一、rsync是什么?
rsync是Linux系统下的开源的快速的数据镜像备份工具,从软件的命名上就可以看出来了——remote sync。它的特性如下:
- 可以镜像保存整个目录树和文件系统。
- 可以很容易做到保持原来文件的权限、时间、软硬链接等等。
- 无须特殊权限即可安装。
- 优化的流程,文件传输效率高。
- 可以使用rcp、ssh等方式来传输文件,当然也可以通过直接的socket连接。
- 支持匿名传输。
二、rsync相关服务部署
配置rsync源的基本思路
建立rsyncd.conf配置文件、独立的账号文件
启用rsync的–daemon模式应用示例 用户backuper,允许下行同步 操作的目录为/var/www/html/
1、部署rsync原服务器
rpm -q rsync #一般系统已默认安装rsync
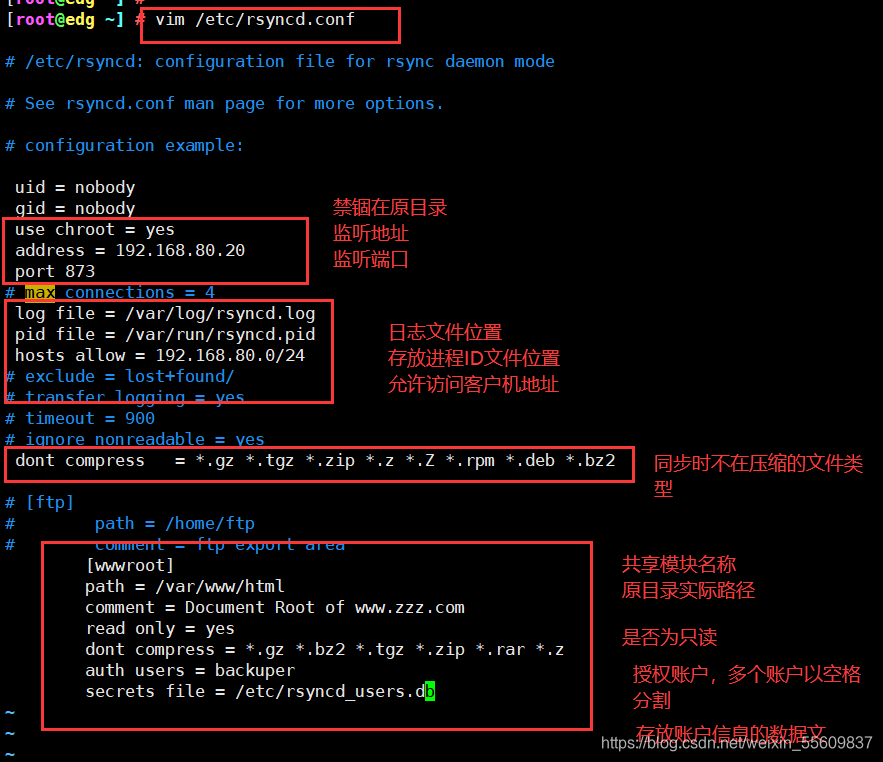
#建立/etc/rsyncd.conf 配置文件
vim /etc/rsyncd.conf #添加以下配置项
uid = nobody #也可以为root
gid = nobody #也可以为root
use chroot = yes #禁锢在源目录
address = 192.168.80.20 #监听地址,监听本机地址
port 873 #监听端口 tcp/udp 873,可通过cat /etc/services | grep rsync查看
log file = /var/log/rsyncd.log #日志文件位置
pid file = /var/run/rsyncd.pid #存放进程 ID 的文件位置
hosts allow = 192.168.80.0/24 #允许同步的客户机网段
[wwwroot] #共享模块名称
path = /var/www/html #源目录的实际路径(同步的目录)
