回顾相关概念
逻辑地址--->线性地址又称虚拟地址--->物理地址
代码段是只读的、数据段是可写的、堆栈段是可增长的
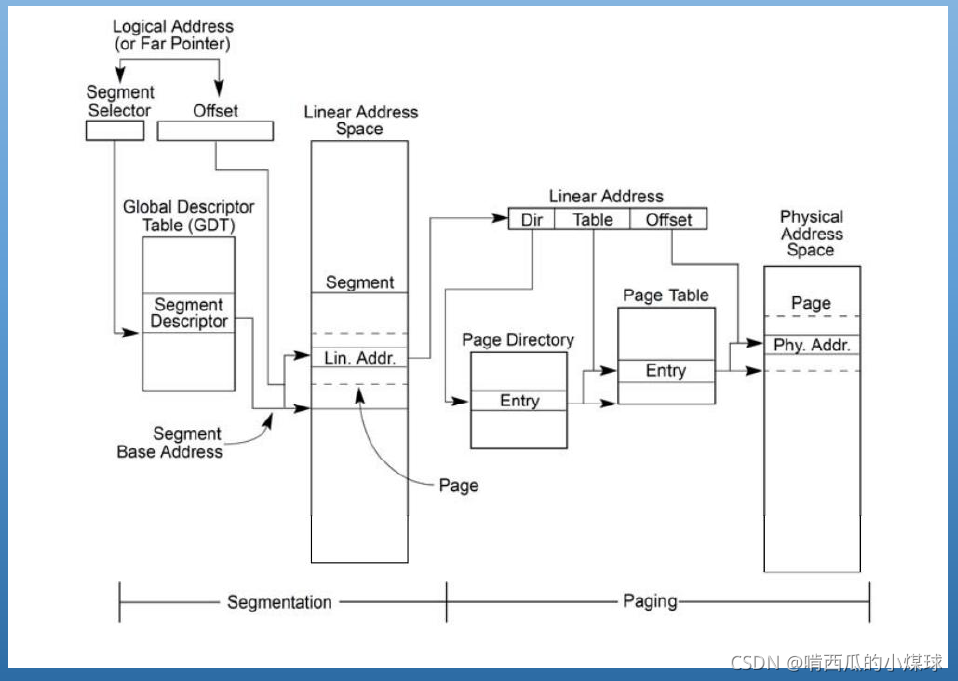
????????在进程中,我们不直接对物理地址进行操作。CPU在运行时,指定的地址要经过MMU转换后才能访问到真正的物理内存。地址转换的过程分为两部分,分段和分页。分段机制简单点来讲就是将进程的代码、数据、栈分在不同的虚拟地址段上。从而避免进程间的互相影响,分段之前的地址我们称之为逻辑地址。
????????逻辑地址由两部分组成,高位的段选择符和低位的段内偏移。在分段时先用段选择符在相应的段描述符表中找到段描述符,也就是某一个段的基地址,再加上段内偏移量就得到了相应的线性地址。在实际的应用中,Linux系统为了增加可移植性并没有完整的使用段机制,它让所有的段都指向相同的地址范围,由于段地址基址都为0,所以逻辑地址和线性地址数值上相同,这里主要分析分页也就是线性地址到物理地址的转换。
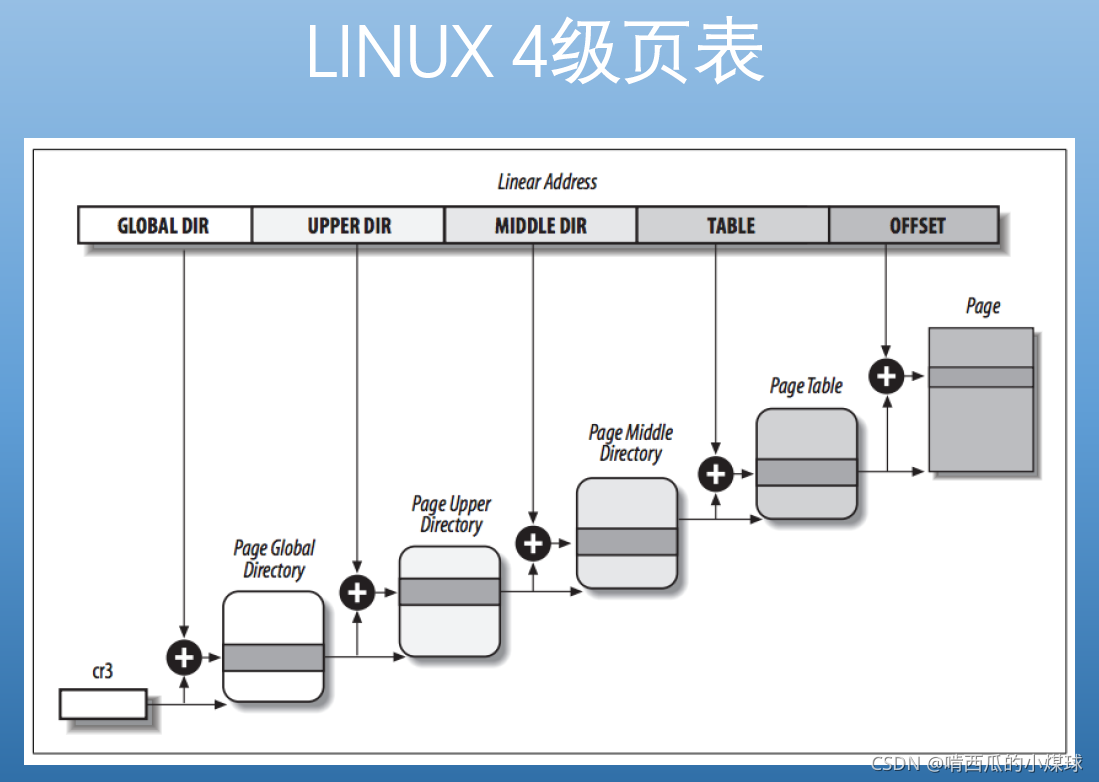
????????linux为了兼容32位和64位的CPU,它需要一个统一的页面地址模型,目前常用的是4级页表模型。4级页表分别包括:PGD页全局目录、PUD页上级目录、PMD页中间目录、PT页表。根据不同的需要,某些页表可能未被使用,线性地址也是每一部分的索引会根据具体的计算机体系结构来做出相应的改变,举例来讲,对于未启用物理地址的32位操作系统来说,两级页表就是足够的。