?内容随时更新,最大程度的分析每个方法?
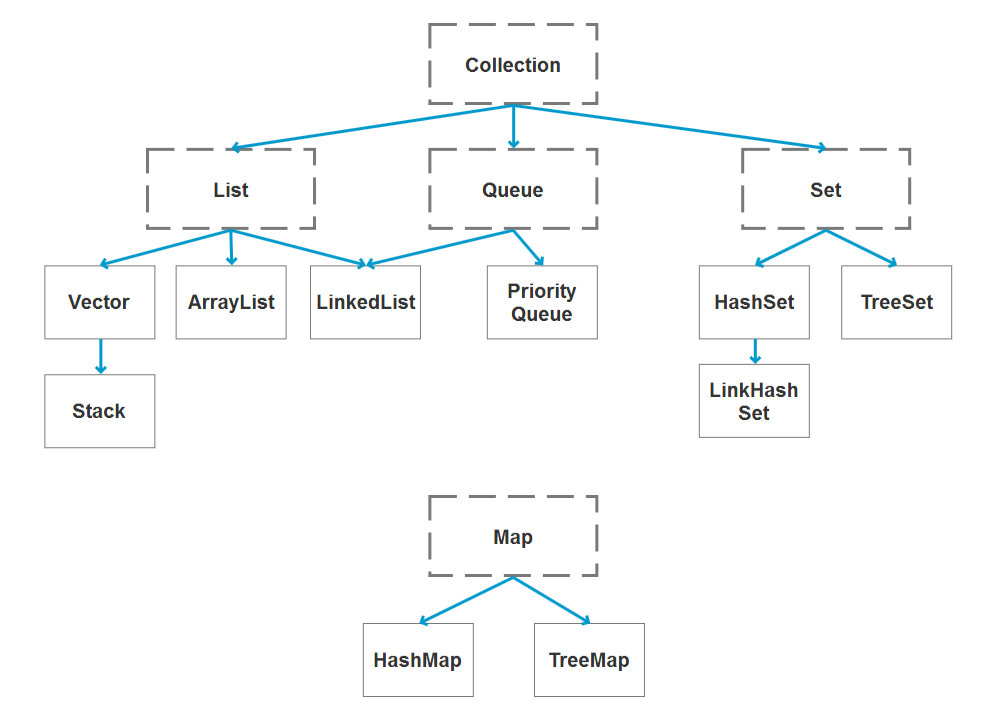
List
1、Vector
vector 是一个弃用的类,里面几乎所有的方法都用synchronized,说明他是一个线程同步的类,访问速度必然变慢,低层的数据结构是一个动态数组
基本用法:用法类似于数组
@Test
public void vectorTest() {
//用空参构造器创建的vector对象,容量默认大小是10
Vector<Object> objects = new Vector<Object>();
//通过capacity()打印得到的容量大小
System.out.println(objects.capacity());//控制台输出 10
//储存1~10的数据
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
objects.add(i+1);
}
//取出储存的数据
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
System.out.println(objects.get(i));
}
}
}构造方法:
 ??查看源码可以发现,创建一个Vector对象可以有四种方法
??查看源码可以发现,创建一个Vector对象可以有四种方法
1、 空参构造方法初始化时的容量大小默认是10?
