Ansible --自动化运维
安装、概念、playbook、ad-hoc并行命令、anaible核心模块
维护企业服务器基础环境,服务器较少的话不太适用
ansible简介
是新出现的自动化运维工具,基于Python开发,集合了众多运维工具的优点(像puppet、cfengine、chef、func、fabric)的优点,实现了批量系统配置、程序部署、批量运行命令等功能。
两种:1.playbook剧本
2. ad-hoc并行命令
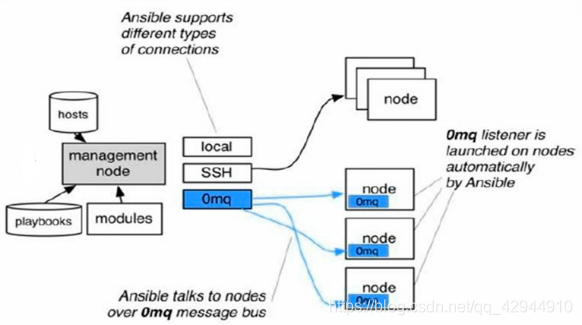
工作原理
ansible通过ssh来实现的
node节点(服务器),对这些节点进行统一的配置操作,通过ansible服务器作为管理节点(management node),使用一台centos7的操作系统来部署一款ansible软件,对node进行远程控制,ansible它不需要安装客户端,那怎么进行管理呢?(就是目标主机们什么都不用装),它会通过ssh来进行通信。0mq是当我们所管理的服务器特别多的时候,会安装消息队列程序,通过消息队列把数据进行中转(关于什么是消息队列,怎么用消息队列,这个以后会有,不过一般用不着,可以先忽略图里的0mq),hosts–主机列表,对主机进行定义和分组,方便操控,modules–模块,如用户模块–这些服务器创建某用户,当任务复杂时,可以使用剧本调用模块进行编排。
- ansible如何跟别的机器连接?------ssh
- ansible如果面对了高并发,怎么对应客户主机呢,当发送的信号拥塞,延迟丢包的时候,怎么办呢?-----消息队列
- ansible如何更好的管理计算机集群呢?—定义主机群—主机组。
install 部署
1.dns域名解析
2.服务端安装ansible
前期准备:纯洁的机器2~5台,centos 7 操作系统,(测试内存不需要很大,1G就够了)
3.一台服务器做为主服务器ip、yum源配好,防火墙selinux都关了,别的都是客户端
1. 先在ansible客户机上hosts文件里加上客户端的ip解析
vim /etc/hosts
192.168.230.110 ansbile
192.168.230.111 host1
192.168.230.112 host2
192.168.230.113 host3
192.168.230.114 host4
2. 完成后进行测试,ping一下,看看都通不通
3. 客户机无需配置
4. 安装ansible
#yum install -y epel-release #####yum源配置过了就不需要这一步了
yum install -y ansible
5. 安装完成后,检查一下看看是不是装上了,使用以下命令(这部只是为了测试一下ansible是不是安装了)
rpm -ql ansible ##列出ansible所有文件,有的话说明你的ansible安装完成了
rpm -qc ansible ##查看配置文件
ansible --help ##查看ansible帮助
ansible-doc -l ##查看ansible模块手册,查看所有模块及作用,市面上常见厂商的都支持。(A10,华为,docker,EC2,aws等等广大厂商设备)
ansible-doc -s yum ##具体到某一个模块的手册,查看yum模块,了解其功能
ssh-key免密登录(这个前面有写过)
详细看这里:免密登录
客户端的免密配不配置都可以,免密后安全性会差点,这里使用host1做免密,其他的不做,进行实验
ansible基础
定义主机清单
vim /etc/ansible/hosts
#在文档最后添加,由于hosts文件中已经定义过主机名了,所以这里不需要写入麻烦的ip了
host1
host2
host3
host4
##注意没有加入主机清单的服务器无法进行下面的操作。
*** 测试连通性***
ansible localhost -m ping
#ansible命令 + 测谁,测主机localhost + -m测试的模块 +什么模块--ping模块
(绿色成功)
##测试host1也可以:
ansible host1 -m ping
##这里会进入远程登录模式,输入yes直接进入,不需要输入密码(因为前面做免密了)绿色成功,"ping":"pong"
##测试别的会不可达,为什么呢?因为没有设置免密。那怎么对没有做免密的机器进行设置呢?
