基础QL语法
CodeQL的查询语法有点像SQL,如果你学过基本的SQL语句,基本模式应该不会陌生。
结构
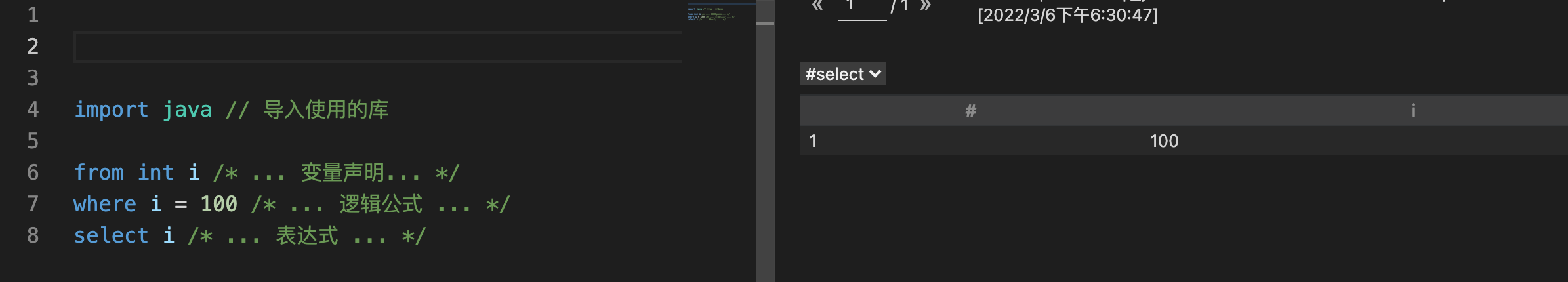
import java // 导入使用的库
from int i /* ... 变量声明... */
where i = 100 /* ... 逻辑公式 ... */
select i /* ... 表达式 ... */
import java,导入使用的库,因为我们分析的项目是java的
from int i,表示我们定义一个变量i,它的类型是int,表示我们获取所有的int类型的数据;
where i = 100, 表示当i等于1的时候,符合条件;(这是= 是一个等于的意思 == ,并不是赋值)
select i,就是输出 i
我们经常会用到的ql类库大体如下:
| 名称 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| Method | 方法类,Method method表示获取当前项目中所有的方法 |
| MethodAccess | 方法调用类,MethodAccess call表示获取当前项目当中的所有方法调用 |
| Parameter | 参数类,Parameter表示获取当前项目当中所有的参数 |
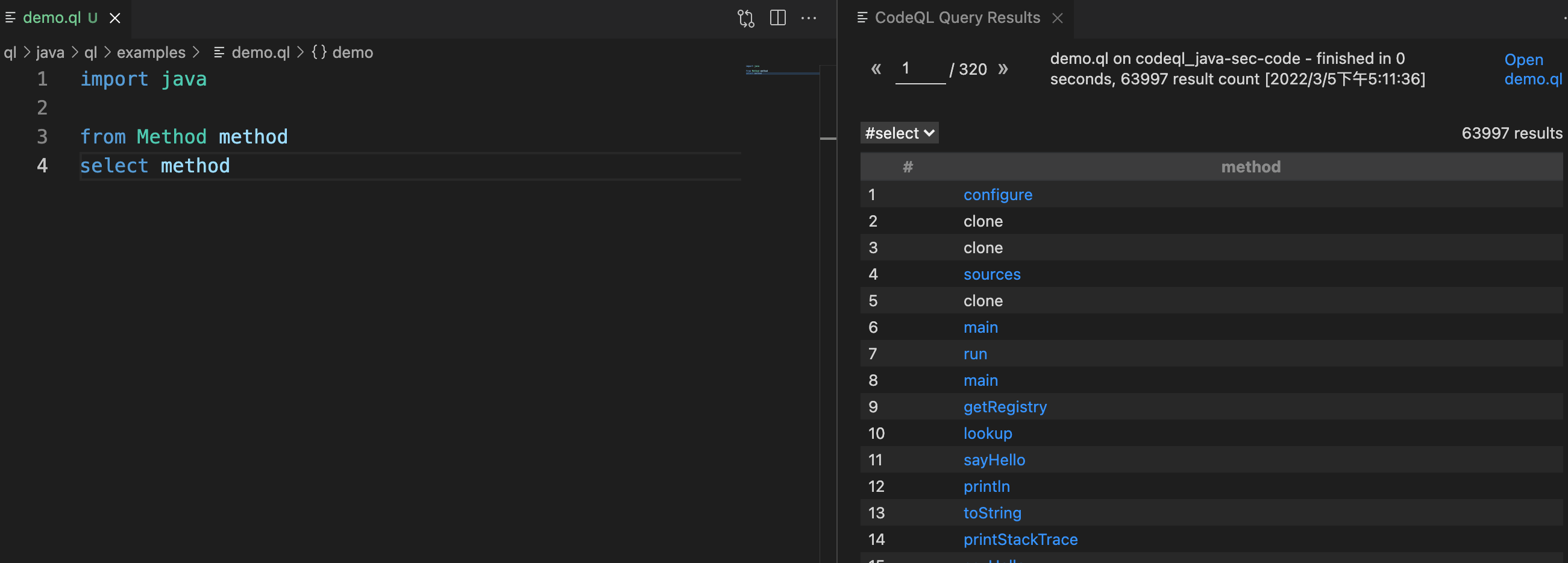
所有方法:
import java
from Method method
select method
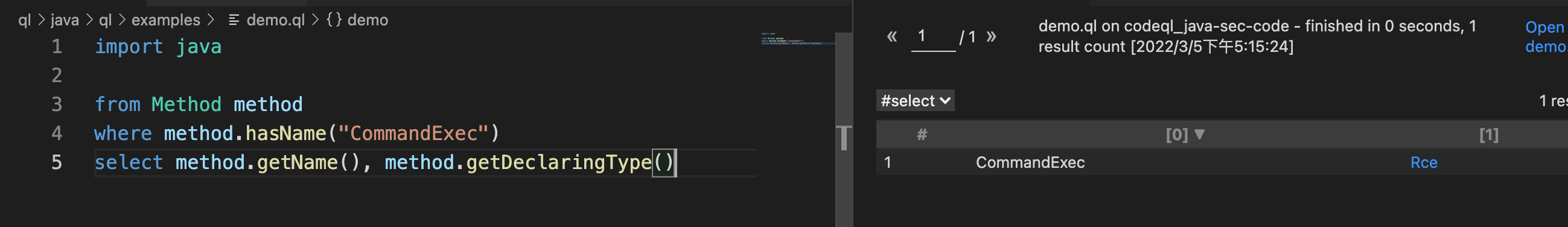
我们再通过Method类内置的一些方法,把结果过滤一下。比如我们获取名字为 CommandExec 的方法名称。
import java
from Method method
where method.hasName("CommandExec")
select method.getName(), method.getDeclaringType()
谓词
和SQL一样,where部分的查询条件如果过长,会显得很乱。CodeQL提供一种机制可以让你把很长的查询语句封装成函数。
这个函数,就叫谓词。
比如上面的案例,我们可以写成如下,获得的结果跟上面是一样的:
import java