Linux会首先在线性地址中将页上级目录和页中间目录索引这两位置为0,从根本上就取消了这两个字段,但是这两个页目录在指针序列中的位置仍然被保留了下来,也就是说寻址过程中不能跳过页上级目录和页中间目录直接由页全局目录直接到页表,内核会将这两个页目录的表项都置为1。
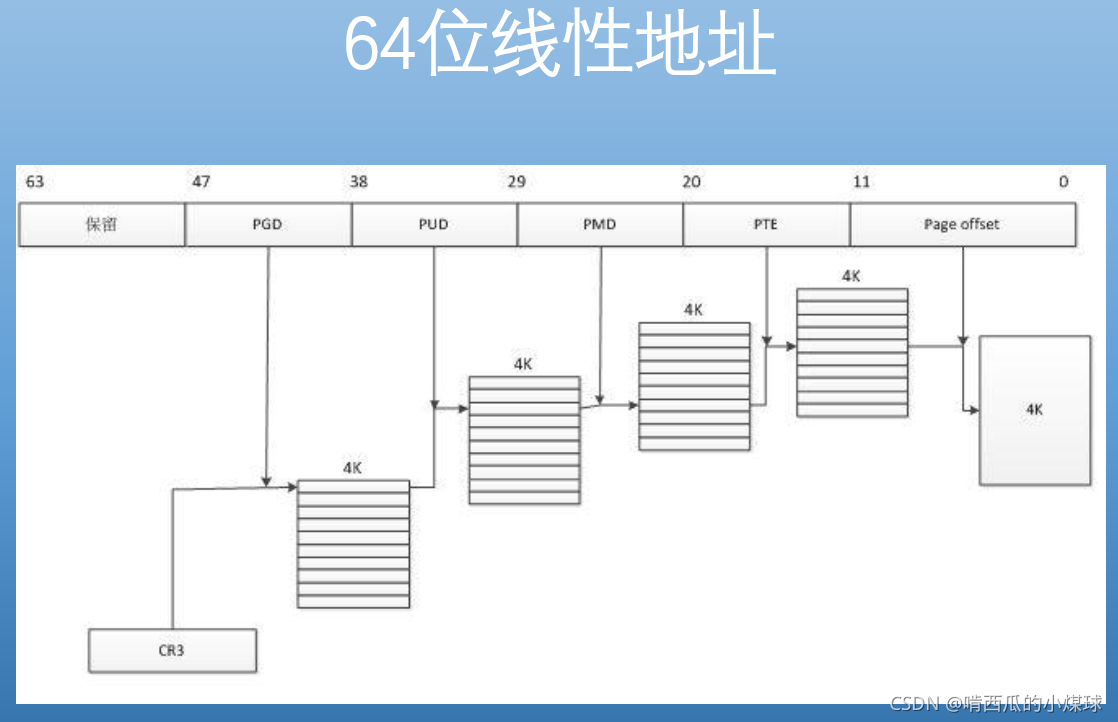
????????由于64系统硬件的限制,它的地址线只有48条,所以线性地址使用的只有48位,在64位Linux中使用了4级页表结构。首先页全局目录的索引、页上级目录的索引、页中间目录的索引、页表的索引分别是占了9位。
0-11??? 12位?? 分给页内偏移
11-20?? 9位??? 分给页表
20-29?? 9位??? 分给页中间目录
29-38?? 9位??? 分给页上级目录
38-47?? 9位??? 分给页全局目录
47-63?? 16位? 留作保留位以后使用
由于页内偏移是12位,则页面的大小是2^12=4k𝐵 (怎么进入和退出公式编辑模式,alt + =)
每一个页表项大小为8bit,整个页表可以映射的空间是256TB
每个页表项为什么是8bit?(未搞清楚,求大神指导)
2^48=256TB?![]()
2的10次方 1KB
2的20次方 1MB
2的30次方 1GB
2的40次方 1TB
2的48次方 256TB
![]()
????????新的Intel芯片的MMU硬件规定可以进行5级的页表管理,所以在4.15的内核中,linux在页全局目录和页上级目录中间增加了一个新的页目录,叫p4d页目录。这个页目录同32位中的情况一样现在还未被使用,它的页目录项只有一个,线性地址中也没有它的索引位。
