本文目录
E. AC Challenge
题目描述
Dlsj is competing in a contest with n (0 < n <= 20) problems. And he knows the answer of all of these problems.
However, he can submit i-th problem if and only if he has submitted (and passed, of course) si problems, the pi,1-th, pi,2-th, …, pi,si-th problem before.(0<pi,j≤n,0<j≤si,0<i≤n) After the submit of a problem, he has to wait for one minute, or cooling down time to submit another problem. As soon as the cooling down phase ended, he will submit his solution (and get “Accepted” of course) for the next problem he selected to solve or he will say that the contest is too easy and leave the arena.
“I wonder if I can leave the contest arena when the problems are too easy for me.”
“No problem.”
—— CCF NOI Problem set
If he submits and passes the i-th problem on t-th minute(or the t-th problem he solve is problem i), he can get t×ai + bi points. (|ai |,|bi |≤109)
Your task is to calculate the maximum number of points he can get in the contest.
输入
The first line of input contains an integer, n, which is the number of problems.
Then follows n lines, the i-th line contains si + 3 integers, ai,bi,si,p1,p2,…,psi as described in the description above.
输出
Output one line with one integer, the maximum number of points he can get in the contest.
样例输入
case1
5
5 6 0
4 5 1 1
3 4 1 2
2 3 1 3
1 2 1 4
case2
1
-100 0 0
样例输出
case1
55
case2
0
提示
In the first sample.
On the first minute, Dlsj submitted the first problem, and get 1×5+6=11 points.
On the second minute, Dlsj submitted the second problem, and get 2×4+5=13 points.
On the third minute, Dlsj submitted the third problem, and get 3×3+4=13 points.
On the forth minute, Dlsj submitted the forth problem, and get 4×2+3=11 points.
On the fifth minute, Dlsj submitted the fifth problem, and get 5×1+2=7 points.
So he can get 11+13+13+11+7=55 points in total.
In the second sample, you should note that he doesn’t have to solve all the problems.
题意:
有n个作业,每个作业都有两个属性值 a , b a,b a,b,以及完成这个任务之前必须要完成其他的任务 p r e i pre_i prei?然后完成一个作业获得的分数为 a ? t i m e + b a*time + b a?time+b,其中 t i m e time time为完成该任务的时间,问做多可以获取多少分数
刚看到这个题的时候以为是前一天遇到的那个题的类似版本,然后就用拓扑排序写了一下,然后根据在拓扑排序过程中的度数变化情况来对图进行分层次,然后对于每一个层次进行相应的操作。本来对同一个层次的作业进行贪心,按照a升序,b升序。可是这样子是不对的,因为有个变量(完成该任务的时间),所以这里就没有办法做了,思路gg
这道题也是非常的坎坷:

正确方法:状压dp
int getOne(ll x) {
int ret = 0;
while(x) {
ret ++;
x &= (x - 1);
}
return ret;
}
ll a[30],b[30];
ll c[30];
int n;
ll dp[maxn << 1];
int main() {
// cout << getOne(15) << endl;
// cout << (1LL<<63) << endl;
n = read;
for(int i=0; i<=n-1; i++) {
a[i] = read,b[i] = read;
int t = read;
while(t --) {
ll x = read;
-- x;
c[i] |= (1LL << x);
}
}
ll ans = 0LL;
ll lim = 1LL << n;///total 2 ** n;
dp[0] = 0LL;
for(int i=1; i<=lim; i++) dp[i] = inf_1;
for(ll i=1; i<=lim-1; i++) {
// dp[i] = 1<<31;
for(ll j=0; j<n; j++) {
if(!(i & (1LL << j))) continue;
ll pre = i ^ (1LL << j);
// debug(pre);
if(dp[pre] == inf_1) continue;///pre status is -inf
if((pre | c[j]) == pre) {/// pre has done
ll time = getOne(i);
ll val = dp[pre] + a[j] * time + b[j];
dp[i] = max(dp[i],val);
}
}
}
for (int i=1; i<=lim; i++) {
ans = max(ans,dp[i]);
}
cout << ans << endl;
return 0;
}
A. An Olympian Math Problem
规律题,输入 x x x,输出 x ? 1 x-1 x?1
G. Lpl and Energy-saving Lamps
题目描述
During tea-drinking, princess, amongst other things, asked why has such a good-natured and cute Dragon imprisoned Lpl in the Castle? Dragon smiled enigmatically and answered that it is a big secret. After a pause, Dragon added:
— We have a contract. A rental agreement. He always works all day long. He likes silence. Besides that, there are many more advantages of living here in the Castle. Say, it is easy to justify a missed call: a phone ring can’t reach the other side of the Castle from where the phone has been left. So, the imprisonment is just a tale. Actually, he thinks about everything. He is smart. For instance, he started replacing incandescent lamps with energy-saving lamps in the whole Castle…
Lpl chose a model of energy-saving lamps and started the replacement as described below. He numbered all rooms in the Castle and counted how many lamps in each room he needs to replace.
