Cap’n Protocol简介
Cap’n Proto is an insanely fast data interchange format and capability-based RPC system.
- cap’n protocol由protobuf的主要设计者kentonv主导,等价于Proto + RPC。提供序列化/反序列化、方法调用、异步Promise流水行等主要功能。
- 特点
- 无encoding/decoding,基于内存布局的编码使得Cap’n Protocol的Structure可以直接写到磁盘上,以二进制文件的形式直接读出。这样在序列化/反序列化过程中,性能将大大提升。
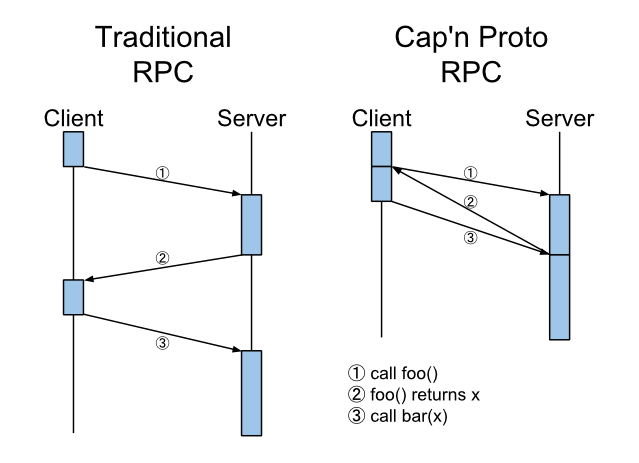
- 异步Promise PipeLine(如下图),传统RPC实现 foo + bar 调用,需要3个步骤: 调用foo,得到返回值x,调用bar(x)。Async Promise Pipelie,不需要返回X这个中间结果,而是一下将请求发送给Server端,server端只需要返回一个Promise即可。
- Four Level RPC:作者将功能划分为4个Level,从低到高分别是Object references and promise pipelining、Persistent capabilities、Three-way interactions、Reference equality / joining,目前最新版0.9.1实现了前两个(Leve1和Leve2),作者给出的公告中说再1.0.0版本将实现 Three-way interactions(三向引用)
- Capnp组件图:capnp基于kj异步框架,使用promise、rpc功能。

使用Cap’n Protocol
- 官网提供了安装及Smaple
- Ubuntu 编译安装Capnp
curl -O https://capnproto.org/capnproto-c++-0.9.1.tar.gz
tar zxf capnproto-c++-0.9.1.tar.gz
cd capnproto-c++-0.9.1
./configure
make -j6 check
sudo make install
Sample(官网)
- 接口文件calculator.capnp
@0x85150b117366d14b;
interface Calculator {
# A "simple" mathematical calculator, callable via RPC.
#
# But, to show off Cap'n Proto, we add some twists:
#
# - You can use the result from one call as the input to the next
# without a network round trip. To accomplish this, evaluate()
# returns a `Value` object wrapping the actual numeric value.
# This object may be used in a subsequent expression. With
# promise pipelining, the Value can actually be used before
# the evaluate() call that creates it returns!
#
# - You can define new functions, and then call them. This again
# shows off pipelining, but it also gives the client the
# opportunity to define a function on the client side and have
# the server call back to it.
#
# - The basic arithmetic operators are exposed as Functions, and
# you have to call getOperator() to obtain them from the server.
# This again demonstrates pipelining -- using getOperator() to
# get each operator and then using them in evaluate() still
# only takes one network round trip.
evaluate @0 (expression :Expression) -> (value :Value);
# Evaluate the given expression and return the result. The
# result is returned wrapped in a Value interface so that you
# may pass it back to the server in a pipelined request. To
# actually get the numeric value, you must call read() on the
# Value -- but again, this can be pipelined so that it incurs
# no additional latency.
struct Expression {
# A numeric expression.
union {
literal @0 :Float64;
# A literal numeric value.
previousResult @1 :Value;
# A value that was (or, will be) returned by a previous
# evaluate().
parameter @2 :UInt32;
# A parameter to the function (only valid in function bodies;
# see defFunction).
call :group {
# Call a function on a list of parameters.
function @3 :Function;
params @4 :List(Expression);
}
}
}
interface Value {
# Wraps a numeric value in an RPC object. This allows the value
# to be used in subsequent evaluate() requests without the client
# waiting for the evaluate() that returns the Value to finish.
read @0 () -> (value :Float64);
