文章目录
Netty搭建简易RPC
什么是RPC
-
RPC 全称 Remote Procedure Call——远程过程调用。
-
在学校学编程,我们写一个函数都是在本地调用就行了。
-
但是在互联网公司,服务都是部署在不同服务器上的分布式系统,如何调用呢?
-
RPC技术简单说就是为了解决远程调用服务的一种技术,使得调用者像调用本地服务一样方便透明。
-
下图是客户端调用远端服务的过程:
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-3oq4suTy-1649126202742)(java_notes.assets/image-20220404235354912-16490876359754.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/dfcb8f0fd19d4918930177a2df0985b6.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_d3F5LXplbmhlaQ,shadow_50,text_Q1NETiBA55Sy57KS5a2Q,size_20,color_FFFFFF,t_70,g_se,x_16)
图片来源网络
- 客户端(Client),服务的调用方。
- 服务端(Server),真正的服务提供者。
- 客户端存根,存放服务端的地址消息,再将客户端的请求参数打包成网络消息,然后通过网络远程发送给服务方。
- 服务端存根,接收客户端发送过来的消息,将消息解包,并调用本地的方法。
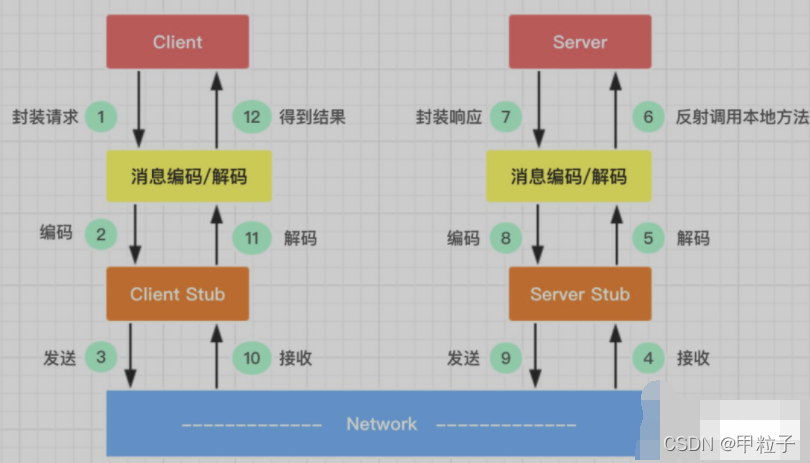
图片来源网络
为什么需要RPC
- 1、首先要明确一点:RPC可以用HTTP协议实现,并且用HTTP是建立在 TCP 之上最广泛使用的 RPC,但是互联网公司往往用自己的私有协议,比如鹅厂的JCE协议,私有协议不具备通用性为什么还要用呢?因为相比于HTTP协议,RPC采用二进制字节码传输,更加高效也更加安全。
- 2、现在业界提倡“微服务“的概念,而服务之间通信目前有两种方式,RPC就是其中一种。RPC可以保证不同服务之间的互相调用。即使是跨语言跨平台也不是问题,让构建分布式系统更加容易。
- 3、RPC框架都会有服务降级、流量控制的功能,保证服务的高可用。
代码实现
项目说明
-
使用SpringBoot 2.6.6
-
netty 4
-
jdk8
项目结构图:
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-GfAgXvZC-1649126202743)(java_notes.assets/image-20220404235717536-16490878389925.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/036584b0e67e44fca33535ce91906800.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_d3F5LXplbmhlaQ,shadow_50,text_Q1NETiBA55Sy57KS5a2Q,size_18,color_FFFFFF,t_70,g_se,x_16)
依赖导入
<dependency>
<groupId>io.netty</groupId>
<artifactId>netty-all</artifactId>
<version>4.1.68.Final</version>
</dependency>
<!--json转换器-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>fastjson</artifactId>
<version>1.2.14</version>
</dependency>
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-Ht4P6qcd-1649126202744)(java_notes.assets/image-20220405103611054-16491261724571.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/79659df9ce514ed0bd5f31c9d2032190.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_d3F5LXplbmhlaQ,shadow_50,text_Q1NETiBA55Sy57KS5a2Q,size_20,color_FFFFFF,t_70,g_se,x_16)
一、消息实体
Message抽象类
package cn.netty.netty_rpc.message;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* Author:甲粒子
* Date: 2022/4/1
* Description:message
*/
public abstract class Message implements Serializable {
public static final Map<Integer,Class<?>> messageClasses = new HashMap<>();
public static final int RPC_MESSAGE_TYPE_REQUEST = 101;
public static final int RPC_MESSAGE_TYPE_RESPONSE = 102;
static {
messageClasses.put(RPC_MESSAGE_TYPE_REQUEST,RpcRequestMessage.class); messageClasses.put(RPC_MESSAGE_TYPE_RESPONSE,RpcResponseMessage.class);
}
//后面用于与promise匹配
private int sequenceId;
private int messageType;
public static Class<?> getMessageClass(int messageType){
return messageClasses.get(messageType);
}
//抽象方法
public abstract int getMessageType();
public int getSequenceId() {
return sequenceId;
}
public void setSequenceId(int sequenceId) {
this.sequenceId = sequenceId;
}
public void setMessageType(int messageType) {
this.messageType = messageType;
}
}
- Message的两个子类
RpcRequestMessage
package cn.netty.netty_rpc.message;
/**
* Author:甲粒子
* Date: 2022/4/1
* Description:
* 想要远程调用一个方法,必须知道以下五个信息
* 方法所在的全限定类名
* 方法名
* 方法返回值类型
* 方法参数类型
* 方法参数值
*/
public class RpcRequestMessage extends Message{
/**
* 调用的接口全限定名,服务端根据它找到实现
*/
private String interfaceName;
/**
* 调用接口中的方法名
*/
private String methodName;
/**
* 方法返回类型
*/
private Class<?> returnType;
/**
* 方法参数类型数组
*/
private Class[] parameterTypes;
/**
* 方法参数值数组
*/
private Object[] parameterValue;
public RpcRequestMessage(int sequenceId, String interfaceName, String methodName, Class<?> returnType, Class[] parameterTypes, Object[] parameterValue) {
super.setSequenceId(sequenceId);
this.interfaceName = interfaceName;
this.methodName = methodName;
this.returnType = returnType;
this.parameterTypes = parameterTypes;
this.parameterValue = parameterValue;
}
public String getInterfaceName() {
return interfaceName;
}
public void setInterfaceName(String interfaceName) {
this.interfaceName = interfaceName;
}
public String getMethodName() {
return methodName;
}
public void setMethodName(String methodName) {
this.methodName = methodName;
}
public Class<?> getReturnType() {
return returnType;
}
public void setReturnType(Class<?> returnType) {
this.returnType = returnType;
}
public Class[] getParameterTypes() {
return parameterTypes;
}
public void setParameterTypes(Class[] parameterTypes) {
this.parameterTypes = parameterTypes;
}
public Object[] getParameterValue() {
return parameterValue;
}
public void setParameterValue(Object[] parameterValue) {
this.parameterValue = parameterValue;
}
@Override
public int getMessageType() {
return RPC_MESSAGE_TYPE_REQUEST;
}
}
RpcResponseMessage
package cn.netty.netty_rpc.message;
/**
* Author:甲粒子
* Date: 2022/4/1
* Description:
*/
public class RpcResponseMessage extends Message{
/**
* 返回值
*/
private Object returnValue;
/**
* 异常值
*/
private Exception exceptionValue;
public Object getReturnValue() {
return returnValue;
}
public void setReturnValue(Object returnValue) {
this.returnValue = returnValue;
}
public Exception getExceptionValue() {
return exceptionValue;
}
public void setExceptionValue(Exception exceptionValue) {
this.exceptionValue = exceptionValue;
}
@Override
public int getMessageType() {
return 0;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "RpcResponseMessage{" +
"returnValue=" + returnValue +
", exceptionValue=" + exceptionValue +
'}';
}
}
二、序列化算法
Serializer接口
package cn.netty.netty_rpc.utils.serializer;
/**
* Author:甲粒子
* Date: 2022/4/1
* Description:
*/
public interface Serializer {
/**
* 序列化
* @param object 被序列化的对象
* @param <T> 被序列化对象类型
* @return 序列化后的字节数组
*/
<T> byte[] serialize(T object);
/**
* 反序列化
* @param clazz 反序列化的目标类的Class对象
* @param bytes 被反序列化的字节数组
* @param <T> 反序列化目标类
* @return 反序列化后的对象
*/
<T> T deserialize(Class<T> clazz, byte[] bytes);
}
枚举类实现
package cn.netty.netty_rpc.utils.serializer;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONObject;
import java.io.*;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
/**
* Author:甲粒子
* Date: 2022/4/1
* Description:枚举序列化算法的具体实现
*/
public enum SerializerAlgorithm implements Serializer{
// JDK的序列化和反序列化
Java{
@Override
public <T> byte[] serialize(T object) {
// 序列化后的字节数组
byte[] bytes = null;
try{