predicate isStudent(Method method) {
exists(|method.hasName("getStudent"))
}
from Method method
where isStudent(method)
select method.getName(), method.getDeclaringType()
语法解释
predicate 表示当前方法没有返回值。
exists子查询,是CodeQL谓词语法里非常常见的语法结构,它根据内部的子查询返回true or false,来决定筛选出哪些数据。
设置Source和Sink
什么是source和sink
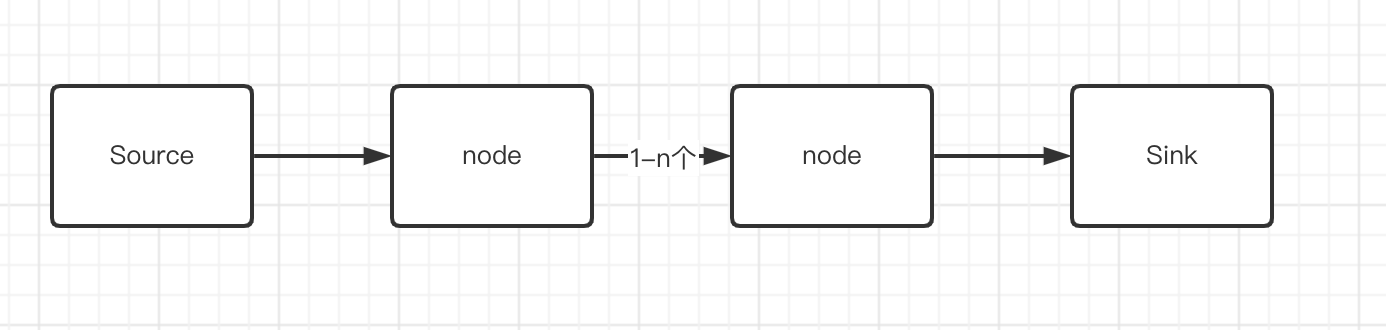
在代码自动化安全审计的理论当中,有一个最核心的三元组概念,就是(source,sink和sanitizer)。
source是指漏洞污染链条的输入点。比如获取http请求的参数部分,就是非常明显的Source。
sink是指漏洞污染链条的执行点,比如SQL注入漏洞,最终执行SQL语句的函数就是sink(这个函数可能叫query或者exeSql,或者其它)。
sanitizer又叫净化函数,是指在整个的漏洞链条当中,如果存在一个方法阻断了整个传递链,那么这个方法就叫sanitizer。
只有当source和sink同时存在,并且从source到sink的链路是通的,才表示当前漏洞是存在的。
设置Source
在CodeQL中我们通过这个格式去设置
override predicate isSource(DataFlow::Node src) {
具体方法。。。
}
例如
正常的Spring Boot 框架
@RequestMapping(value="/list",method = {RequestMethod.GET, RequestMethod.POST})
@ResponseBody
public ResultData list(@ModelAttribute @ApiIgnore CategoryEntity category, HttpServletResponse response, HttpServletRequest request, @ApiIgnore ModelMap model, BindingResult result) {
