name}.{method-name}.{config-item}={config-item-value}
# 方法argument配置
dubbo.reference.{interface-name}.{method-name}.{argument-index}.{config-item}={config-item-value}
基本配置文件
## application.properties
# Spring boot application
spring.application.name=dubbo-externalized-configuration-provider-sample
# 扫描 Dubbo 组件的基础包: 类似注解@com.alibaba.dubbo.config.annotation.Service
dubbo.scan.base-packages=com.alibaba.boot.dubbo.demo.provider.service
# Dubbo Application
## The default value of dubbo.application.name is ${spring.application.name}
## dubbo.application.name=${spring.application.name}
# Dubbo 协议
dubbo.protocol.name=dubbo
dubbo.protocol.port=12345
## Dubbo 注册中心:N/A表示直连,也可以使用其他注册中心,例如zookeeper,配置例子:zookeeper://39.108.184.64:2181
dubbo.registry.address=N/A
## 服务默认版本
dubbo.provider.version=1.0.0
3. 注解配置
需要 2.6.3 及以上版本支持
**@EnableDubbo:**开启注解Dubbo功能
其中可以加入scanBasePackages属性配置包扫描的路径,用于扫描并注册bean
scanBasePackages = “com.zhan.service” 等同于 dubbo.scan.base-packages=com.zhan.service
@EnableDubbo(scanBasePackages = "com.zhan.service")
@Service:暴露服务
- 只能定义在一个类上,表示一个服务的具体实现
- interfaceClass:指定服务提供方实现的 interface 的类
- interfaceName:指定服务提供方实现的 interface 的类名
- version:指定服务的版本号
- group:指定服务的分组
- export:是否暴露服务
- registry:是否向注册中心注册服务
- application:应用配置
- module:模块配置
- provider:服务提供方配置
- protocol:协议配置
- monitor:监控中心配置
- registry:注册中心配置
@Service
public class AnnotationServiceImpl implements AnnotationService {
@Override
public String sayHello(String name) {
return "annotation: hello, " + name;
}
}
@Reference
- 可以定义在类中的一个字段上,也可以定义在一个方法上,甚至可以用来修饰另一个 annotation,表示一个服务的引用。通常 @Reference 定义在一个字段上
- interfaceClass:指定服务的 interface 的类
- interfaceName:指定服务的 interface 的类
- version:指定服务的版本号
- group:指定服务的分组
- url:通过指定服务提供方的 URL 地址直接绕过注册中心发起调用
- application:应用配置
- module:模块配置
- consumer:服务消费方配置
- protocol:协议配置
- monitor:监控中心配置
- registry:注册中心配置
@Controller
public class HelloController {
@Reference(group = "impl")
private HelloService helloService;
@GetMapping("/hello/{name}")
@ResponseBody
public String sayHello(@PathVariable("name") String name){
return helloService.sayHello(name);
}
}
6. 集群拓展
当有多个服务提供方时,将多个服务提供方组织成一个集群,并伪装成一个提供方。
7. 高级用法
1. 启动时检查
在启动时检查依赖的服务是否可用,一般在测试时使用,生产服务不设置
Dubbo 缺省会在启动时检查依赖的服务是否可用,不可用时会抛出异常,阻止 Spring 初始化完成,以便上线时,能及早发现问题,默认 check="true"。
可以通过 check="false" 关闭检查,比如,测试时,有些服务不关心,或者出现了循环依赖,必须有一方先启动。
另外,如果你的 Spring 容器是懒加载的,或者通过 API 编程延迟引用服务,请关闭 check,否则服务临时不可用时,会抛出异常,拿到 null 引用,如果 check="false",总是会返回引用,当服务恢复时,能自动连上。
配置方法
1. 通过xml
关闭某个服务的启动时检查 (没有提供者时报错):
<dubbo:reference interface="com.foo.BarService" check="false" />
关闭所有服务的启动时检查 (没有提供者时报错):
<dubbo:consumer check="false" />
关闭注册中心启动时检查 (注册订阅失败时报错):
<dubbo:registry check="false" />
2. 通过properties文件
dubbo.reference.com.foo.BarService.check=false
dubbo.consumer.check=false
dubbo.registry.check=false
3. 通过 -D 参数
java -Ddubbo.reference.com.foo.BarService.check=false
java -Ddubbo.consumer.check=false
java -Ddubbo.registry.check=false
2. 多版本控制
灰度发布:
灰度发布也叫金丝雀发布,起源是,矿井工人发现,金丝雀对瓦斯气体很敏感,矿工会在下井之前,先放一只金丝雀到井中,如果金丝雀不叫了,就代表瓦斯浓度高。
顾名思义,灰度发布指的是在新版本发布时,让部分流量来调用,对新版本做运行状态观察,其余仍用的是老版本,比如先导入10%观察一下运行情况,然后再导入20%,如此累加直到将流量全部导入到新版本上,最后完成升级,如果期间发现问题,就立即取消升级,将流量切回到老版本。
也就是服务提供者内部同时存在两个不同版本的服务,那么这两个不同版本的服务是如何为同时存在的,又是如何呗消费者识别调用的呢?