# Read back the raw numeric value.
}
defFunction @1 (paramCount :Int32, body :Expression)
-> (func :Function);
# Define a function that takes `paramCount` parameters and returns the
# evaluation of `body` after substituting these parameters.
interface Function {
# An algebraic function. Can be called directly, or can be used inside
# an Expression.
#
# A client can create a Function that runs on the server side using
# `defFunction()` or `getOperator()`. Alternatively, a client can
# implement a Function on the client side and the server will call back
# to it. However, a function defined on the client side will require a
# network round trip whenever the server needs to call it, whereas
# functions defined on the server and then passed back to it are called
# locally.
call @0 (params :List(Float64)) -> (value :Float64);
# Call the function on the given parameters.
}
getOperator @2 (op :Operator) -> (func :Function);
# Get a Function representing an arithmetic operator, which can then be
# used in Expressions.
enum Operator {
add @0;
subtract @1;
multiply @2;
divide @3;
}
}
- Clien端实现 calculator-client.c++
// Copyright (c) 2013-2014 Sandstorm Development Group, Inc. and contributors
// Licensed under the MIT License:
//
// Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
// of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
// in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
// to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
// copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
// furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
//
// The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in
// all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
//
// THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
// IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
// FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
// AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
// LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
// OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN
// THE SOFTWARE.
#include "calculator.capnp.h"
#include <capnp/ez-rpc.h>
#include <kj/debug.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <iostream>
class PowerFunction final: public Calculator::Function::Server {
// An implementation of the Function interface wrapping pow(). Note that
// we're implementing this on the client side and will pass a reference to
// the server. The server will then be able to make calls back to the client.
public:
kj::Promise<void> call(CallContext context) {
auto params = context.getParams().getParams();
KJ_REQUIRE(params.size() == 2, "Wrong number of parameters.");
context.getResults().setValue(pow(params[0], params[1]));
return kj::READY_NOW;
}
};
int main(int argc, const char* argv[]) {
if (argc != 2) {
std::cerr << "usage: " << argv[0] << " HOST:PORT\n"
"Connects to the Calculator server at the given address and "
"does some RPCs." << std::endl;
return 1;
}
capnp::EzRpcClient client(argv[1]);
Calculator::Client calculator = client.getMain<Calculator>();
// Keep an eye on `waitScope`. Whenever you see it used is a place where we
// stop and wait for the server to respond. If a line of code does not use
// `waitScope`, then it does not block!
auto& waitScope = client.getWaitScope();
{
// Make a request that just evaluates the literal value 123.
//
// What's interesting here is that evaluate() returns a "Value", which is
// another interface and therefore points back to an object living on the
// server. We then have to call read() on that object to read it.
// However, even though we are making two RPC's, this block executes in
// *one* network round trip because of promise pipelining: we do not wait
// for the first call to complete before we send the second call to the
// server.
std::cout << "Evaluating a literal... ";
std::cout.flush();
// Set up the request.
auto request = calculator.evaluateRequest();
request.getExpression().setLiteral(123);
// Send it, which returns a promise for the result (without blocking).
auto evalPromise = request.send();
// Using the promise, create a pipelined request to call read() on the
// returned object, and then send that.
auto readPromise = evalPromise.getValue().readRequest().send();
// Now that we've sent all the requests, wait for the response. Until this
// point, we haven't waited at all!
auto response = readPromise.wait(waitScope);
KJ_ASSERT(response.getValue() == 123);
std::cout << "PASS" << std::endl;
}
{
// Make a request to evaluate 123 + 45 - 67.
