1.什么是RPC
RPC一般指远程过程调用。 RPC是远程过程调用(Remote Procedure Call)的缩写形式。
首先看下服务的演变过程:
- 单一应用架构 -> MVC三层架构 -> PRC分布式服务 -> 弹性计算架构
接口请求也在慢慢演变:
- TCP/IP报文协议 -> RMI(仅JAVA可用) -> WebService ->HTTP -> GPRC(Thrift,Dubbo) ->SpringRestful(路径风格)
总体而言就是随着服务的增多,也伴随着服务之间的调用频繁和繁琐,这就有了PRC这代名词。
PRC普通应用在分布式架构中,先看下分布式服务派系
- 阿里系:dubbo zookeeper nginx
- spring生态:cloud eureka gateway
RPC的核心职能,以dubbo图解为例
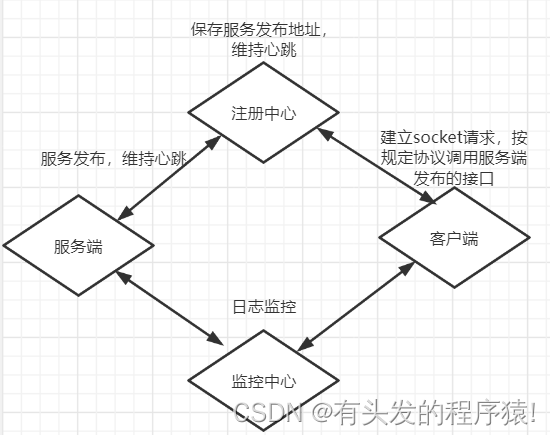
这个机制现在用的很广泛了,例如cloud中的注册中心和配置中心。
大概了解一下理论后,接下来我们用代码来实操,以便更深入的认识PRC。
2.Netty实现一个RPC
2.1 原理概述
- 客户端
1.通过bean的初始化回调判断是否需要注入动态代理
2.在动态代理回调类中使用Netty调用远程服务,并发送约定协议的消息
3.使用回调机制返回服务端响应,并返回原始类 - 服务端
1.在bean的回调判断是否为发布的服务,是的话保存在公共map中,初始化时启动Rpc服务
2.调用服务解析消息后,通过请求的service获取指定的service,通过反射调用,并将结果返回
2.2 pom.xml依赖
基于springboot 2.5.6版本,额外引入lombok和fastjson
//netty依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>io.netty</groupId>
<artifactId>netty-all</artifactId>
<version>4.1.42.Final</version>
</dependency>
2.3 api jar包
自定义注解,api目录为待发布的API接口,protocol为公用的协议和工具包
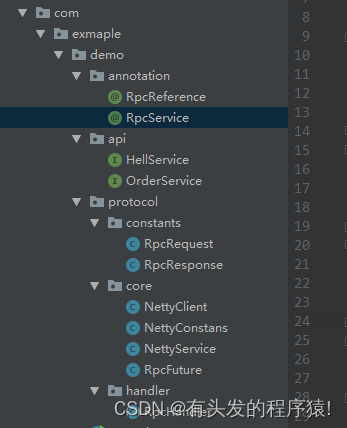
2.4. 客户端架构
2.4.1 rpc目录下为公用代码,可以单独抽离的
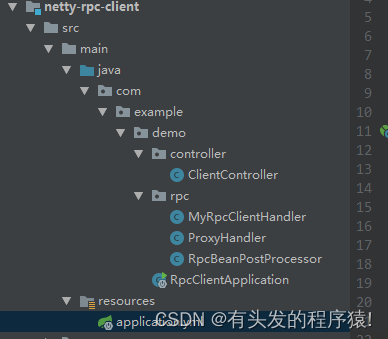
2.4.2 Controller代码
//注意这两个声明,并没有加@Autowired或@Resource
@RpcReference
HellService hellService;
@RpcReference
OrderService orderService;
@GetMapping("/hello")
public String hello(@RequestParam String orderId) {
return orderService.getOrder(orderId);
}
@GetMapping("/add")
public int add(@RequestParam Integer a, @RequestParam Integer b) {
return hellService.add(a, b);
}
PS说明:上面的两个声明没有加@Autowired或@Resource,所以spring容器在注入的时候不会处理这里两个,本文使用的是反射注入。如果想交由spring处理可以参考mybatis第九话 - 手写实现一个简单的mybatis版本中的Mapper接口注入原理
2.4.3 核心动态代理处理类RpcBeanPostProcessor
- 实现环境配置回调EnvironmentAware
//该类为初始化类之后的回调 还没到注入阶段
//因此在这里接收环境的回调,读取RPC的配置传递到代理类中
Environment environment;
//注册之前 设置坏境变量
@Override
public void setEnvironment(Environment environment) {
this.environment = environment;
}
- 实现了
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor接口,重写postProcessAfterInitialization方法
//可以在bean初始化之前后返回继承类或者代理类,aop就是典型的例子
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
Class<?> clazz = bean.getClass();
//遍历所有的声明
for (Field field : clazz.getDeclaredFields()) {
//如果包含这个注解就创建代理类,并用反射注入
if (field.isAnnotationPresent(RpcReference.class)) {
Object instance;
String beanClassName = field.getType().getName();
try {
//单例缓存
if (cacheProxyMap.containsKey(beanClassName)) {
instance = cacheProxyMap.get(beanClassName);
} else {
//根据不同的服务名称参数传递不同的rpc调用地址
RpcReference annotation = field.getAnnotation(RpcReference.class);
//生成动态代理
instance = Proxy.newProxyInstance(
field.getType().getClassLoader(),
new Class[]{field.getType()},
//可以配置注解参数以获取不同的RPC连接配置
new ProxyHandler(bean, beanClassName,
this.environment.getProperty(annotation.name() + ".rpcHost"),
Integer.valueOf(this.environment.getProperty(annotation.name() + ".rpcPort"))));
}
log.info("create proxy bean:{}", beanClassName);
//反射注入
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(bean, instance);