At the beginning of each month, Lpl buys m energy-saving lamps and replaces lamps in rooms according to his list. He starts from the first room in his list. If the lamps in this room are not replaced yet and Lpl has enough energy-saving lamps to replace all lamps, then he replaces all ones and takes the room out from the list. Otherwise, he ‘ll just skip it and check the next room in his list. This process repeats until he has no energy-saving lamps or he has checked all rooms in his list. If he still has some energy-saving lamps after he has checked all rooms in his list, he’ll save the rest of energy-saving lamps for the next month.
As soon as all the work is done, he ceases buying new lamps. They are very high quality and have a very long-life cycle.
Your task is for a given number of month and descriptions of rooms to compute in how many rooms the old lamps will be replaced with energy-saving ones and how many energy-saving lamps will remain by the end of each month.
输入
Each input will consist of a single test case.
The first line contains integers n and m (1?≤?n?≤?100000,?1?≤?m?≤?100) — the number of rooms in the Castle and the number of energy-saving lamps, which Lpl buys monthly.
The second line contains n integers k1,?k2,?…,?kn (1?≤?kj?≤?10000,?j?=?1,?2,?…,?n) — the number of lamps in the rooms of the Castle. The number in position j is the number of lamps in j-th room. Room numbers are given in accordance with Lpl’s list.
The third line contains one integer q (1?≤?q?≤?100000) — the number of queries.
The fourth line contains q integers d1,?d2,?…,?dq (1?≤?dp?≤?100000,?p?=?1,?2,?…,?q) — numbers of months, in which queries are formed.
Months are numbered starting with 1; at the beginning of the first month Lpl buys the first m energy-saving lamps.
输出
Print q lines.
Line p contains two integers — the number of rooms, in which all old lamps are replaced already, and the number of remaining energy-saving lamps by the end of dp month.
样例输入
5 4
3 10 5 2 7
10
5 1 4 8 7 2 3 6 4 7
样例输出
4 0
1 1
3 6
5 1
5 1
2 0
3 2
4 4
3 6
5 1
提示
In the first month, he bought 4 energy-saving lamps and he replaced the first room in his list and remove it. And then he had 1 energy-saving lamps and skipped all rooms next. So, the answer for the first month is 1,1------1 room’s lamps were replaced already, 1 energy-saving lamp remain.
队友的线段树
ac_code:
const int maxn=1e5+7;
const int inf=0x3f3f3f3f;
#define ls i<<1
#define rs i<<1|1
ll n,m,a[maxn],q,x,y,id;
struct node{ ll x,y; }c[maxn];
struct tree{ ll l,r,mi; }t[maxn<<4];
void pushup(ll i){ t[i].mi=min(t[ls].mi,t[rs].mi); }
void build(ll i,ll l,ll r){
t[i].l=l; t[i].r=r;
if(l==r){
t[i].mi=a[l];
return;
}
ll mid=l+r>>1;
build(ls,l,mid); build(rs,mid+1,r);
pushup(i);
}
void update(ll i,ll x){
if(t[i].r<x||t[i].l>x) return;
if(t[i].l==t[i].r&&t[i].l==x){
t[i].mi=inf;
return;
}
update(ls,x); update(rs,x);
pushup(i);
}
ll ask(ll i,ll v){
if(t[i].l==t[i].r) return t[i].l;
if(t[ls].mi<=v) return ask(ls,v);
return ask(rs,v);
}
int main(){
n=read(); m=read();
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) a[i]=read();
build(1,1,n);
for(int i=1;i<=100000;i++){
x+=m;
if(t[1].mi==inf) x-=m;
c[i].y=c[i-1].y; c[i].x=x;
while(x>=t[1].mi){
ll t=ask(1,x);
x-=a[t]; c[i].x-=a[t];
c[i].y++;
update(1,t);
}
}
q=read();
while(q--){
ll i=read();
printf("%lld %lld\n",c[i].y,c[i].x);
}
}
J. Nanjing Sum
题目描述
A square-free integer is an integer which is indivisible by any square number except 1. For example, 6 = 2·3 is square-free, but 12 = 22·3 is not, because 22 is a square number. Some integers could be decomposed into product of two square-free integers, there may be more than one decomposition ways. For example, 6 = 1·6=6·1=2·3=3·2, n=ab and n=ba are considered different if a≠b. f(n) is the number of decomposition ways that n=ab such that a and b are square-free integers. The problem is calculating 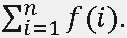
.
输入
The first line contains an integer T(T≤20), denoting the number of test cases. For each test case, there first line has a integer n(n≤2·107).
输出
For each test case, print the answer 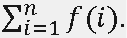
.