CR3寄存器是用来干什么的?
????????它是一系列CPU控制寄存器之一 ,这些控制寄存器主要是用来保存控制系统级别操作的数据和信息,其中这个CR3就是用来保存当前进程的页全局目录的地址的。寻页的开始就是从页全局目录开始。
页全局目录的地址又在哪里?怎么进行页表的切换?
????????内核在创建一个进程时就会为它分配页全局目录,在进程描述符task_struct结构中有一个指向mm_struct结构的指针mm,而mm_struct结构就是用来描述进程的虚拟地址空间的,在mm_struct中有一个字段PGD就是用来保存全局目录的(物理)地址的,所以在进程切换的时候,操作系统通过访问task_struct结构,在访问mm_struct结构,最终找到PGD字段,取得新进程的页全局目录的地址填充到CR3寄存器中完成页表的切换。
接下来进行实际操作,看看寻页过程是如何完成的。
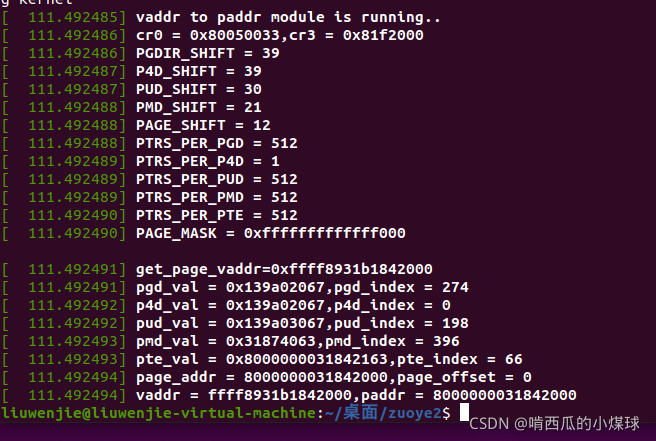
????????可以看出PGD_SHIFT和P4D_SHIFT都是39,意味着在线性地址中,P4D这个字段是空的
在页目录项中,P4D的页目录项也是为1的,说明现在的Linux系统使用了五级的页表模型,
但实际上使用的页表也只有四个。
????????PAGE_MASK字段它是低12位都为0,其余位都为1的一个64位的数。
我们已经通过线性地址得到了物理地址,现在想通过直接访问物理地址看看里面存放的是什么??
