1、传输层协议中有两个非常重要的协议:
- 传输控制协议TCP(Transmission Control Protocol)
- 用户数据报协议UDP(User Datagram Protocol)。
2、TCP/IP 以其两个主要协议:传输控制协议(TCP)和网络互联协议(IP)而得 名,实际上是一组协议,包括多个具有不同功能且互为关联的协议。
3、IP(Internet Protocol)协议是网络层的主要协议,支持网间互连的数据通信。
4、TCP/IP协议模型从更实用的角度出发,形成了高效的四层体系结构,即 物理链路层、IP层、传输层和应用层。
5、TCP协议(类似电话):
-
使用TCP协议前,须先建立TCP连接,形成传输数据通道
-
传输前,采用“三次握手”方式,点对点通信,是可靠的 ? TCP协议进行通信的两个应用进程:客户端、服务端。 在连接中可进行大数据量的传输
-
传输完毕,需释放已建立的连接,效率低
UDP协议(类似短信):
-
将数据、源、目的封装成数据包,不需要建立连接
-
每个数据报的大小限制在64K内
-
发送不管对方是否准备好,接收方收到也不确认,故是不可靠的
-
可以广播发送
-
发送数据结束时无需释放资源,开销小,速度快
6、TCP三次握手(引自b站尚硅谷java零基础):
(三次握手是建立连接的时候)
客户端向服务端第一次握手表示,服务端知道客户端发送数据
服务端向客户端第二次握手表示,客户端知道(服务端知道客户端发送数据)
客户端向服务端第三次握手表示,服务端知道(客户端知道(服务端知道客户端发送数据))
7、TCP四次挥手(引自b站尚硅谷java零基础):
(四次挥手是断开连接的时候)
客户端向服务端第一次挥手表示,服务端收到客户端的断开网络连接通知
服务端向客户端第二次挥手表示,服务端发送报文给客户端,(我知道你要断开连接了)
服务端向客户端第三次挥手表示,服务端发送报文给客户端,(我已经断开连接)
客户端向服务端第四次挥手表示,客户端发送报文给服务端,(测试是否断开连接)
示例代码01:
public class TcpTest01 {
//客户端(模拟客户端向服务端发送数据,服务端接受并在控制台展示出来)
@Test
public void client() throws Exception{
//定义网络Ip
InetAddress inet1 = InetAddress.getByName("127.0.0.1");
//创建网络连接对象
Socket socket = new Socket(inet1,8899);
//获取输出流,写入数据
OutputStream os = socket.getOutputStream();
//写数据
os.write("我是客户端的工作人员,你好!".getBytes());
//流关闭
os.close();
socket.close();
}
//服务端
@Test
public void server() throws Exception{
//创建服务端网络连接对象
ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket(8899);
//调用accept()表示接收来自于客户端的socket
Socket socket = ss.accept();
//获取输入流读取数据
InputStream is = socket.getInputStream();
//创建安全的输出流对象
ByteArrayOutputStream bos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
byte[] bytes = new byte[5];
int readConut =0;
while ((readConut = is.read(bytes)) != -1) {
bos.write(bytes,0,readConut);
}
System.out.println(bos.toString());
System.out.println("收到了来自于:" + socket.getInetAddress().getHostAddress() + "的数据");
//流关闭
bos.close();
is.close();
socket.close();
ss.close();
}
}
运行结果:
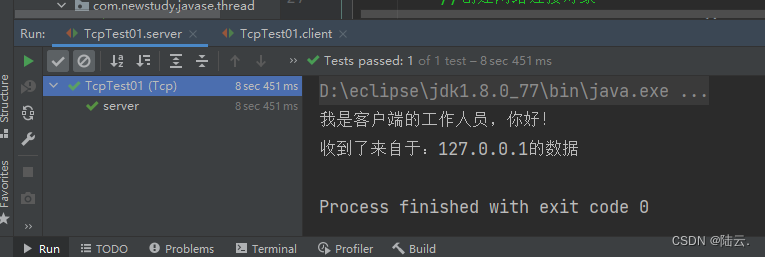
客户端发送文件给服务端,服务端将文件保存在本地。
示例代码02:
public class TcpTest02 {
@Test
public void client() throws Exception {
Socket socket = new Socket(InetAddress.getByName("127.0.0.1"), 8899);
InputStream ins = socket.getInputStream();
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("008-哈希表或者散列表数据结构.png");
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024 * 1024];
int readCount = 0;
while((readCount = ins.read()) != -1){
fos.write(bytes,0,readCount);
}
fos.close();
ins.close();
socket.close();
}
@Test
public void server() throws Exception {
ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket(8899);