简洁输出
ansible host1 -m ping -o
## -o参数代表简洁输出,显示一行输出。看着简洁。
已知主机know_hosts
ansible host2 -m ping
##注意这台主机没有免密
出现红色,失败
|
|
\/
ansible host2 -m ping -o -u root -k
#提示输入密码。输入后成功。
# 也就是说,做了免密的主机与没有做免密的主机,只需要多加两个参数,-u -k
# 会询问你是否连接,下面去掉这个询问
vim /etc/ssh/ssh_config
StrictHostKeyChecking no
systemctl restart sshd ##重启生效
##注意ping和ssh
ping是基于ICMP网际消息管理协议
关闭主机hosts的sshd进程可以ping通不能使用ansible进行连通性测试,它会失败
主要就是因为ansible的ping模块主要是测试ssh程序是否连接的,而不是icmp协议。
Inventory主机清单
官网:https://docs.ansible.com/
vim /etc/ansible/hosts 里的主机可以被ansible操控,没有定义的不能被操作,这里详细阐述以下关于主机清单。
- 增加主机组(下面只是一个例子)
[webserver]
host1
host2
[mysql]
host3
host4
ansible webserver -m ping -o
##没有做免密的会显示失败。
- 增加用户名密码的变量
[webserver]
host[1:2] ansible_ssh_user='root' ansible_ssh_pass='66666'
[mysql]
host3 ansible_ssh_user='root' ansible_ssh_pass='88888'
host4 ansible_ssh_user='root' ansible_ssh_pass='99999'
ansible webserver -m ping -o
##绿色成功
- 增加端口,正常登录的端口应该是22端口
修改host1的端口,进入host1服务器里,vim /etc/ssh/sshd_config 文件修改端口号为2222
然后到ansible主机里修改
[webserver]
host1 ansible_ssh_user='root' ansible_ssh_pass='66666' ansible_ssh_port='2222'
host2 ansible_ssh_user='root' ansible_ssh_pass='66666'
[mysql]
host3 ansible_ssh_user='root' ansible_ssh_pass='88888'
host4 ansible_ssh_user='root' ansible_ssh_pass='99999'
- 组变量 vars -----帮助我们简化主机清单
(信息不一样就要独立定义。)
vim /etc/ansible/hosts
[webserver]
host[1:4]
[webserver:vars]
ansible_ssh_user='root'
ansible_ssh_pass='66666'
ansible_ssh_port='22'
测试:ansible webserver -m ping -o
常用变量:
ansible_ssh_host='192.168.230.222'
ansible_ssh_user='root'
ansible_ssh_port='22'
ansible_ssh_pass='pass'
ansible_sudo='www'
ansible_sudo_pass='pass'
ansible_sudo_exe=/usr/bin/sudo
ansible_connection=local
ansible_ssh_private_key_file=/root/key
ansible_ssh_shell_type=bash
ansible_phton_interpreter=/usr/bin/python3.2
ansible_*_interpreter=/usr/bin/ruby
- 子分组children
将不同的分组进行组合
vim /etc/ansible/hosts
[apache]
host[1:2]
[nginx]
host[3:4]
[webserver:children]
#webserver组包括的子分组children包括apache组和nginx组
apache
nginx
[webserver:vars]
ansible_ssh_user='root'
ansible_ssh_pass='66666'
ansible_ssh_port='22'
测试:ansible webserver -m ping -o
- 自定义主机列表
vim /etc/ansible/hosts
[dockers]
host1
host2
[dockers:vars]
ansible_ssh_user='root'
ansible_ssh_pass='66666'
测试:ansible -i hostlist dockers -m ping -o
## -i 链接外部主机清单 hostlist
Ad-Hoc-点对点模式(划重点。这个不学好,下边一脸懵)
在ansible中快速执行的单条命令,并且不需要保存的命令(没有记录),对于复杂的命令则为playbook(重点)
- 复制模块 copy
ansible-doc copy #copy模块的使用文档
ansible webserver -m copy -a 'src=/etc/hosts dest=/tmp/2.txt owner=xiaoyi group=bin mode=700'