????????需要dram.c,主要功能是用mmap将物理内存中的数据映射到设备文件中,通过对于这个设备文件的访问就可以达到访问物理内存的功能。
????????另一个工具是fileview.cpp,可以让我们按照想要的格式来阅读二进制文件。
????????现在使用这两个小工具对物理内存进行访问。
liuwenjie@liuwenjie-virtual-machine:~/桌面/zuoye3$ sudo make
liuwenjie@liuwenjie-virtual-machine:~/桌面/zuoye3$ sudo insmod dram.ko
liuwenjie@liuwenjie-virtual-machine:~/桌面/zuoye3$ sudo mknod /dev/dram c 85 0
liuwenjie@liuwenjie-virtual-machine:~/桌面/zuoye3$ gcc -S fileview.cpp -o fileview.s
liuwenjie@liuwenjie-virtual-machine:~/桌面/zuoye3$ gcc -c fileview.s -o fileview.o
liuwenjie@liuwenjie-virtual-machine:~/桌面/zuoye3$ gcc fileview.cpp -o fileview.out
liuwenjie@liuwenjie-virtual-machine:~/桌面/zuoye3$ ./fileview.out
liuwenjie@liuwenjie-virtual-machine:~/桌面/zuoye3$ ./fileview.out /dev/dram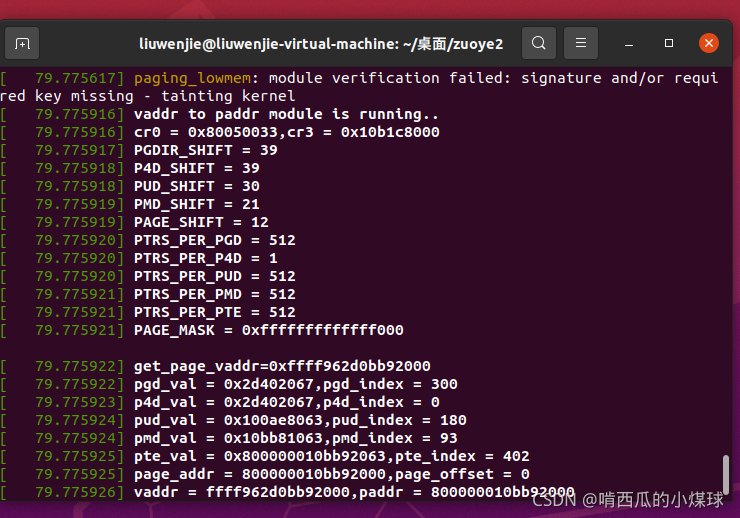
?
paging_lowmem.c 源文件
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/mm.h>
#include <linux/mm_types.h>
#include <linux/sched.h>
#include <linux/export.h>
/*
该内核模块的主要功能是在内核中申请一个页面,然后利用内核提供的函数按照寻页的步骤一步步查询各级页目录
最终找到对应的物理地址,这些步骤就像我们手动模拟了MMU单元的寻页过程。
*/
static unsigned long cr0,cr3;
static unsigned long vaddr = 0;
// get_pgtable_macro这个函数的作用是打印页机制中一些重要参数的
static void get_pgtable_macro(void)
{
cr0 = read_cr0();
cr3 = read_cr3_pa();//cr3寄存器的值通过 read_cr3_pa函数来获得
printk("cr0 = 0x%lx,cr3 = 0x%lx\n",cr0,cr3);
//_shift这些宏是用来指示线性地址中相应字段所能映射区域大小的对数
printk("PGDIR_SHIFT = %d\n",PGDIR_SHIFT);//页全局目录
printk("P4D_SHIFT = %d\n",P4D_SHIFT);//4.15内核中新加入的页目录p4d
printk("PUD_SHIFT = %d\n",PUD_SHIFT);//页上级目录
printk("PMD_SHIFT = %d\n",PMD_SHIFT);//页中级目录
printk("PAGE_SHIFT = %d\n",PAGE_SHIFT);//PAGE_SHIFT就是指示page offset字段所能映射区域大小的对数 page offset字段映射的是一个页面的大小 页面大小是4KB,转换为以2为底的对数就是12
//下面这个宏 PTRS_PER_x 是用来指示相应的页目录表中项的个数
printk("PTRS_PER_PGD = %d\n",PTRS_PER_PGD);//页全局目录表中项的个数
printk("PTRS_PER_P4D = %d\n",PTRS_PER_P4D);//p4d目录表中项的个数
printk("PTRS_PER_PUD = %d\n",PTRS_PER_PUD);//页上级目录表中项的个数
printk("PTRS_PER_PMD = %d\n",PTRS_PER_PMD);//页中级目录表中项的个数
printk("PTRS_PER_PTE = %d\n",PTRS_PER_PTE);// 页表中项的个数
printk("PAGE_MASK = 0x%lx\n",PAGE_MASK);// PAGE_MASK是页内偏移掩码 是用来屏蔽掉page offset字段的
//这些宏是为了方便寻页时进行位运算的
}
// vaddr2paddr是我们用来进行线性地址到物理地址转换的函数
static unsigned long vaddr2paddr(unsigned long vaddr)
{
//为每一个页目录项创建一个变量来将他们保存起来
pgd_t *pgd;
p4d_t *p4d;
pud_t *pud;
pmd_t *pmd;
pte_t *pte;
unsigned long paddr = 0;
unsigned long page_addr = 0;
unsigned long page_offset = 0;
// pgd_offset函数传入的第一个参数时当前进程的mm_struct结构
//我们申请的线性地址是在内核空间的,所以我们要查的页表也是内核页表
//所有的进程都共享同一个内核页表,所以可以用当前进程的
//我们在查找得到第一个页全局目录项PGD之后,将其作为下级查找的参数传入到p4d_offset中 作下一级的查找 就找到了p4d