comment = Document Root of www.gcc.com
read only = yes #是否为只读
dont compress = *.gz *.bz2 *.tgz *.zip *.rar *.z #同步时不再压缩的文件类型
auth users = backuper #授权账户,多个账号以空格分隔
secrets file = /etc/rsyncd_users.db #存放账户信息的数据文件
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
uid = nobody
gid = nobody
use chroot = yes
address = 192.168.80.20
port 873
log file = /var/log/rsyncd.log
pid file = /var/run/rsyncd.pid
hosts allow = 192.168.80.0/24
[wwwroot]
path = /var/www/html
comment = Document Root of www.gcc.com
read only = yes
dont compress = *.gz *.bz2 *.tgz *.zip *.rar *.z
auth users = backuper
secrets file = /etc/rsyncd_users.db
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
#如采用匿名的方式,只要将其中的“auth users”和“secrets file”配置项去掉即可。
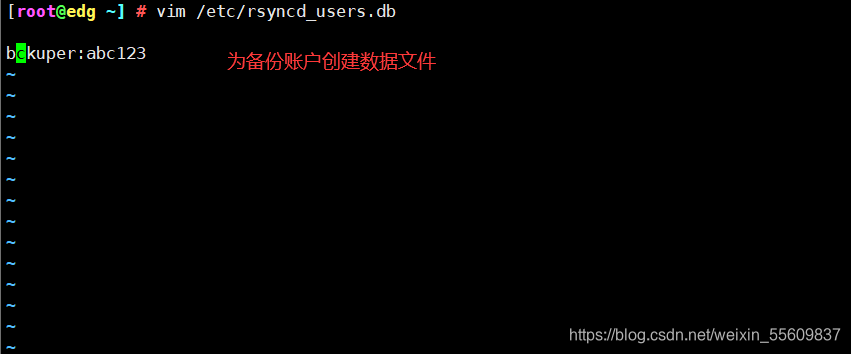
#为备份账户创建数据文件
vim /etc/rsyncd_users.db
backuper:abc123 #无须建立同名系统用户