//
// The Calculator interface requires that we first call getOperator() to
// get the addition and subtraction functions, then call evaluate() to use
// them. But, once again, we can get both functions, call evaluate(), and
// then read() the result -- four RPCs -- in the time of *one* network
// round trip, because of promise pipelining.
std::cout << "Using add and subtract... ";
std::cout.flush();
Calculator::Function::Client add = nullptr;
Calculator::Function::Client subtract = nullptr;
{
// Get the "add" function from the server.
auto request = calculator.getOperatorRequest();
request.setOp(Calculator::Operator::ADD);
add = request.send().getFunc();
}
{
// Get the "subtract" function from the server.
auto request = calculator.getOperatorRequest();
request.setOp(Calculator::Operator::SUBTRACT);
subtract = request.send().getFunc();
}
// Build the request to evaluate 123 + 45 - 67.
auto request = calculator.evaluateRequest();
auto subtractCall = request.getExpression().initCall();
subtractCall.setFunction(subtract);
auto subtractParams = subtractCall.initParams(2);
subtractParams[1].setLiteral(67);
auto addCall = subtractParams[0].initCall();
addCall.setFunction(add);
auto addParams = addCall.initParams(2);
addParams[0].setLiteral(123);
addParams[1].setLiteral(45);
// Send the evaluate() request, read() the result, and wait for read() to
// finish.
auto evalPromise = request.send();
auto readPromise = evalPromise.getValue().readRequest().send();
auto response = readPromise.wait(waitScope);
KJ_ASSERT(response.getValue() == 101);
std::cout << "PASS" << std::endl;
}
{
// Make a request to evaluate 4 * 6, then use the result in two more
// requests that add 3 and 5.
//
// Since evaluate() returns its result wrapped in a `Value`, we can pass
// that `Value` back to the server in subsequent requests before the first
// `evaluate()` has actually returned. Thus, this example again does only
// one network round trip.
std::cout << "Pipelining eval() calls... ";
std::cout.flush();
Calculator::Function::Client add = nullptr;
Calculator::Function::Client multiply = nullptr;
{
// Get the "add" function from the server.
auto request = calculator.getOperatorRequest();
request.setOp(Calculator::Operator::ADD);
add = request.send().getFunc();
}
{
// Get the "multiply" function from the server.
auto request = calculator.getOperatorRequest();
request.setOp(Calculator::Operator::MULTIPLY);
multiply = request.send().getFunc();
}
// Build the request to evaluate 4 * 6
auto request = calculator.evaluateRequest();
auto multiplyCall = request.getExpression().initCall();
multiplyCall.setFunction(multiply);
auto multiplyParams = multiplyCall.initParams(2);
multiplyParams[0].setLiteral(4);
multiplyParams[1].setLiteral(6);
auto multiplyResult = request.send().getValue();
// Use the result in two calls that add 3 and add 5.
auto add3Request = calculator.evaluateRequest();
auto add3Call = add3Request.getExpression().initCall();
add3Call.setFunction(add);
auto add3Params = add3Call.initParams(2);
add3Params[0].setPreviousResult(multiplyResult);
add3Params[1].setLiteral(3);
auto add3Promise = add3Request.send().getValue().readRequest().send();
auto add5Request = calculator.evaluateRequest();
auto add5Call = add5Request.getExpression().initCall();
add5Call.setFunction(add);
auto add5Params = add5Call.initParams(2);
add5Params[0].setPreviousResult(multiplyResult);
add5Params[1].setLiteral(5);
auto add5Promise = add5Request.send().getValue().readRequest().send();
// Now wait for the results.
KJ_ASSERT(add3Promise.wait(waitScope).getValue() == 27);
KJ_ASSERT(add5Promise.wait(waitScope).getValue() == 29);
std::cout << "PASS" << std::endl;
}
{
// Our calculator interface supports defining functions. Here we use it
// to define two functions and then make calls to them as follows:
//
// f(x, y) = x * 100 + y
// g(x) = f(x, x + 1) * 2;
// f(12, 34)
// g(21)
//
// Once again, the whole thing takes only one network round trip.
std::cout << "Defining functions... ";
std::cout.flush();
Calculator::Function::Client add = nullptr;
Calculator::Function::Client multiply = nullptr;
Calculator::Function::Client f = nullptr;
Calculator::Function::Client g = nullptr;
{
// Get the "add" function from the server.