Socket socket = ss.accept();
OutputStream oos = socket.getOutputStream();
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("008-哈希表或者散列表数据结构.png");
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024 * 1024];
int readCount = 0;
while((readCount = fis.read()) != -1){
oos.write(bytes,0,readCount);
}
fis.close();
oos.close();
socket.close();
ss.close();
}
}
运行结果:
从客户端发送文件给服务端,服务端保存到本地。并返回“发送成功”给 客户端。并关闭相应的连接。
示例代码03:
public class TcpTest03 {
@Test
public void client() throws IOException {
Socket socket = new Socket(InetAddress.getByName("127.0.0.1"),9090);
OutputStream os = socket.getOutputStream();
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(new File("008-哈希表或者散列表数据结构.png"));
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int len;
while((len = fis.read(buffer)) != -1){
os.write(buffer,0,len);
}
//关闭数据的输出
socket.shutdownOutput();
//接收来自于服务器端的数据,并显示到控制台上
InputStream is = socket.getInputStream();
ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
byte[] bufferr = new byte[20];
int len1;
while((len1 = is.read(buffer)) != -1){
baos.write(buffer,0,len1);
}
System.out.println(baos.toString());
//6.
fis.close();
os.close();
socket.close();
baos.close();
}
@Test
public void server() throws IOException {
ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket(9090);
Socket socket = ss.accept();
InputStream is = socket.getInputStream();
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(new File("008-哈希表或者散列表数据结构.png"));
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int len;
while((len = is.read(buffer)) != -1){
fos.write(buffer,0,len);
}
System.out.println("图片传输完成");
//服务器端给予客户端反馈
OutputStream os = socket.getOutputStream();
os.write("你好,美女,照片我已收到,非常漂亮!".getBytes());
fos.close();
is.close();
socket.close();
ss.close();
os.close();
}
}
运行结果:
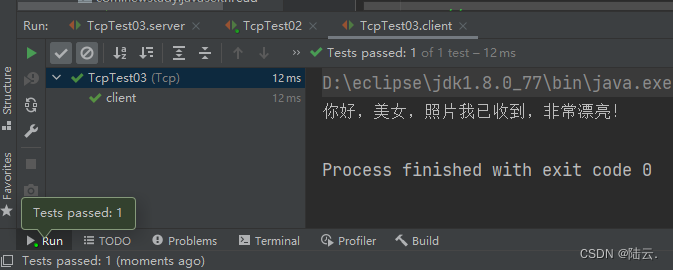
使用UDP协议客户端发送信息给服务端,服务端将数据显示在控制台上
示例代码04:
public class UdpTest01 {
//发送端
@Test
public void sender() throws IOException {
DatagramSocket socket = new DatagramSocket();
String str = "我是UDP方式发送的导弹";
byte[] data = str.getBytes();
InetAddress inet = InetAddress.getLocalHost();
DatagramPacket packet = new DatagramPacket(data,0,data.length,inet,9090);
socket.send(packet);
socket.close();
}
//接收端
@Test
public void receiver() throws IOException {
DatagramSocket socket = new DatagramSocket(9090);
byte[] buffer = new byte[100];
DatagramPacket packet = new DatagramPacket(buffer,0,buffer.length);
socket.receive(packet);
System.out.println(new String(packet.getData(),0,packet.getLength()));
socket.close();
}
}