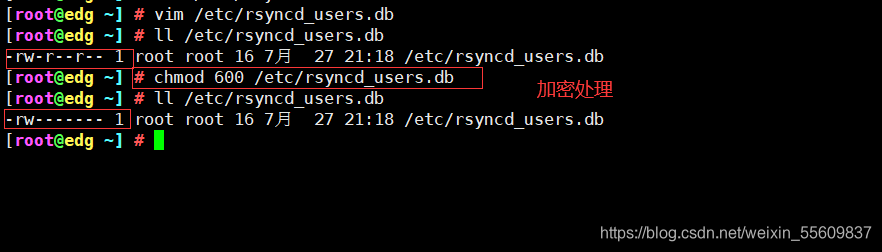
chmod 600 /etc/rsyncd_users.db
#补充:SSH -i 密钥文件位置 root@192.168.80.1 #授权远程登录
#密钥文件的权限需要是600
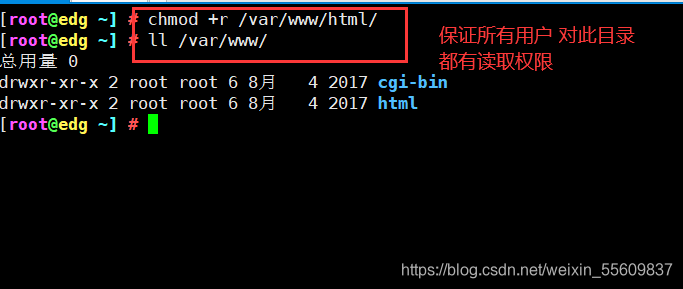
#保证所有用户对源目录/var/www/html 都有读取权限
#安装http服务
yum -y install httpd
systemctl start httpd
systemctl enable httpd
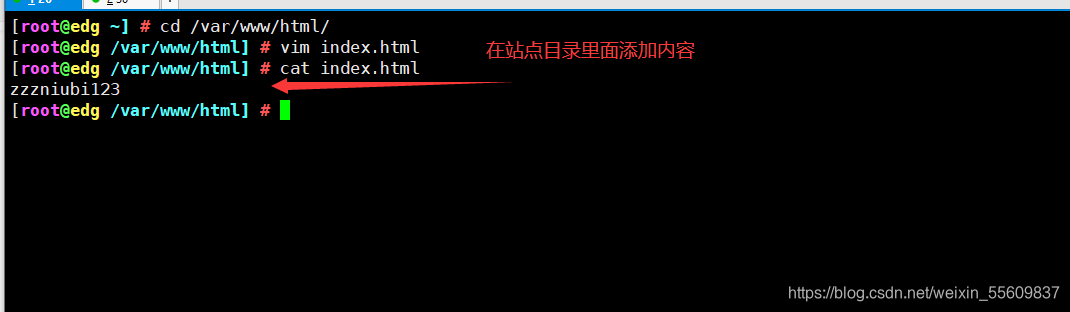
mkdir -p /var/www/html
echo “this is gcc” > /var/www/html/gcc.txt
chmod +r /var/www/html/
ls -ld /var/www/html/ #以长格式显示文件目录权限
drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 6 2月 28 09:01 /var/www/html/
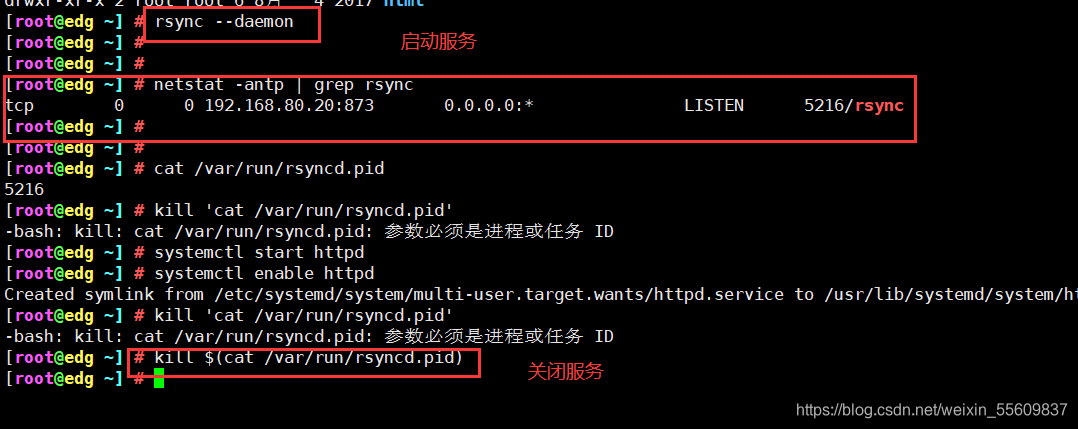
#启动 rsync 服务程序
rsync --daemon #启动 rsync 服务,以独立监听服务的方式(守护进程)运行
netstat -anpt | grep rsync
#关闭 rsync 服务的方法
kill $(cat /var/run/rsyncd.pid)
rm -rf /var/run/rsyncd.pid
2、发起端配置
基本格式:
rsync [选项] 原始位置 目标位置
常用选项:
-r; 递归模式,包含目录及子目录中的所有文件。
-l: 对于符号链接文件仍然复制为符号链接文件。.