auto request = calculator.getOperatorRequest();
request.setOp(Calculator::Operator::ADD);
add = request.send().getFunc();
}
{
// Get the "multiply" function from the server.
auto request = calculator.getOperatorRequest();
request.setOp(Calculator::Operator::MULTIPLY);
multiply = request.send().getFunc();
}
{
// Define f.
auto request = calculator.defFunctionRequest();
request.setParamCount(2);
{
// Build the function body.
auto addCall = request.getBody().initCall();
addCall.setFunction(add);
auto addParams = addCall.initParams(2);
addParams[1].setParameter(1); // y
auto multiplyCall = addParams[0].initCall();
multiplyCall.setFunction(multiply);
auto multiplyParams = multiplyCall.initParams(2);
multiplyParams[0].setParameter(0); // x
multiplyParams[1].setLiteral(100);
}
f = request.send().getFunc();
}
{
// Define g.
auto request = calculator.defFunctionRequest();
request.setParamCount(1);
{
// Build the function body.
auto multiplyCall = request.getBody().initCall();
multiplyCall.setFunction(multiply);
auto multiplyParams = multiplyCall.initParams(2);
multiplyParams[1].setLiteral(2);
auto fCall = multiplyParams[0].initCall();
fCall.setFunction(f);
auto fParams = fCall.initParams(2);
fParams[0].setParameter(0);
auto addCall = fParams[1].initCall();
addCall.setFunction(add);
auto addParams = addCall.initParams(2);
addParams[0].setParameter(0);
addParams[1].setLiteral(1);
}
g = request.send().getFunc();
}
// OK, we've defined all our functions. Now create our eval requests.
// f(12, 34)
auto fEvalRequest = calculator.evaluateRequest();
auto fCall = fEvalRequest.initExpression().initCall();
fCall.setFunction(f);
auto fParams = fCall.initParams(2);
fParams[0].setLiteral(12);
fParams[1].setLiteral(34);
auto fEvalPromise = fEvalRequest.send().getValue().readRequest().send();
// g(21)
auto gEvalRequest = calculator.evaluateRequest();
auto gCall = gEvalRequest.initExpression().initCall();
gCall.setFunction(g);
gCall.initParams(1)[0].setLiteral(21);
auto gEvalPromise = gEvalRequest.send().getValue().readRequest().send();
// Wait for the results.
KJ_ASSERT(fEvalPromise.wait(waitScope).getValue() == 1234);
KJ_ASSERT(gEvalPromise.wait(waitScope).getValue() == 4244);
std::cout << "PASS" << std::endl;
}
{
// Make a request that will call back to a function defined locally.
//
// Specifically, we will compute 2^(4 + 5). However, exponent is not
// defined by the Calculator server. So, we'll implement the Function
// interface locally and pass it to the server for it to use when
// evaluating the expression.
//
// This example requires two network round trips to complete, because the
// server calls back to the client once before finishing. In this
// particular case, this could potentially be optimized by using a tail
// call on the server side -- see CallContext::tailCall(). However, to
// keep the example simpler, we haven't implemented this optimization in
// the sample server.
std::cout << "Using a callback... ";
std::cout.flush();
Calculator::Function::Client add = nullptr;
{
// Get the "add" function from the server.
auto request = calculator.getOperatorRequest();
request.setOp(Calculator::Operator::ADD);
add = request.send().getFunc();
}
// Build the eval request for 2^(4+5).
auto request = calculator.evaluateRequest();
auto powCall = request.getExpression().initCall();
powCall.setFunction(kj::heap<PowerFunction>());
auto powParams = powCall.initParams(2);
powParams[0].setLiteral(2);
auto addCall = powParams[1].initCall();
addCall.setFunction(add);
auto addParams = addCall.initParams(2);
addParams[0].setLiteral(4);
addParams[1].setLiteral(5);
// Send the request and wait.
auto response = request.send().getValue().readRequest()
.send().wait(waitScope);
KJ_ASSERT(response.getValue() == 512);
std::cout << "PASS" << std::endl;
}
return 0;
}
- Server端实现 calculator-server.c++
// Copyright (c) 2013-2014 Sandstorm Development Group, Inc. and contributors
// Licensed under the MIT License:
//
// Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
// of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
// in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
// to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
// copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
// furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
//
// The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in
// all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
//
// THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
// IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
// FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
// AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
// LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
// OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN
// THE SOFTWARE.