pgd = pgd_offset(current->mm,vaddr);
printk("pgd_val = 0x%lx,pgd_index = %lu\n",pgd_val(*pgd),pgd_index(vaddr));
if(pgd_none(*pgd))
{
printk("not mapped in pgd\n");
return -1;
}
p4d = p4d_offset(pgd,vaddr);
printk("p4d_val = 0x%lx,p4d_index = %lu\n",p4d_val(*p4d),p4d_index(vaddr));
if(p4d_none(*p4d))
{
printk("not mapped in p4d\n");
return -1;
}
//然后再去找相应的PUD页目录项 PMD页目录项
pud = pud_offset(p4d,vaddr);
printk("pud_val = 0x%lx,pud_index = %lu\n",pud_val(*pud),pud_index(vaddr));
if(pud_none(*pud))
{
printk("not mapped in pud\n");
return -1;
}
pmd = pmd_offset(pud,vaddr);
printk("pmd_val = 0x%lx,pmd_index = %lu\n",pmd_val(*pmd),pmd_index(vaddr));
if(pmd_none(*pmd))
{
printk("not mapped in pmd\n");
return -1;
}
//最后就会找到PTE页表项了 pte_offset_kernel与上面有所不同,这是为了表示我们是在主内核页表中查找的而在进程页表中查找是有一个完全不同的函数
//最后我们取得了页表的线性地址
pte = pte_offset_kernel(pmd,vaddr);
printk("pte_val = 0x%lx,pte_index = %lu\n",pte_val(*pte),pte_index(vaddr));
if(pte_none(*pte))
{
printk("not mapped in pte\n");
return -1;
}
//从页表的线性地址也就是这个页表项中取出该页表所映射页框的物理地址
//将其与 PAGE_MASK这个变量进行位或操作 取出高48位 就得到了页框的物理地址
page_addr = pte_val(*pte) & PAGE_MASK;
//接下来取出页偏移地址 也就是线性地址中的低12位
page_offset = vaddr & ~PAGE_MASK;
//将两个地址拼接起来 就得到了物理地址
paddr = page_addr | page_offset;
//将这些物理地址都打印出来就得完成线性地址到物理地址转换的过程
printk("page_addr = %lx,page_offset = %lx\n",page_addr,page_offset);
printk("vaddr = %lx,paddr = %lx\n",vaddr,paddr);
return paddr;
}
//内核模块的注册函数
static int __init v2p_init(void)
{
unsigned long vaddr = 0;
printk("vaddr to paddr module is running..\n");
get_pgtable_macro();
printk("\n");
//使用get_free_page函数在内核的ZONE_NORMAL中申请了一块页面
//GFP_KERNEL是用来指示它是优先从内存的ZONE_NORMAL区中申请页框的
vaddr = __get_free_page(GFP_KERNEL);
if(vaddr == 0)
{
printk("__get_free_page failed..\n");
return 0;
}
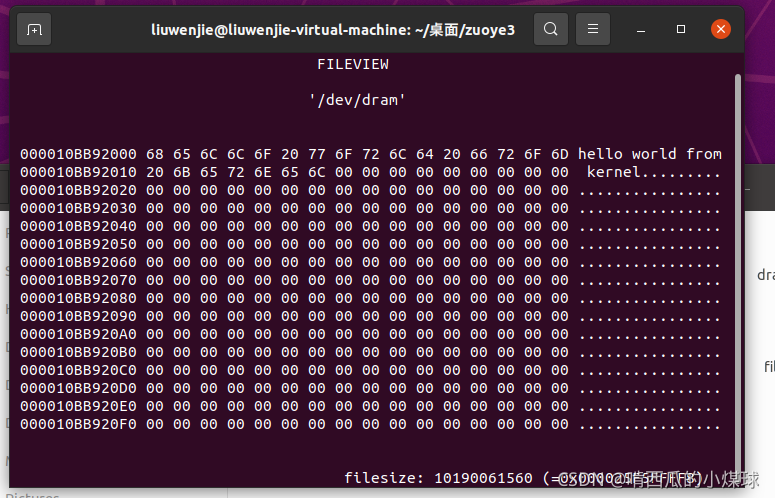
sprintf((char *)vaddr,"hello world from kernel");
printk("get_page_vaddr=0x%lx\n",vaddr);
vaddr2paddr(vaddr);
return 0;
}
//内核模块的卸载函数 将我们申请的线性地址空间释放掉
static void __exit v2p_exit(void)
{
printk("vaddr to paddr module is leaving..\n");
free_page(vaddr);
}
module_init(v2p_init);
module_exit(v2p_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");dram.c 源文件
//-------------------------------------------------------------------
// dram.c
//
// This module implements a Linux character-mode device-driver
// for the processor's installed physical memory. It utilizes
// the kernel's 'kmap()' function, as a uniform way to provide
// access to all the memory-zones (including the "high memory"
// on systems with more than 896MB of installed physical ram).