##管理webserver的服务器,调用copy模块,-a(属性)拷贝什么文件+'src(source资源的意思)=在哪 dest=(destination目的地的意思)存放位置 指定用户属主和属组 和以及权限 ' 。
## 提示"changed" : true黄色字体
ansible webserver -m copy -a 'src=/etc/hosts dest=/tmp/2.txt owner=xiaoyi group=bin mode=700'
##提示"changed" : false 绿色字体
ansible webserver -m copy -a 'src=/etc/hosts dest=/tmp/2.txt owner=xiaoyi group=bin mode=700 backup=yes'
## backup=yes 不覆盖前面的文件
- 用户模块user
- 创建用户
看一下手册:ansible-doc user
##创建用户
ansible webserver -m user -a 'name=xiaoer state=present'
##创建了一个xiaoer的用户,state(状态)=present(创建)
##change :true,一些属性就被列出来了。
[root@localhost ~]# ansible webserver -m user -a 'name=xiaoer state=present'
host1 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": true, ##已改变
"comment": "", ##
"create_home": true, ##创建家目录成功
"group": 1001, ##组为1001
"home": "/home/xiaoer", ##家目录为/home/xiaoer
"name": "xiaoer", ##用户名为xiaoer
"shell": "/bin/bash", ##用/bin/bash执行脚本
"state": "present", ##状态:创建
"system": false, ##不是系统用户
"uid": 1001 ##uid为1001
}
##可以检查一下别的服务器有没有这个用户
- 修改密码
3. 生成密码
echo "1234567" | openssl passwd -1 -stdin
##echo一个密码 openssl加密管道 ,加密什么,加密passwd -1是密码的类型(还有-2 -3 -4 -5 -6)-stdin标准输入输出,不等会话,直接输出
4. 修改密码
#通过ansible指令给目标主机改密码
ansible webserver -m user -a 'name=xiaoer password="上面的密钥"'
- 修改shell
ansible webserver -m user -a 'name=xiaoer shell=/sbin/nologin append=yes'
##在属性-a里添加 shall指定路径 和 append=yes 追加修改的意思
在目标计算机上看看有没有发生变化 tail -1 /etc/passwd
- 删除用户
ansible webserver -m user -a 'name=xiaoer state=absent'
##state状态 absent删除状态。
- 软件包管理yum
ansible-doc yum
#注意:examples里的内容,使用的时候进行阅读
#升级所有包的命令:yum updata * (慎用,慢)
ansible host1 -m yum -a 'name="*" state=latest' #升级host1所有包,测试环境慎用,浪费时间。
ansible webserver -m yum -a 'name="httpd" state=latest'
##下面呈现的内容,就是软件包升级的一堆过程。
##到目标机上看一下httpd是不是真的安装了,验证一下
##删除文件包。把状态改一下就可以了。
ansible webserver -m yum -a 'name="httpd" state=absent'
- 服务模块service
ansible webserver -m service -a 'name="httpd" state=started'
##批量启动httpd服务
ansible webserver -m service -a 'name="httpd" state=started enabled=yes'
##批量启动httpd服务,并开机自启
ansible webserver -m service -a 'name="httpd" state=stopped'
##停止服务
ansible webserver -m service -a 'name="httpd" state=restarted‘
##重启服务
ansible webserver -m service -a 'name="httpd" state=started enabled=no‘
##开机禁用启用
- 文件模块file
ansible-doc file
ansible webserver -m file -a 'path=/tmp/1.txt mode=771 state=touch'
##创建一个权限为771的1.txt在/tmp目录下。path路径,mode权限 state状态
ansible webserver -m file -a 'path=/tmp/888 mode=771 state=directory'
##dirctory目录 创建一个888的目录权限为771
- 收集模块setup
ansible-doc setup
ansible host1 -m setup
##搜集host1的各种信息(n多)