ByteArrayOutputStream bos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(bos);
oos.writeObject(object);
bytes = bos.toByteArray();
}catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
return bytes;
}
@Override
public <T> T deserialize(Class<T> clazz, byte[] bytes) {
T target = null;
// System.out.println(Arrays.toString(bytes));
try{
ByteArrayInputStream bis = new ByteArrayInputStream(bytes);
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(bis);
target =(T) ois.readObject();
}catch (IOException | ClassNotFoundException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
return target;
}
},
// Json的序列化和反序列化
Json{
@Override
public <T> byte[] serialize(T object) {
if( object == null){
return new byte[0];
}
return JSON.toJSONString(object).getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
}
@Override
public <T> T deserialize(Class<T> clazz, byte[] bytes) {
if (null == bytes || bytes.length <= 0) {
return null;
}
String str = new String(bytes, StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
return (T) JSON.parseObject(str, clazz);
}
}
}
三、自定义协议与解析
自定义可共享MessageCodecSharable
package cn.netty.netty_rpc.protocol;
import cn.netty.netty_rpc.message.Message;
import cn.netty.netty_rpc.utils.serializer.SerializerAlgorithm;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandler;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.handler.codec.MessageToMessageCodec;
import java.util.List;
/**
* Author:甲粒子
* Date: 2022/4/1
* Description:自定义协议,编码,解码
*/
@ChannelHandler.Sharable
public class MessageCodecSharable extends MessageToMessageCodec<ByteBuf,Message> {
@Override
protected void encode(ChannelHandlerContext channelHandlerContext, Message msg, List<Object> outList) throws Exception {
ByteBuf out = channelHandlerContext.alloc().buffer();
// 设置魔数 4个字节
out.writeBytes(new byte[]{1,0,1,6});
// 设置版本号 1个字节
out.writeByte(1);
// 设置序列化方式 1个字节
out.writeByte(1);
// 设置指令类型 1个字节
out.writeByte(msg.getMessageType());
// 设置请求序号 4个字节
out.writeInt(msg.getSequenceId());
// 为了补齐为16个字节,填充1个字节的数据
out.writeByte(0xff);
/* 使用指定的序列化方式
获得Json序列化后的msg
*/
SerializerAlgorithm[] values = SerializerAlgorithm.values();
/* 获得序列化后的对象
* out.getByte(5):第六个字节就是序列化方式
* */
byte[] bytes = values[out.getByte(5)-1].serialize(msg);
// 获得并设置正文长度 长度用4个字节标识 all 16Bytes
out.writeInt(bytes.length);
// 设置消息正文
out.writeBytes(bytes);
outList.add(out);
}
/*
* 解码器负责将ByteBuf中的信息取出,并放入List中,该List用于将信息传递给下一个handler
* 这里的ByteBuf in不用考虑安全性问题,因为我们能够明确传过来的的ByteBuf是完整的(从粘包半包处理器过来肯定是完整的)
* */
@Override
protected void decode(ChannelHandlerContext channelHandlerContext, ByteBuf in, List<Object> outList) throws Exception {
// 获取魔数
int magic = in.readInt();
// 获取版本号
byte version = in.readByte();
// 获得序列化方式
byte seqType = in.readByte();
// 获得指令类型
byte messageType = in.readByte();
// 获得请求序号
int sequenceId = in.readInt();
// 移除补齐字节
in.readByte();
// 获得正文长度
int length = in.readInt();
// 获得正文
byte[] bytes = new byte[length];
in.readBytes(bytes, 0, length);
// 获得反序列化方式
SerializerAlgorithm[] values = SerializerAlgorithm.values();
// 通过指定方式进行反序列化
// 需要通过Message的方法获得具体的消息类型
Message message = (Message) values[seqType-1].deserialize(Message.getMessageClass(messageType), bytes);