// The access here is 'read-only' because we deem it too risky
// to the stable functioning of our system to allow every user
// the unrestricted ability to arbitrarily modify memory-areas
// which might contain some "critical" kernel data-structures.
// We implement an 'llseek()' method so that users can readily
// find out how much physical processor-memory is installed.
//
// NOTE: Developed and tested with Linux kernel version 2.6.10
//
// programmer: ALLAN CRUSE
// written on: 30 JAN 2005
// revised on: 28 JAN 2008 -- for Linux kernel version 2.6.22.5
// revised on: 06 FEB 2008 -- for machines having 4GB of memory
//-------------------------------------------------------------------
#include <linux/module.h> // for module_init()
#include <linux/highmem.h> // for kmap(), kunmap()
#include <linux/uaccess.h> // for copy_to_user()
char modname[] = "dram"; // for displaying driver's name
int my_major = 85; // note static major assignment
unsigned long dram_size; // total bytes of system memory
loff_t my_llseek( struct file *file, loff_t offset, int whence );
ssize_t my_read( struct file *file, char *buf, size_t count, loff_t *pos );
struct file_operations
my_fops = {
owner: THIS_MODULE,
llseek: my_llseek,
read: my_read,
};
static int __init dram_init( void )
{
printk( "<1>\nInstalling \'%s\' module ", modname );
printk( "(major=%d)\n", my_major );
dram_size = 0x25f5ffff8;
printk( "<1> ramtop=%08lX (%lu MB)\n", dram_size, dram_size >> 20 );
return register_chrdev( my_major, modname, &my_fops );
}
static void __exit dram_exit( void )
{
unregister_chrdev( my_major, modname );
printk( "<1>Removing \'%s\' module\n", modname );
}
ssize_t my_read( struct file *file, char *buf, size_t count, loff_t *pos )
{
struct page *pp;
void *from;
int page_number, page_indent, more;
// we cannot read beyond the end-of-file
if ( *pos >= dram_size ) return 0;
// determine which physical page to temporarily map
// and how far into that page to begin reading from
page_number = *pos / PAGE_SIZE;
page_indent = *pos % PAGE_SIZE;
// map the designated physical page into kernel space
/*If kerel vesion is 2.6.32 or later, please use pfn_to_page() to get page, and include
asm-generic/memory_model.h*/
pp = pfn_to_page( page_number);
from = kmap( pp ) + page_indent;
// cannot reliably read beyond the end of this mapped page
if ( page_indent + count > PAGE_SIZE ) count = PAGE_SIZE - page_indent;
// now transfer count bytes from mapped page to user-supplied buffer
more = copy_to_user( buf, from, count );
// ok now to discard the temporary page mapping
kunmap( pp );
// an error occurred if less than count bytes got copied
if ( more ) return -EFAULT;
// otherwise advance file-pointer and report number of bytes read
*pos += count;
return count;
}
loff_t my_llseek( struct file *file, loff_t offset, int whence )
{
loff_t newpos = -1;
switch( whence )
{
case 0: newpos = offset; break; // SEEK_SET
case 1: newpos = file->f_pos + offset; break; // SEEK_CUR
case 2: newpos = dram_size + offset; break; // SEEK_END
}
if (( newpos < 0 )||( newpos > dram_size )) return -EINVAL;
file->f_pos = newpos;
return newpos;
}
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
module_init( dram_init );
module_exit( dram_exit );
fileview.cpp 源文件
//----------------------------------------------------------------
// fileview.cpp
//
// This program displays the contents of a specified file
// in hexadecimal and ascii formats (including any device
// special files representing storage media). A user may
// navigate the file's contents using arrow-key commands,
// or may adjust the format of the hexadecimal display to
// select from among five data-sizes: byte (B), word (W),
// doubleword (D), quadword (Q) or octaword (O). It also
// is possible to seek to a specified position within the
// file by hitting the <ENTER>-key and then typing in the
// desired (hexadecimal) address. Type <ESCAPE> to quit.