-V: 显示同步过程的详细(verbose) 信息。
-z: 在传输文件时进行压缩( compress) 。
-a: 归档模式,保留文件的权限、属性等信息,等同于组合选项"-rlptgoD"。
-p: 保留文件的权限标记。
-t: 保留文件的时间标记。
-g: 保留文件的属组标记(仅超级用户使用)。
-o: 保留文件的属主标记(仅超级用户使用)。
-H: 保留硬连接文件。
-A: 保留ACL属性信息。
-D: 保留设备文件及其他特殊文件。
--delete: 删除目标位置有而原始位置没有的文件。
--checksum:根据校验和(而不是文件大小、修改时间)来决定是否跳过文件。
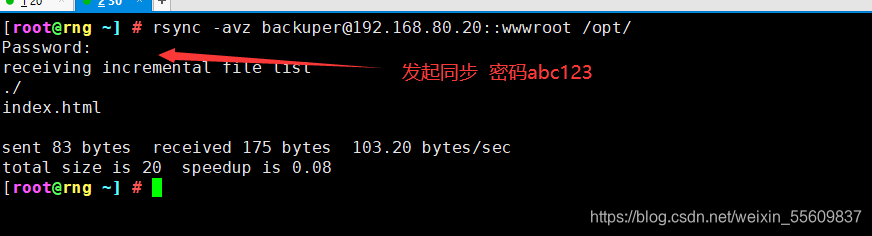
#将指定的资源下载到本地/opt 目录下进行备份。
格式一:
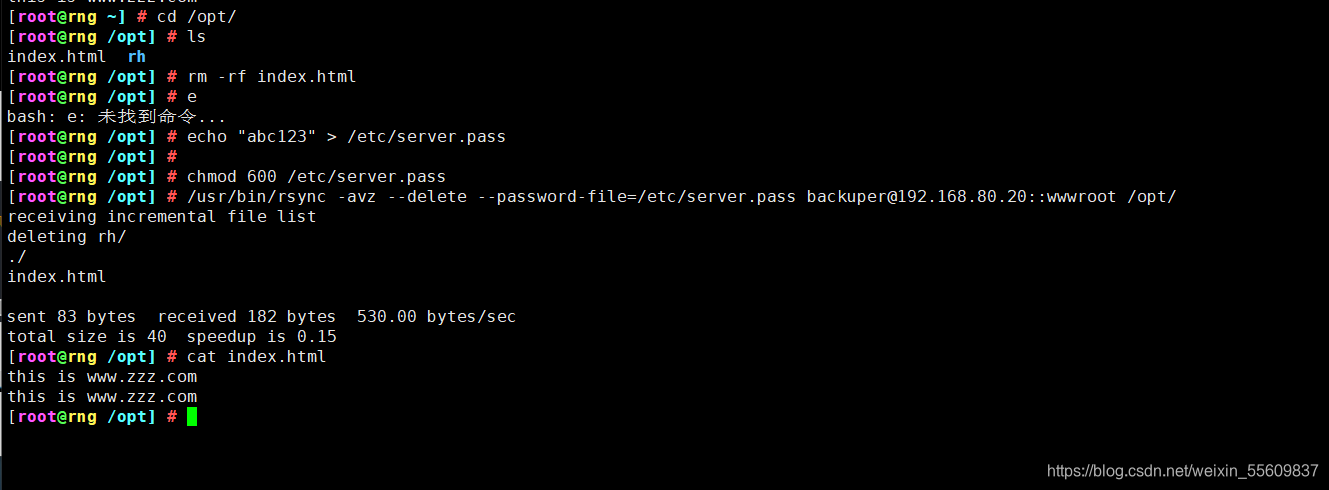
rsync -avz backuper@192.168.80.20::wwwroot /opt/ #密码abc123
格式二:
rsync -avz rsync://backuper@192.168.80.20/wwwroot /opt/
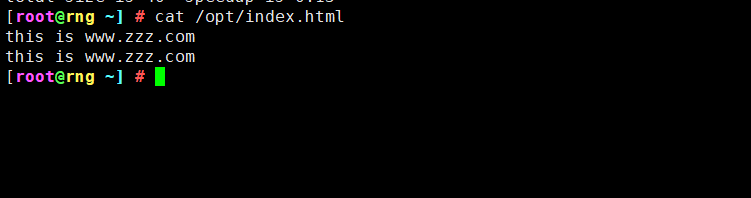
#查看同步获取的文件
cat /opt/gcc.txt
this is gcc
#免交互格式配置:
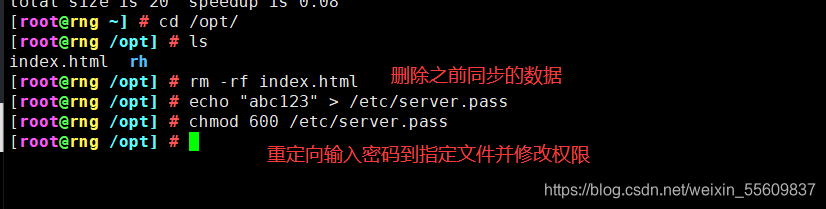