// 将信息放入List中,传递给下一个handler
outList.add(message);
}
}
四、远程调用接口
IHelloService
package cn.netty.netty_rpc.service;
/**
* Author:甲粒子
* Date: 2022/4/2
* Description:
*/
public interface IHelloService {
String sayHello(String name);
}
HelloServiceImpl
package cn.netty.netty_rpc.service.impl;
import cn.netty.netty_rpc.service.IHelloService;
/**
* Author:甲粒子
* Date: 2022/4/2
* Description:
*/
public class HelloServiceImpl implements IHelloService {
@Override
public String sayHello(String name) {
return "hello, "+name;
}
}
ServiceFactory
package cn.netty.netty_rpc.factory;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* Author:甲粒子
* Date: 2022/4/2
* Description:
*/
public class ServiceFactory {
static Map<Class<?>,Object> map = new HashMap<>(16);
public static Object getInstance(Class<?> interfaceClass){
//根据Class创建实例
try{
Class<?> clazz = Class.forName("cn.netty.netty_rpc.service.IHelloService");
Object instance = Class.forName("cn.netty.netty_rpc.service.impl.HelloServiceImpl").newInstance();
// 放入 InterfaceClass -> InstanceObject 的映射
map.put(clazz, instance);
}catch ( ClassNotFoundException | InstantiationException | IllegalAccessException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
return map.get(interfaceClass);
}
}
五、Handler
RpcRequestMessageHandler
package cn.netty.netty_rpc.handler;
import cn.netty.netty_rpc.factory.ServiceFactory;
import cn.netty.netty_rpc.message.RpcRequestMessage;
import cn.netty.netty_rpc.message.RpcResponseMessage;
import cn.netty.netty_rpc.service.IHelloService;
import cn.netty.netty_rpc.service.impl.HelloServiceImpl;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandler;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.channel.SimpleChannelInboundHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
/**
* Author:甲粒子
* Date: 2022/4/2
* Description:该handler用于服务端,
* 远程调用方法主要是通过反射实现的,大致步骤如下
*
* 通过请求消息传入被调入方法的各个参数
* 通过全限定接口名,在map中查询到对应的类并实例化对象
* 通过反射获取Method,并调用其invoke方法的返回值,并放入响应消息中
* 若有异常需要捕获,并放入响应消息中
*/
@ChannelHandler.Sharable
public class RpcRequestMessageHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<RpcRequestMessage> {
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, RpcRequestMessage rpcRequestMessage) throws Exception {
RpcResponseMessage rpcResponseMessage = new RpcResponseMessage();
try{
//设置返回值的属性
rpcResponseMessage.setSequenceId(rpcRequestMessage.getSequenceId());
//返回一个实例
IHelloService helloService = (IHelloService)ServiceFactory.getInstance(Class.forName(rpcRequestMessage.getInterfaceName()));
//通过反射调用方法
Method method = helloService.getClass().getMethod(rpcRequestMessage.getMethodName(),rpcRequestMessage.getParameterTypes());
//获取返回值
Object invoke = method.invoke(helloService, rpcRequestMessage.getParameterValue());
//设置返回值
rpcResponseMessage.setReturnValue(invoke);
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
//设置异常值
rpcResponseMessage.setExceptionValue(e);
}
//向channel中写入Message
ctx.writeAndFlush(rpcResponseMessage);
}
}
RpcResponseMessageHandler
package cn.netty.netty_rpc.handler;
import cn.netty.netty_rpc.message.RpcResponseMessage;