实现多版本服务
由于Dubbo的服务是面向接口实现的远程RPC调用,而对外暴露的服务接口在服务提供者内部是可以有多个实现类的,只需要对不同实现类配置上版本号即可,即配置@Service的version属性(或者使用xml配置)。
而对于消费者,在引用配置的时候带上要使用的接口服务的版本号即可
HelloServiceImpl.java
@Component
@Service(version = "0.0.1") //设置版本号为0.0.1
public class HelloServiceImpl implements HelloService {
@Override
public String sayHello(String name) {
return "provider 向 "+name+" say Hello";
}
}
**创建新的服务接口实现类:NewHelloServiceImpl.java (新版本服务) **
@Component
@Service(version = "0.0.2") // 设置版本号为0.0.2
public class NewHelloServiceImpl implements HelloService {
@Override
public String sayHello(String name) {
return "HelloService(0.0.2版本)" + name ;
}
}
修改消费者模块Controller的有引用服务配置,加上引用服务的版本号
@Controller
public class HelloController {
@Reference(version = "0.0.2")//调用0.0.2版本的服务
private HelloService helloService;
@GetMapping("/hello/{name}")
@ResponseBody
public String sayHello(@PathVariable("name") String name) {
return helloService.sayHello(name);
}
}
启动后运行结果
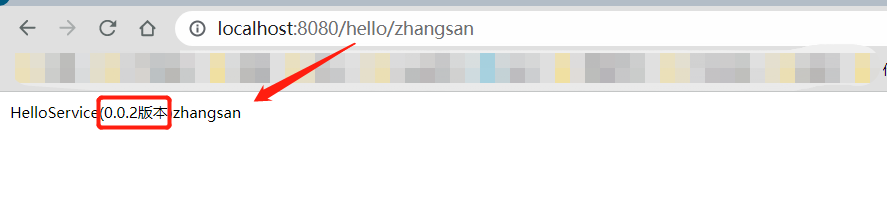
version体现的是版本迭代,而新旧版本之间并不存在互相调用。而服务分组则体现的是服务并存,服务属于不同的组别,能够共存也能互相调用
3. 服务分组
使用服务分组区分服务接口的不同实现,可以用 group 区分。
XML配置
服务
<dubbo:service group="feedback" interface="com.xxx.IndexService" />
<dubbo:service group="member" interface="com.xxx.IndexService" />
引用
<dubbo:reference id="feedbackIndexService" group="feedback" interface="com.xxx.IndexService" />
<dubbo:reference id="memberIndexService" group="member" interface="com.xxx.IndexService" />
任意组:(与负载均衡不同。确定后引用的服务不更改)
<dubbo:reference id="barService" interface="com.foo.BarService" group="*" />
注解配置
服务
@Service(group = "feedback")
public class HelloServiceImpl implements HelloService {
//……
}
@Service(group = "member")
public class NewHelloServiceImpl implements HelloService {
//……
}
引用
@Reference(group = "*")
//@Service(group = "member")
//@Service(group = "feedback")
private HelloService helloService;
4. 多协议
Dubbo 允许配置多协议,在不同服务上支持不同协议或者同一服务上同时支持多种协议。
Dubbo支持8种协议,分别是 dubbo(默认)、rmi、hessian、http、webservice、thrift、memcached、redis、rest ( 就是 RestFull)。其中比较重要的是dubbo、hession两种协议。
Dubbo协议(小数据高并发)
- dubbo 缺省协议 采用单一长连接和NIO异步通讯,适合于小数据量大并发的服务调用,以及服务消费者机器数远大于服务提供者机器数的情况
- 不适合传送大数据量的服务,比如传文件,传视频等,除非请求量很低。
特点
连接个数:单连接
连接方式:长连接
传输协议:TCP
传输方式:NIO异步传输
序列化:Hessian 二进制序列化
适用范围:传入传出参数数据包较小(建议小于100K),消费者比提供者个数多,单一消费者无法压满提供者,尽量不要用dubbo协议传输大文件或超大字符串。
适用场景:常规远程服务方法调用
hessian协议(大数据低并发)
Hessian 1 协议用于集成 Hessian 的服务,Hessian 底层采用 Http 通讯,采用 Servlet 暴露服务,Dubbo 缺省内嵌 Jetty 作为服务器实现。
Dubbo 的 Hessian 协议可以和原生 Hessian 服务互操作,即:
- 提供者用 Dubbo 的 Hessian 协议暴露服务,消费者直接用标准 Hessian 接口调用
- 或者提供方用标准 Hessian 暴露服务,消费方用 Dubbo 的 Hessian 协议调用。‘
特性
- 连接个数:多连接
- 连接方式:短连接
- 传输协议:HTTP
- 传输方式:同步传输
- 序列化:Hessian二进制序列化
- 适用范围:传入传出参数数据包较大,提供者比消费者个数多,提供者压力较大,可传文件。
- 适用场景:页面传输,文件传输,或与原生hessian服务互操作
依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>com.caucho</groupId>
<artifactId>hessian</artifactId>
<version>4.0.7</version>
</dependency>
约束
- 参数及返回值需实现
Serializable接口 - 参数及返回值不能自定义实现
List,Map,Number,Date,Calendar等接口,只能用 JDK 自带的实现,因为 hessian 会做特殊处理,自定义实现类中的属性值都会丢失。
配置
xml 配置
定义 hessian 协议:
<dubbo:protocol name="hessian" port="8080" server="jetty" />
设置默认协议:
<dubbo:provider protocol="hessian" />
设置 service 协议:
<dubbo:service protocol="hessian" />
多端口:
<dubbo:protocol id="hessian1" name="hessian" port="8080" />