cd /opt
rm -rf gcc.txt
echo "abc123" > /etc/server.pass
chmod 600 /etc/server.pass
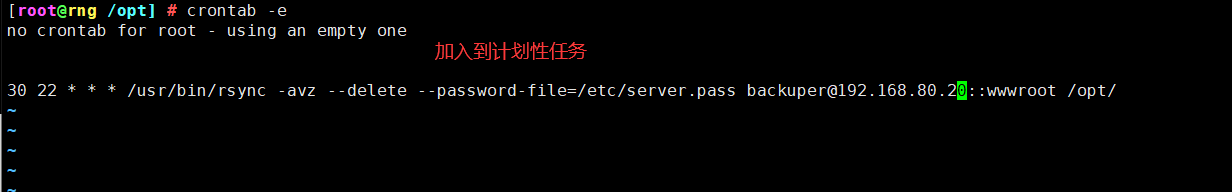
crontab -e
30 22 * * * /usr/bin/rsync -avz --delete --password-file=/etc/server.pass backuper@192.168.200.40::wwwroot /opt/
systemctl restart crond
systemctl enable crond

3、发起端配置 rsync+inotify
- 使用inotify通知接口,可以用来监控文件系统的各种变化情况,如文件存取、删除、移动、修改等。利用这一机制,可以非常方便地实现文件异动告警、增量备份,并针对目录或文件的变化及时作出响应
- 将 inotify 机制与 rsync 工具相结合,可以实现触发式备份(实时同步),即只要原始位置的文档发生变化,则立即启动增量备份操作;否则处于静默等待状态
- 因为 inotify 通知机制由 Linux 内核提供,因此主要做本机监控,在触发式备份中应用时更适合上行同步
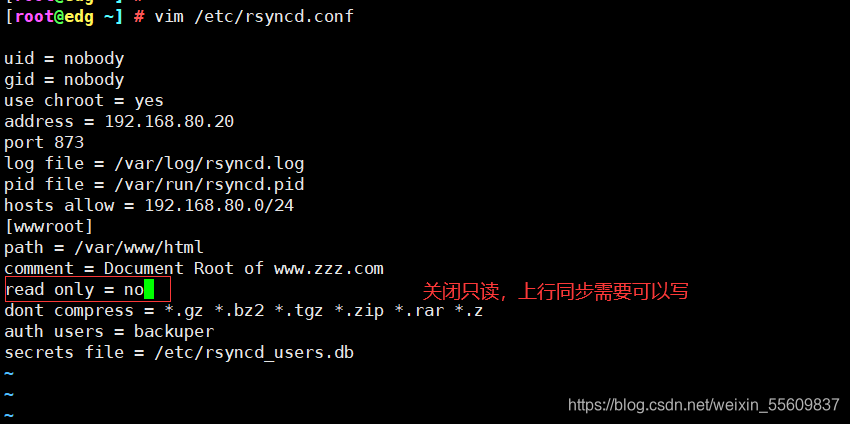
1.修改rsync源服务器(192.168.80.20)配置文件
vim /etc/rsyncd.conf
......