import cn.netty.netty_rpc.server.RpcServer;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandler;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.channel.SimpleChannelInboundHandler;
import io.netty.util.concurrent.Promise;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
/**
* Author:甲粒子
* Date: 2022/4/2
* Description:
*/
@ChannelHandler.Sharable
public class RpcResponseMessageHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<RpcResponseMessage> {
/**
* 用于存放Promise的集合,Promise用于主线程与NIO线程之间传递返回值
*
* 远程调用方法返回值获取
* 调用方法的是主线程,处理返回结果的是NIO线程(RpcResponseMessageHandler)。
* 要在不同线程中进行返回值的传递,需要用到Promise
*
* 在RpcResponseMessageHandler中创建一个Map
* Key为SequenceId
* Value为对应的Promise
* 主线程的代理类将RpcResponseMessage发送给服务器后,需要创建Promise对象,
* 并将其放入到RpcResponseMessageHandler的Map中。需要使用await等待结果被放入Promise中。获取结果后,根据结果类型(判断是否成功)来返回结果或抛出异常
*/
public static Map<Integer, Promise<Object>> promiseMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(16);
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext channelHandlerContext, RpcResponseMessage rpcResponseMessage) throws Exception {
// 将返回结果放入对应的Promise中,并移除Map中的Promise
Promise<Object> promise = promiseMap.remove(rpcResponseMessage.getSequenceId());
if(promise != null){
Object returnValue = rpcResponseMessage.getReturnValue();
Exception exceptionValue = rpcResponseMessage.getExceptionValue();
if(exceptionValue != null){
// 返回结果中有异常信息
promise.setFailure(exceptionValue);
}else {
// 方法正常执行,没有异常
promise.setSuccess(returnValue);
}
}
// 拿到返回结果并打印
System.out.println(rpcResponseMessage);
}
}
六、服务端
package cn.netty.netty_rpc.server;
import cn.netty.netty_rpc.handler.RpcRequestMessageHandler;
import cn.netty.netty_rpc.protocol.MessageCodecSharable;
import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.Channel;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel;
import io.netty.handler.codec.LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder;
import io.netty.handler.logging.LogLevel;
import io.netty.handler.logging.LoggingHandler;
/**
* Author:甲粒子
* Date: 2022/4/2
* Description:服务端
*/
public class RpcServer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
NioEventLoopGroup boss = new NioEventLoopGroup();//专门用于accept
NioEventLoopGroup worker = new NioEventLoopGroup();//用于write 和 read事件
LoggingHandler loggingHandler = new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.DEBUG);
MessageCodecSharable messageSharableCodec = new MessageCodecSharable();
// PRC 请求消息处理器
RpcRequestMessageHandler rpcRequestMessageHandler = new RpcRequestMessageHandler();
try {
ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
serverBootstrap.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class);
serverBootstrap.group(boss, worker);
serverBootstrap.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder(1024*1024,12,4,0,0));//防半包粘包
ch.pipeline().addLast(loggingHandler);//netty自带日志
ch.pipeline().addLast(messageSharableCodec);
ch.pipeline().addLast(rpcRequestMessageHandler);
}
});
Channel channel = serverBootstrap.bind(8080).sync().channel();
channel.closeFuture().sync();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
boss.shutdownGracefully();
worker.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}
七、客户端
省略无数个包...