//
// compile-and-link using: $ make fileview
//
// programmer: ALLAN CRUSE
// written on: 26 OCT 2002
// revised on: 07 JUN 2006 -- removed reliance on 'ncurses'
//----------------------------------------------------------------
#include <stdio.h> // for printf(), perror(), fflush()
#include <fcntl.h> // for open()
#include <string.h> // for strncpy()
#include <unistd.h> // for read(), lseek64()
#include <stdlib.h> // for exit()
#include <termios.h> // for tcgetattr(), tcsetattr()
#define MAXNAME 80
#define BUFHIGH 16
#define BUFWIDE 16
#define BUFSIZE 256
#define ROW 6
#define COL 2
#define KB_SEEK 0x0000000A
#define KB_QUIT 0x0000001B
#define KB_BACK 0x0000007F
#define KB_HOME 0x00315B1B
#define KB_LNUP 0x00415B1B
#define KB_PGUP 0x00355B1B
#define KB_LEFT 0x00445B1B
#define KB_RGHT 0x00435B1B
#define KB_LNDN 0x00425B1B
#define KB_PGDN 0x00365B1B
#define KB_END 0x00345B1B
#define KB_DEL 0x00335B1B
char progname[] = "FILEVIEW";
char filename[ MAXNAME + 1 ];
char buffer[ BUFSIZE ];
char outline[ 80 ];
int main( int argc, char *argv[] )
{
// setup the filename (if supplied), else terminate
if ( argc > 1 ) strncpy( filename, argv[1], MAXNAME );
else { fprintf( stderr, "argument needed\n" ); exit(1); }
// open the file for reading
int fd = open( filename, O_RDONLY );
if ( fd < 0 ) { perror( filename ); exit(1); }
// obtain the filesize (if possible)
long long filesize = lseek64( fd, 0LL, SEEK_END );
if ( filesize < 0LL )
{
fprintf( stderr, "cannot locate \'end-of-file\' \n" );
exit(1);
}
long long incmin = ( 1LL << 8 );
long long incmax = ( 1LL << 36 );
long long posmin = 0LL;
long long posmax = (filesize - 241LL)&~0xF;
if ( posmax < posmin ) posmax = posmin;
// initiate noncanonical terminal input
struct termios tty_orig;
tcgetattr( STDIN_FILENO, &tty_orig );
struct termios tty_work = tty_orig;
tty_work.c_lflag &= ~( ECHO | ICANON ); // | ISIG );
tty_work.c_cc[ VMIN ] = 1;
tty_work.c_cc[ VTIME ] = 0;
tcsetattr( STDIN_FILENO, TCSAFLUSH, &tty_work );
printf( "\e[H\e[J" );
// display the legend
int i, j, k;
k = (77 - strlen( progname ))/2;
printf( "\e[%d;%dH %s ", 1, k, progname );
k = (77 - strlen( filename ))/2;
printf( "\e[%d;%dH\'%s\'", 3, k, filename );
char infomsg[ 80 ];
sprintf( infomsg, "filesize: %llu (=0x%013llX)", filesize, filesize );
k = (78 - strlen( infomsg ));
printf( "\e[%d;%dH%s", 24, k, infomsg );
fflush( stdout );
// main loop to navigate the file
long long pageincr = incmin;
long long lineincr = 16LL;
long long position = 0LL;
long long location = 0LL;
int format = 1;
int done = 0;
while ( !done )
{
// erase prior buffer contents
for (j = 0; j < BUFSIZE; j++) buffer[ j ] = ~0;
// restore 'pageincr' to prescribed bounds
if ( pageincr == 0LL ) pageincr = incmax;
else if ( pageincr < incmin ) pageincr = incmin;
else if ( pageincr > incmax ) pageincr = incmax;
// get current location of file-pointer position
location = lseek64( fd, position, SEEK_SET );
// try to fill 'buffer[]' with data from the file
char *where = buffer;
int to_read = BUFSIZE;
while ( to_read > 0 )
{
int nbytes = read( fd, where, to_read );
if ( nbytes <= 0 ) break;
to_read -= nbytes;
where += nbytes;
}
int datalen = BUFSIZE - to_read;
// display the data just read into the 'buffer[]' array
unsigned char *bp;
unsigned short *wp;
unsigned int *dp;
unsigned long long *qp;
for (i = 0; i < BUFHIGH; i++)
{
int linelen;
// draw the line-location (13-digit hexadecimal)
linelen = sprintf( outline, "%013llX ", location );