read only = no #关闭只读,上行同步需要可以写
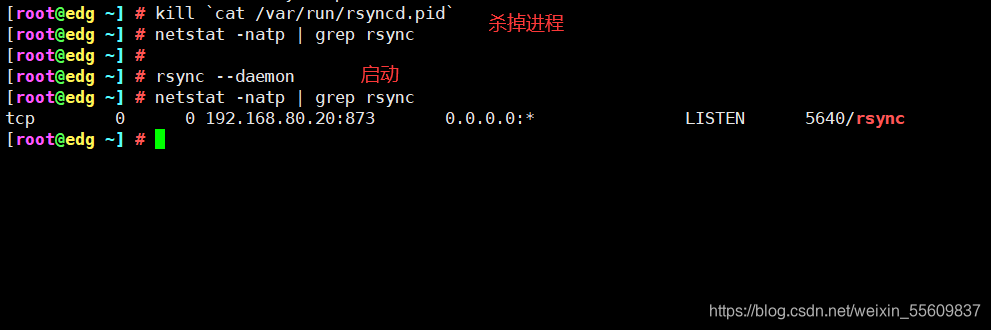
kill `cat /var/run/rsyncd.pid`
netstat -natp | grep rsync
rsync --daemon
netstat -natp | grep rsync
chmod 777 /var/www/html

2.调整 inotify 内核参数(在客户端配置:192.168.80.30)
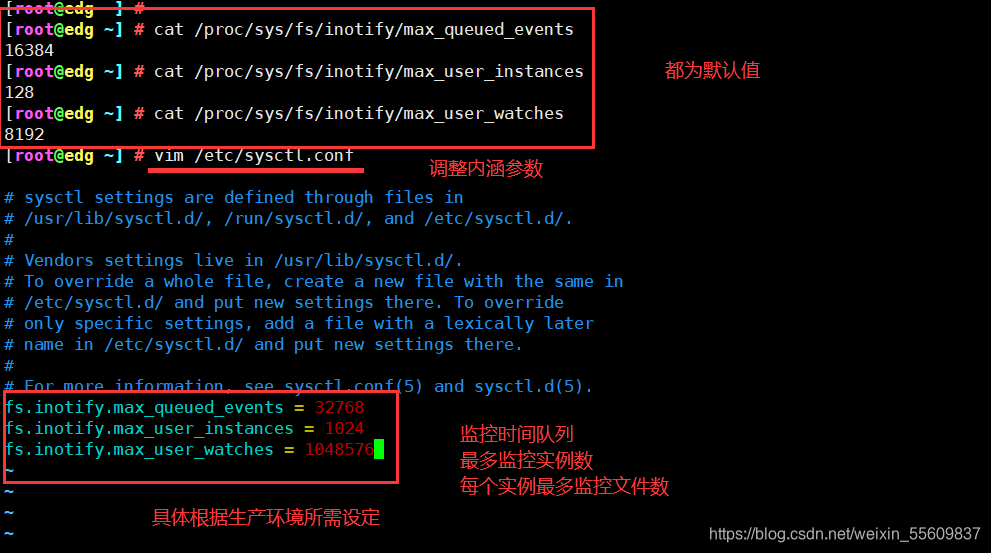
在Linux内核中,默认的inotify机制提供了三个调控参数:max_queue_events(监控事件队列,默认值为16384)、max_user_instances(最多监控实例数,默认值为128)、max_user_watches(每个实例最多监控文件数,默认值为8192)。当要监控的目录、文件数量较多或者变化较频繁时,建议加大这三个参数的值
cat /proc/sys/fs/inotify/max_queued_events
cat /proc/sys/fs/inotify/max_user_instances
cat /proc/sys/fs/inotify/max_user_watches
vim /etc/sysctl.conf
fs.inotify.max_queued_events = 32768
fs.inotify.max_user_instances = 1024
fs.inotify.max_user_watches = 1048576
sysctl -p

3.安装 inotify-tools(在客户端配置:192.168.80.30)
- 用 inotify 机制还需要安装 inotify-tools,以便提供 inotifywait、inotifywatch 辅助工具程序
- notifywait:可监控modify(修改)、create(创建)、move(移动)、delete(删除)、attrib(属性更改)等各种事件,一有变动立即输出结果
- inotifywatch:可用来收集文件系统变动情况,并在运行结束后输出汇总的变化情况
#依赖环境
mount /dev/cdrom /mnt #挂载磁盘
yum install gcc gcc-c++ make -y
#将压缩包inotify-tools-3.14.tar.gz上传至/opt目录下,然后进行解压
tar zxvf inotify-tools-3.14.tar.gz -C /opt/
cd /opt/inotify-tools-3.14
./configure
make && make install
#执行“inotifywait”命令,然后在另一个终端向/var/www/html 目录下添加文件、移动文件,跟踪屏幕输出结果。
#执行下面命令后会进入监听模式,无法操作,所以需要另开一个终端页面进行作
inotifywait -mrq -e modify,create,move,delete /opt
#选项“-e”:用来指定要监控哪些事件
#选项“-m”:表示持续监控
#选项“-r”:表示递归整个目录
#选项“-q”:简化输出信息