/**
* Author:甲粒子
* Date: 2022/4/2
* Description:客户端
*/
public class RpcClient {
/**
* 产生SequenceId
*/
public static AtomicInteger sequenceId = new AtomicInteger(0);
public static volatile Channel channel = null;
public static final Object lock = new Object();
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 通过代理对象执行方法
/*
* 远程调用方法
* 为了让方法的调用变得简洁明了,将RpcRequestMessage的创建与发送过程通过JDK的动态代理来完成
*
* 通过返回的代理对象调用方法即可,方法getProxy参数为被调用方法接口的Class类
*
* */
// 创建代理对象
IHelloService service = (IHelloService) getProxy(IHelloService.class);
System.out.println(service.sayHello("小翟"));
System.out.println(service.sayHello("甲粒子"));
}
/**
* 单例模式创建Channel
*/
public static Channel getChannel(){
if (channel == null){
synchronized (lock){
if (channel == null){
init();
}
}
}
return channel;
}
/**
* 使用代理模式,帮助我们创建请求消息并发送
*
* * 远程调用方法返回值获取
* * 调用方法的是主线程,处理返回结果的是NIO线程(RpcResponseMessageHandler)。
* * 要在不同线程中进行返回值的传递,需要用到Promise
* *
* * 在RpcResponseMessageHandler中创建一个Map
* * Key为SequenceId
* * Value为对应的Promise
* * 主线程的代理类将RpcRequestMessage发送给服务器后,需要创建Promise对象,
* * 并将其放入到RpcResponseMessageHandler的Map中。需要使用await等待结果被放入Promise中。
* 获取结果后,根据结果类型(判断是否成功)来返回结果或抛出异常
*/