ansible host1 -m setup -a 'filter=ansible_all_ipv4_addresses'
##filter过滤 加上某一段关键字"ansible_all_ipv4_addresses" :
- shell模块
万能的模块,其实就是之前敲的shell命令
ansible-doc shell
ansible webserver -m shell -a 'hostname' -o
## -o 简洁执行
ansible webserver -m shell -a 'hostname' -o -f 2
## -f 指定线程数,意思是让目的地址开放几个进程来为主机群发,加快任务的完成,(此参数注意设备配置。)
ansible webserver -m shell -a 'yum -y install httpd' -o
##执行安装httpd服务的命令
ansible webserver -m shell -a 'yum -y install mariadb-server' -o
##批量安装mariadb服务端
ansible webserver -m shell -a 'df -Th' -o
YAML非标记语言
编写剧本playbook
完成web部署,配置,启动的全过程
#准备工作:清理环境。
ansible all -m yum -a 'name=httpd state=removed' -o
#在ansible服务器上安装httpd
yum -y install httpd
mkdir apache
cd apache
cp -rf /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf .
grep '^Listen' httpd.conf
#默认80
vim http.conf
#修改端口号为8080
vim apache.yaml
- hosts: webserver #主机组
tasks: #任务
- name: install apache packages #起的名字
yum: name=httpd state=present #运用的模块和命令,安装httpd服务
- name: copy apache conf
copy: src=./httpd.conf dest=/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
- name: ensure appache is running
service: name=httpd state=started enable=yes
########################################
ansible-playbook apache.yaml --syntax-check #检查语法错误
ansible-playbook apache.yaml --list-tasks #列出任务
ansible-playbook apache.yaml --list-hosts #列出主机
ansible-playbook apache.yaml #执行这个文件。
#######################################
handlers触发模块
因果判断机制
handlers
运行条件,当某条件执行成功时,才会去触发另外一个模块。
::::先决条件:如果配置文件发生变化::::::
1.定义处理程序
handlers:
- name: restart apache service service: name=httpd state=restarted
vim apache.yaml
- hosts: webserver #主机组
tasks: #任务
- name: install apache packages #起的名字
yum: name=httpd state=present #运用的模块和命令,安装httpd服务
- name: copy apache conf
copy: src=./httpd.conf dest=/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
notify: restart apache service
- name: ensure appache is running
service: name=httpd state=started enable=yes
handlers:
- name: restart apache service
service: name=httpd state=restarted
2.引用处理程序 notify: restart apache service
role-角色扮演(剧本编写,超级重要哦)
roles时ansible中,playbooks的目录组织结构,将代码或文件进行模块化,成为roles的文件目录组织结构,易读、代码可重用,层次清晰。
:通过role远程部署nginx并配置。
- 目录结构----tree roles/
#创建目录
mkdir roles/nginx/{files,handlers,tasks,templates,vars} -p
#创建文件
touch roles/site.yaml roles/nginx/{handlers,tasks,vars}/main.yaml
#查看目录结构
tree roles/
roles/
├── nginx #角色名
│ ├── files #普通文件
│ ├── handlers #触发器程序
│ │ └── main.yaml
│ ├── tasks #主任务
│ │ └── main.yaml
│ ├── templates #金甲模板(有变量的文件)
│ └── vars #自定义变量
│ └── main.yaml
└── site.yaml
6 directories, 4 files
#创建完毕!