<dubbo:protocol id="hessian2" name="hessian" port="8081" />
直连:
<dubbo:reference id="helloService" interface="HelloWorld" url="hessian://10.20.153.10:8080/helloWorld" />
yml配置: protocols(复数)
dubbo:
# 定义两个协议 dubbo,rest(使用jetty作为服务器)
protocols:
dubbo:
name: dubbo
port: 20880
rest:
name: Hessian
port: 9091
server: jetty
5. 负载均衡
在集群负载均衡时,Dubbo 提供了多种均衡策略,缺省为 random 随机调用。
具体实现上,Dubbo 提供的是客户端负载均衡,即由 Consumer 通过负载均衡算法得出需要将请求提交到哪个 Provider 实例。
可以自行扩展负载均衡策略,参见:负载均衡扩展
| 算法 | 特性 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|
| RandomLoadBalance | 加权随机 | 默认算法,默认权重相同 |
| RoundRobinLoadBalance | 加权轮询 | 借鉴于 Nginx 的平滑加权轮询算法,默认权重相同, |
| LeastActiveLoadBalance | 最少活跃优先 + 加权随机 | 背后是能者多劳的思想(间接限流方案之一) |
| ShortestResponseLoadBalance | 最短响应优先 + 加权随机 | 更加关注响应速度 |
| ConsistentHashLoadBalance | 一致性 Hash | 确定的入参,确定的提供者,适用于有状态请求 |
具体算法逻辑实现参见:官方文档
配置
服务端服务级别
<dubbo:service interface="..." loadbalance="roundrobin" />
客户端服务级别
<dubbo:reference interface="..." loadbalance="roundrobin" />
服务端方法级别
<dubbo:service interface="...">
<dubbo:method name="..." loadbalance="roundrobin"/>
</dubbo:service>
客户端方法级别
<dubbo:reference interface="...">
<dubbo:method name="..." loadbalance="roundrobin"/>
</dubbo:reference>
权重参数:weight
6. 集群容错
集群调用失败时,Dubbo 提供的容错方案
在集群调用失败时,Dubbo 提供了多种容错方案,缺省为 failover 重试。
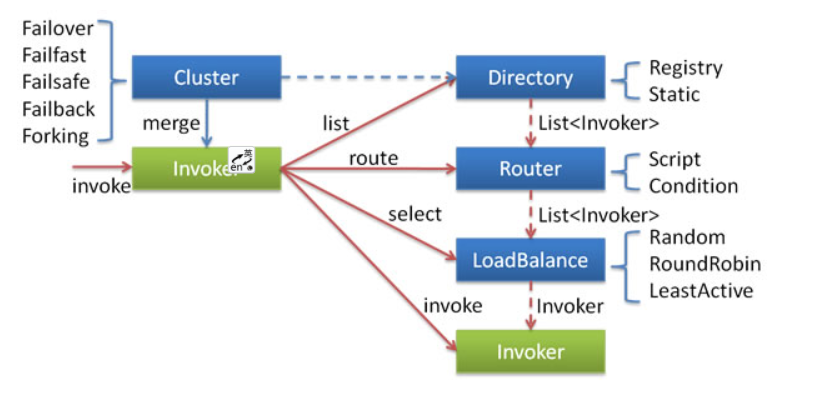
集群容错模式
Failover Cluster
失败自动切换,当出现失败,重试其它服务器。通常用于读操作,但重试会带来更长延迟。可通过 retries="2" 来设置重试次数(不含第一次)。
重试次数配置如下:
<dubbo:service retries="2" />
或
<dubbo:reference retries="2" />
或
<dubbo:reference>
<dubbo:method name="findFoo" retries="2" />
</dubbo:reference>
提示
该配置为缺省配置
Failfast Cluster
快速失败,只发起一次调用,失败立即报错。通常用于非幂等性的写操作,比如新增记录。
Failsafe Cluster
失败安全,出现异常时,直接忽略。通常用于写入审计日志等操作。
Failback Cluster
失败自动恢复,后台记录失败请求,定时重发。通常用于消息通知操作。
Forking Cluster
并行调用多个服务器,只要一个成功即返回。通常用于实时性要求较高的读操作,但需要浪费更多服务资源。可通过 forks="2" 来设置最大并行数。
Broadcast Cluster
广播调用所有提供者,逐个调用,任意一台报错则报错。通常用于通知所有提供者更新缓存或日志等本地资源信息。
现在广播调用中,可以通过 broadcast.fail.percent 配置节点调用失败的比例,当达到这个比例后,BroadcastClusterInvoker 将不再调用其他节点,直接抛出异常。 broadcast.fail.percent 取值在 0~100 范围内。默认情况下当全部调用失败后,才会抛出异常。 broadcast.fail.percent 只是控制的当失败后是否继续调用其他节点,并不改变结果(任意一台报错则报错)。broadcast.fail.percent 参数 在 dubbo2.7.10 及以上版本生效。
Broadcast Cluster 配置 broadcast.fail.percent。
broadcast.fail.percent=20 代表了当 20% 的节点调用失败就抛出异常,不再调用其他节点。
@reference(cluster = "broadcast", parameters = {"broadcast.fail.percent", "20"})
Available Cluster
调用目前可用的实例(只调用一个),如果当前没有可用的实例,则抛出异常。通常用于不需要负载均衡的场景。
Mergeable Cluster
将集群中的调用结果聚合起来返回结果,通常和group一起配合使用。通过分组对结果进行聚合并返回聚合后的结果,比如菜单服务,用group区分同一接口的多种实现,现在消费方需从每种group中调用一次并返回结果,对结果进行合并之后返回,这样就可以实现聚合菜单项。
ZoneAware Cluster
多注册中心订阅的场景,注册中心集群间的负载均衡。对于多注册中心间的选址策略有如下四种
- 指定优先级:
preferred="true"注册中心的地址将被优先选择
<dubbo:registry address="zookeeper://127.0.0.1:2181" preferred="true" />
- 同中心优先:检查当前请求所属的区域,优先选择具有相同区域的注册中心
<dubbo:registry address="zookeeper://127.0.0.1:2181" zone="beijing" />
- 权重轮询:根据每个注册中心的权重分配流量
<dubbo:registry id="beijing" address="zookeeper://127.0.0.1:2181" weight="100" />
<dubbo:registry id="shanghai" address="zookeeper://127.0.0.1:2182" weight="10" />
- 缺省值:选择一个可用的注册中心
集群模式配置
按照以下示例在服务提供方和消费方配置集群模式
<dubbo:service cluster="failsafe" />
或
<dubbo:reference cluster="failsafe" />
解决高并发的三把利器:
- 降级
- 限流
- 缓存
7. 服务降级
什么是服务降级?