public static Object getProxy(Class<?> serviceClass){
Class<?>[] classes = new Class<?>[]{serviceClass};
//使用JDK代理创建代理对象
Object proxy = Proxy.newProxyInstance(serviceClass.getClassLoader(), classes, new InvocationHandler() {
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
//创建请求消息
int id = sequenceId.getAndIncrement();
RpcRequestMessage message = new RpcRequestMessage(id,serviceClass.getName(),
method.getName(),method.getReturnType(),method.getParameterTypes(),args);
//发送消息 一时半会回不来
getChannel().writeAndFlush(message);
//创建promise,用于获取NIO线程中的返回结果,获取的过程是异步的
DefaultPromise<Object> promise = new DefaultPromise<>(getChannel().eventLoop());
// 将Promise放入Map中
RpcResponseMessageHandler.promiseMap.put(id,promise);
// 等待被放入Promise中结果
promise.await(); //在RpcResponseMessageHandler 放入了值就会结束等待
if (promise.isSuccess()) {
// 调用方法成功,返回方法执行结果
return promise.getNow();
} else {
// 调用方法失败,抛出异常
throw new RuntimeException(promise.cause());
}
}
});
return proxy;
}
/*
获得Channel
建立连接,获取Channel的操作被封装到了init方法中,当连接断开时,通过addListener方法异步关闭group
通过单例模式创建与获取Channel
* */
private static void init() {
NioEventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