样例输入
2
5
8
样例输出
8
14
提示
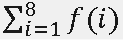 =f(1)+?+f(8)=1+2+2+1+2+4+2+0=14
=f(1)+?+f(8)=1+2+2+1+2+4+2+0=14
素数的f()一定是2
如果说对一个数x进行唯一分解之后,其某一项的指数
≥
3
\geq 3
≥3,那么说这个f()值一定是0
n
=
p
1
e
1
?
x
n=p_1^{e1}? x
n=p1e1??x ,则有
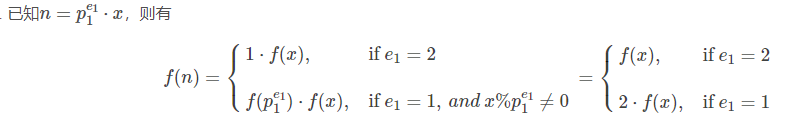
为什么哩,因为如果
e
1
=
2
e_1=2
e1?=2,那么对于
n
n
n,
p
e
1
p^{e_1}
pe1?的贡献就只有
1
1
1,
p
1
2
=
p
1
?
p
1
p_1^2=p_1?p_1
p12?=p1??p1?,所以
f
(
p
1
2
)
=
1
f(p_1^2)=1
f(p12?)=1,而当
e
1
=
1
e1=1
e1=1时,贡献为
2
2
2,因为此时
p
1
p_1
p1?为质数,
f
(
p
1
)
=
2
f(p_1)=2
f(p1?)=2,但是得同时保证
x
x
x和
p
1
e
1
p_1^{e1}
p1e1?没有大于
x
x
x和
p
1
e
1
p_1^{e1}
p1e1?没有大于
1
1
1 的共同因子.
最后前缀和一下就可以完成了
可以参考:博客
bool vis[maxn];
int cnt = 0;
int Pri[maxn];
ll f[maxn];
void _Get_Prime(int lim) {
f[1] = 1LL;
for (ll i = 2; i <= lim; i++) {
if (vis[i] == 0) {
Pri[++cnt] = i;
f[i] = 2;///prime
}
for (ll j = 1; j <= cnt; j++) {
ll val = i * Pri[j];
if(val > lim) break;
vis[val] = 1;
if (i % Pri[j]) f[val] = f[i] * f[Pri[j]];
else if(i % (Pri[j] * Pri[j]) == 0) {
f[val] = 0;
} else {
f[val] = f[val / (Pri[j] * Pri[j])];
break;
}
}
}
}
int main() {
_Get_Prime(20000000);
for(int i=1; i<=20000000; i++) {
f[i] += f[i-1];
}
int _ = read;
while(_ --) {
ll x = read;
printf("%lld\n",f[x]);
}
return 0;
}
/**
**/
L. Magical Girl Haze
题目描述
There are N cities in the country, and M directional roads from u to v(1<=u, v<=n).Every road has a distance ci. Haze is a Magical Girl that lives in City 1, she can choose no more than K roads and make their distances become 0. Now she wants to go to City N, please help her calculate the minimum distance.
输入
The first line has one integer T(1<=T<=5), then following T cases.
For each test case, the first line has three integers N, M and K. Then the following M lines each line has three integers, describe a road, Ui, Vi, Ci. There might be multiple edges between u and v.
It is guaranteed that N<=100000, M<=200000, K<=10, 0<=c[i]<=1e9. There is at least one path between City 1 and City N.
输出
For each test case, print the minimum distance.
样例输入
1
5 6 1
1 2 2
1 3 4
2 4 3
3 4 1
3 5 6
4 5 2
样例输出
3
题意:
从可以将图中不超过k条有向边的边权设置为0,然后问从1到n的最短路径是多少
可以用分层图最短路来实现
const int maxn=5e6+7;
const int inf=0x3f3f3f3f;
int T,n,m,k;
int tot,head[maxn];
ll d[maxn];
bool f[maxn];
struct edge{ int to,next,w; }e[maxn];
struct node{
int dis,u;
node(int dis,int u):dis(dis),u(u){};
bool operator<(const node &t)const{ return dis>t.dis; }
};
void add(int u,int v,int w){
e[++tot].w=w; e[tot].to=v;
e[tot].next=head[u]; head[u]=tot;
}
void dij(){
priority_queue<node>q;
memset(f,0,sizeof(f)); memset(d,inf,sizeof(d));
d[0]=0;
q.push(node(0,0));
while(!q.empty()){
node x=q.top(); q.pop();
int u=x.u,dis=x.dis;
if(f[u]) continue; f[u]=1;
for(int i=head[u];i;i=e[i].next){
int y=e[i].to;
// cout<<y<<endl;
if(d[y]>d[u]+e[i].w){
d[y]=d[u]+e[i].w;
q.push(node(d[y],y));
}
}
}
}
int main(){
T=read();
while(T--){
n=read(); m=read(); k=read();
memset(head,0,sizeof(head)); tot=0;
while(m--){
int u,v,w;
u=read()-1; v=read()-1; w=read();
for(int i=0;i<=k;i++){
add(u*(k+1)+i,v*(k+1)+i,w);
if(i<k) add(u*(k+1)+i,v*(k+1)+i+1,0);
}
}
dij();
int sum=inf;
for(int i=0;i<=k;i++) sum=min(1ll*sum,d[(n-1)*(k+1)+i]);
cout<<sum<<endl;
}
}
/*
1
5 6 1
1 2 2
1 3 4
2 4 3
3 4 1
3 5 6
4 5 2
*/