#echo一个界面
echo 1234 > roles/nginx/files/index.html
##把nginx的配置文件放到roles里,当然要先安装nginx
yum install -y nginx && cp /etc/nginx/nginx.conf roles/nginx/templates/nginx.conf.j2
tree roles/
roles/
├── nginx #角色名
│ ├── files #普通文件
│ │ └── index.html
│ ├── handlers #触发器程序
│ │ └── main.yaml
│ ├── tasks #主任务
│ │ └── main.yaml
│ ├── templates #金甲模板(有变量的文件)
│ │ └── nginx.conf.j2
│ └── vars #自定义变量
│ └── main.yaml
└── site.yaml
6 directories, 6 files
######
#######编写任务tasks(#注释的东西写的时候要删掉哦)
#####
vim roles/nginx/tasks/main.yaml
---
- name: install epel-release packge
yum: name=epel-release state=latest
#安装扩展源
- name: install nginx packge
yum: name=nginx state=latest
#安装nginx
- name: copy index.html
copy: src=index.html dest=/usr/share/nginx/html/index.html
#正常情况下,index.html跟本文件夹不在同一个路径,应该加上路径,这里没有添加路径是因为在同一个剧本里。路径省了,文件名没省。
- name: copy nginx.conf template
template: src=nginx.conf.j2 dest=/etc/nginx/nginx.conf
notify: restart nginx
#notify通知,restart模块是一个触发机关,只有拷贝了文件才触发,这里还没有写入触发模块handlers。
- name: make sure nginx service running
service: name=nginx state=started enabled=yes
#开启nginx服务,并且开机启动。
#######
#######准备配置文件,准备一个即将要拷贝的金甲文件,什么是金甲模板文件,就是带变量的。
#######金甲模板中允许写变量,别的模板不允许
#######
vim roles/nginx/templates/nginx.j2
worker_processes {{ ansible_processor_cores }};
## ansible_processor_cores是一个ansible的内置变量,ansible处理器的核心数量。
##它能够调用具体的cpu数量,拷贝完文件后(把变量改成数了),把cpu具体数量写在这里。这里是写成固定的数字还是不固定的数字?既不能 写固定的,也不能写auto自动。
##写几比较合适呢?这要ansible的内置变量自己查,几个cpu写几。
## 原句是:worker_processes auto;
worker_connections {{ worker_connections }};
## worker_connerctions 连接数 这个变量ansible里没有这个变量,需要自创,当然金甲模板中允许插入ansible中已有变量,也允许插入自定义变量。
######
#####编写变量
######
vim roles/nginx/vars/main.yaml
worker_connections: 10240
#####
#####编写处理程序
#####
vim roles/nginx/handlers/main.yaml
---
- name: restart nginx
service: name=nginx state=restarted
##保存退出。
######
#####编写剧本
#######
vim roles/site.yaml
- hosts: webserver
roles:
- nginx #文件夹叫什么,这里的剧本任务就写什么。
##实施
进入到剧本roles
cd roles #进入roles目录
ansible-playbook site.yaml --syntax-check #检查剧本语法
ansible-playbook site.yaml #执行剧本
##验证
看看host1服务有没有起。查看nginx的配置文件,之前改的变量,会变成数字。可以查看 一下昂。
ansible生产场景
会有一个角色roles文件夹,里面会有多个角色。每个角色又有属于自己的剧本。
一些作业
1.DELL的一款服务器的价格、型号、配置(CPU,内存、硬盘、支持的RAID功能)
2.HP常见一款服务器的价格、型号、配置(CPU,内存、硬盘、支持的RAID功能)
3.列举三款不同硬盘品牌,型号,接口类型、速率、价格。
4.什么是服务器托管。服务器托管收费的标准是什么?列举一家北京服务器托管商的信息。如:厂商名称、托管的标准和价格、地理位置等信息。
5.一年一万元人民币,能购买什么规格的阿里云服务器?(请从地理位置,CPU,mem,network,带宽方面说明。)
6.列举五款主流的域名后缀名称和含义。(如:.com 商业组织)列举三家国内域名服务商。
7.什么是CDN技术。列出三家国内的CDN服务商名称,举例说明一种CDN收费标准。
- 如何在ansible中,使用不同的用户登录不同的主机?
9.如何加密hosts主机清单文件
10.使用ansible制作一个剧本,判断主机地址为10.18.46.37的主机。关闭该主机