当访问量剧增,服务出现问题时,需要做一些处理,比如服务降级。服务降级就是将某些服务停掉或者不进行业务处理,释放资源来维持主要服务的功能。(最好的方式就是利用 Docker 来实现。当需要对某个服务进行降级时,直接将这个服务所有的容器停掉,需要恢复的时候重新启动就可以了。)
服务降级的方式
能够实现服务降级方式很多,常见的有如下几种情况:
- 部分服务暂停
- 全部服务暂停
- 随机拒绝服务
- 部分服务延迟
Dubbo服务降级策略 – Mock机制
可以通过服务降级功能临时屏蔽某个出错的非关键服务,并定义降级后的返回策略。
Dubbo的服务降级采用的是mock机制。mock只支持客户端,不支持服务端,2.7.0之后的版本如果在定义的Service中加了mock会导致启动失败,如:@Service(mock = "true")。具体有两种降级处理方式:
-
Mock Null降级处理
-
与Mock Class降级处理。
Mock Null
- mock = force : return + null (XXX): 表示消费方对该服务的方法调用都直接返回 null (XXX)值,不发起远程调用。用来屏蔽不重要服务不可用时对调用方的影响。
- mock = fail : return + null (XXX):表示消费方对该服务的方法**调用在失败后,再返回 null (XXX)值,不抛异常**。用来容忍不重要服务不稳定时对调用方的影响。
Mock Class
- mock=“true( / default)”:消费方对该服务的方法调用在失败后,会调用消费方定义的服务降级Mock 类实例的相应方法。而该 Mock 类的类名为**“业务接口名+Mock**”,且放在与接口相同的包中
- mock = 降级类的全限定性类名:与 mock = "true"功能类似,不同的是,该方式中的降级类名可以是任意名称,在任何包中
详细配置规则
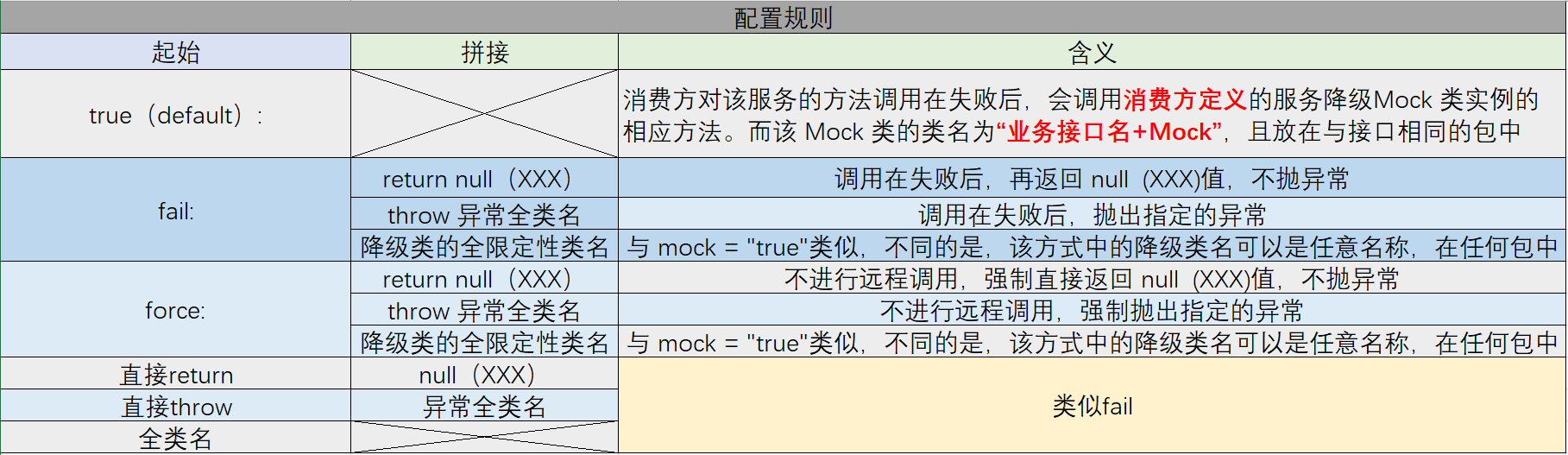
8. 服务调用超时与重试机制
dubbo启动时默认有重试机制和超时机制。
超时机制:
如果在一定的时间内,provider没有返回,则认为本次调用失败。
重试机制
在出现调用失败时,会再次调用。如果在配置的调用次数内都失败,则认为此次请求异常,抛出异常。
如果出现超时,通常是业务处理太慢,可在服务提供方执行:jstack PID > jstack.log 分析线程都卡在哪个方法调用上,这里就是慢的原因。如果不能调优性能,请将timeout设大。
Dubbo超时设置以及重试设置:
1. 注解方式:
提供者
reties的值设置在@Service中 默认retries=2,timeout=0
@Service(retries = 3,timeout = 3000)
public class HelloServiceImpl implements HelloService {}
消费者
reties的值设置在@Reference中
@Reference(retries = 3,timeout = 3000,check = false)//check 默认为true,启动时检查服务是否可用
private HelloService helloService;
方法级别
在注解配置方法级别时,是以参数的形式添加到@Service或@Reference注解中,参数格式:“方法名. 参数”,"参数值"
提供者
@Service(group = "zhangsan", parameters = {"sayHello.timeout", "3000", "sayHello.retries", "4"})
public class HelloServiceImpl implements HelloService{
@Override
public String sayHello(String name) {
try {
log.info("消费者调用HelloServiceImpl服务~");
Thread.sleep(4000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "provider 向 " + name + " 说 Hello";
}
}
消费者
@Reference(group = "zhangsan", mock ="fail:com.zhan.controller.mock.HelloServiceMock", parameters = {"sayHello.timeout", "3000", "sayHello.retries", "3"})
private HelloService helloService;
2. xml方式:
消费端配置:
全局配置
<dubbo:consumer timeout="超时时间" retries="重试次数"></dubbo:consumer>
接口级配置
<dubbo:reference interface="XXXXXXX" id="XXXXXX" timeout="超时时间" retries="重试次数">
<dubbo:method name="XXXXXX" timeout="3000" retries="2"></dubbo:method>
</dubbo:reference>
方法级配置
<dubbo:reference interface="XXXXX" id="XXXXX">
<dubbo:method name="XXXXX" timeout="超时时间" retries="重试次数"></dubbo:method>
</dubbo:reference>
服务端配置:
全局配置
<dubbo:provider timeout="超时时间" retries="2"></dubbo:provider>
接口级配置
<dubbo:service interface="XXXXX" ref="XXXXX" timeout="超时时间" retries="重试次数">
<dubbo:method name="XXXXX"></dubbo:method>
</dubbo:service>
方法级配置
<dubbo:service interface="XXXXXX" ref="XXXXX" >
<dubbo:method name="XXXXX" timeout="超时时间" retries="重试次数"></dubbo:method>
</dubbo:service>
9. 服务限流
为了防止某个消费者的QPS(全名 Queries Per Second,意思是“每秒查询率”)或是所有消费者的QPS总和突然飙升而导致的重要服务的失效,系统可以对访问流量进行控制,这种对集群的保护措施称为服务限流。
Dubbo中能够实现服务限流的方式较多,可以划分为两类:直接限流与间接限流
- 直接限流:通过对**连接数量**直接进行限制来达到限流的目的。(官方方案汇总)
- 间接限流:通过一些**非连接数量设置**来达到限制流量的目的。(我的偶像总结-Reythor雷)
直接限流
1. 并发控制
1.1. executes限流:服务器端并发执行(或占用线程池线程数)不能超过 10 个:
该属性**仅能设置在提供者端**。可以设置为接口级别,也可以设置为方法级别。限制的是服务(方法)并发执行数量。
接口級別
<dubbo:service interface="com.foo.BarService" executes="10" />
方法级别
<dubbo:service interface="com.foo.BarService">
<dubbo:method name="sayHello" executes="10" />
</dubbo:service>
1.2. actives限流 :每客户端并发执行(或占用连接的请求数)不能超过 10 个
actives限流在消费者端和提供者端所体现出来的效果有所不同
提供者
长连接:表示当前的长连接最多可以处理的请求个数。与长连接的数量没有问题。
短连接:表示当前服务可以同时处理的短连接数量。
<dubbo:service interface="com.foo.BarService" actives="10" />
消费者
