文章目录
往期
四、Netty异步操作
Netty任务队列的 Task 有3中使用场景
- 用户程序自定义的普通任务
- 用户自定义定时任务
- 非当前Reactor线程调用Channel的各种方法
举个例子:
如果我们有一个非常耗时长的业务,我们可以异步执行,例如:
在NettyServerHandler中:
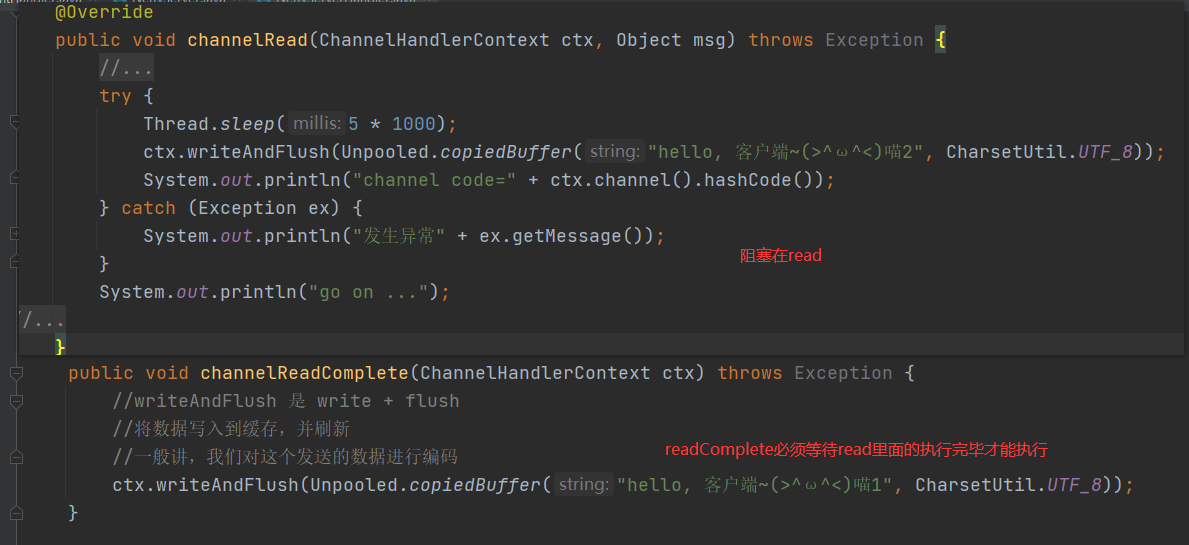
channelRead中业务耗时很长(sleep 5s 模拟)
这样readComplete就是读完后返回send业务必须阻塞等待read里面执行完毕才能执行
如下看解决方案
4.1 taskQueue任务队列
ctx.channel().eventLoop().execute(线程)
注意:任务队列只有一个线程,是一个任务一个任务执行的
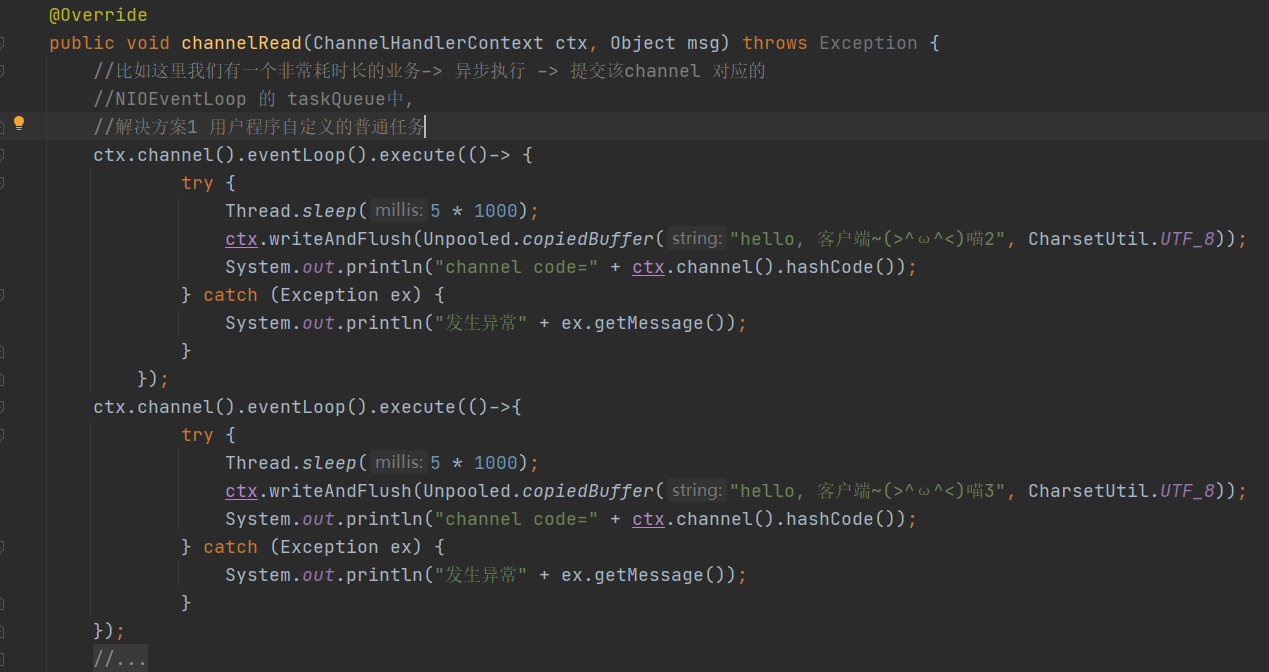
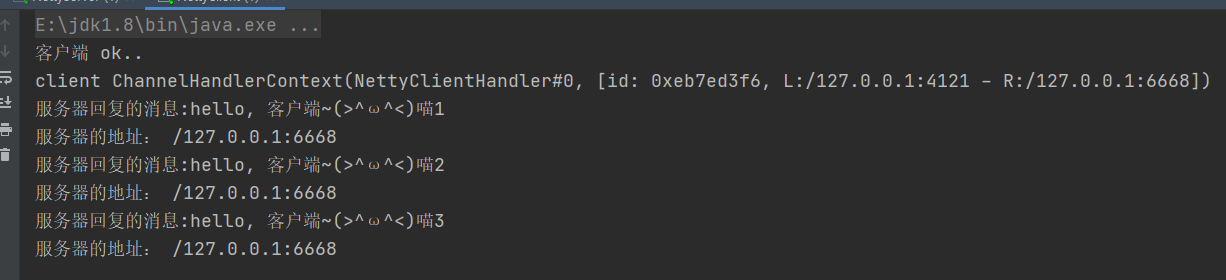
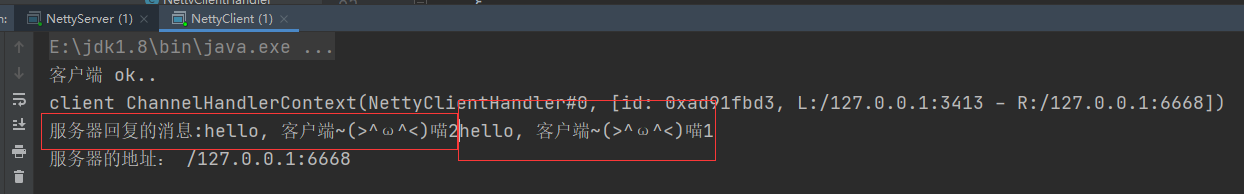
这里的输出,喵1和喵2的并行执行的,首先执行不阻塞的喵1,过5s执行喵2,再过5s执行喵3
把任务放进eventLoop的任务队列taskQueue里,让其异步执行
4.2 scheduleTaskQueue定时任务
ctx.channel().eventLoop().schedule(线程,延迟时间,时间单位)
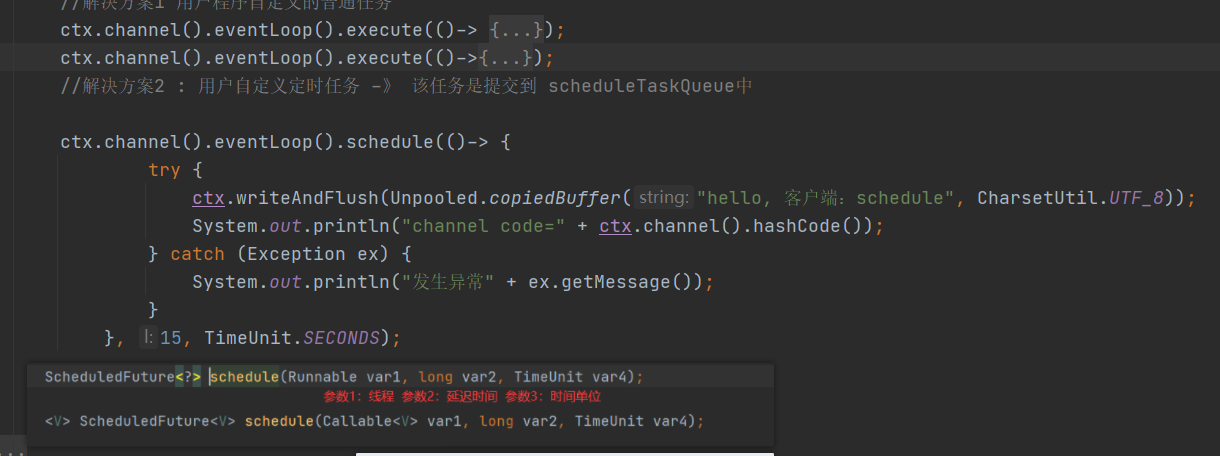
延迟时间是指:从scheduleTask队列开始处理任务时延迟多少时间执行内部的线程 ,这里时间计算是和TaskQueue同步计算的
如果前面TaskQueue队列里两个线程内部延迟5s,而scheduleTaskQueue队列里这个任务设置延迟时间为5的话是会和第二个TaskQueue任务同时执行的
所以可以得出结论:scheduleTaskQueue和TaskQueue之间也是异步的
4.3 非当前Reactor调用Channel的方法
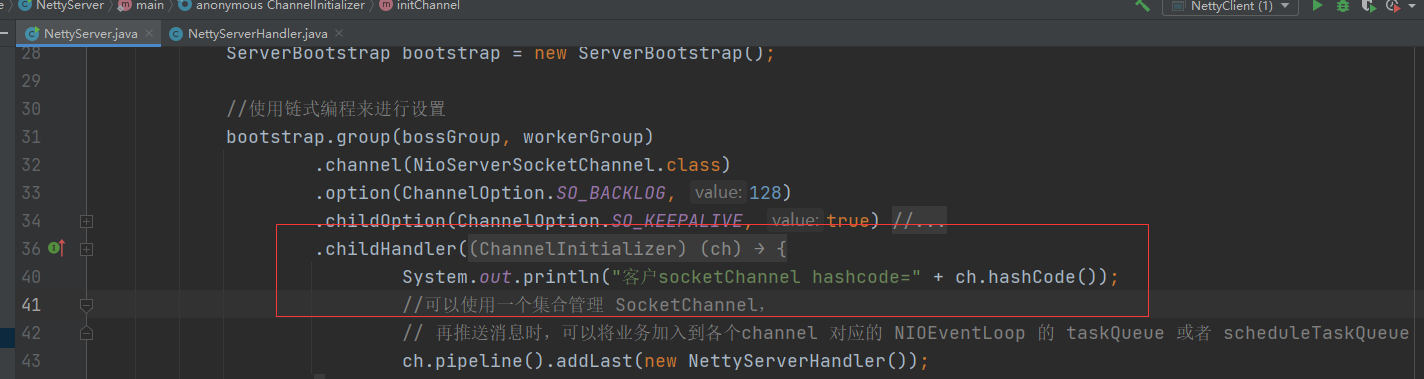