2、publlic Vector(int initialCapacity); 这个构造方法指定一个初始化容量大小
@Test
public void vectorTest1() {
//使用public Vector(int initialCapacity)构造器构建Vector对象
Vector<Object> objects = new Vector<Object>(20);
//打印objects容量大小
System.out.println(objects.capacity());//控制台输出 20
}3、public Vector(int initialCapacity, int capacityIncrement); 该构造方法不仅指定容量初始化大小而且还指定该容器的自增大小
@Test
public void vectorTest2() {
//1、用public Vector(int initialCapacity, int capacityIncrement)构造器 构建Vector对象
Vector<Object> objects = new Vector<Object>(20,1);
for (int i = 0; i < 21; i++) {
objects.add(i + 1);
if (i==19) {
//当i等于19时,打印出容器的容量大小
System.out.println(objects.capacity());//控制台输出 20
}
}
//打印objects容量大小
System.out.println(objects.capacity());//控制台输出 21 表明自增的大小是我们指定的capacityIncrement
}4、public Vector(Conllection c); 这个方法传递一个Collection集合进行构建vector对象
@Test
public void vectorTest3() {
// 构建一个Collection对象
Collection<Object> objects = new ArrayList<Object>();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
//储存数据
objects.add(i + 1);
}
//使用迭代器 进行遍历
Iterator<Object> iterator = objects.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
System.out.print(iterator.next()+" ");//经过遍历输出的结果:1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
}
System.out.println();
//使用public Vector(Collection<? extends E> c) 构建一个vector 对象
Vector<Object> objects1 = new Vector<Object>(objects);
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
System.out.print(objects1.get(i)+" ");//经过遍历输出的结果:1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
}
}?方法源码:
?boolean | add(E?e)??????????将指定元素添加到此向量的末尾。 |
?void | add(int?index, E?element)??????????在此向量的指定位置插入指定的元素。 |
?boolean | addAll(Collection<? extends E>?c)??????????将指定 Collection 中的所有元素添加到此向量的末尾,按照指定 collection 的迭代器所返回的顺序添加这些元素。 |
?boolean | addAll(int?index, Collection<? extends E>?c)??????????在指定位置将指定 Collection 中的所有元素插入到此向量中。 |
?void | addElement(E?obj) |

?add调用了private void add()查看且传入了被添加的元素e,还有elementData数组,int 型的elementCount
/**