长连接:表示当前消费者所发出的长连接中最多可以提交的请求个数。与长连接的数量没有关系。
短连接:表示当前消费者可以提交的短连接数量
<dubbo:reference interface="com.foo.BarService" actives="10" />
2. 连接控制
2.1. 服务端连接控制:限制服务器端接受的连接
限制当前提供者在**使用dubbo协议**最多接受10个消费者连接
<dubbo:provider protocol="dubbo" accepts="10" />
或者
<dubbo:protocol name="dubbo" accepts="10" />
2.2. 客户端连接控制:限制客户端服务使用连接
如果 <dubbo:service> 和 <dubbo:reference> 都配了 connections,<dubbo:reference> 优先
<dubbo:reference interface="com.foo.BarService" connections="10" />
或
<dubbo:service interface="com.foo.BarService" connections="10" />
🙃建议:可以设置在提供者端,也可以设置在消费者端。限定连接的个数。对于短连接,该属性效果与[actives](#1.2. actives限流 :每客户端并发执行(或占用连接的请求数)不能超过 10 个)相同。但对于长连接,其限制的是长连接的个数。
一般情况下,会使connectons与[actives](#1.2. actives限流 :每客户端并发执行(或占用连接的请求数)不能超过 10 个)联用,让connections限制长连接个数,让[actives](#1.2. actives限流 :每客户端并发执行(或占用连接的请求数)不能超过 10 个)限制一个长连接中可以处理的请求个数。联用前提:使用默认的Dubbo服务暴露协议
间接限流
1. 延迟连接 ---- 仅作用于Dubbo服务暴露协议
延迟连接用于减少长连接数。当有调用发起时,再创建长连接。延迟连接仅可以设置在消费者端,并且**不能设置为方法级别。仅作用于Dubbo服务暴露协议**。将长连接的建立推迟到消费者真正调用提供者时。 可以减少长连接的数量。
<dubbo:protocol name="dubbo" lazy="true" />
2. 粘滞连接 ---- 仅作用于Dubbo服务暴露协议
粘滞连接用于有状态服务,尽可能让客户端总是向同一提供者发起调用,除非该提供者挂了,再连另一台。粘滞连接将自动开启[延迟连接](#1. 延迟连接),以减少长连接数。
接口级别
<dubbo:reference id="xxxService" interface="com.xxx.XxxService" sticky="true" />
方法级别
<dubbo:reference id="xxxService" interface="com.xxx.XxxService">
<dubbo:mothod name="sayHello" sticky="true" />
</dubbo:reference>
负载均衡
可以设置在消费者端,亦可设置在提供者端;可以设置在接口级别,亦可设置在方法级别。其限制的是流向,而非流量。
配置服务的客户端的 loadbalance 属性为 leastactive,此 Loadbalance 会调用并发数最小的 Provider(Consumer端并发数)。
<dubbo:reference interface="com.foo.BarService" loadbalance="leastactive" />
或
<dubbo:service interface="com.foo.BarService" loadbalance="leastactive" />
10. 声明式缓存
提高消费者的响应速度,减轻提供者的压力,Dubbo提供了基于结果的声明式缓存。该缓存是基于消费者的,只需修改消费者配置文件,与提供者无关
缓存类型
lru基于最近最少使用原则删除多余缓存,保持最热的数据被缓存。threadlocal当前线程缓存,比如一个页面渲染,用到很多 portal,每个 portal 都要去查用户信息,通过线程缓存,可以减少这种多余访问。jcache与 JSR107 集成,可以桥接各种缓存实现。
缓存类型可扩展,参见:缓存扩展
配置
开启缓存
@Reference(group = "zhangsan", cache = "true")
private HelloService helloService;
缓存策略配置
<dubbo:reference interface="com.foo.BarService" cache="lru" />
或:
<dubbo:reference interface="com.foo.BarService">
<dubbo:method name="findBar" cache="lru" />
</dubbo:reference>
11. 多注册中心
Dubbo 支持同一服务向多注册中心同时注册,或者不同服务分别注册到不同的注册中心上去,甚至可以同时引用注册在不同注册中心上的同名服务。另外,注册中心是支持自定义扩展。
1. 多注册中心注册
比如:中文站有些服务来不及在青岛部署,只在杭州部署,而青岛的其它应用需要引用此服务,就可以将服务同时注册到两个注册中心。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:dubbo="http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.3.xsd http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo/dubbo.xsd">
<dubbo:application name="world" />
<!-- 多注册中心配置 -->
<dubbo:registry id="hangzhouRegistry" address="10.20.141.150:9090" />
<dubbo:registry id="qingdaoRegistry" address="10.20.141.151:9010" default="false" />
<!-- 向多个注册中心注册 -->
<dubbo:service interface="com.alibaba.hello.api.HelloService" version="1.0.0" ref="helloService" registry="hangzhouRegistry,qingdaoRegistry" />
</beans>
2. 不同服务使用不同注册中心
比如:CRM 有些服务是专门为国际站设计的,有些服务是专门为中文站设计的。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:dubbo="http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.3.xsd http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo/dubbo.xsd">
<dubbo:application name="world" />
<!-- 多注册中心配置 -->
<dubbo:registry id="chinaRegistry" address="10.20.141.150:9090" />
<dubbo:registry id="intlRegistry" address="10.20.154.177:9010" default="false" />
<!-- 向中文站注册中心注册 -->
<dubbo:service interface="com.alibaba.hello.api.HelloService" version="1.0.0" ref="helloService" registry="chinaRegistry" />
<!-- 向国际站注册中心注册 -->