BasicUtil.startPage();
List categoryList = categoryBiz.query(category);
return ResultData.build().success(new EUListBean(categoryList,(int) BasicUtil.endPage(categoryList).getTotal()));
}
本例中我们设置Source的代码为:
override predicate isSource(DataFlow::Node src) { src instanceof RemoteFlowSource }
这是SDK自带的规则,里面包含了大多常用的Source入口。我们使用的SpringBoot也包含在其中, 我们可以直接使用。
注: instanceof 语法是CodeQL提供的语法,后面在CodeQL进阶部分我们会讲到。
设置Sink
在CodeQL中我们通过 isSink
override predicate isSink(DataFlow::Node sink) {
具体方法。。。
}
这里的 sink我们就正常的去定义一个construtorCall,然后这个construtorCall限定在processBuilder下就行。
codeql官方有一个ExternalProcess.qll库里面有一个ArgumentToExec类,这个类会覆盖到这个sink
那么就直接写一个
override predicate isSink(DataFlow::Node sink) {
sink.asExpr() instanceof ArgumentToExec
}
这样就设置了一个命令执行的 Sink
Flow数据流
设置好Source和Sink后,如果一个受污染的变量,能够毫无阻拦的流转到危险函数,就表示存在漏洞。
比如如下代码:
from VulConfig config, DataFlow::PathNode source, DataFlow::PathNode sink
where config.hasFlowPath(source, sink)
select source.getNode(), source, sink, "source"