可以看到,每有一个客户端连接BossGroup时都能获取到一个SocketChannel
前面两种方法都是通过channel获取到eventLoop,在eventLoop里面设置任务TaskQueue
如果我们对SocketChannel用一个集合进行管理,就可以实现指定客户端推送指定任务的功能,只需要用SocketChannel获取到eventLoop就行了
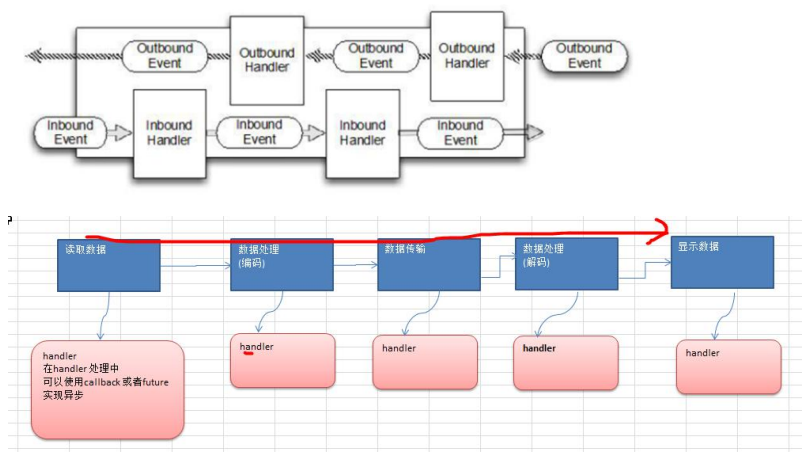
4.4 Netty异步模型原理剖析
-
Netty 中的 I/O 操作是异步的,包括 Bind、Write、Connect 等操作会简单的返回一个 ChannelFuture
-
调用者并不能立刻获得结果,而是通过 Future-Listener 机制,用户可以方便的主动获取或者通过通知机制获得 IO 操作结果
-
Netty 的异步模型是建立在 future 和 callback 的之上的。
- callback 就是回调。
- 重点说 Future,它的核心思想是:假设一个方法 fun,计算过程可能非常耗时,等待 fun返回显然不合适。那么可以在调用fun的时候,立马返回一个 Future,后续可以通过 Future去监控方法 fun 的处理过程(即 : Future-Listener 机制)
4.4.1 ChannelFuture
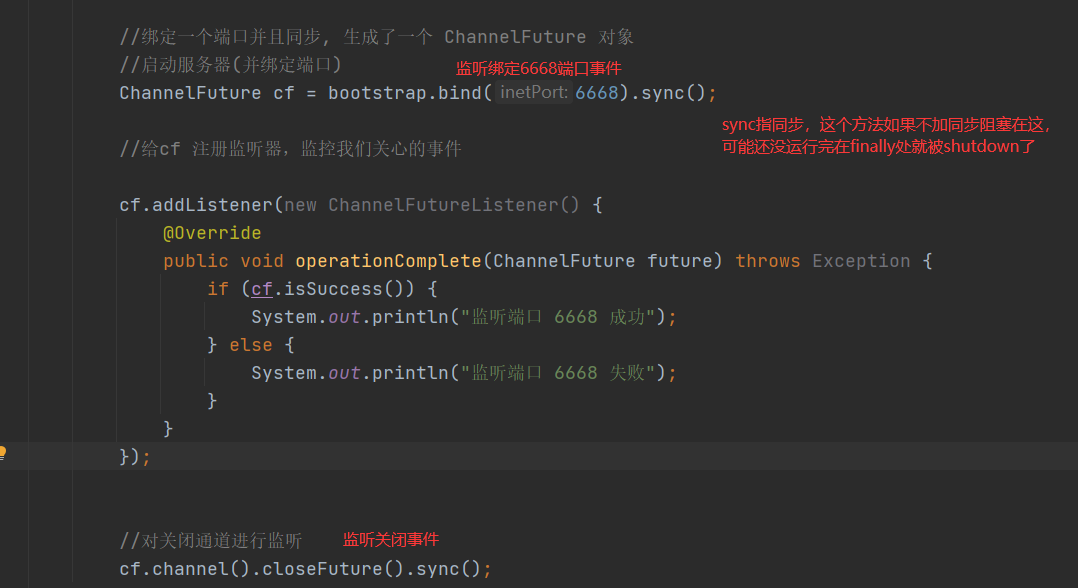
ChannelFuture 是一个接口 :public interface ChannelFuture extends Future<Void>,可以添加监听器,当监听的事件发生时,就会通知到监听器
工作原理图:
4.4.2 Future-Listener 机制
当 Future 对象刚刚创建时,处于非完成状态,调用者可以通过返回的 ChannelFuture 来获取操作执行的状态,注册监听函数来执行完成后的操作
常用操作如下:
- 通过
isDone方法来判断当前操作是否完成; - 通过
isSuccess方法来判断已完成的当前操作是否成功; - 通过