<dubbo:service interface="com.alibaba.hello.api.DemoService" version="1.0.0" ref="demoService" registry="intlRegistry" />
</beans>
3. 多注册中心引用
比如:CRM 需同时调用中文站和国际站的 PC2 服务,PC2 在中文站和国际站均有部署,接口及版本号都一样,但连的数据库不一样。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:dubbo="http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.3.xsd http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo/dubbo.xsd">
<dubbo:application name="world" />
<!-- 多注册中心配置 -->
<dubbo:registry id="chinaRegistry" address="10.20.141.150:9090" />
<dubbo:registry id="intlRegistry" address="10.20.154.177:9010" default="false" />
<!-- 引用中文站服务 -->
<dubbo:reference id="chinaHelloService" interface="com.alibaba.hello.api.HelloService" version="1.0.0" registry="chinaRegistry" />
<!-- 引用国际站站服务 -->
<dubbo:reference id="intlHelloService" interface="com.alibaba.hello.api.HelloService" version="1.0.0" registry="intlRegistry" />
</beans>
如果只是测试环境临时需要连接两个不同注册中心,使用竖号分隔多个不同注册中心地址:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:dubbo="http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.3.xsd http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo/dubbo.xsd">
<dubbo:application name="world" />
<!-- 多注册中心配置,竖号分隔表示同时连接多个不同注册中心,同一注册中心的多个集群地址用逗号分隔 -->
<dubbo:registry address="10.20.141.150:9090|10.20.154.177:9010" />
<!-- 引用服务 -->
<dubbo:reference id="helloService" interface="com.alibaba.hello.api.HelloService" version="1.0.0" />
</beans>
4. 注解形式:多Dubbo配置bean(Dubbo外部化配置)
application.properties
注意bean的名字不能出现大写,可以用横杠连接。例如 :china-registry,intl-registry
dubbo.registries.china-registry.id=chinaRegistry
dubbo.registries.china-registry.address=zookeeper://10.20.141.150:2181
dubbo.registries.intl-registry.id=intlRegistry
dubbo.registries.intl-registry.address=zookeeper://39.108.184.64:2181
提供者
启动类
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableDubbo
public class DubboProviderApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(DubboProviderApplication.class, args);
}
@EnableDubboConfig(multiple = true)
@PropertySource("application.properties")
private static class DubboMultipleConfiguration {
}
}
服务类
@Service(group = "zhangsan", registry = {"china-registry", "intl-registry"})
public class HelloServiceImpl implements HelloService {
12. 单功能注册中心
只订阅
只订阅不注册
为方便开发测试,经常会在线下共用一个所有服务可用的注册中心,这时,如果一个正在开发中的服务提供者注册,可能会影响消费者不能正常运行。
可以让服务提供者开发方,只订阅服务(开发的服务可能依赖其它服务),而不注册正在开发的服务,通过直连测试正在开发的服务。即可调用其他服务,但是不会被发现调用
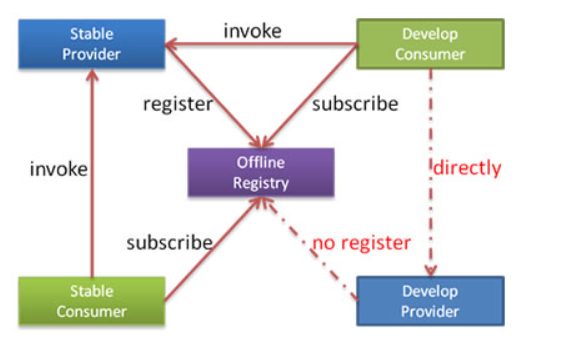
xml配置
禁用注册配置
<dubbo:registry address="10.20.153.10:9090" register="false" />
或者
<dubbo:registry address="10.20.153.10:9090?register=false" />
注解配置
只对某个被配置的服务有效
@Service(register = false)
public class HelloServiceImpl implements HelloService {
//....
}
properties文件配置
dubbo.registry.register=false
仅注册
对于某服务来说,其可以被注册中心的其它服务发现和调用,但不能发现和调用注册中
心中的其它服务,这种情形称为仅注册。
简单来说就是,仅可被发现,但不能去发现。
从底层实现来说就是,当前服务可以写入到注册列表,但其不能下载注册列表。
XML配置
<dubbo:registry address="10.20.153.10:9090" subscribe="false"/>
properties文件配置
dubbo.registry.subscribe=false
13. 服务延迟暴露
如果你的服务需要预热时间,比如初始化缓存,等待相关资源就位等,可以使用 delay 进行延迟暴露。在 Dubbo 2.6.5 版本中对服务延迟暴露逻辑进行了细微的调整,将需要**延迟暴露(delay > 0)服务的倒计时动作推迟到了 Spring 初始化完成后进行。你在使用 Dubbo 的过程中,并不会感知到此变化**,因此请放心使用。
delay的参数意义:
- 整数:单位为毫秒 ,表示提供者对象创建完毕的指定时间后再发布服务
- 0:默认值,表示提供者对象创建完毕后马上发布服务
- -1:表示在Spring容器初始化完毕后再想注册中心暴露服务
Dubbo 2.6.5 之前版本
延迟到 Spring 初始化完成后,再暴露服务1
<dubbo:service delay="-1" />
延迟 5 秒暴露服务
<dubbo:service delay="5000" />
Dubbo 2.6.5 及以后版本
所有服务都将在 Spring 初始化完成后进行暴露,如果你不需要延迟暴露服务,无需配置 delay。
延迟 5 秒暴露服务
<dubbo:service delay="5000" />
注解配置
@Service( delay = 5000)
public class HelloServiceImpl implements HelloService {
//....