我们传递给config.hasFlowPath(source, sink)我们定义好的source和sink,系统就会自动帮我们判断是否存在漏洞了。
这一段其实基本上都是固定的,都是从Source到sink,不必深究。
简单demo
/**
* @id java/examples/vuldemo
* @name Rce
* @description Rce
* @kind path-problem
* @problem.severity warning
*/
import java
import semmle.code.java.dataflow.FlowSources
import DataFlow::PathGraph
class VulConfig extends TaintTracking::Configuration {
VulConfig() { this = "rceConfig" }
override predicate isSource(DataFlow::Node src) {
src instanceof RemoteFlowSource
}
override predicate isSink(DataFlow::Node sink) {
sink.asExpr() instanceof ArgumentToExec
}
}
from VulConfig config, DataFlow::PathNode source, DataFlow::PathNode sink
where config.hasFlowPath(source, sink)
select source.getNode(), source, sink, "source"
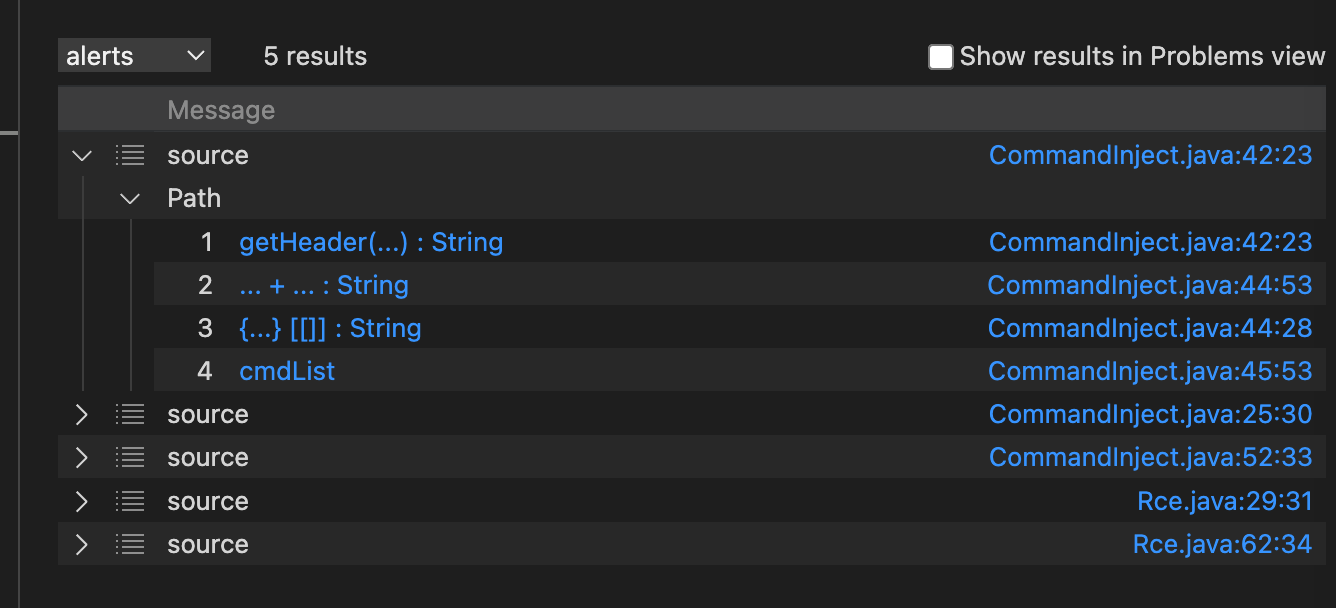
isSanitizer方法
从上面的demo中存在的一个数据,就是误报,这个参数其实是通过了安全函数过滤了,但是还是扫出来了,这种情况就得消除这种误报。就得使用isSanitizer。
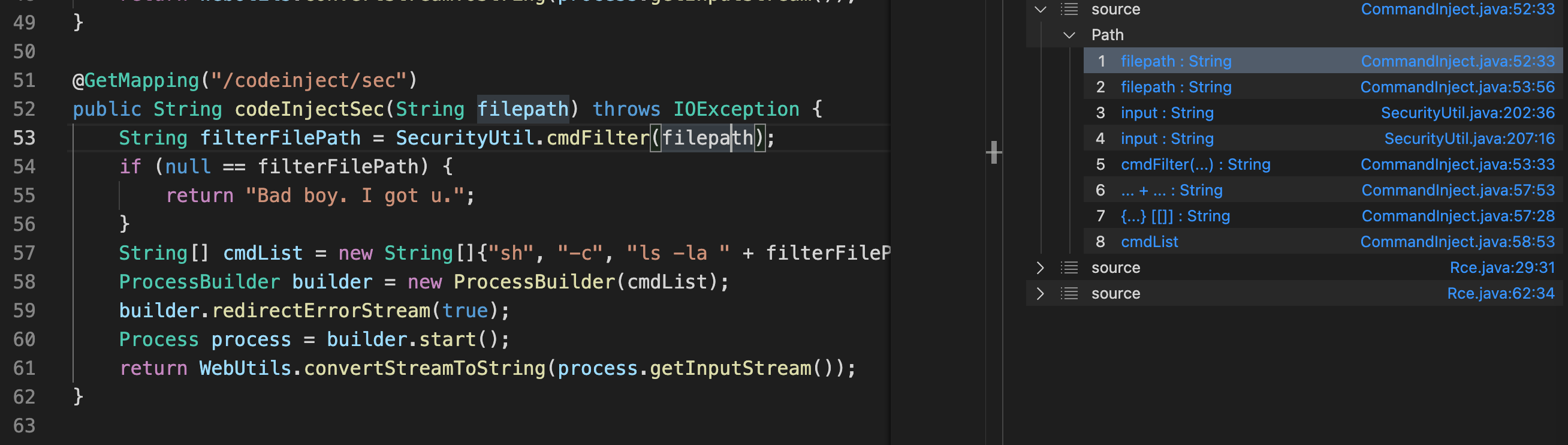
isSanitizer是CodeQL的类TaintTracking::Configuration提供的净化方法。
override predicate isSanitizer(DataFlow::Node node) {
exists(...)