LoggingHandler loggingHandler = new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.DEBUG);
MessageCodecSharable messageCodecSharable = new MessageCodecSharable();
// RPC 请求消息处理器
RpcResponseMessageHandler rpcResponseMessageHandler = new RpcResponseMessageHandler();
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
bootstrap.channel(NioSocketChannel.class);
bootstrap.group(group);
bootstrap.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception {
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder(1024*1024,12,4,0,0));
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(loggingHandler);
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(messageCodecSharable);
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(rpcResponseMessageHandler);
}
});
try {
//channel连接建立后就会返回
channel = bootstrap.connect(new InetSocketAddress("localhost",8080)).sync().channel();
// 异步关闭 group,避免Channel被阻塞
channel.closeFuture().addListener(future -> {
group.shutdownGracefully();
});
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
客户端
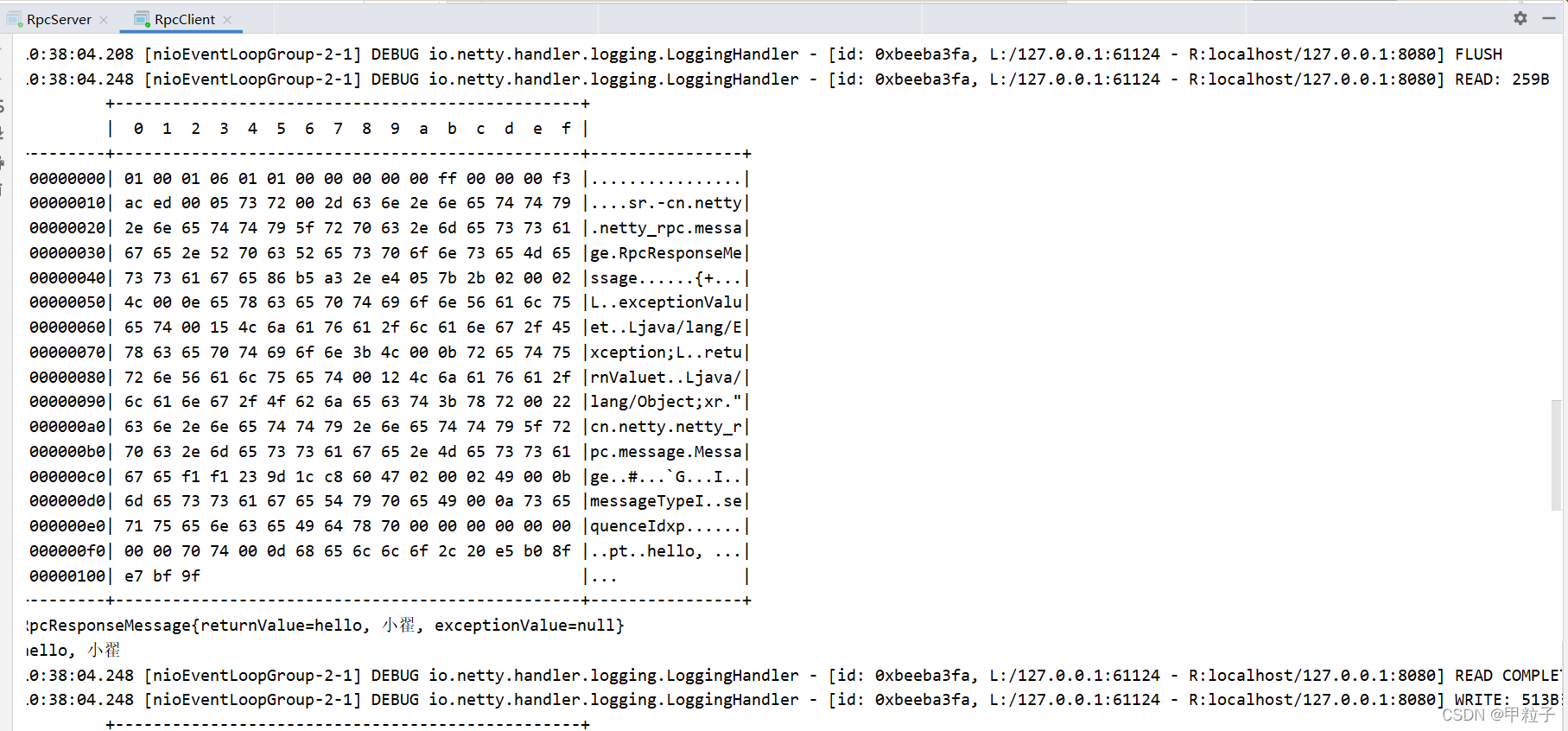
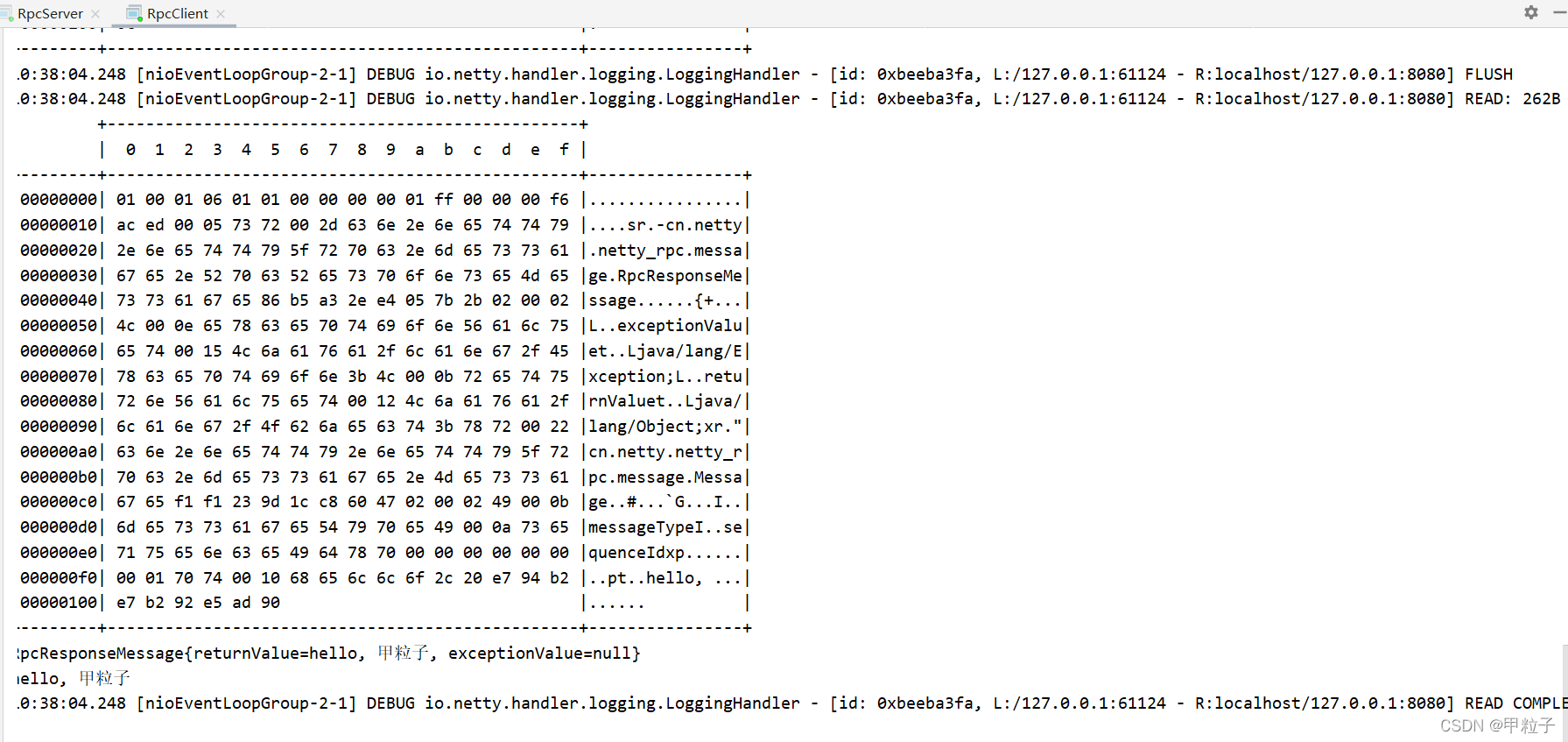
服务器端:
与客户端一样会触发四次 日志handler