4.在客户端(192.168.116.70)编写触发式同步脚本
vim /opt/inotify.sh
#!/bin/bash
INOTIFY_CMD="inotifywait -mrq -e modify,create,attrib,move,delete /var/www/html/" #持续监控
RSYNC_CMD="rsync -apzH --delete --password-file=/etc/server.pass /var/www/html/ backuper@192.168.200.40::wwwroot/" #进行同步
$INOTIFY_CMD #输出监控内容
$INOTIFY_CMD | while read DIRECTORY EVENT FILE #遍历
##while判断是否接收到监控记录
do
if [ $(pgrep rsync | wc -l) -le 0 ] ; then #判断是否正在执行同步
$RSYNC_CMD
fi
done
chmod +x /opt/inotify.sh
chmod 777 /var/www/html
chmod +x /etc/rc.d/rc.local
echo '/opt/inotify.sh' >> /etc/rc.d/rc.local #加入开机自动执行
mkdir -p /var/www/html/ #创建脚本中进行同步的目录
#注意!192.168.200.40 是远程同步服务器ip(即源端IP)
上述脚本用来检测本机/ var/ www/html 目录的变动情况,一旦有更新触发rsync同步操作,上传备份至服务器192.168.80.20的wwwroot 共享目录下。
触发式上行同步的验证过程如下:
- 在本机运行/opt/inotify_ rsync.sh 脚本程序
- 切换到本机的/var/www/html 目录,执行增加、删除、修改文件等操作
- 查看远端服务器中的wwwroot目录下的变化情况


三、使用rsync来实现快速删除大量文件
假如要在Linux下删除大量文件,比如100万、1000万,像/usr/local/nginx/proxy_ temp的nginx缓存等,那么rm -rf *可能就不好使了,因为要等待很长一段时间。在这种情况下我们可以使用rsync来巧妙处理。rsync实际用 的是替换原理。
先建立一个空的文件夹:
mkdir /home/blank
用rsync删除目标目录:
rsync --delete-before -a -H -v --progress --stats /tmp/linuxany /usr/local/nginx/proxy_temp
选项说明:
| –delete-before | 接收者在传输进行删除操作 |
| -a | 归档模式,表示以递归方式传输文件,并保持所有文件属性 |
| -H | 保持硬连接的文件 |
| -v | 详细输出模式 |
| –progress | 在传输时显示传输过程 |
| –stats | 给出某些文件的传输状态 |
总结
提示:这里对文章进行总结:
例如:以上就是今天要讲的内容,本文仅仅简单介绍了pandas的使用,而pandas提供了大量能使我们快速便捷地处理数据的函数和方法。