// draw the line in the selected hexadecimal format
switch ( format )
{
case 1: // 'byte' format
bp = (unsigned char*)&buffer[ i*BUFWIDE ];
for (j = 0; j < BUFWIDE; j++)
linelen += sprintf( outline+linelen,
"%02X ", bp[j] );
break;
case 2: // 'word' format
wp = (unsigned short*)&buffer[ i*BUFWIDE ];
for (j = 0; j < BUFWIDE/2; j++)
linelen += sprintf( outline+linelen,
" %04X ", wp[j] );
break;
case 4: // 'dword' format
dp = (unsigned int*)&buffer[ i*BUFWIDE ];
for (j = 0; j < BUFWIDE/4; j++)
linelen += sprintf( outline+linelen,
" %08X ", dp[j] );
break;
case 8: // 'qword' format
qp = (unsigned long long*)&buffer[ i*BUFWIDE ];
for (j = 0; j < BUFWIDE/8; j++)
linelen += sprintf( outline+linelen,
" %016llX ", qp[j] );
break;
case 16: // 'octaword'
qp = (unsigned long long*)&buffer[ i*BUFWIDE ];
linelen += sprintf( outline+linelen, " " );
linelen += sprintf( outline+linelen,
" %016llX%016llX ", qp[1], qp[0] );
linelen += sprintf( outline+linelen, " " );
break;
}
// draw the line in ascii format
for (j = 0; j < BUFWIDE; j++)
{
char ch = buffer[ i*BUFWIDE + j ];
if (( ch < 0x20 )||( ch > 0x7E )) ch = '.';
linelen += sprintf( outline+linelen, "%c", ch);
}
// transfer this output-line to the screen
printf( "\e[%d;%dH%s", ROW+i, COL, outline );
// advance 'location' for the next output-line
location += BUFWIDE;
}
printf( "\e[%d;%dH", 23, COL );
fflush( stdout );
// await keypress
long long inch = 0LL;
read( STDIN_FILENO, &inch, sizeof( inch ) );
printf( "\e[%d;%dH%60s", 23, COL, " " );
// interpret navigation or formatting command
inch &= 0x00FFFFFFLL;
switch ( inch )
{
// move to the file's beginning/ending
case 'H': case 'h':
case KB_HOME: position = posmin; break;
case 'E': case 'e':
case KB_END: position = posmax; break;
// move forward/backward by one line
case KB_LNDN: position += BUFWIDE; break;
case KB_LNUP: position -= BUFWIDE; break;
// move forward/packward by one page
case KB_PGDN: position += pageincr; break;
case KB_PGUP: position -= pageincr; break;
// increase/decrease the page-size increment
case KB_RGHT: pageincr >>= 4; break;
case KB_LEFT: pageincr <<= 4; break;
// reset the hexadecimal output-format
case 'B': case 'b': format = 1; break;
case 'W': case 'w': format = 2; break;
case 'D': case 'd': format = 4; break;
case 'Q': case 'q': format = 8; break;
case 'O': case 'o': format = 16; break;
// seek to a user-specified file-position
case KB_SEEK:
printf( "\e[%d;%dHAddress: ", 23, COL );
fflush( stdout );
{
char inbuf[ 16 ] = {0};
//tcsetattr( STDIN_FILENO, TCSANOW, &tty_orig );
int i = 0;
while ( i < 15 )
{
char ch = 0;
read( STDIN_FILENO, &ch, sizeof( ch ) );
ch &= 0xFFFFFF;
if ( ch == '\n' ) break;
if ( ch == KB_QUIT ) { inbuf[0] = 0; break; }
if ( ch == KB_LEFT ) ch = KB_BACK;
if ( ch == KB_DEL ) ch = KB_BACK;
if (( ch == KB_BACK )&&( i > 0 ))
{
inbuf[--i] = 0;
printf( "\b \b" );
fflush( stdout );
}
if (( ch < 0x20 )||( ch > 0x7E )) continue;
inbuf[ i++ ] = ch;
printf( "%c", ch );
fflush( stdout );
}
printf( "\e[%d;%dH%70s", 23, COL, " " );
fflush( stdout );
position = strtoull( inbuf, NULL, 16 );
position &= ~0xFLL; // paragraph align
}
break;
// program termination
case KB_QUIT: done = 1; break;
default:
printf( "\e[%d;%dHHit <ESC> to quit", 23, 2 );
}
fflush( stdout );
// insure that 'position' remains within bounds
if ( position < posmin ) position = posmin;
if ( position > posmax ) position = posmax;
}
// restore canonical terminal behavior
tcsetattr( STDIN_FILENO, TCSAFLUSH, &tty_orig );
printf( "\e[%d;%dH\e[0J\n", 23, 0 );
}