getCause方法来获取已完成的当前操作失败的原因; - 通过
isCancelled方法来判断已完成的当前操作是否被取消; - 通过
addListener方法来注册监听器,当操作已完成(isDone 方法返回完成),将会通知指定的监听器;如果 Future 对象已完成,则通知指定的监听器
//绑定端口是异步操作,当绑定操作处理完,将会调用相应的监听器处理逻辑
serverBootstrap.bind(port).addListener(future -> {
if(future.isSuccess()) {
System.out.println(newDate() + ": 端口["+ port + "]绑定成功!");
} else{
System.err.println("端口["+ port + "]绑定失败!");
}
});
相比传统阻塞 I/O,执行 I/O 操作后线程会被阻塞住,直到操作完成;异步处理的好处是不会造成线程阻塞,线程在 I/O 操作期间可以执行别的程序,在高并发情形下会更稳定和更高的吞吐量
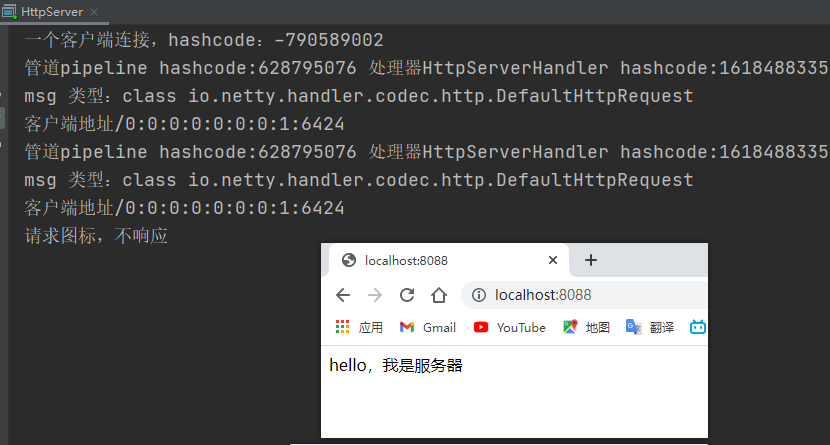
4.5 Http服务Demo
Netty 服务器在 8088 端口监听,浏览器发出请求 "http://localhost:8088/ "
服务器可以回复消息给客户端 “Hello! 我是服务器” , 并对特定请求资源进行过滤
HttpServer
public class HttpServer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1);
EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
serverBootstrap.group(bossGroup,workerGroup)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.childHandler(new HttpServerInitializer());
System.out.println("Server ok");