cacheProxyMap.put(field.getType().getName(), instance);
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
log.error("create bean error,beanClassName {}", beanClassName);
}
}
}
return bean;
}
2.4.4 动态代理调用类ProxyHandler
- invoke方法
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
//组装协议
RpcRequest request = new RpcRequest();
//设置一个唯一ID,用来回调
request.setReqId(UUID.randomUUID().toString());
request.setService(this.service);
request.setMethod(method.getName());
request.setParamterType(method.getParameterTypes());
request.setArgs(args);
//发起服务调用
NettyClient nettyClient = new NettyClient();
nettyClient.start(rpcHost, rpcPort, new MyRpcClientHandler());
//返回结果
return nettyClient.sendRequest(request);
}
2.4.5 NettyClient 公共类
- 该类不是单例的,但是保存通道和回调的Map是单例的
public Channel channel;
public void start(String host, int port, RpcHandler rpcHandler) {
String mapKey = "/" + host + ":" + port;
if (NettyConstans.clientMap.containsKey(mapKey)) {
this.channel = NettyConstans.clientMap.get(mapKey);
return;
}
NioEventLoopGroup b1 = new NioEventLoopGroup();
Bootstrap bs = new Bootstrap()
.group(b1)
.channel(NioSocketChannel.class)
.handler(new ChannelInitializer<Channel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(Channel channel) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline pipeline = channel.pipeline();
//这里偷懒就直接用string的编解码了
pipeline.addLast(new StringEncoder());
pipeline.addLast(new StringDecoder());
pipeline.addLast(rpcHandler);
}
});
try {
//客户端连接服务端
ChannelFuture future = bs.connect(host, port).sync();
future.addListener(listen -> {
if (listen.isSuccess()) {
log.info("connect rpc service success,{}:{}", host, port);
}
});
channel = future.channel();
//保存为单例
NettyConstans.clientMap.put(mapKey, channel);
} catch (Exception e) {
b1.shutdownGracefully();
log.error("connect rpc service error,{}:{}", host, port);
}
}
public Object sendRequest(RpcRequest rpcRequest) throws Exception {
//自定义一个返回结果的回调 保存到单例Map中
RpcFuture<RpcResponse> rpcFuture = new RpcFuture<>(
new DefaultPromise<RpcResponse>(new DefaultEventLoop()));
NettyConstans.rpcFutureMap.put(rpcRequest.getReqId(), rpcFuture);
//消息发送,编解码为string,所以发送的是string
channel.writeAndFlush(JSONObject.toJSONString(rpcRequest));
//实际上为阻塞等待回调 由接收消息那里回调
//其实还有一个熔断线程处理这些超时或者一直没有回调的
return rpcFuture.getPromise().get().getContent();
}
2.4.6 客户端接收消息handler
//MyRpcClientHandler
/**
* 协议 RpcResponse
*/
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, String msg) throws Exception {
log.info("RpcResponse receive msg:{}", msg);
RpcResponse response = JSONObject.parseObject(msg, RpcResponse.class);
//未知的消息直接忽略
if (response == null || !NettyConstans.rpcFutureMap.containsKey(response.getReqId())) return;
//给指定的ReqId回调
NettyConstans.rpcFutureMap.get(response.getReqId()).getPromise().setSuccess(response);
NettyConstans.rpcFutureMap.remove(response.getReqId());
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