}
isAdditionalTaintStep方法
isAdditionalTaintStep方法是CodeQL的类TaintTracking::Configuration提供的的方法,它的原型是:
override predicate isAdditionalTaintStep(DataFlow::Node node1, DataFlow::Node node2) {
isTaintedString(node1.asExpr(), node2.asExpr())
}
}
它的作用是将一个可控节点
A强制传递给另外一个节点B,那么节点B也就成了可控节点。
批量检测命令
CodeQL除了提供VSCode的检测插件,也提供了大量的命令行,来实现项目的集成检测。
比如:
codeql database analyze /Users/zy/Documents/project/codeql/vscode-codeql-starter-main/database/codeql_java-sec-code /Users/zy/Documents/project/codeql/vscode-codeql-starter-main/ql/java/ql/src/codeql-suites/java-security-extended.qls --format=csv --output=java-results.csv
查询制定类的的方法
import java
from Method method
where method.hasName("Deserialize")
and
method.getDeclaringType().hasQualifiedName("org.joychou.controller", "Fastjson")
select method
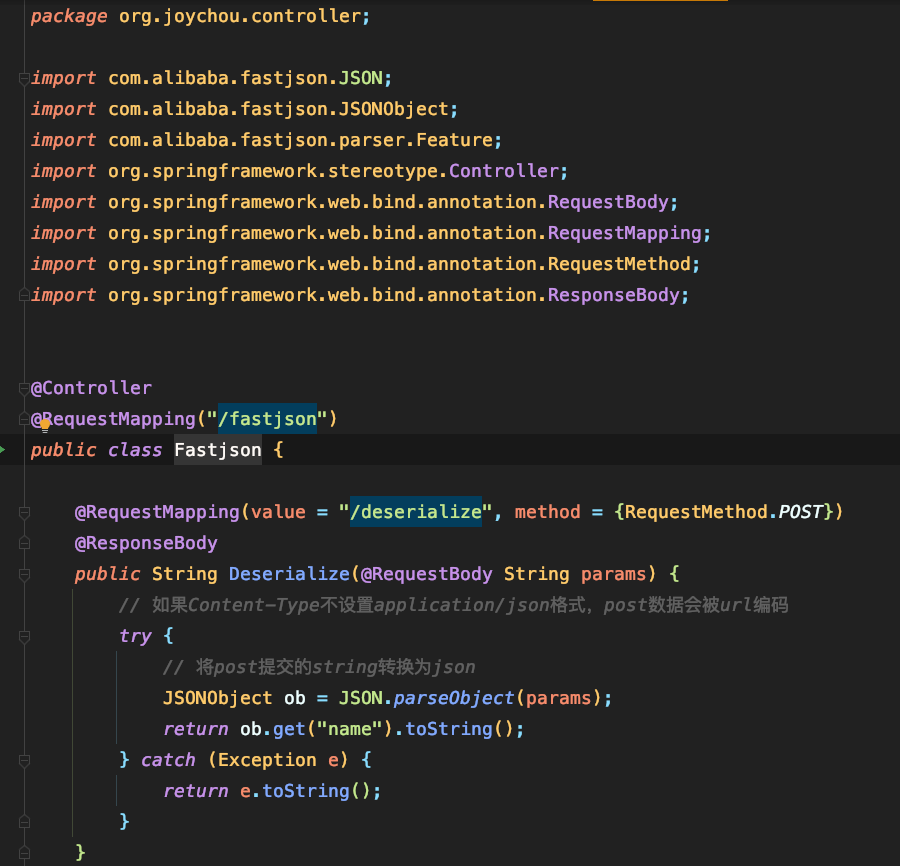
根据Method name 和 interface name 查询
比如我想查询ContentTypeHandler 的所有子类toObject方法
import java
from Method method
where method.hasName("toObject") and method.getDeclaringType().getASupertype().hasQualifiedName("org.apache.struts2.rest.handler", "ContentTypeHandler")
select method