* The array buffer into which the components of the vector are
* stored. The capacity of the vector is the length of this array buffer,
* and is at least large enough to contain all the vector's elements.
*
* <p>Any array elements following the last element in the Vector are null.
*
* @serial
*/
protected Object[] elementData;//查看源码可以知道(The capacity of the vector is the length of this array buffer)这个数组的长度是vector容器的容量
/**
* The number of valid components in this {@code Vector} object.
* Components {@code elementData[0]} through
* {@code elementData[elementCount-1]} are the actual items.
*
* @serial
*/
protected int elementCount;//储存元素的有效个数?源码跟进查看private void add()
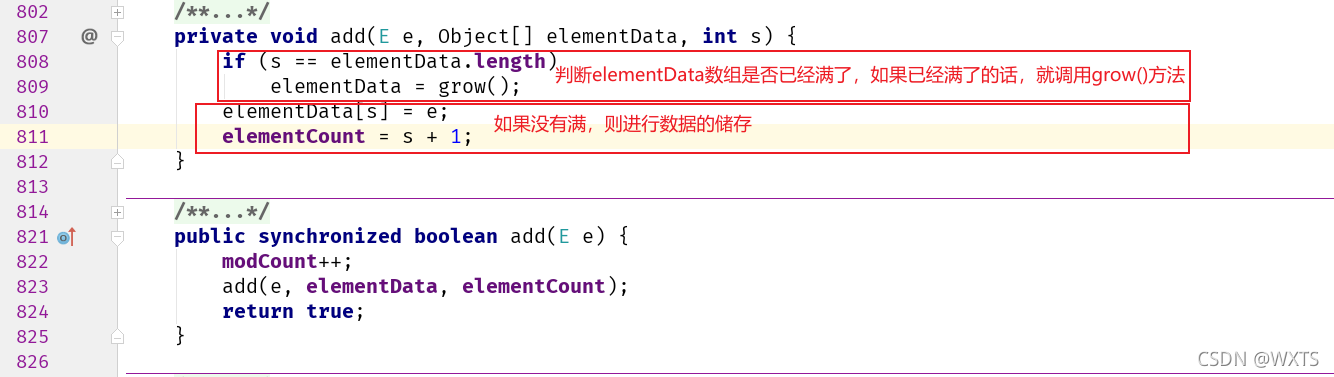
源码跟进查看grow()方法
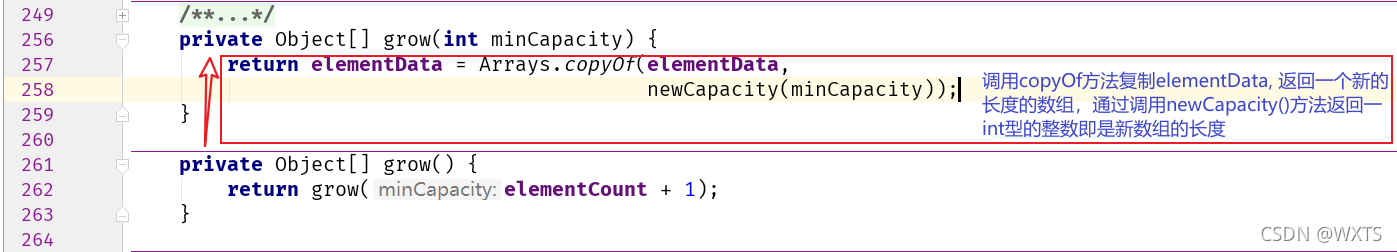
?源码跟进查看newCapacity()方法
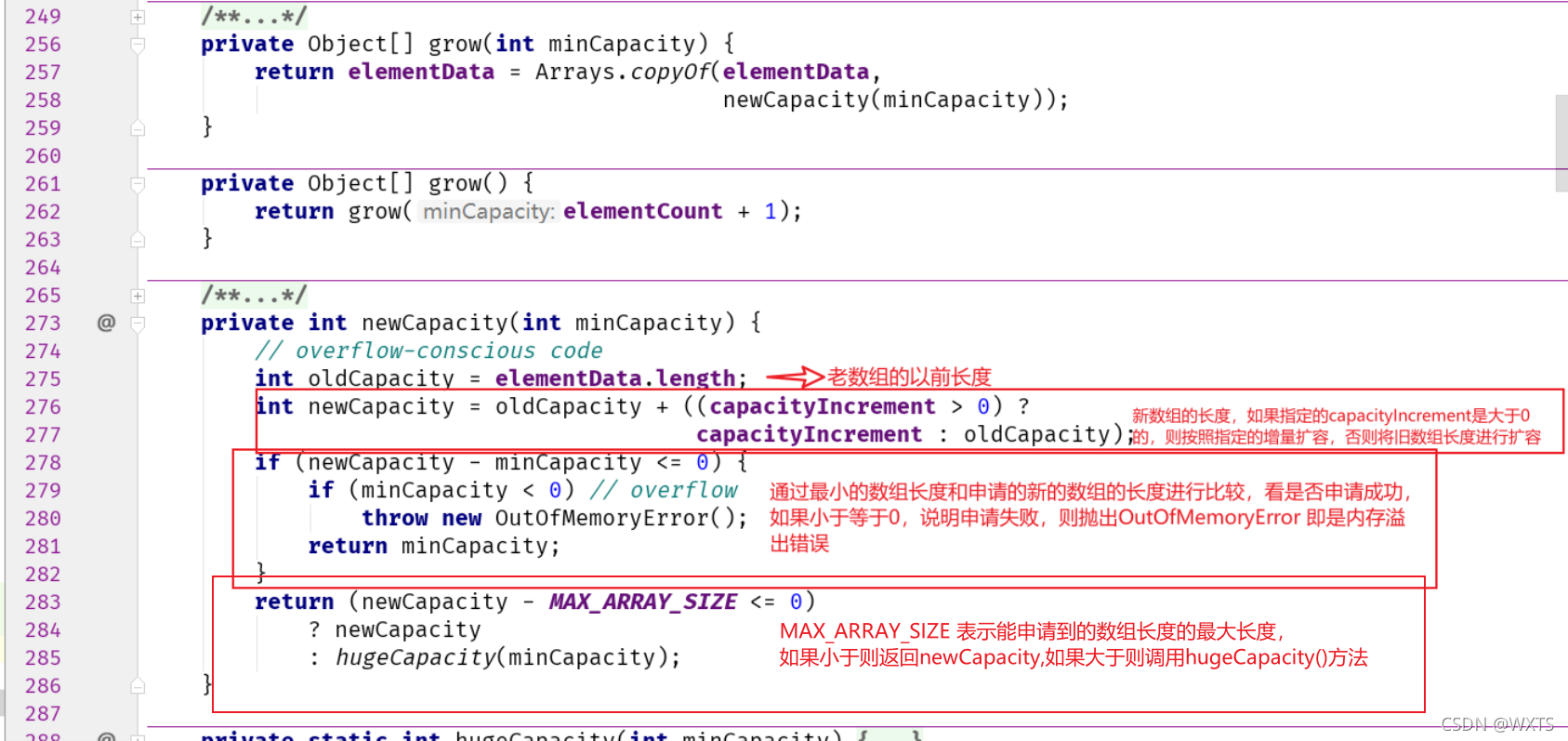
跟进源码查看hugeCapacity()方法
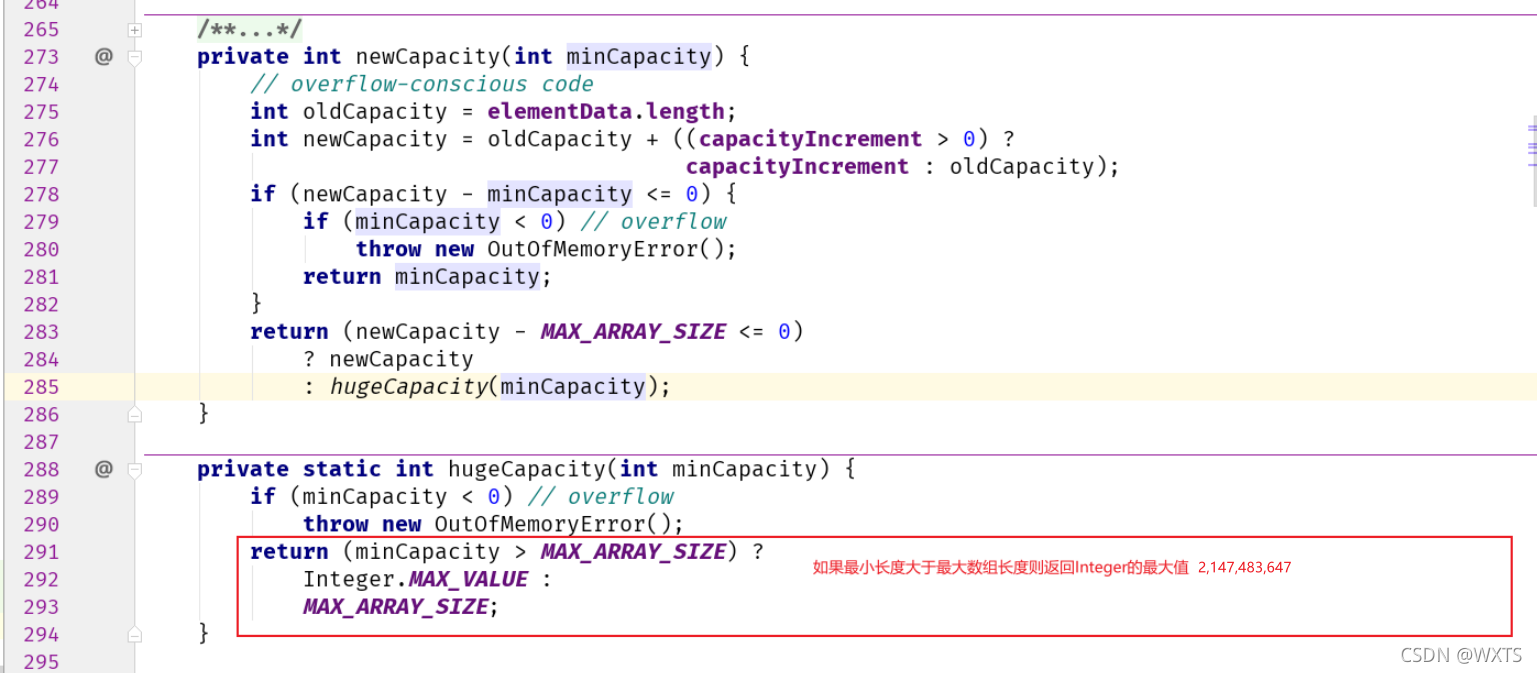
总结:Vector容器是一个基于数组的数据结构储存方式,每次扩容都是对对数组复制操作,且是线程同步的方式,对于要求性能高的应用,不应用此方法,且Vector现在已经弃用了。