}
Spring 2.x 初始化死锁问题
触发条件
在 Spring 解析到 <dubbo:service /> 时,就已经向外暴露了服务,而 Spring 还在接着初始化其它 Bean。如果这时有请求进来,并且服务的实现类里有调用 applicationContext.getBean() 的用法。
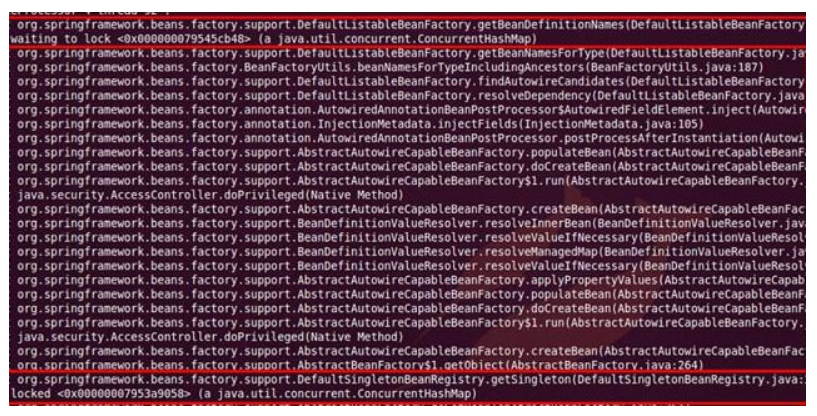
-
请求线程的 applicationContext.getBean() 调用,先同步 singletonObjects 判断 Bean 是否存在,不存在就同步 beanDefinitionMap 进行初始化,并再次同步 singletonObjects 写入 Bean 实例缓存。
-
而 Spring 初始化线程,因不需要判断 Bean 的存在,直接同步 beanDefinitionMap 进行初始化,并同步 singletonObjects 写入 Bean 实例缓存。
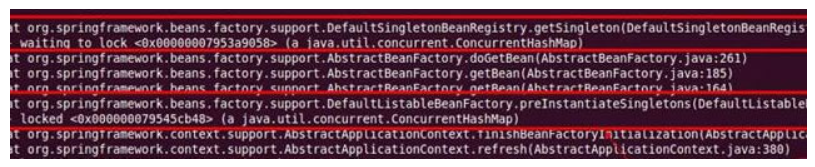
这样就导致 getBean 线程,先锁 singletonObjects,再锁 beanDefinitionMap,再次锁 singletonObjects。
而 Spring 初始化线程,先锁 beanDefinitionMap,再锁 singletonObjects。反向锁导致线程死锁,不能提供服务,启动不了。
规避办法
- 强烈建议不要在服务的实现类中有 applicationContext.getBean() 的调用,全部采用 IoC 注入的方式使用 Spring的Bean。
- 如果实在要调 getBean(),可以将 Dubbo 的配置放在 Spring 的最后加载。
- 如果不想依赖配置顺序,可以使用
<dubbo:provider delay=”-1” />,使 Dubbo 在 Spring 容器初始化完后,再暴露服务。 - 如果大量使用 getBean(),相当于已经把 Spring 退化为工厂模式在用,可以将 Dubbo 的服务隔离单独的 Spring 容器。
- 基于 Spring 的 ContextRefreshedEvent 事件触发暴露 ??
14. 异步调用
1 增加consumer配置
这种方式很简单,只需要在服务引用时增加dubbo:method配置即可,如下所示,其中name为需要异步调用的方法名,async表示是否启用异步调用。
<dubbo:reference id="asyncService" check="false" interface="com.alibaba.dubbo.demo.AsyncService" url="localhost:20880">
<dubbo:method name="sayHello" async="true" />
</dubbo:reference>
此时consumer端有3种调用方式:
- 由于配置了异步调用,因此此时直接调用将返回null:
String result = asyncService.sayHello("world");
- 通过RpcContext获取Future对象,调用get方法时阻塞知道返回结果:
asyncService.sayHello("world");
Future<String> future = RpcContext.getContext().getFuture();
String result = future.get();
- 通过ResponseFuture设置回调,执行完成会回调done方法,抛异常则会回调caught方法:
asyncService.sayHello("world");
ResponseFuture responseFuture = ((FutureAdapter)RpcContext.getContext().getFuture()).getFuture();
responseFuture.setCallback(new ResponseCallback() {
@Override
public void done(Object response) {
System.out.println("done");
}
@Override
public void caught(Throwable exception) {
System.out.println("caught");
}
});
try {
System.out.println("result = " + responseFuture.get());
} catch (RemotingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
如果只想异步调用,不需要返回值,则可以配置 return=“false”,这样可以避免Future对象的创建,此时RpcContext.getContext().getFuture()将返回null;
2 直接定义返回CompletableFuture的服务接口
在上述方式中,想获取异步调用的结果,需要从RpcContext中获取,使用起来不是很方便。基于java 8中引入的CompletableFuture,dubbo在2.7.0版本中也增加了对CompletableFuture的支持,我们可以直接定义一个返回CompletableFuture类型的接口。
public interface AsyncService {
String sayHello(String name);
CompletableFuture<String> sayHelloAsync(String name);
}
服务端实现如下:
public class AsyncServiceImpl implements AsyncService {
@Override
public String sayHello(String name) {
try {
Thread.sleep(5000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return name;
}
@Override
public CompletableFuture<String> sayHelloAsync(String name) {
return CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> name);
}
}
如此一来,我们就实现了服务端的异步,客户端直接调用接口即可,不需要再从RpcContext中获取返回值:
CompletableFuture<String> completableFuture = asyncService.sayHelloAsync("async");
String result = completableFuture.get();
3 事件通知
dubbo允许consumer 端在调用之前、调用之后或出现异常时,触发 oninvoke、onreturn、onthrow 三个事件。类似于Spring中的前置增强、后置增强和异常抛出增强。只需要在服务引用时,增加以下配置指定事件通知的方法即可:
<dubbo:reference id="asyncService" check="false" interface="com.alibaba.dubbo.demo.AsyncService" url="localhost:20880">
<dubbo:method name="sayHello"
oninvoke="notifyServiceImpl.onInvoke"
onreturn="notifyServiceImpl.onReturn"
onthrow="notifyServiceImpl.onThrow" />
</dubbo:reference>
事件通知服务如下:
public class NotifyServiceImpl implements NotifyService {
// 方法参数与调用方法参数相同
@Override
public void onInvoke(String name) {
System.out.println("onInvoke: " + name);
}
// 第一个参数为调用方法的返回值,其余为调用方法的参数
@Override
public void onReturn(String retName, String name) {
System.out.println("onReturn: " + name);
}
// 第一个参数为调用异常,其余为调用方法的参数
@Override
public void onThrow(Throwable ex, String name) {
System.out.println("onThrow: " + name);
}
}
与Spring增强不同的是,dubbo中的事件通知也可以是异步,只需要将调用方法配置为async="true"即可,但oninvoke方法无法异步执行。
4 异步调用源码分析
dubbo中的异步调用实际上是通过引入一个FutureFilter来实现的,关键源码如下。
4.1 调用前获取方法信息
@Activate(group = Constants.CONSUMER)
public class FutureFilter implements PostProcessFilter {
protected static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(FutureFilter.class);
@Override
public Result invoke(final Invoker<?> invoker, final Invocation invocation) throws RpcException {
fireInvokeCallback(invoker, invocation);
// need to configure if there's return value before the invocation in order to help invoker to judge if it's
// necessary to return future.
return postProcessResult(invoker.invoke(invocation), invoker, invocation);
}
...
