cube工程和生成的代码上区别
1,选择systick

Keil:
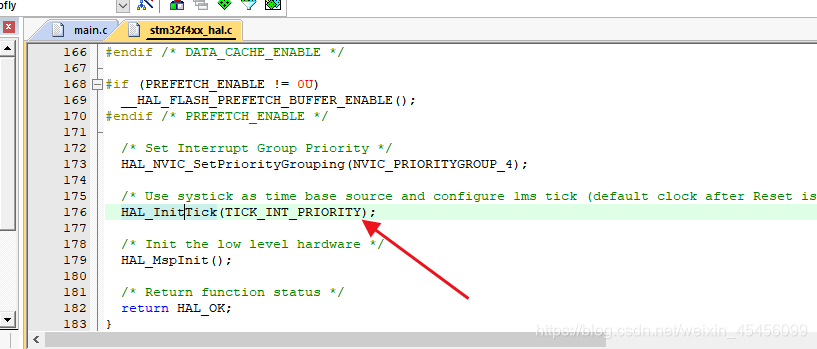
此时,中断优先级的抢占优先级是最低级的15,子优先级是0(分组4)
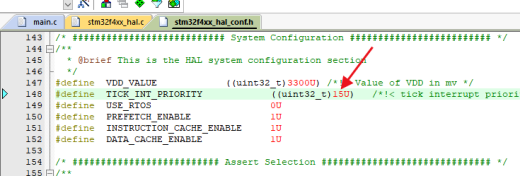
只有带__weak 的 HAL_InitTick
2,选择某一定时器:TIM1
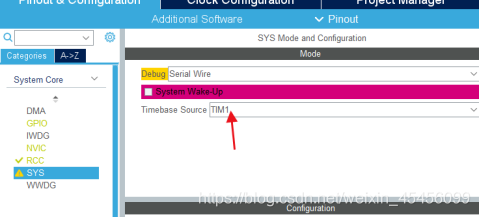
Keil:
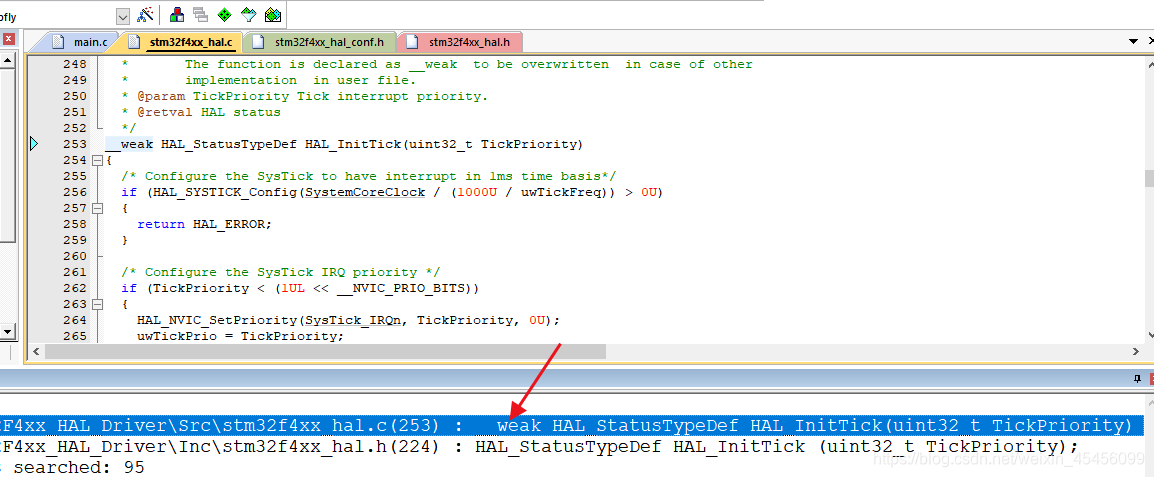
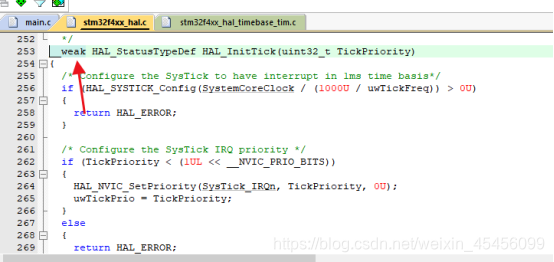
有带__weak 的 HAL_InitTick,被overwrite
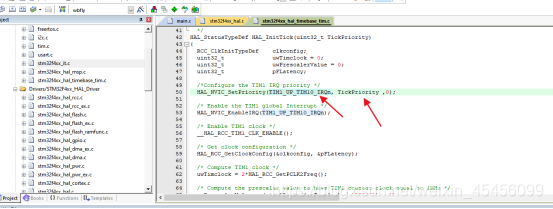
也有真正被调用的HAL_InitTick
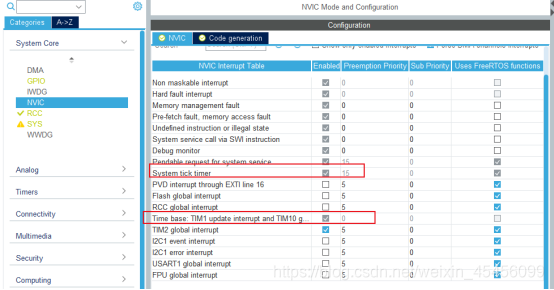
此时,中断优先级的抢占优先级是最高级的0,子优先级是0(分组4)