ChannelFuture channelFuture = serverBootstrap.bind(8088).sync();
channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}
HttpServerInitializer
public class HttpServerInitializer extends ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel> {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception {
System.out.println("一个客户端连接,hashcode:"+socketChannel.hashCode());
//先拿到管道
ChannelPipeline pipeline = socketChannel.pipeline();
//HttpServerCodec 是netty提供的处理http的 编-解码器
pipeline.addLast("MyHttpServerCodec",new HttpServerCodec());
//添加一个自定义的handler
pipeline.addLast("MyHttpServerHandler",new HttpServerHandler());
}
}
HttpServerHandler
/**
* SimpleChannelInboundHandler 继承的 ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter
* HttpObject:客户端和服务器端相互通讯的数据被封装成 HttpObject
*/
public class HttpServerHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<HttpObject> {
//channelRead0 读取客户端数据
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, HttpObject msg) throws Exception {
// 判断 msg 是不是 HttpRequest请求
if (msg instanceof HttpRequest){
System.out.println("管道pipeline hashcode:"+ctx.pipeline().hashCode()+" 处理器HttpServerHandler hashcode:"+this.hashCode());
System.out.println("msg 类型:"+msg.getClass());
System.out.println("客户端地址"+ctx.channel().remoteAddress());
HttpRequest httpRequest = (HttpRequest) msg;
//获取uri
URI uri = new URI(httpRequest.uri());
if ("/favicon.ico".equals(uri.getPath())){
System.out.println("请求图标,不响应");
return;
}
//回复消息给浏览器(客户端)[http协议]
ByteBuf content = Unpooled.copiedBuffer("hello,我是服务器", CharsetUtil.UTF_8);
//构建一个response
FullHttpResponse response = new DefaultFullHttpResponse(HttpVersion.HTTP_1_1, HttpResponseStatus.OK, content);
response.headers().set(HttpHeaderNames.CONTENT_TYPE,"text/html;charset=utf-8");
response.headers().set(HttpHeaderNames.CONTENT_LENGTH,content.readableBytes());
//返回response
ctx.writeAndFlush(response);
}
}
}