}
在fireInvokeCallback()方法中,会首先调用getAsyncMethodInfo()获取目标方法的方法信息,看是否有配置事件通知:
private ConsumerMethodModel.AsyncMethodInfo getAsyncMethodInfo(Invoker<?> invoker, Invocation invocation) {
// 首先获取消费者信息
final ConsumerModel consumerModel = ApplicationModel.getConsumerModel(invoker.getUrl().getServiceKey());
if (consumerModel == null) {
return null;
}
// 获取消费者对应的方法信息
ConsumerMethodModel methodModel = consumerModel.getMethodModel(invocation.getMethodName());
if (methodModel == null) {
return null;
}
// 获取消费者对应方法的事件信息,即是否有配置事件通知
final ConsumerMethodModel.AsyncMethodInfo asyncMethodInfo = methodModel.getAsyncInfo();
if (asyncMethodInfo == null) {
return null;
}
return asyncMethodInfo;
}
4.2 同步触发oninvoke事件
获取到调用方法对应的信息后,回到fireInvokeCallback()方法:
private void fireInvokeCallback(final Invoker<?> invoker, final Invocation invocation) {
final ConsumerMethodModel.AsyncMethodInfo asyncMethodInfo = getAsyncMethodInfo(invoker, invocation);
if (asyncMethodInfo == null) {
return;
}
// 获取事件配置信息
final Method onInvokeMethod = asyncMethodInfo.getOninvokeMethod();
final Object onInvokeInst = asyncMethodInfo.getOninvokeInstance();
if (onInvokeMethod == null && onInvokeInst == null) {
return;
}
if (onInvokeMethod == null || onInvokeInst == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("service:" + invoker.getUrl().getServiceKey() + " has a oninvoke callback config , but no such " + (onInvokeMethod == null ? "method" : "instance") + " found. url:" + invoker.getUrl());
}
if (!onInvokeMethod.isAccessible()) {
onInvokeMethod.setAccessible(true);
}
// 获取方法参数
Object[] params = invocation.getArguments();
try {
// 触发oninvoke事件
onInvokeMethod.invoke(onInvokeInst, params);
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
// 触发onthrow事件
fireThrowCallback(invoker, invocation, e.getTargetException());
} catch (Throwable e) {
fireThrowCallback(invoker, invocation, e);
}
}
4.3 调用结果处理
方法调用完成后,会回到postProcessResult()方法:
@Override
public Result postProcessResult(Result result, Invoker<?> invoker, Invocation invocation) {
// 如果是异步调用,返回结果会被封装成AsyncRpcResult类型的对象,具体在哪里封装的,后面会讲到
if (result instanceof AsyncRpcResult) {
AsyncRpcResult asyncResult = (AsyncRpcResult) result;
asyncResult.thenApplyWithContext(r -> {
asyncCallback(invoker, invocation, r);
return r;
});
return asyncResult;
} else {
syncCallback(invoker, invocation, result);
return result;
}
}
syncCallback和asyncCallback里面的逻辑比较简单,就是根据方法是正常返回还是抛异常,触发对应的事件。可以看到,如果被调用方法是同步的,则这两个事件也是同步的,反之亦然。
4.4 方法调用核心过程
在postProcessResult()方法中,第一个参数是invoker.invoke(invocation),这里就会走到下一个Filter链完成filter链的处理,最终调到原始服务,走到DubboInvoker#doInvoke方法
protected Result doInvoke(final Invocation invocation) throws Throwable {
...
try {
// 读取async配置
boolean isAsync = RpcUtils.isAsync(getUrl(), invocation);
// 读取future_generated/future_returntype配置,还没搞明白是干啥的
boolean isAsyncFuture = RpcUtils.isGeneratedFuture(inv) || RpcUtils.isFutureReturnType(inv);
// 读取return配置
boolean isOneway = RpcUtils.isOneway(getUrl(), invocation);
int timeout = getUrl().getMethodParameter(methodName, Constants.TIMEOUT_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_TIMEOUT);
if (isOneway) {
// 如果配置return="true",future对象就直接设置为null
boolean isSent = getUrl().getMethodParameter(methodName, Constants.SENT_KEY, false);
currentClient.send(inv, isSent);
RpcContext.getContext().setFuture(null);
return new RpcResult();
} else if (isAsync) {
// 如果配置async="true",构建future对象
ResponseFuture future = currentClient.request(inv, timeout);
// For compatibility
FutureAdapter<Object> futureAdapter = new FutureAdapter<>(future);
RpcContext.getContext().setFuture(futureAdapter);
// 同时将返回结果包装为AsyncResult对象
Result result;
if (isAsyncFuture) {
// register resultCallback, sometimes we need the asyn result being processed by the filter chain.
result = new AsyncRpcResult(futureAdapter, futureAdapter.getResultFuture(), false);
} else {
result = new SimpleAsyncRpcResult(futureAdapter, futureAdapter.getResultFuture(), false);
}
return result;
} else {
// 否则就是同步调用,future当然也是null
RpcContext.getContext().setFuture(null);
return (Result) currentClient.request(inv, timeout).get();
}
}
...
}
通过这个过程不难发现,不管是同步调用还是异步调用,最终都会走到ExchangeClient#send方法,再往下会走到HeaderExchangeChannel#request方法,这个一个异步方法,返回ResponseFuture对象。
@Override
public ResponseFuture request(Object request, int timeout) throws RemotingException {
if (closed) {
throw new RemotingException(this.getLocalAddress(), null, "Failed to send request " + request + ", cause: The channel " + this + " is closed!");
}
// create request.
Request req = new Request();
req.setVersion(Version.getProtocolVersion());
req.setTwoWay(true);
req.setData(request);
DefaultFuture future = DefaultFuture.newFuture(channel, req, timeout);
try {
channel.send(req);
} catch (RemotingException e) {
future.cancel();
throw e;
}
return future;
}
看到这里我才恍然大悟,原来dubbo中同步调用也是通过异步调用来实现,只是同步调用发起后,直接调用future#get的方法来同步等待结果的返回,而异步调用只返回Future Response,在用户需要关心其结果时才调用get方法。
8. 配置建议
Provider 上配置合理的 Provider 端属性,在 Provider 上尽量多配置 Consumer 端属性
原因如下:
作服务的提供者,比服务使用方更清楚服务性能参数,如调用的超时时间,合理的重试次数,等等
在 Provider 配置后,Consumer 不配置则会使用 Provider 的配置值,即 Provider 配置可以作为 Consumer 的缺省值 [1]。否则,Consumer 会使用 Consumer 端的全局设置,这对于 Provider 不可控的,并且往往是不合理的
Provider 上尽量多配置 Consumer 端的属性,让 Provider 实现者一开始就思考 Provider 服务特点、服务质量的问题。
更详细参考:博客
3. Dubbo源码
……