定时器选择TIM6或TIM7比较好

基本定时器(TIM6,TIM7)的主要功能: 只有最基本的定时功能。基本定时器TIM6和TIM7各包含一个16位自动装载计数器,由各自的可编程预分频器驱动。
通用定时器(TIM2~TIM5)的主要功能: 除了基本的定时器的功能外,还具有测量输入信号的脉冲长度( 输入捕获) 或者产生输出波形( 输出比较和PWM)。
高级定时器(TIM1,TIM8)的主要功能: 高级定时器不但具有基本,通用定时器的所有的功能,还具有控制交直流电动机所有的功能,你比如它可以输出6路互补带死区的信号,刹车功能等等。


__weak void HAL_Delay(uint32_t Delay)
{
uint32_t tickstart = HAL_GetTick();
uint32_t wait = Delay;
/* Add a freq to guarantee minimum wait */
if (wait < HAL_MAX_DELAY)
{
wait += (uint32_t)(uwTickFreq);
}
while((HAL_GetTick() - tickstart) < wait)
{
}
}
总结:systick作为操作系统时基钟,好处是方便移植,操作系统需要的是一个时基,systick又是属于内核外设(24位的倒计时定时器,也有中断服务函数,中断优先级通过设置内核寄存器SHPR3,可以设置的最低优先级为15),移植到任意的相同内核的都能使用,不需要再做修改。不好的地方就是,比如有中断服务函数中调用HAL_delay()来延时,它是通过while来判断是否达到时间,但是每次得到一个节拍数,和前面的对比不变,由于其中断优先级比systick(看上面的图片可知优先级是15)高,抢占中断,导致systick的中断服务函数无法工作(它的工作就是递减,减小tick),没“人”减小tick,而HAL_delay()又在等tick减少,又是它自己导致tick不能减少,OS调度也在等,这样就崩了,一般也不在中断中搞延时,中断都是为了尽快的执行完,实时操作系统也更加要求快速。
而使用一个基本定时器来提供时基,定时器优先级设置为最高优先级(看上面的图片可知优先级是0),其他中断也无法抢占,不会影响systick工作,操作系统又得到了一个时基,不好的地方是,移植代码,需要找个相同的定时器来使用,如果被占用,还得选择其他定时器
综上,systick偏向公用,定时器偏向专用

NVIC_SetPriority (SysTick_IRQn, (1UL << __NVIC_PRIO_BITS) - 1UL);
其中宏__NVIC_PRIO_BITS为4,
其他参考资料:
void SysTick_Handler(void)
{
if(xTaskGetSchedulerState()!=taskSCHEDULER_NOT_STARTED)//系统已经运行
{
xPortSysTickHandler();
}
}
sysTick属于内核外设,跟普通外设的中断优先级有些区别,并没有抢占优先级和子优先级的说法,在STM32F429中,内核外设的中断优先级由内核SCB这个外设的寄存器:SHPRx(x=1.2.3)来配置。
内核外设的中断优先级可编程为:0~15,只有16个可编程优先级,数值越小,优先级越高。如果软件优先级配置相同,那就根据他们在中断向量表里面的位置编号来决定优先级大小,编号越小,优先级越高。
SysTick定时器的计数器是向下递减计数的,计数一次的时间TDEC=1/CLKAHB,当重装载寄存器中的值VALUELOAD减到0的时候,产生中断,可知中断一次的时间TINT=VALUELOAD * TDEC中断= VALUELOAD/CLKAHB
NVIC的中断优先级分组不仅对片上外设有效,同样对内核的外设也有效。我们把systick的优先级15转换成二进制值就是1111(0b),又因为NVIC的优先级分组2,那么前两位的11(0b)就是3,后两位的11(0b)也是3。无论从抢占还是子优先级都比我们设定的外设的优先级低。如果当两个的软件优先级都配置成一样,那么就比较他们在中断向量表中的硬件编号,编号越小,优先级越高
systick虽然作为与CPU紧耦合的内核外设,但其中断优先级并不比普通外设要高,并不因为它是内核外设而特殊,它还是遵循中断优先级高低的规则来响应。
NVIC_SetPriority (SysTick_IRQn, (1<<__NVIC_PRIO_BITS) - 1); /* set Priority for Cortex-M0 System Interrupts */
延时;
void SysTick_us(uint32_t us)
{
uint32_t us_tick=SystemCoreClock / 1000000UL;;
uint32_t start_val,real_val,JianGe;
start_val=SysTick->VAL; //把最开始获得的计数值作为基准值
do{
real_val=SysTick->VAL; //获取当前值
if(start_val>real_val) //应对计时器提前下溢
{
JianGe=start_val-real_val;
}
else
{
JianGe=SysTick->LOAD+start_val-real_val;
}
}while(JianGe<us*us_tick); //判断是否到达间隔
}
void rt_hw_us_delay(rt_uint32_t us)
{
rt_uint32_t start, now, delta, reload, us_tick;
start = SysTick->VAL;
reload = SysTick->LOAD;
us_tick = SystemCoreClock / 1000000UL;
do {
now = SysTick->VAL;
delta = start > now ? start - now : reload + start - now;
} while(delta < us_tick * us);
}
其他区别:
111