#include "calculator.capnp.h"
#include <kj/debug.h>
#include <capnp/ez-rpc.h>
#include <capnp/message.h>
#include <iostream>
typedef unsigned int uint;
kj::Promise<double> readValue(Calculator::Value::Client value) {
// Helper function to asynchronously call read() on a Calculator::Value and
// return a promise for the result. (In the future, the generated code might
// include something like this automatically.)
return value.readRequest().send()
.then([](capnp::Response<Calculator::Value::ReadResults> result) {
return result.getValue();
});
}
kj::Promise<double> evaluateImpl(
Calculator::Expression::Reader expression,
capnp::List<double>::Reader params = capnp::List<double>::Reader()) {
// Implementation of CalculatorImpl::evaluate(), also shared by
// FunctionImpl::call(). In the latter case, `params` are the parameter
// values passed to the function; in the former case, `params` is just an
// empty list.
switch (expression.which()) {
case Calculator::Expression::LITERAL:
return expression.getLiteral();
case Calculator::Expression::PREVIOUS_RESULT:
return readValue(expression.getPreviousResult());
case Calculator::Expression::PARAMETER: {
KJ_REQUIRE(expression.getParameter() < params.size(),
"Parameter index out-of-range.");
return params[expression.getParameter()];
}
case Calculator::Expression::CALL: {
auto call = expression.getCall();
auto func = call.getFunction();
// Evaluate each parameter.
kj::Array<kj::Promise<double>> paramPromises =
KJ_MAP(param, call.getParams()) {
return evaluateImpl(param, params);
};
// Join the array of promises into a promise for an array.
kj::Promise<kj::Array<double>> joinedParams =
kj::joinPromises(kj::mv(paramPromises));
// When the parameters are complete, call the function.
return joinedParams.then([KJ_CPCAP(func)](kj::Array<double>&& paramValues) mutable {
auto request = func.callRequest();
request.setParams(paramValues);
return request.send().then(
[](capnp::Response<Calculator::Function::CallResults>&& result) {
return result.getValue();
});
});
}
default:
// Throw an exception.
KJ_FAIL_REQUIRE("Unknown expression type.");
}
}
class ValueImpl final: public Calculator::Value::Server {
// Simple implementation of the Calculator.Value Cap'n Proto interface.
public:
ValueImpl(double value): value(value) {}
kj::Promise<void> read(ReadContext context) {
context.getResults().setValue(value);
return kj::READY_NOW;
}
private:
double value;
};
class FunctionImpl final: public Calculator::Function::Server {
// Implementation of the Calculator.Function Cap'n Proto interface, where the
// function is defined by a Calculator.Expression.
public:
FunctionImpl(uint paramCount, Calculator::Expression::Reader body)
: paramCount(paramCount) {
this->body.setRoot(body);
}
kj::Promise<void> call(CallContext context) {
auto params = context.getParams().getParams();
KJ_REQUIRE(params.size() == paramCount, "Wrong number of parameters.");
return evaluateImpl(body.getRoot<Calculator::Expression>(), params)
.then([KJ_CPCAP(context)](double value) mutable {
context.getResults().setValue(value);
});
}
private:
uint paramCount;
// The function's arity.
capnp::MallocMessageBuilder body;
// Stores a permanent copy of the function body.