log.error("连接出现异常,重置连接:{}", ctx.channel().remoteAddress());
//异常重连 服务端重启之类的
NettyConstans.clientMap.remove(ctx.channel().remoteAddress().toString());
}
客户端的代码基本上贴完了,比较复杂,服务端会比较简单,接下来看看服务端的代码
2.5 服务端架构
2.5.1 Rpc可以抽离共用,bean初始化后的回调
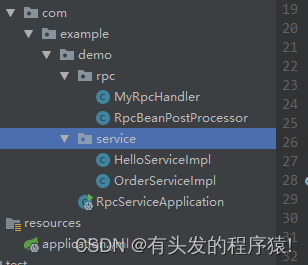
2.5.2 bean的初始化回调RpcBeanPostProcessor
static Map<String, Object> beanMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
Class<?> clazz = bean.getClass();
//只要包含该注解的就报保存到Map中
if (clazz.isAnnotationPresent(RpcService.class)) {
//存的是服务发布的接口类名称
beanMap.put(clazz.getInterfaces()[0].getName(), bean);
log.info("register rpc service:{}", clazz.getInterfaces()[0].getName());
}
return bean;
}
这里没有往注册中心上发布了,直接以本地Map的形式保存的。主要是为弄懂原理
2.5.3 NettyService初始化
//使用springboot的启动回调开始一个RPC服务
@Override
public void run(String... args) throws Exception {
//启动代码就不贴了 编解码为String
NettyService.start(port, new MyRpcHandler());
}
//自定义handler类MyRpcHandler
/**
* 协议 RpcRequest
*/
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, String msg) throws Exception {
log.info("RpcRequest receive msg:{}", msg);
RpcRequest request = JSONObject.parseObject(msg, RpcRequest.class);
if (request == null || request.getReqId() == null) return;
String service = request.getService();
Object bean = RpcBeanPostProcessor.beanMap.get(service);
//根据方法名称和参数类型获取类中的方法
Method method = bean.getClass().getMethod(request.getMethod(), request.getParamterType());
Object result = method.invoke(bean, request.getArgs());
//响应协议
RpcResponse response = new RpcResponse();
response.setReqId(request.getReqId());
response.setContent(result);
//写出 和发送同理
ctx.writeAndFlush(JSONObject.toJSONString(response));
}
3. RPC测试
分别启动客户端和服务端
3.1 客户端调用
- 控制台日志
create proxy bean:com.exmaple.demo.api.HellService
create proxy bean:com.exmaple.demo.api.OrderService
//执行http://127.0.0.1:8080/hello?orderId=1234567
connect rpc service success,127.0.0.1:18080
RpcResponse receive msg:{"content":"select order service by orderId: 1234567","reqId":"61a37ef5-6a97-4fe7-9ba9-d8c3a955c8c0"}
- 网页截图
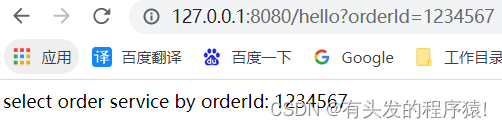
3.2 服务端调用日志
start remote service:18080
RpcRequest receive msg:{"args":["1234567"],"method":"getOrder","paramterType":["java.lang.String"],"reqId":"61a37ef5-6a97-4fe7-9ba9-d8c3a955c8c0","service":"com.exmaple.demo.api.OrderService"}
//第二次调用http://127.0.0.1:8080/add?a=4545&b=12日志
RpcRequest receive msg:{"args":[4545,12],"method":"add","paramterType":["int","int"],"reqId":"4f312678-b463-4db9-a861-d8b4b9c9fc4a","service":"com.exmaple.demo.api.HellService"}
4.总结
4.1 关于bean的回调实现
可以参考Spring源码分析第五弹 - 神级的spring还有其他什么功效?来选择合适的回调
4.1 关于反射注入
正常应该使用的是FactoryBean的方式注入的,这里只是为了搞懂原理,忽略!
4.2 关于Rpc服务地址
正常的RPC服务,会先从注册中心获取这个服务发布的地址,也就是我们配置中的地址实际上是注册中心的地址
建立连接后,应该会保持心跳,第二次调用不再重新建立连接
4.3 关于阻塞异步回调
实际上还有熔断机制,应该处理掉一直等待的回调
本内容仅供了解RPC源码,请勿做其他用途!!!
源码地址:传送门
以上就是本章的全部内容了。
上一篇:通信框架之Netty第四话 - Netty深入了解之简易群聊功能的实现
下一篇:Redis第一话 – Redis介绍以及基于Docker安装Redis
书卷多情似故人,晨昏忧乐每相亲