};
class OperatorImpl final: public Calculator::Function::Server {
// Implementation of the Calculator.Function Cap'n Proto interface, wrapping
// basic binary arithmetic operators.
public:
OperatorImpl(Calculator::Operator op): op(op) {}
kj::Promise<void> call(CallContext context) {
auto params = context.getParams().getParams();
KJ_REQUIRE(params.size() == 2, "Wrong number of parameters.");
double result;
switch (op) {
case Calculator::Operator::ADD: result = params[0] + params[1]; break;
case Calculator::Operator::SUBTRACT:result = params[0] - params[1]; break;
case Calculator::Operator::MULTIPLY:result = params[0] * params[1]; break;
case Calculator::Operator::DIVIDE: result = params[0] / params[1]; break;
default:
KJ_FAIL_REQUIRE("Unknown operator.");
}
context.getResults().setValue(result);
return kj::READY_NOW;
}
private:
Calculator::Operator op;
};
class CalculatorImpl final: public Calculator::Server {
// Implementation of the Calculator Cap'n Proto interface.
public:
kj::Promise<void> evaluate(EvaluateContext context) override {
return evaluateImpl(context.getParams().getExpression())
.then([KJ_CPCAP(context)](double value) mutable {
context.getResults().setValue(kj::heap<ValueImpl>(value));
});
}
kj::Promise<void> defFunction(DefFunctionContext context) override {
auto params = context.getParams();
context.getResults().setFunc(kj::heap<FunctionImpl>(
params.getParamCount(), params.getBody()));
return kj::READY_NOW;
}
kj::Promise<void> getOperator(GetOperatorContext context) override {
context.getResults().setFunc(kj::heap<OperatorImpl>(
context.getParams().getOp()));
return kj::READY_NOW;
}
};
int main(int argc, const char* argv[]) {
if (argc != 2) {
std::cerr << "usage: " << argv[0] << " ADDRESS[:PORT]\n"
"Runs the server bound to the given address/port.\n"
"ADDRESS may be '*' to bind to all local addresses.\n"
":PORT may be omitted to choose a port automatically." << std::endl;
return 1;
}
// Set up a server.
capnp::EzRpcServer server(kj::heap<CalculatorImpl>(), argv[1]);
// Write the port number to stdout, in case it was chosen automatically.
auto& waitScope = server.getWaitScope();
uint port = server.getPort().wait(waitScope);
if (port == 0) {
// The address format "unix:/path/to/socket" opens a unix domain socket,
// in which case the port will be zero.
std::cout << "Listening on Unix socket..." << std::endl;
} else {
std::cout << "Listening on port " << port << "..." << std::endl;
}
// Run forever, accepting connections and handling requests.
kj::NEVER_DONE.wait(waitScope);
}
- 编译文件(CMakeLists.txt)
project("Cap'n Proto Samples" CXX)
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.1)
find_package(CapnProto CONFIG REQUIRED)
# Don't build the rpc sample if find_package() found an installation of Cap'n Proto lite.
if(TARGET CapnProto::capnp-rpc)
capnp_generate_cpp(calculatorSources calculatorHeaders calculator.capnp)
add_executable(calculator-client calculator-client.c++ ${calculatorSources})
add_executable(calculator-server calculator-server.c++ ${calculatorSources})
target_link_libraries(calculator-client PRIVATE CapnProto::capnp-rpc)
target_link_libraries(calculator-server PRIVATE CapnProto::capnp-rpc)
target_include_directories(calculator-client PRIVATE ${CMAKE_CURRENT_BINARY_DIR})
target_include_directories(calculator-server PRIVATE ${CMAKE_CURRENT_BINARY_DIR})
endif()
- 执行,编译后会生成 calculator-client和calculator-server两个执行文件。
#先启动Server ip:port
./calculator-server 192.168.205.100:1234
# 另起终端启动Client
./calculator-client 192.168.205.100:1234
Cap’n proto的优缺点
- 优点:
- 无encode和decode。
- 异步Promise PipeLine。
- 缺点:
- 不支持广播、组播。
- 无服务动态方法。
- 无Qos
- 无加密传输
- 没有E2E安全校验
总的来说,Capn proto实现了一套简单的Ez(easy promise base rpc),只适用于简单的点对点通信场景。但是复杂场景下的通信,比如系统状态广播这种,无法原生支持。目前版本,同系统内的进程间通信,仍然是socket通信,效率不高。并且没有服务发现功能,在跨域的通信场景下,与其他方式比如(someip)相比,目前的版本下无明显的优势。
